Heim >Web-Frontend >H5-Tutorial >HTML5 Canvas: Schwenken, Zoomen, Drehen von Bild- und Textcodedetails
HTML5 Canvas: Schwenken, Zoomen, Drehen von Bild- und Textcodedetails
- 黄舟Original
- 2017-03-03 16:13:553270Durchsuche
HTML5 Canvas bietet APIs für die grafische Übersetzung, Drehung und Skalierung.
Übersetzung (übersetzen)
Übersetzungskoordinaten translator(x, y) bedeutet (0,0) Die Koordinaten werden in (x, y) übersetzt und die ursprünglichen (0,0)-Koordinaten werden zu (-x, -y)
Das Diagramm sieht wie folgt aus:
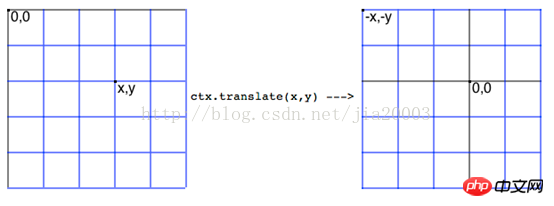
Der Koordinatenpunkt jedes ursprünglichen Koordinatenpunkts p(ox, oy) nach der Übersetzung ist p(ox-x, oy-y) und sein Mittelpunkt (x, y) ist die Übersetzung
Punktkoordinaten translator(x, y).
Code-Demo:
// translate is move the startpoint to centera and back to top left corner
function renderText(width, height, context) {
context.translate(width/ 2, height / 2);// 中心点坐标为(0, 0)
context.font="18px Arial";
context.fillStyle="blue";
context.fillText("Please Press <Esc> to Exit Game",5,50);
context.translate(-width/2,-height/2); // 平移恢复(0,0)坐标为左上角
context.fillText("I'm Back to Top",5,50);
}
Skalieren
Skalieren(a, b) bedeutet, das Objekt entlang der XY-Achse auf die Größe a*x bzw. b*y zu skalieren. Der Effekt ist wie im Bild dargestellt:

// translation the rectangle.
function drawPath(context) {
context.translate(200,200);
context.scale(2,2);// Scale twice size of original shape
context.strokeStyle= "green";
context.beginPath();
context.moveTo(0,40);
context.lineTo(80,40);
context.lineTo(40,80);
context.closePath();
context.stroke();
}Drehen(drehen)
Drehwinkel drehen(Math.PI/8)

Die Koordinate p(x, y) vor der Drehung und die entsprechende Koordinate P(rx, ry) nach der Drehung sind
Rx = x * cos(-angle)- y * sin(-angle); Ry = y * cos(-angle) + x * sin(-angle);
Rotation90 Grad kann vereinfacht werden zu:
Rx = y; Ry = -x;
Die Standarddrehrichtung in Canvas ist im Uhrzeigersinn. Der Democode lautet wie folgt:
// new point.x = x * cos(-angle) -y * sin(-angle),
// new point.y = y * cos(-angle) +x * sin(-angle)
function renderRotateText(context) {
context.font="24px Arial";
context.fillStyle="red";
context.fillText("i'm here!!!",5,50);
// rotate -90 degreee
// context.rotate(-Math.PI/2);
// context.fillStyle="blue";
// context.fillText("i'm here!!!", -400,30);
// rotate 90 degreee
context.rotate(Math.PI/2);
context.fillStyle="blue";
context.fillText("i'm here!!!",350,-420);
console.log(Math.sin(Math.PI/2));
// rotae 90 degree and draw 10 lines
context.fillStyle="green";
for(var i=0; i<4;
i++) {
var x = (i+1)*20;
var y = (i+1)*60;
var newX = y;
var newY =-x;
context.fillRect(newX,newY, 200, 6);
}
}Der übliche Ansatz besteht darin, Rotation und Übersetzung zusammen zu verwenden, erste Änderung die Koordinaten (0,0)In die Mittelposition verschieben
übersetzen (Breite/2, Höhe/2)Dann verwenden Sie rotate(Math.PI/2)Vollständige Drehung
Das Codebeispiel lautet wie folgt:
function saveAndRestoreContext(context) {
context.save();
context.translate(200,200);
context.rotate(Math.PI/2);
context.fillStyle="black";
context.fillText("2D Context Rotate And Translate", 10, 10);
context.restore();
context.fillText("2D Context Rotate And Translate", 10, 10);
}Alle JavaScript-Codes:
var tempContext = null; // global variable 2d context
window.onload = function() {
var canvas = document.getElementById("target");
canvas.width = 450;
canvas.height = 450;
if (!canvas.getContext) {
console.log("Canvas not supported. Please install a HTML5 compatible browser.");
return;
}
// get 2D context of canvas and draw image
tempContext = canvas.getContext("2d");
// renderText(canvas.width, canvas.height, tempContext);
saveAndRestoreContext(tempContext);
// drawPath(tempContext);
}
// translate is move the start point to centera and back to top left corner
function renderText(width, height, context) {
context.translate(width / 2, height / 2);
context.font="18px Arial";
context.fillStyle="blue";
context.fillText("Please Press <Esc> to Exit Game",5,50);
context.translate(-width / 2, -height / 2);
context.fillText("I'm Back to Top",5,50);
}
// translation the rectangle.
function drawPath(context) {
context.translate(200, 200);
context.scale(2,2); // Scale twice size of original shape
context.strokeStyle = "green";
context.beginPath();
context.moveTo(0, 40);
context.lineTo(80, 40);
context.lineTo(40, 80);
context.closePath();
context.stroke();
}
// new point.x = x * cos(-angle) - y * sin(-angle),
// new point.y = y * cos(-angle) + x * sin(-angle)
function renderRotateText(context) {
context.font="24px Arial";
context.fillStyle="red";
context.fillText("i'm here!!!",5,50);
// rotate -90 degreee
// context.rotate(-Math.PI/2);
// context.fillStyle="blue";
// context.fillText("i'm here!!!", -400,30);
// rotate 90 degreee
context.rotate(Math.PI/2);
context.fillStyle="blue";
context.fillText("i'm here!!!", 350,-420);
console.log(Math.sin(Math.PI/2));
// rotae 90 degree and draw 10 lines
context.fillStyle="green";
for(var i=0; i<4; i++) {
var x = (i+1)*20;
var y = (i+1)*60;
var newX = y;
var newY = -x;
context.fillRect(newX, newY, 200, 6);
}
}
function saveAndRestoreContext(context) {
context.save();
context.translate(200,200);
context.rotate(Math.PI/2);
context.fillStyle="black";
context.fillText("2D Context Rotate And Translate", 10, 10);
context.restore();
context.fillText("2D Context Rotate And Translate", 10, 10);
}Das Obige ist der Inhalt des HTML5-Canvas-Schwenkens, Zoomens und Drehens von Grafikcodedetails. Weitere verwandte Inhalte finden Sie auf der chinesischen PHP-Website (www.php.cn)!
In Verbindung stehende Artikel
Mehr sehen- Das Vollbild-Bildlauf-Plug-in AlloyTouch erstellt in 30 Sekunden eine flüssige H5-Seite
- Tatsächlicher HTML5-Kampf und Analyse von Touch-Ereignissen (Touchstart, Touchmove und Touchend)
- Ausführliche Erläuterung der Beispiele für Bildzeichnungen in HTML5 Canvas 9
- Reguläre Ausdrücke und neue HTML5-Elemente
- So kombinieren Sie NodeJS und HTML5, um mehrere Dateien per Drag-and-Drop auf den Server hochzuladen

