Implementieren Sie ein einfaches Beispiel für ein Warenkorbsystem mit MongoDB und JSP
- 高洛峰Original
- 2016-12-29 15:36:041903Durchsuche
In diesem Artikel wird die JSP-Programmiertechnologie zur Implementierung eines einfachen Einkaufswagenprogramms wie folgt vorgestellt:
1 Problembeschreibung
Verwendung der JSP-Programmiertechnologie zur Implementierung eines einfachen Einkaufswagenprogramms Cart-Car-Verfahren, spezifische Anforderungen sind wie folgt.
(1) Verwenden Sie JSP, um eine Anmeldeseite zu schreiben. Verwenden Sie zwei Schaltflächen, um die Anmeldeinformationen zu übermitteln.
(2) Schreiben Sie ein JSP-Programm, um die vom Benutzer übermittelten Anmeldeinformationen abzurufen und die Datenbank abzufragen. Wenn der Benutzername der Name eines Mitglieds dieser Gruppe und das Passwort die entsprechende Studentennummer ist, verwenden Sie Verwenden Sie die in JSP integrierte Objektmethode, um zur Bestellseite zu gelangen (Anzeige von Kataloginformationen wie Art und Stückpreis der Produkte im Geschäft). Andernfalls verwenden Sie die JSP-Aktion, um den Benutzer erneut aufzufordern, sich anzumelden (Hinweis: Dies Die Seite muss die vorherige Anmeldeschnittstelle enthalten.
(3) Wenn der Kunde die Menge der gewünschten Waren eingibt und auf die Schaltfläche „Senden“ klickt, werden die zuvor bestellten Waren in den Warenkorb gelegt und die relevanten Informationen im Warenkorb angezeigt, einschließlich des Namens und Menge der Waren sowie der Gesamtpreis aller Artikel.
(4) Schreiben Sie die Produktinformationen in die Datenbank und berechnen Sie den Preis, indem Sie die Datenbank durchsuchen.
Wählen Sie die folgenden Funktionen aus:
(5) Implementieren Sie eine einfache Registrierungsfunktion, damit neue Benutzer ihre Informationen (Name und Matrikelnummer) zur späteren Anmeldung in die Datenbank schreiben können. Verwenden Sie
(6) Um die relevanten Operationen der Datenbank in ein JavaBean umzuschreiben
2 Lösung
2.1 Implementieren Sie die Funktion
( 1) Benutzer Login. (Vollständige Anmeldeauthentifizierung durch Abfrage der MongoDB-Datenbank)
(2) Benutzerregistrierung. (Die Benutzerregistrierung wird durch Schreiben in die MongoDB-Datenbank abgeschlossen)
(3) Merken Sie sich das Passwort. (Durch die Verwendung von Cookies wird die Funktion realisiert, sich den Benutzernamen und das Passwort der Homepage zu merken)
(4) Produkte anzeigen. (Durch Abfrage der MongoDB-Datenbank werden spezifische Produktinformationen zurückgegeben und auf der Client-Schnittstelle angezeigt)
(5) Kaufen Sie das Produkt.
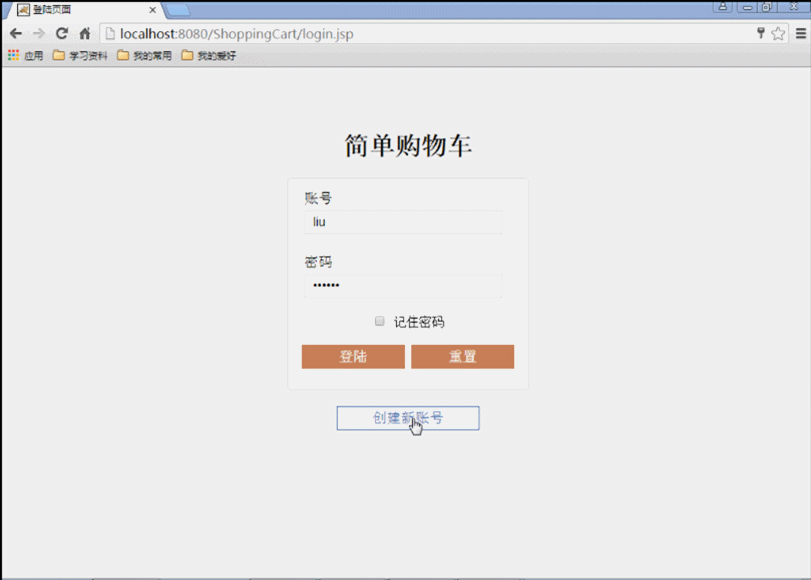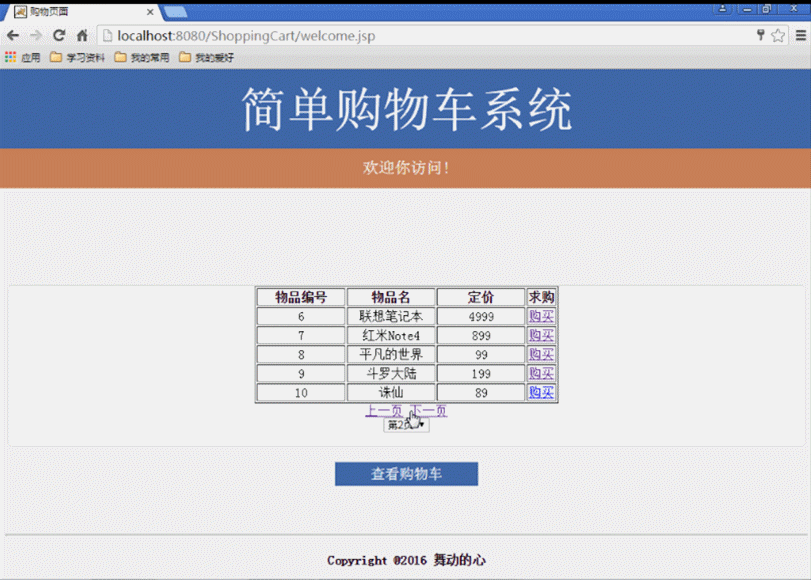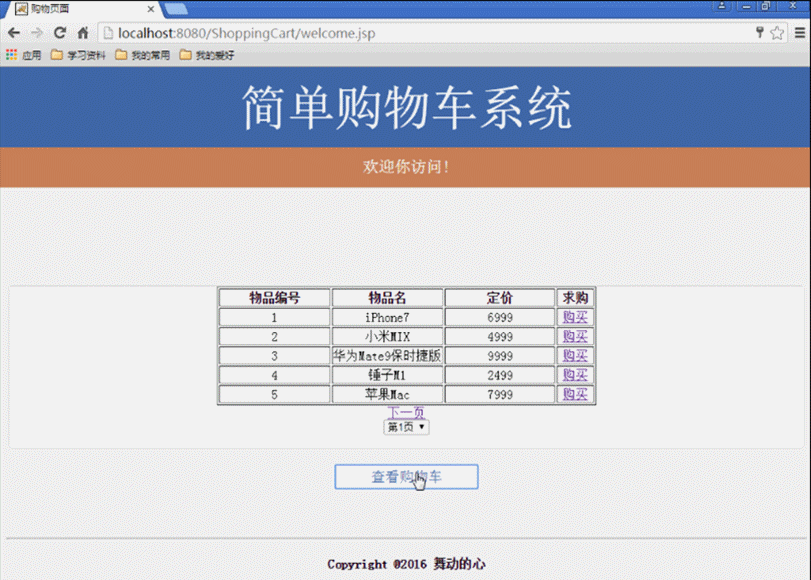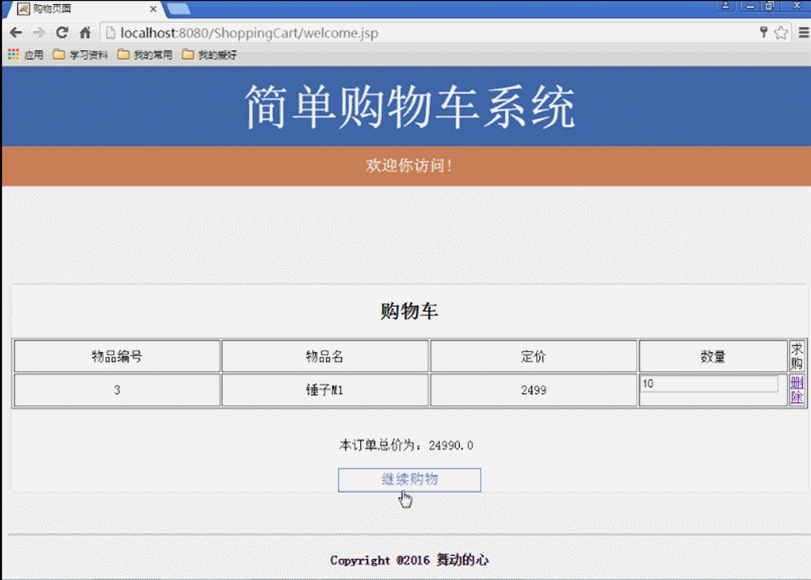
(6) Warenkorb. (Zeigen Sie die spezifischen Informationen des vom Benutzer gekauften Produkts an, löschen Sie das gekaufte Produkt oder fügen Sie die Menge des gekauften Produkts hinzu und berechnen Sie den Gesamtpreis des derzeit vom Benutzer gekauften Produkts.)
2.2 Rendern des Endvorgangs
2.3 Schematische Darstellung des Systemfunktionsrahmens
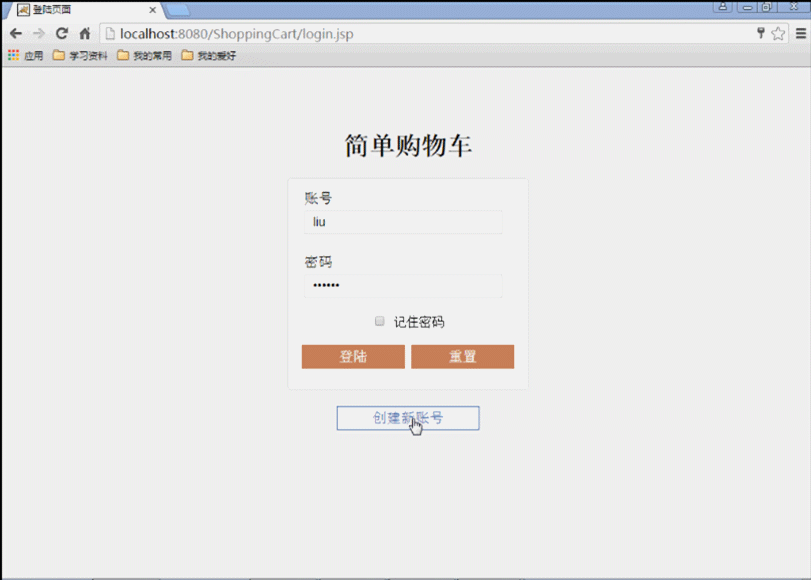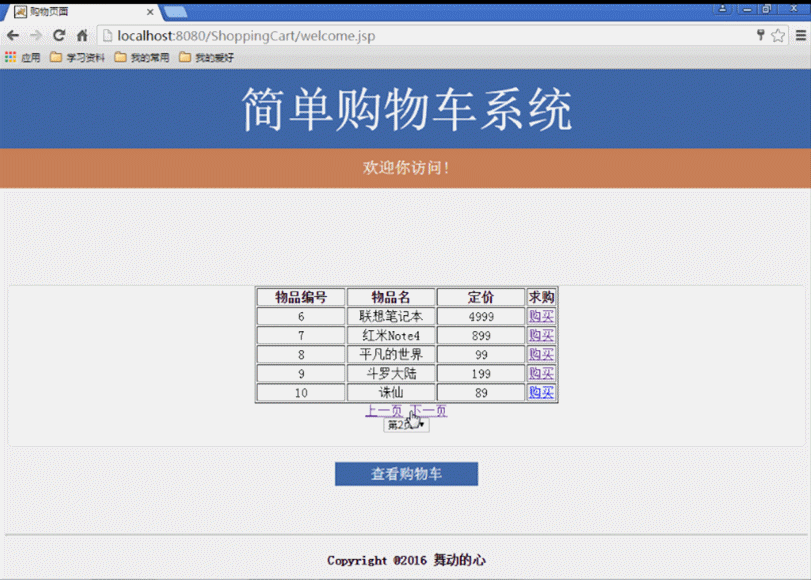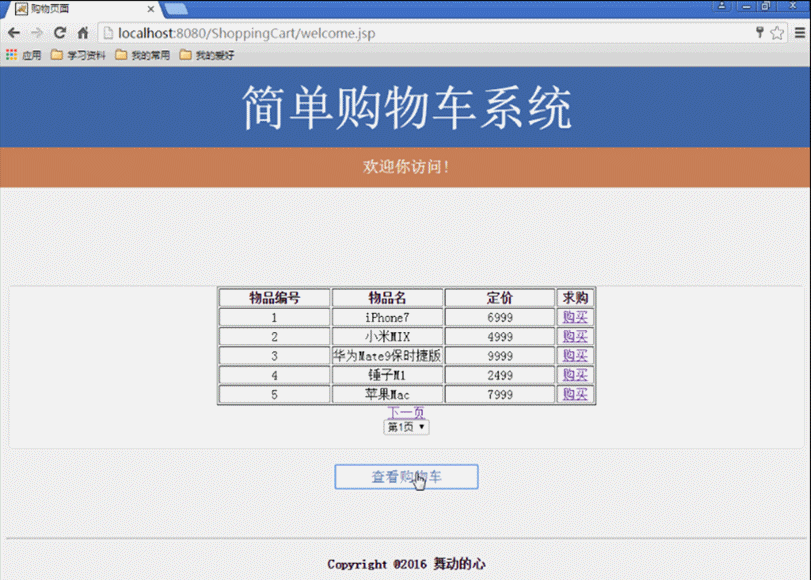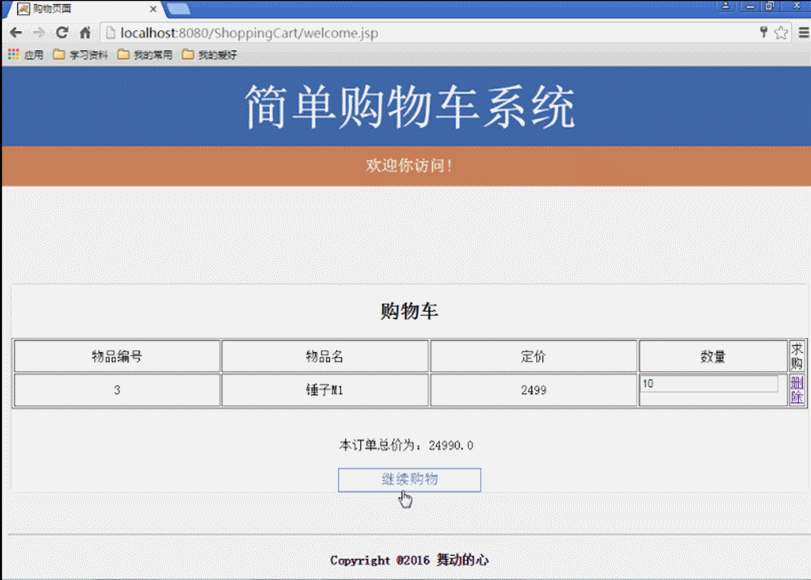
Abbildung 1: Beispieldiagramm des Systemfunktionsrahmens
Detaillierte Erklärung:
(1) Durchsuchen Öffnen Sie die Anmeldeseite des Benutzers login.jsp im Browser.
(2) Klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche „Neuen Benutzer erstellen“, um den Benutzer „register.jsp“ einzugeben Registrierungsseite;
(3) Wenn die Registrierung fehlschlägt, bleibt die Registrierung auf der ursprünglichen Seite von jsp. Klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche „Zurück“. Kehren Sie zur Seite login.jsp auf der Startseite zurück.
(4) Geben Sie den Benutzernamen und das Passwort auf der Seite login.jsp der Startseite ein. Die Anfrage wird an die Seite login_action.jsp für das Anmeldeverarbeitungsskript gesendet Der erfolgreiche Datenabgleich springt zur Startseite von „Welcome.jsp Shopping“, andernfalls wird zur Seite „Login-Video login_Fail.jsp“ gesprungen. (5) Geben Sie „Welcome.jsp Shopping“ ein. Klicken Sie nach der Startseite auf die nächste Seite und auf die vorherige Seite Klicken Sie auf die Seitenschaltflächen, um die aktuellen Produktinformationen anzuzeigen. Klicken Sie einmal auf die Schaltfläche „Kaufen“, um ein Produkt zu kaufen, und klicken Sie mehrmals auf die Schaltfläche „Warenkorb anzeigen“, um einen internen Sprung zur Warenkorbseite von Cart.jsp zu erhalten , wo Sie die aktuell gekaufte Produktnummer, den Namen, den Preis, die Kaufmenge und die Gesamtpreisinformationen aller Produkte anzeigen und die Funktionen zum Löschen gekaufter Produkte und zum Hinzufügen der Anzahl der gekauften Produkte bereitstellen können
(6) Die Shopping-Homepage welcom.jsp besteht aus drei Seiten: header.jsp, main_shop.jsp und bottom.jsp, wie in Abbildung 2 unten dargestellt:
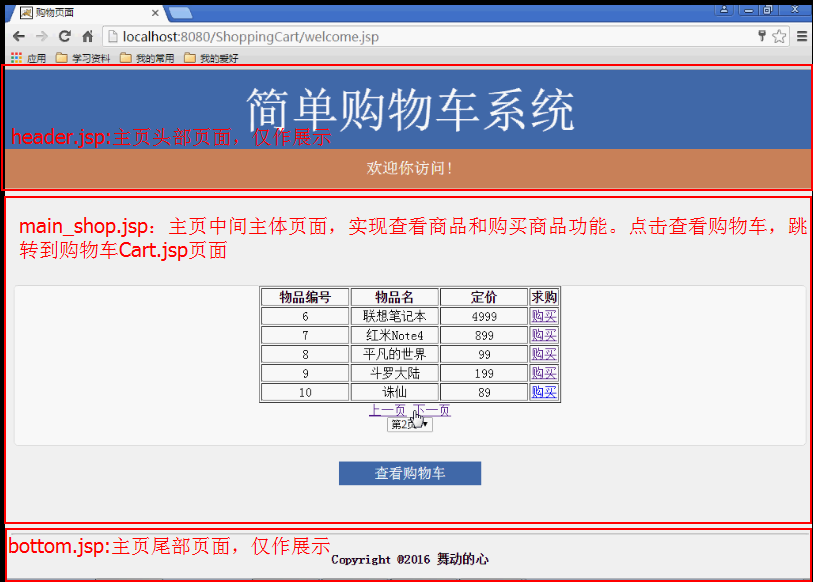 Abbildung 2: Shopping-Homepage willkommen.jsp-Seite
Abbildung 2: Shopping-Homepage willkommen.jsp-Seite
2.4 Über MongoDB-Einführung und Systemumgebungskonfiguration
MongoDB ist ein Mitglied der NoSQL-Familie und eine häufig verwendete relationale Datenbank (z. B. MySQL). , SQLserver usw.) werden die komplexen Beziehungen und Assoziationen zwischen Entitäten aufgegeben. Mit anderen Worten: MongoDB ist eine Dokumentendatenbank, so wie wir jeden Tag Dokumente schreiben. Wir müssen uns nicht um den spezifischen Inhalt verschiedener Dokumente kümmern oder sie sorgfältig klassifizieren. Sie können alle auf der Festplatte unseres Computers gespeichert werden. Nachfolgend finden Sie eine Vergleichstabelle der Substantivkonzepte zwischen MongoDB und relationalen Datenbanken:
Wie aus der obigen Tabelle ersichtlich ist, entspricht in der uns bekannten relationalen Datenbank die spezifische Entitätstabelle der Sammlung in MongoDB, die Zeilen in der Tabelle entsprechen den Dokumenten in der MongoDB-Sammlung und die Spalten in Die Tabelle entspricht den Feldern im MongoDB-Dokument. Der von MongoDB automatisch generierte Primärschlüssel besteht aus 12 Bytes wie folgt generiert:
0 |1|2|3 | 4|5|6 | 9|10|11
Zeitstempel | PID |. Counter
Das Obige ist mein vorläufiges Lernen. Wenn bei der Einführung von MongoDB Fehler auftreten, können Sie mich gerne korrigieren.
Nachdem wir über das Konzept gesprochen haben, müssen wir uns der spezifischen Anwendung zuwenden. Das in MongoDB gespeicherte und gelesene Datenformat ist eine Art von Daten, die dem JSON-Format ähnelt folgt:
/* 7 createdAt:2016/11/22 下午3:52:51*/
{
"_id" : ObjectId("5833f953e9d60125601a8c8b"),
"sid" : "7",
"sname" : "红米Note4",
"sprice" : "899"
},
/* 8 createdAt:2016/11/22 下午3:53:19*/
{
"_id" : ObjectId("5833f96fe9d60125601a8c8c"),
"sid" : "8",
"sname" : "平凡的世界",
"sprice" : "99"
},
/* 9 createdAt:2016/11/22 下午3:53:43*/
{
"_id" : ObjectId("5833f987e9d60125601a8c8d"),
"sid" : "9",
"sname" : "斗罗大陆",
"sprice" : "199"
},Wenn wir Daten aus der MongoDB-Datenbank abfragen und abrufen, ist ihr Format das BSON-Format und kann nicht direkt mit den vom Client erhaltenen Daten abgeglichen werden. Nachdem ich die BSON-Formatdaten in der Datenbank abgerufen habe, rufe ich hier die BSON.toMap()-Methode im MongoDB-Treiberpaket auf, um das BSON-Format in eine Zeichenfolge im Map-Schlüssel-Wert-Paarformat zu konvertieren, und rufe dann Map.get(" auf. name“ in der Map-Methode, um den Wert des spezifischen Schlüssel-Wert-Paares zu erhalten und so die Daten auf der Client-Seite abzugleichen.
Schließlich ist der wichtigste Punkt der Import des MongoDB-Treiberpakets in das neue Projekt, um dem Client und der Geschäftsschicht den Betrieb der Datenbank zu erleichtern. Hier verwende ich das Paket mongo-java-driver-3.3.0.jar und den Download-Link für jede Version des Treiberpakets: http://central.maven.org/maven2/org/mongodb/mongo-java- Treiber/
2.5 Erklärung des Kernfunktionscodes
(1) Benutzeranmeldefunktion
realisiert die Benutzeranmeldung, die hauptsächlich durch den Code in login_action.jsp implementiert wird Skript, das im Code angegeben wurde. Spezifische Kommentare werden wie folgt angegeben:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*,com.mongodb.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'login_action.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<%
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8"); //确保显示的汉字信息以正确编码方式显示
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); //确保获取的汉字信息以正确编码方法获取
String userName=(String)request.getParameter("username"); //获取登录页面用户名
String passWord=(String)request.getParameter("password");//获取登陆页面密码
String checkBox = request.getParameter("save_password");//获取登陆页面记住密码选择框属性值
boolean login_test = false; //设定登陆布尔值,若用户名和密码成功匹配,则为true
try{
// 连接到 mongodb 服务
MongoClient mongoClient = new MongoClient( "localhost" , 27017 );
//此处采用无用户名和密码验证方式登陆
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
DB db = mongoClient.getDB( "library" ); //连接到数据库library
DBCollection coll = db.getCollection("userInfo"); //获取library数据库中集合userInfo
System.out.println("Collection userInfo selected successfully");
DBCursor cursor = coll.find(); //查询集合userInfo中文档信息
int i=1;
while (cursor.hasNext()) { //检索集合userInfo中所有文档信息
System.out.println("userInfo Document: "+i);
DBObject show = cursor.next();
System.out.println(show);
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
Map show1 = show.toMap(); //将检索结果show(Bson类型)转换为Map类型
String toname = (String)show1.get("username"); //提取Map中字段名为username的属性值
String topassword = (String)show1.get("password"); //提取Map中字段名为password的属性值
if(toname.equals(userName) && topassword.equals(passWord)){
//将从数据库中获取的用户名和密码与表单中获取的数据进行验证,匹配成功则使login_test值为true
System.out.println("登陆成功!!!!!"+"username:"+toname+" password:"+topassword);
//request.getRequestDispatcher("welcome.jsp").forward(request, response);
login_test = true;
}
System.out.println(show1.get("username"));
i++;
}
}catch(Exception e){
System.err.println( e.getClass().getName() + ": " + e.getMessage() );
}
if(login_test) {
if ("save".equals(checkBox)) {
//Cookie存取时用URLEncoder.encode进行编码(PS:读取时URLDecoder.decode进行解码)
String name1 = java.net.URLEncoder.encode(userName,"UTF-8");
//创建两个Cookie对象
Cookie nameCookie = new Cookie("username", name1);
//设置Cookie的有效期为3天
nameCookie.setMaxAge(60 * 60 * 24 * 3);
String pwd = java.net.URLEncoder.encode(passWord,"UTF-8");
Cookie pwdCookie = new Cookie("password", pwd);
pwdCookie.setMaxAge(60 * 60 * 24 * 3);
response.addCookie(nameCookie);
response.addCookie(pwdCookie);
}
// request.getRequestDispatcher("welcome.jsp").forward(request, response);
response.sendRedirect("welcome.jsp");
}
else{
response.sendRedirect("login_Fail.jsp");
// request.getRequestDispatcher("loginFail.jsp").forward(request, response);
}
%>
</body>
</html>(2) Benutzerregistrierungsfunktion
Das Implementierungsprinzip der Benutzerregistrierungsfunktion ist grundsätzlich das gleiche wie Der einzige Unterschied besteht darin, dass die Benutzeranmeldung die Datenbank abfragt und die Benutzerregistrierung in die Datenbank geschrieben wird. Der spezifische Code wird hier nicht veröffentlicht, sondern in der spezifischen Codierung unten angezeigt.
(3) Funktion „Passwort merken“
Hier werden zwei Cookies verwendet. Wenn sich der Benutzer korrekt anmeldet, erhält er den Benutzernamen und fügt ihn dem aktuellen Browser-Cookie hinzu. Cookie_two ruft das Passwort ab und fügt es auch dem aktuellen Browser-Cookie hinzu. Geben Sie in den Eingabefeldern für Benutzername und Passwort auf der Anmelde-Homepage den Benutzernamen und das Passwort ein, die das System aus dem Cookie erhalten hat, und realisieren Sie so die Passwort-Erinnerungsfunktion. Die Details lauten wie folgt:
if(login_test) {
if ("save".equals(checkBox)) {
//Cookie存取时用URLEncoder.encode进行编码(PS:读取时URLDecoder.decode进行解码)
String name1 = java.net.URLEncoder.encode(userName,"UTF-8");
//创建两个Cookie对象
Cookie nameCookie = new Cookie("username", name1);
//设置Cookie的有效期为3天
nameCookie.setMaxAge(60 * 60 * 24 * 3);
String pwd = java.net.URLEncoder.encode(passWord,"UTF-8");
Cookie pwdCookie = new Cookie("password", pwd);
pwdCookie.setMaxAge(60 * 60 * 24 * 3);
response.addCookie(nameCookie);
response.addCookie(pwdCookie);
}
// request.getRequestDispatcher("welcome.jsp").forward(request, response);
response.sendRedirect("welcome.jsp");
}
else{
response.sendRedirect("login_Fail.jsp");
// request.getRequestDispatcher("loginFail.jsp").forward(request, response);
}<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
String username = "";
String password = "";
//获取当前站点的所有Cookie
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
for (int i = 0; i < cookies.length; i++) {
//对cookies中的数据进行遍历,找到用户名、密码的数据
if ("username".equals(cookies[i].getName())) {
//读取时URLDecoder.decode进行解码(PS:Cookie存取时用URLEncoder.encode进行编码)
username = java.net.URLDecoder.decode(cookies[i].getValue(),"UTF-8");
} else if ("password".equals(cookies[i].getName())) {
password = java.net.URLDecoder.decode(cookies[i].getValue(),"UTF-8");
}
}
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>登陆页面</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/login.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="content">
<div class="head">
<h1>简单购物车</h1>
</div>
<!-- 登录面板 -->
<div class="panel">
<form action="login_action.jsp" method="post">
<!-- 账号和密码组 -->
<div class="group">
<label>账号</label>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入账号" name="username" value="<%=username%>">
</div>
<div class="group">
<label>密码</label>
<input type="password" placeholder="请输入密码" name="password" value="<%=password%>">
</div>
<div>
<input type="checkbox" value="save" name="save_password">
<label>记住密码</label>
</div>
<div class="group">
<label></label>
</div>
<!-- 登录按钮 -->
<div class="login">
<button type="submit" name="login">登陆</button>
<button type="reset" name="reset">重置</button>
</div>
</form>
</div>
<!-- 注册按钮 -->
<div class="register">
<button onclick="window.location.href='register.jsp'">创建新账号</button>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>(4) Produkte abfragen und Produkte kaufen
Die Funktion hier besteht hauptsächlich darin, die MongoDB-Datenbank zu betreiben und die spezifischen Informationen des Produkts zurückzugeben Solange Sie die Benutzeranmeldefunktion verstehen, wird der Funktionscode hier schnell verstanden und der spezifische Code wird später angezeigt.
(5) Warenkorb
Die Funktion besteht auch hier hauptsächlich darin, MongoDB-Daten zu verwalten und Warenkorb-bezogene Funktionen durch Benutzerinteraktion mit dem Client zu implementieren. Der spezifische Code wird später angezeigt.
2.6 Spezifische Codierung
Die Erläuterung der spezifischen Codierung wird in der groben Reihenfolge der Implementierung von Funktionen wie folgt eingeführt:
2.6.1 Benutzeranmeldung und -merkung Passwort
Das erste, was Sie sich ansehen, ist die Seite login.jsp auf der Startseite. Um sie schön anzuzeigen, verwendet dieses Ding eine login.css-Datei (die folgenden Seiten verwenden alle login. CSS-Dateien). Der spezifische Code von login.css lautet wie folgt:
@CHARSET "UTF-8";
/*按照样图要求,添加一个浅灰色背景*/
body{
background-color: #F2F2F2;
}
/*设置内容模块距离顶部一个有一段距离100px*/
.content {
margin-top: 80px;
}
/*登录和注册按钮的整体样式*/
.content button {
height: 30px;/*登录和注册按钮的高度*/
color: white;/*登录和注册按钮字体颜色为白色*/
font-size: 18px;/*登录和注册按钮的字体大小*/
border: 0px;/*无边框*/
padding: 0px;/*无内边距*/
cursor: pointer;/*登录和注册按钮的选择时为手形状*/
}
/*头部名称*/
.content .head {
text-align: center;/*子内容居中*/
}
/*登录面板*/
.content .panel {
background-color: white;/*登录面板背景颜色为白色*/
width: 302px;/*宽度为302px*/
text-align: center;/*子内容居中*/
margin: 0px auto;/*自身居中*/
padding-top: 10px;/*顶部的内边距为20px*/
padding-bottom: 10px;/*底部的内边距为20px*/
border: 1px solid #ddd;/*边框颜色为灰色*/
border-radius: 5px;/*边框边角有5px的弧度*/
}
/*购物主页购物面板*/
.content .panel1 {
background-color: white;/*购物主页面板背景颜色为白色*/
width: 1000px;/*宽度为600px*/
text-align: center;/*子内容居中*/
margin: 0px auto;/*自身居中*/
border: 1px solid #ddd;/*边框颜色为灰色*/
border-radius: 5px;/*边框边角有5px的弧度*/
}
/*登录和密码组*/
.content .panel .group {
text-align: left;/*子内容居中*/
width: 262px;/*宽度为262px*/
margin: 0px auto 20px;/*自身居中,并距离底部有20px的间距*/
}
.content .panel .group label {
line-height: 30px;/*高度为30px*/
font-size: 18px;/*字体大小为18px*/
}
.content .panel .group input {
display: block;/*设置为块,是为了让输入框独占一行*/
width: 250px;/*宽度为250px*/
height: 30px;/*高度为30px*/
border: 1px solid #ddd;/*输入框的边框*/
padding: 0px 0px 0px 10px;/*左边内边距为10px,显得美观*/
font-size: 16px;/*字体大小*/
}
.content .panel .group input:focus{
border-left: 1px solid #CC865E;/*当输入框成为焦点时,左边框颜色编程褐色*/
}
.content .panel .login button {
background-color: #CC865E;/*按钮的背景颜色*/
width: 130px;/*按钮的宽度*/
}
.content .panel .login button:hover {
background-color: white;/*按钮选中后背景颜色为白色*/
color: #CC865E;/*按钮选中后字体颜色为褐色*/
border: 1px solid #CC865E;/*按钮选中后边框颜色为褐色*/
}
/*注册按钮*/
.content .register {
text-align: center;/*子内容居中*/
margin-top: 20px;/*顶部的内边距为20px*/
}
.content .register button {
background-color: #466BAF;/*按钮的背景颜色为蓝色*/
width: 180px;/*按钮的宽度*/
}
.content .register button:hover {
background-color: white;/*按钮选中后背景颜色为白色*/
color: #466BAF;/*按钮选中后字体颜色为蓝色*/
border: 1px solid #466BAF;/*按钮选中后边框颜色为蓝色*/
}Der spezifische Code von Login.jsp lautet wie folgt:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
String username = "";
String password = "";
//获取当前站点的所有Cookie
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
for (int i = 0; i < cookies.length; i++) {
//对cookies中的数据进行遍历,找到用户名、密码的数据
if ("username".equals(cookies[i].getName())) {
//读取时URLDecoder.decode进行解码(PS:Cookie存取时用URLEncoder.encode进行编码)
username = java.net.URLDecoder.decode(cookies[i].getValue(),"UTF-8");
} else if ("password".equals(cookies[i].getName())) {
password = java.net.URLDecoder.decode(cookies[i].getValue(),"UTF-8");
}
}
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>登陆页面</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/login.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="content">
<div class="head">
<h1>简单购物车</h1>
</div>
<!-- 登录面板 -->
<div class="panel">
<form action="login_action.jsp" method="post">
<!-- 账号和密码组 -->
<div class="group">
<label>账号</label>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入账号" name="username" value="<%=username%>">
</div>
<div class="group">
<label>密码</label>
<input type="password" placeholder="请输入密码" name="password" value="<%=password%>">
</div>
<div>
<input type="checkbox" value="save" name="save_password">
<label>记住密码</label>
</div>
<div class="group">
<label></label>
</div>
<!-- 登录按钮 -->
<div class="login">
<button type="submit" name="login">登陆</button>
<button type="reset" name="reset">重置</button>
</div>
</form>
</div>
<!-- 注册按钮 -->
<div class="register">
<button onclick="window.location.href='register.jsp'">创建新账号</button>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Der Code des Anmeldeverarbeitungsskripts login_action.jsp lautet wie folgt:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*,com.mongodb.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'login_action.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<%
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8"); //确保显示的汉字信息以正确编码方式显示
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); //确保获取的汉字信息以正确编码方法获取
String userName=(String)request.getParameter("username"); //获取登录页面用户名
String passWord=(String)request.getParameter("password");//获取登陆页面密码
String checkBox = request.getParameter("save_password");//获取登陆页面记住密码选择框属性值
boolean login_test = false; //设定登陆布尔值,若用户名和密码成功匹配,则为true
try{
// 连接到 mongodb 服务
MongoClient mongoClient = new MongoClient( "localhost" , 27017 );
//此处采用无用户名和密码验证方式登陆
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
DB db = mongoClient.getDB( "library" ); //连接到数据库library
DBCollection coll = db.getCollection("userInfo"); //获取library数据库中集合userInfo
System.out.println("Collection userInfo selected successfully");
DBCursor cursor = coll.find(); //查询集合userInfo中文档信息
int i=1;
while (cursor.hasNext()) { //检索集合userInfo中所有文档信息
System.out.println("userInfo Document: "+i);
DBObject show = cursor.next();
System.out.println(show);
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
Map show1 = show.toMap(); //将检索结果show(Bson类型)转换为Map类型
String toname = (String)show1.get("username"); //提取Map中字段名为username的属性值
String topassword = (String)show1.get("password"); //提取Map中字段名为password的属性值
if(toname.equals(userName) && topassword.equals(passWord)){
//将从数据库中获取的用户名和密码与表单中获取的数据进行验证,匹配成功则使login_test值为true
System.out.println("登陆成功!!!!!"+"username:"+toname+" password:"+topassword);
//request.getRequestDispatcher("welcome.jsp").forward(request, response);
login_test = true;
}
System.out.println(show1.get("username"));
i++;
}
}catch(Exception e){
System.err.println( e.getClass().getName() + ": " + e.getMessage() );
}
if(login_test) {
if ("save".equals(checkBox)) {
//Cookie存取时用URLEncoder.encode进行编码(PS:读取时URLDecoder.decode进行解码)
String name1 = java.net.URLEncoder.encode(userName,"UTF-8");
//创建两个Cookie对象
Cookie nameCookie = new Cookie("username", name1);
//设置Cookie的有效期为3天
nameCookie.setMaxAge(60 * 60 * 24 * 3);
String pwd = java.net.URLEncoder.encode(passWord,"UTF-8");
Cookie pwdCookie = new Cookie("password", pwd);
pwdCookie.setMaxAge(60 * 60 * 24 * 3);
response.addCookie(nameCookie);
response.addCookie(pwdCookie);
}
// request.getRequestDispatcher("welcome.jsp").forward(request, response);
response.sendRedirect("welcome.jsp");
}
else{
response.sendRedirect("login_Fail.jsp");
// request.getRequestDispatcher("loginFail.jsp").forward(request, response);
}
%>
</body>
</html>Der login_Fail.jsp-Seitencode für fehlgeschlagene Anmeldung lautet wie folgt:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>登陆失败</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/login.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="content">
<div class="panel1">
<h1>输入用户名和密码不正确,请重新登陆!!!</h1>
</div>
<div class="register">
<button onclick="window.location.href='login.jsp'">返回</button>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>2.6.2 Benutzerregistrierung
Das Register Der .jsp-Seitencode für die Registrierungs-Homepage lautet wie folgt:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>注册页面</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/login.css">
<Script Language="JavaScript">
function check()
{
var tmp,str;
str=document.myform.password1.value;
tmp=document.myform.password2.value;
if(str != tmp)
alert("两次密码输入不一致,请重新确认密码!!!");
}
</Script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="content">
<div class="head">
<h1>欢迎来到简单购物车系统注册页面</h1>
</div>
<!-- 注册面板 -->
<div class="panel">
<form name="myform" action="register_action.jsp" method="post">
<!-- 账号和密码组 -->
<div class="group">
<label></label>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入注册账号" name="username1">
</div>
<div class="group">
<label></label>
<input type="password" placeholder="请输入注册密码" name="password1">
</div>
<div class="group">
<label></label>
<input type="password" placeholder="请确认注册密码" name="password2">
</div>
<!-- 注册按钮 -->
<div class="login">
<button type="submit" name="register" onclick="check()">注册</button>
<button type="reset" name="reset1">重置</button>
</div>
</form>
<div class="register">
<button onclick="window.location.href='login.jsp'">返回</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Der Registrierungsverarbeitungsskript-Code register_action.jsp lautet wie folgt:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*,com.mongodb.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
String text_change = "等待注册";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'register_action.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
</head>
<body>
<%
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8"); //确保显示的汉字信息以正确编码方式显示
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); //确保获取的汉字信息以正确编码方法获取
String userName1=(String)request.getParameter("username1"); //获取页面用户名
String passWord1=(String)request.getParameter("password1");//获取注册页面密码1
String passWord2=(String)request.getParameter("password2");//获取注册页面密码2
if(!passWord1.equals(passWord2)){
//如果用户两次输入密码不一致,则跳转到注册原页面register.jsp,即实现未跳转效果
response.sendRedirect("register.jsp");
}
try{
// 连接到 mongodb 服务
MongoClient mongoClient = new MongoClient( "localhost" , 27017 );
//此处采用无用户名和密码验证方式登陆
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
DB db = mongoClient.getDB( "library" ); //连接到数据库library
DBCollection coll = db.getCollection("userInfo"); //获取library数据库中集合userInfo
System.out.println("Collection userInfo selected successfully");
DBObject user = new BasicDBObject();//定义一个Bson变量,用于存储注册的用户名和密码
user.put("username", userName1);
user.put("password", passWord1);
coll.insert(user); //向集合userInfo中插入注册用户信息
response.sendRedirect("register_success.jsp"); //注册成功后,自动跳转到注册成功提示页面
}catch(Exception e){
System.err.println( e.getClass().getName() + ": " + e.getMessage() );
}
%>
</body>
</html>Die erfolgreiche Registrierungsaufforderungsseite register_success.jsp Der Seitencode lautet wie folgt:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>注册成功</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/login.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="content">
<div class="panel1">
<h1>恭喜您,您已经成功注册简单购物车系统</h1>
</div>
<div class="register">
<button onclick="window.location.href='login.jsp'">返回</button>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>2.6.3 Produkte anzeigen
Werfen Sie zunächst einen Blick auf den Seitencode „welcome.jsp“ auf der Shopping-Homepage:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; %> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> <html> <head> <base href="<%=basePath%>"> <title>购物页面</title> <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> <meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> <!-- <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css"> --> </head> <frameset rows="30%,60%,10%" cols="*" frameborder="no" border="0" framespacing="0"> <frame src="header.jsp"> <frame src="main_shop.jsp"> <frame src="bottom.jsp"> </frameset> <body> </body> </html>
Der Header.jsp-Seitencode auf der Startseite:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" contentType="text/html;charset=gb2312" pageEncoding="gb2312"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title></title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=gb2312">
</head>
<body topmargin="0" leftmargin="0" rightmargin="0" style="background-color: #F2F2F2;overflow-x:hidden;overflow-y:hidden">
<form action="">
<table width="100%" height="79" border="0" cellpadding="0"
cellspacing="0" align=center>
<tr>
<td bgcolor="F9A859" valign="top">
<table width="100%" height="100" border="0" align="center"
cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" bgcolor="#466BAF">
<tr>
<td align="center" style="font-size:60px;color: white;">
简单购物车系统
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td bgcolor="F9A859" valign="top">
<table width="100%" height="50" border="0" align="center" cellpadding="0"
cellspacing="0" bgcolor="#CC865E">
<tr>
<td align="center" style="font-size:20px;color: white;">
欢迎你访问!</td>
</tr>
</table>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>Der Bottom.jsp-Seitencode am Ende:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'bottom.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
</head>
<body style="background-color: #F2F2F2;overflow-x:hidden;overflow-y:hidden">
<hr>
<h4 style="width:100%;text-align:center">Copyright @2016 舞动的心</h4>
</body>
</html>Zwischenkörper der Startseite main_shop.jsp Seitencode;
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=GBK" import="java.util.*,com.liuzhen.shop.MongodbBean" %>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
String cp=request.getParameter("cp");//cp为分页数
//int page_number = DBBean.getTotalPage();
//int currpage = page_number;
int currpage=(cp==null||cp=="")?1:Integer.parseInt(cp);
String[][] ss = MongodbBean.getGoodList(currpage);
int n = MongodbBean.getlength(ss);
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>购物页面</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/login.css">
</head>
<body style="overflow-x:hidden;overflow-y:hidden">
<div class="content">
<div class="panel1">
<table border="1" align="center">
<tr>
<th width="30%" align="center">物品编号</th>
<th width="30%" align="center">物品名</th>
<th width="30%" align="center">定价</th>
<th width="50%" align="center">求购</th>
</tr>
<%
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
%>
<tr>
<td height="30%" align="center"><%= ss[i][0] %></td>
<td height="30%" align="center"><%= ss[i][1] %></td>
<td height="30%" align="center"><%= ss[i][2] %></td>
<td height="30%" align="center"><a href="Buy.jsp?sid=<%= ss[i][0] %>&action=buy">购买</a></td>
</tr>
<%
}
%>
</table>
<%
int tp=MongodbBean.getTotalPage();
if(currpage!=1)
{
%>
<a href="main_shop.jsp?cp=<%=currpage-1%>">上一页</a>
<%
}
if(currpage!=tp)
{
%>
<a href="main_shop.jsp?cp=<%=currpage+1%>">下一页</a>
<%
}
%>
<form action="main_shop.jsp" name="myform">
<select name="cp" onchange="document.myform.submit()">
<%
for(int i=1;i<=tp;i++)
{
%>
<option value="<%=i%>" <%= (i==currpage)?"selected":"" %>>第<%=i%>页</option>
<%
}
%>
</select>
</form>
</div>
<div class="register">
<button onclick="window.location.href='Cart.jsp'">查看购物车</button>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Die Funktion zum Anzeigen von Produkten wird hauptsächlich durch Aufrufen der Klasse MongodbBean.java implementiert. Der spezifische Code lautet wie folgt:
package com.liuzhen.shop;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Vector;
import com.mongodb.*;
public class MongodbBean {
static int span=5; //设定JSP页面表单单页显示物品信息行数为5行
//返回数据库中全部货物编号sid
public static String[] getGood_sid(){
String[] good_sid_temporary = new String[100]; //定义一个长度为100的暂时存放货物编号的一维数组
// 连接到 mongodb 服务
MongoClient mongoClient = new MongoClient( "localhost" , 27017 );
//此处采用无用户名和密码验证方式登陆
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
DB db = mongoClient.getDB( "library" ); //连接到数据库library
DBCollection coll = db.getCollection("good"); //获取library数据库中集合good
System.out.println("Collection userInfo selected successfully");
DBCursor cursor = coll.find(); //查询集合good中文档信息
int i=0;
while (cursor.hasNext()) { //检索集合good中所有文档信息
DBObject show = cursor.next();
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
Map show1 = show.toMap(); //将检索结果show(Bson类型)转换为Map类型
String tosid = (String)show1.get("sid"); //提取Map中字段名为sid的属性值
good_sid_temporary[i] = tosid; //将数据库中查询的货物编号存储入数组good_sid
i++;
}
String[] good_sid = new String[i]; //根据查询数据遍历集合中文档信息i值来确定最终返回数组长度
for(int j=0;j<i;j++){
good_sid[j] = good_sid_temporary[j];
}
return good_sid;
}
//返回数据库中全部货物名称sname
public static String[] getGood_sname(){
String[] good_sname_temporary = new String[100]; //定义一个长度为100的暂时存放货物名称的一维数组
// 连接到 mongodb 服务
MongoClient mongoClient = new MongoClient( "localhost" , 27017 );
//此处采用无用户名和密码验证方式登陆
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
DB db = mongoClient.getDB( "library" ); //连接到数据库library
DBCollection coll = db.getCollection("good"); //获取library数据库中集合good
System.out.println("Collection userInfo selected successfully");
DBCursor cursor = coll.find(); //查询集合good中文档信息
int i=0;
while (cursor.hasNext()) { //检索集合good中所有文档信息
DBObject show = cursor.next();
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
Map show1 = show.toMap(); //将检索结果show(Bson类型)转换为Map类型
String tosname = (String)show1.get("sname"); //提取Map中字段名为sname的属性值
good_sname_temporary[i] = tosname; //将数据库中查询的货物名称存储入数组good_sname
i++;
}
String[] good_sname = new String[i]; //根据查询数据遍历集合中文档信息i值来确定最终返回数组长度
for(int j=0;j<i;j++){
good_sname[j] = good_sname_temporary[j];
}
return good_sname;
}
//返回数据库中全部货物价格sprice
public static String[] getGood_sprice(){
String[] good_sprice_temporary = new String[100]; //定义一个长度为100的暂时存放货物价格的一维数组
// 连接到 mongodb 服务
MongoClient mongoClient = new MongoClient( "localhost" , 27017 );
//此处采用无用户名和密码验证方式登陆
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
DB db = mongoClient.getDB( "library" ); //连接到数据库library
DBCollection coll = db.getCollection("good"); //获取library数据库中集合good
System.out.println("Collection userInfo selected successfully");
DBCursor cursor = coll.find(); //查询集合good中文档信息
int i=0;
while (cursor.hasNext()) { //检索集合good中所有文档信息
DBObject show = cursor.next();
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
Map show1 = show.toMap(); //将检索结果show(Bson类型)转换为Map类型
String tosprice = (String)show1.get("sprice"); //提取Map中字段名为sname的属性值
good_sprice_temporary[i] = tosprice; //将数组库中查询的货物价格存储入数组good_sprice
i++;
}
String[] good_sprice = new String[i]; //根据查询数据遍历集合中文档信息i值来确定最终返回数组长度
for(int j=0;j<i;j++){
good_sprice[j] = good_sprice_temporary[j];
}
return good_sprice;
}
//根据分页当前page数,从数据库中获取当前单个页面货物种类的具体信息,并以二维数据返回具体信息
public static String[][] getGoodList(int page)
{
String[][] result=null;
Vector<String[]> v=new Vector<String[]>(); //定义一个Vector集合,一个记录存放一个货物的具体信息
String[] good_sid = getGood_sid(); //获取货物编号
String[] good_sname = getGood_sname(); //获取货物名称
String[] good_sprice = getGood_sprice(); //获取货物价格
int len = good_sid.length;
for(int i=0;i<span;i++){
int t = (page-1)*span+i; //获取货物编号
if(t >= len){
//如果当前货物编号大于数据库中已有编号,则跳出循环
break;
}
String[] good_temp=new String[3]; //定义一个长度为3的数组,用于存放一个物品的编号、名称、价格信息
good_temp[0]=good_sid[t];
good_temp[1]=good_sname[t];
good_temp[2]=good_sprice[t];
v.add(good_temp); //将1个物品的信息存入Vector集合中
}
int size = v.size();
result=new String[size][]; //根据Vercotr大小,给result指定行数大小
for(int j=0;j<size;j++)
{
//返回Vector中一个值(其中即表示一个物品的sid,名称和价格),并赋值给result[j],即result二维数组一行表示一个物品具体信息
result[j]=(String[])v.elementAt(j);
}
return result;
}
//根据货物sid,返回其价格信息
public static double getPrice(String sid)
{
double price = 0; //定义返回物品的价格
String[] good_sprice = getGood_sprice(); //获取全部物品的价格
int i = Integer.parseInt(sid); //将String类型的物品编号sid转换为int型
String sprice = good_sprice[i]; //根据sid获取物品的价格
price = Double.parseDouble(sprice); //将String类型的价格信息转换为double型,并赋值给price
return price;
}
//根据货物sid,返回货物的名称和价格,一一个长度为2的数组返回
public static String[] getDetail(String sid)
{
String[] good_detail=null;
good_detail = new String[2];
String[] good_sname = getGood_sname(); //获取全部物品名称
String[] good_sprice = getGood_sprice(); //获取全部物品价格
int i = Integer.parseInt(sid); //将String类型的物品编号sid转换为int型
good_detail[0] = good_sname[i]; //根据物品编号sid,得到名称存入数组good_detail中
good_detail[1] = good_sprice[i]; //根据物品编号sid,得到物品价格存入数组good_detail中
return good_detail;
}
//通过查询数据库中货物种类数目,以5行为一页,返回现有货物页数
public static int getTotalPage()
{
int page = 0;
String[] good_sid = getGood_sid();
int len = good_sid.length;
page = len/span+((len%span==0)?0:1); //以span(span值为5)行为一页,计算货物具有的页数page
return page;
}
//返回一个二维数组的行数大小
public static int getlength(String[][] a){
return a.length;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
// String[] good_sid = getGood_sid(); //定义一个存放货物编号的一维数组
// String[] good_sname = getGood_sname(); //定义一个存放货物名称的一维数组
// String[] good_sprice = getGood_sprice(); //定义一个存放货物价格的一维数组
//
// for(int j=0;j<10;j++){
// System.out.println("货物sid:"+good_sid[j]);
// System.out.println("货物sname:"+good_sname[j]);
// System.out.println("货物是price:"+good_sprice[j]);
// System.out.println("**************************");
// System.out.println();
// }
System.out.println("分页数目(测试):"+MongodbBean.getTotalPage());
String[][] ss=MongodbBean.getGoodList(MongodbBean.getTotalPage());
for(int i=0;i<ss.length;i++)
{
System.out.println(ss[i][0]);
System.out.println(ss[i][1]);
System.out.println(ss[i][2]);
System.out.println("***********");
}
int n = ss.length;
System.out.println("数组长度为:"+n);
}
}2.6.4 Waren kaufen
Um Waren zu kaufen, rufen Sie die Klasse ShopCartBean.java über das Geschäftsverarbeitungsskript Buy.jsp auf.
ShopCartBean.java-Klassencode lautet wie folgt:
package com.liuzhen.shop;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class ShopCartBean {
//ShopCartBean类构造函数
public ShopCartBean(){
}
//定义一个存储整形数值的键值对hashMap
HashMap<String, Integer> hm=new HashMap<String, Integer>();
//定义购物车总物品总价格,初始值为0
double total=0;
//添加购买的物品,存入哈希表hm中,并计算购买成功后的总价格
public void add(String sid)
{
if(hm.containsKey(sid))
{
//如果hm中包含键值对sid,则获取该键值对中的值,并加1
int xc=((Integer)hm.get(sid)).intValue()+1;
//把上面获取的xc值存入hm中
hm.put(sid,new Integer(xc));;
}
else
{
//如果hm中不包含键值对sid,则将该键值对存入hm中,并该键值对值为1
hm.put(sid,new Integer(1));
}
total=total+MongodbBean.getPrice(sid); //购买物品后,计算物品总价格
}
//获取购物车当前物品总价格
public double getTotal()
{
return total;
}
//根据物品编号sid,设定购买物品数目,并将购买数目存入哈希表hm中,并更新当前购物车物品总价格
public void setCount(int c,String sid)
{
int yc=((Integer)hm.get(sid)).intValue();
total=total+(c-yc)*MongodbBean.getPrice(sid);
hm.put(sid,new Integer(c));
}
//根据物品编号sid,从购物车中删除物品,并删除存入哈希表hm中物品的数目,以及当前购物车物品总价格
public void deleteFromCart(String sid)
{
int yc=((Integer)hm.get(sid)).intValue();
total=total-yc*MongodbBean.getPrice(sid);
hm.remove(sid);
}
//判断当前哈希表hm是否为空
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return hm.isEmpty();
}
//返回用户购买物品的详细信息(物品编号、物品名称、物品价格、物品购买数量)
public String[][] getCart()
{
//定义一个set集合,存放哈希表hm中键值对的键名称
Set<String> ks=hm.keySet();
//定义一个迭代器,用于遍历set集合
Iterator<String> ii=ks.iterator();
//获取哈希表hm中键值对的个数
int size=hm.size();
//定义二维数组,存放购买物品的信息
String rs[][]=new String[size][];
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
{
String sid=(String)ii.next(); //存放键值对的键名,即货物的编号sid
String[] sa=new String[4];
sa[0]=sid; //获取购买货物sid
String[] sat=MongodbBean.getDetail(sid); //根据货物sid,获取购买货物的名称和价格
sa[1]=sat[0]; //获取购买货物名称
sa[2]=sat[1]; //获取购买货物价格
sa[3]=((Integer)hm.get(sid)).toString(); //获取购买货物数量
rs[i]=sa; //将上述单个物品详细存入二维数组rs中
}
return rs;
}
}Buy.jps-Einkaufsverarbeitungsskriptcode lautet wie folgt:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" contentType="text/html;charset=utf-8" pageEncoding="gb2312"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<jsp:useBean id="cart" scope="session" class="com.liuzhen.shop.ShopCartBean"/>
<%
String action=request.getParameter("action");
if(action==null)
{
%>
<jsp:forward page="main_shop.jsp"/>
<%
}
else if(action.trim().equals("buy"))
{
String sid=request.getParameter("sid");
cart.add(sid.trim());
%>
<jsp:forward page="main_shop.jsp"/>
<%
}
else if(action.trim().equals("gc"))
{
String sid=request.getParameter("sid");
String count=request.getParameter("count");
cart.setCount(Integer.parseInt(count),sid);
%>
<jsp:forward page="Cart.jsp"/>
<%
}
else if(action.trim().equals("del"))
{
String sid=request.getParameter("sid");
cart.deleteFromCart(sid);
%>
<jsp:forward page="Cart.jsp"/>
<%
}
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title></title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>2.6.5 Warenkorb
Die Warenkorbfunktion wird hauptsächlich durch Aufrufen der ShopCartBean.java-Klasse über die Cart.jsp-Seite implementiert. Der Code der ShopCartBean.java-Klasse ist oben angegeben :
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" contentType="text/html;charset=gb2312" import="com.liuzhen.shop.MongodbBean"
pageEncoding="gb2312"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<jsp:useBean id="cart" scope="session" class="com.liuzhen.shop.ShopCartBean"/>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>购物车</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=gb2312">
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css/login.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="content">
<div class="panel1">
<%
if(cart.isEmpty())
{
%>
<font color="red" size="20">购物车中没有任何商品!!!</Font>
<%
}
else
{
%>
<h2>购物车</h2>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<td width="27%" align="center">物品编号</td>
<td width="27%" align="center">物品名</td>
<td width="27%" align="center">定价</td>
<td width="27%" align="center">数量</td>
<td width="27%" align="center">求购</td>
</tr>
<%
String[][] ssa=cart.getCart();
for(int i=0;i<ssa.length;i++)
{
%>
<tr>
<td height="30%" align="center"><%= ssa[i][0] %></td>
<td height="30%" align="center"><%= ssa[i][1] %></td>
<td height="30%" align="center"><%= ssa[i][2] %></td>
<td>
<form action="Buy.jsp" method="post">
<input type="text" name="count" value="<%= ssa[i][3] %>">
<input type="hidden" name="sid" value="<%= ssa[i][0] %>">
<input type="hidden" name="action" value="gc">
</form>
</td>
<td><a href="Buy.jsp?sid=<%= ssa[i][0] %>&action=del">删除</a></td>
</tr>
<%
}
%>
</table>
<br>
<br>
本订单总价为:<%= Math.round(cart.getTotal()*100)/100.0%>
<%
}
%>
<br>
<div class="register">
<button onclick="window.location.href='main_shop.jsp'">继续购物</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Das Obige ist der gesamte Inhalt dieses Artikels. Ich hoffe, dass er zum Lernen aller beiträgt. Ich hoffe auch, dass jeder die PHP-Chinesisch-Website unterstützt.
Weitere verwandte Artikel, in denen MongoDB und JSP zur Implementierung eines einfachen Beispiels für ein Warenkorbsystem verwendet werden, finden Sie auf der chinesischen PHP-Website!

