Die AIxiv-Kolumne ist eine Kolumne, in der diese Website akademische und technische Inhalte veröffentlicht. In den letzten Jahren sind in der AIxiv-Kolumne dieser Website mehr als 2.000 Berichte eingegangen, die Spitzenlabore großer Universitäten und Unternehmen auf der ganzen Welt abdecken und so den akademischen Austausch und die Verbreitung wirksam fördern. Wenn Sie hervorragende Arbeiten haben, die Sie teilen möchten, können Sie gerne einen Beitrag leisten oder uns für die Berichterstattung kontaktieren. Einreichungs-E-Mail: liyazhou@jiqizhixin.com; zhaoyunfeng@jiqizhixin.com
Die Autoren dieses Papiers sind Lehrer und Studenten des Instituts für Multi-Agent und verkörperte Intelligenz des Pengcheng Laboratory der Southern University of Science Technologie und Sun Yat-sen-Universität. Zum Team gehören Professor Lin Liang (Direktor des Instituts, National Distinguished Young Scholar, IEEE Fellow), Professor Zheng Feng, Professor Liang Xiaodan, Wang Zhiqiang (Southern University of Science and Technology) und Zheng Hao (Southern University of Science and Technology), Nie Yunshuang (CUHK), Xu Wenjun (Pengcheng), Ye Hua (Pengcheng) usw. Das Team von Professor Lin Liang vom Pengcheng Laboratory widmet sich dem Aufbau allgemeiner Basisplattformen wie Multi-Agenten-Kollaborations- und Simulationstrainingsplattformen sowie Cloud-kollaborativer verkörperter multimodaler Großmodelle, um wichtige Anwendungsanforderungen wie das industrielle Internet sowie soziale Governance und Dienste zu erfüllen . Seit diesem Jahr entwickelt sich verkörperte Intelligenz zu einem heißen Feld in Wissenschaft und Industrie, und verwandte Produkte und Ergebnisse entstehen nacheinander. Heute hat das Institute of Multi-Agent and Embodied Intelligence des Pengcheng Laboratory (im Folgenden als Pengcheng Embodied Institute bezeichnet) zusammen mit der Southern University of Science and Technology und der Sun Yat-sen University seine neuesten akademischen Errungenschaften auf dem Gebiet offiziell veröffentlicht und als Open Source bereitgestellt Der verkörperte groß angelegte Datensatz von ARIO (All Robots) In One zielt darauf ab, die Datenerfassungsprobleme zu lösen, mit denen derzeit im Bereich der verkörperten Intelligenz konfrontiert ist. 

Papiertitel: All Robots in One: A New Standard and Unified Dataset for Versatile.General-Purpose Embodied Agents
Link zum Papier: http://arxiv.org/abs/2408.10899
Projekt-Homepage: https://imaei.github.io/project_pages/ario/
Link zur Website des Pengcheng Laboratory Embodiment Institute: https://imaei.github.io/
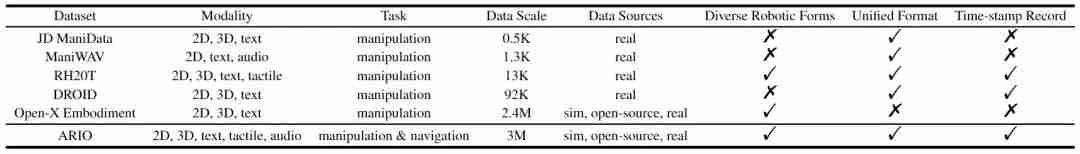
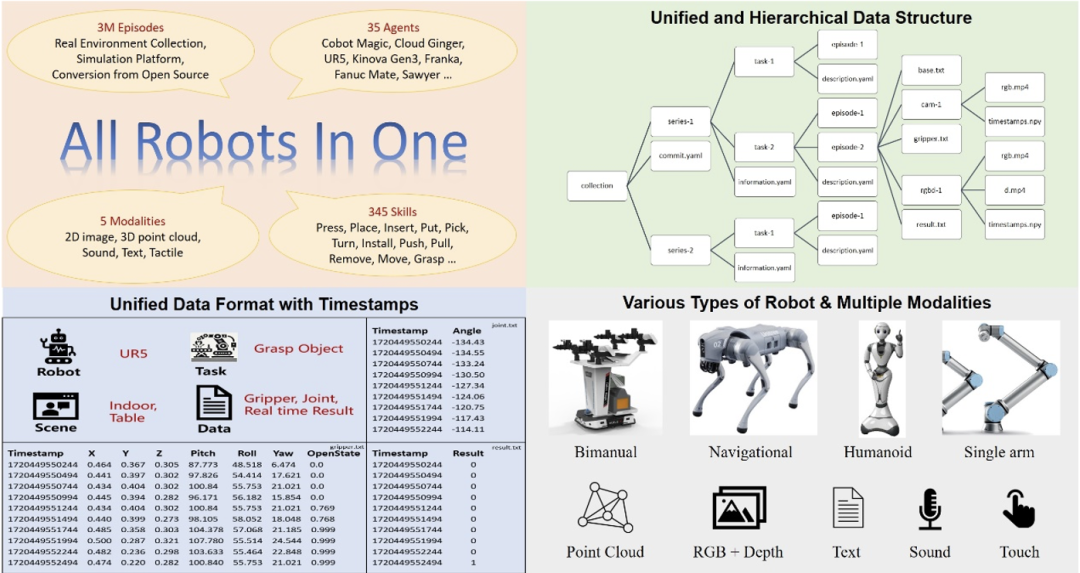
As the brain of the embodied robot, the key to making the performance of the embodied large model better is to obtain high-quality embodied big data. Different from the text or image data used in large language models or large visual models, embodied data cannot be directly obtained from the massive content of the Internet, but needs to be collected through real robot operations or generated by advanced simulation platforms. Therefore, the collection of embodied data It requires high time and cost, and it is difficult to achieve large scale. At the same time, the current open source data sets also have many shortcomings. As shown in the table above, the data volume of JD ManiData, ManiWAV and RH20T is not large, and the robot hardware platform used for DROID data is relatively single. Open-X Embodiment Although it has reached a large amount of data, its sensory data modalities are not rich enough, and the data formats between sub-data sets are not uniform and the quality is also uneven. It takes a lot of time to filter and process the data before using it, and it is difficult to Meet the needs for efficient and targeted training of embodied intelligent models in complex scenarios. In comparison, the ARIO data set released this time contains sensory data in 5 modalities: 2D, 3D, text, touch, and sound, covering two major categories: operation and navigation The tasks include both simulation data and real scene data, and contain a variety of robot hardware, which is very rich. While the data scale reaches three million, it also ensures a unified format of the data. It is currently an open source data set that simultaneously achieves high quality, diversity and large-scale in the field of embodied intelligence. For the data set of embodied intelligence, since robots have many forms, such as single-arm, double-arm, humanoid, four-legged, etc., and the perception and control methods are also different, some are controlled through joint angles , and some are driven by the body or end pose coordinates, so the embodied data itself is much more complex than simple image and text data, and many control parameters need to be recorded. And if there is no unified format, when multiple types of robot data are aggregated together, a lot of energy will be spent on additional preprocessing. Therefore, the Embodiment Institute of Pengcheng Laboratory first designed a set of format standards for embodied big data. This standard can record various forms of robot control parameters, has a clear structure of data organization form, and can also It is compatible with sensors with different frame rates and records corresponding timestamps to meet the precise requirements of the embodied intelligent large model for sensing and control timing. The figure below shows the overall design of the ARIO dataset. O Figure 1. ARIO data set design 
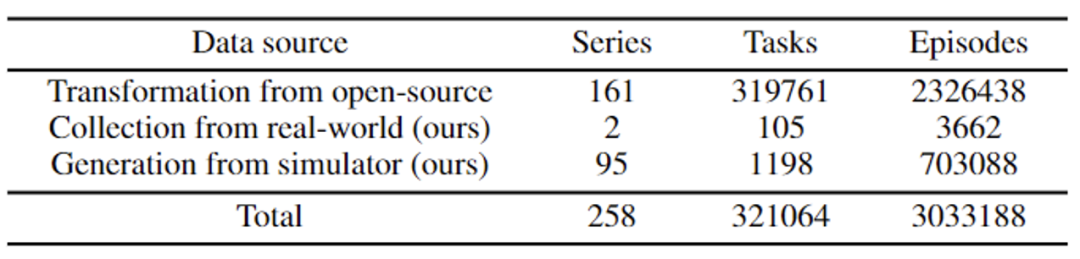
Ario dataset, with a total of 258 scene sequences, 32,1064 tasks, and 3.03 million samples. ARIO's data comes from three major sources. One is real-person collection by arranging scenes and tasks in real environments; the other is based on simulation engines such as MuJoCo and Habitat
to design virtual scenes and object models, and drive the robot model through the simulation engine. The third step is to analyze and process the currently open source embodied data sets one by one and convert them into data that conforms to the ARIO format standard. The following shows the specific composition of the ARIO dataset, as well as the processes and examples from the 3 sources.
High-quality robotics data is hard to come by, but it’s incredibly valuable. Based on the Cobot Magic master-slave dual-arm robot, Pengcheng Laboratory has designed more than 30 tasks, including 3 operation difficulty levels: simple - medium - difficult, and by adding interfering objects, randomly changing the positions of objects and robots, and changing the layout The environment and other methods were used to increase the diversity of samples, and finally more than 3,000 pieces of trajectory data containing 3 RGBD cameras were obtained. Collection examples for different tasks and collection videos are shown below.

O Figure 3. Ario Real Robot Data Collection Example COBOT MAGIC Robotic Kimneys Collection Data Example Video  MUJOCO simulation data collection example video
MUJOCO simulation data collection example video 

 Example video of simulation data generation based on the platform
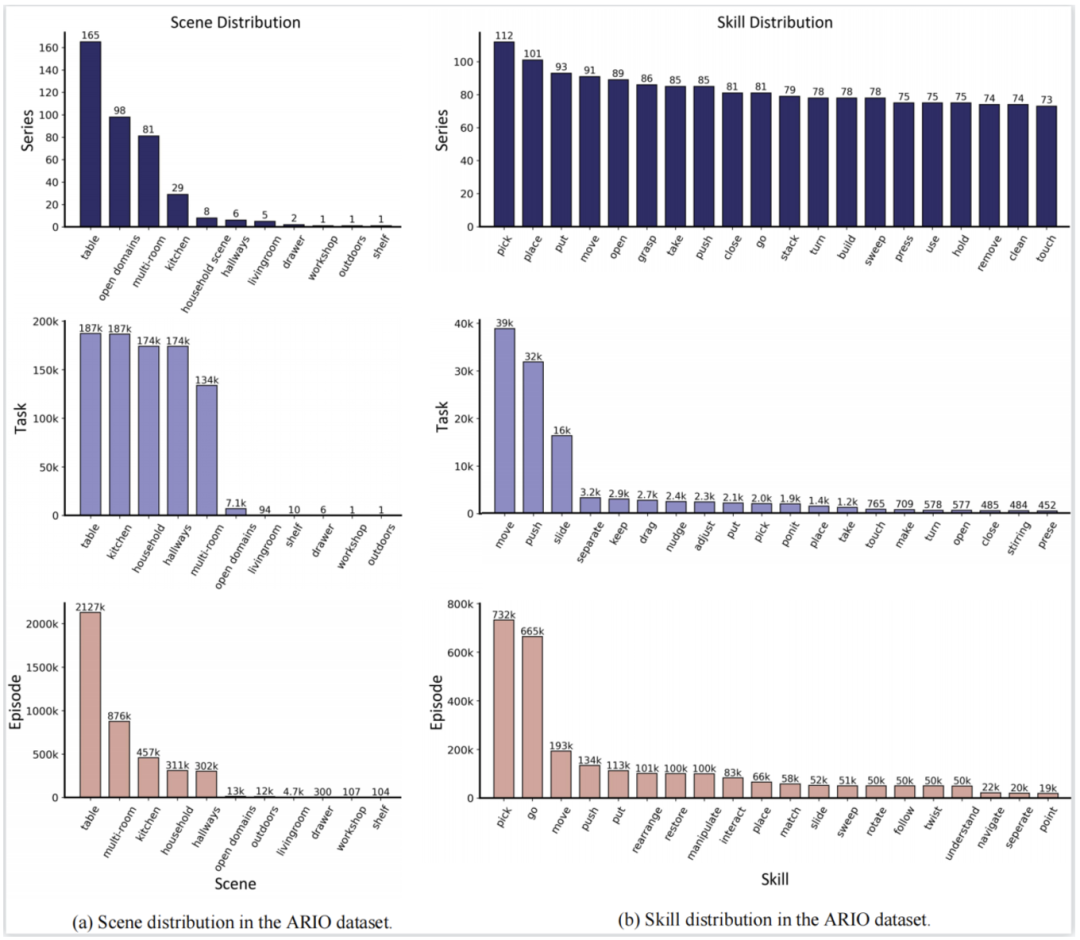
Example video of simulation data generation based on the platform  Data example video converted from RH20T thanks to ARIO The unified format design of the data makes it easy to perform statistical analysis on its data composition. The figure below shows the statistics of the distribution of ARIO scenes (figure a) and skills (figure b) from the three levels of series, task, and episode. It can be seen that most of the embodied data currently focus on scenes and skills in indoor living and home environments.
Data example video converted from RH20T thanks to ARIO The unified format design of the data makes it easy to perform statistical analysis on its data composition. The figure below shows the statistics of the distribution of ARIO scenes (figure a) and skills (figure b) from the three levels of series, task, and episode. It can be seen that most of the embodied data currently focus on scenes and skills in indoor living and home environments.
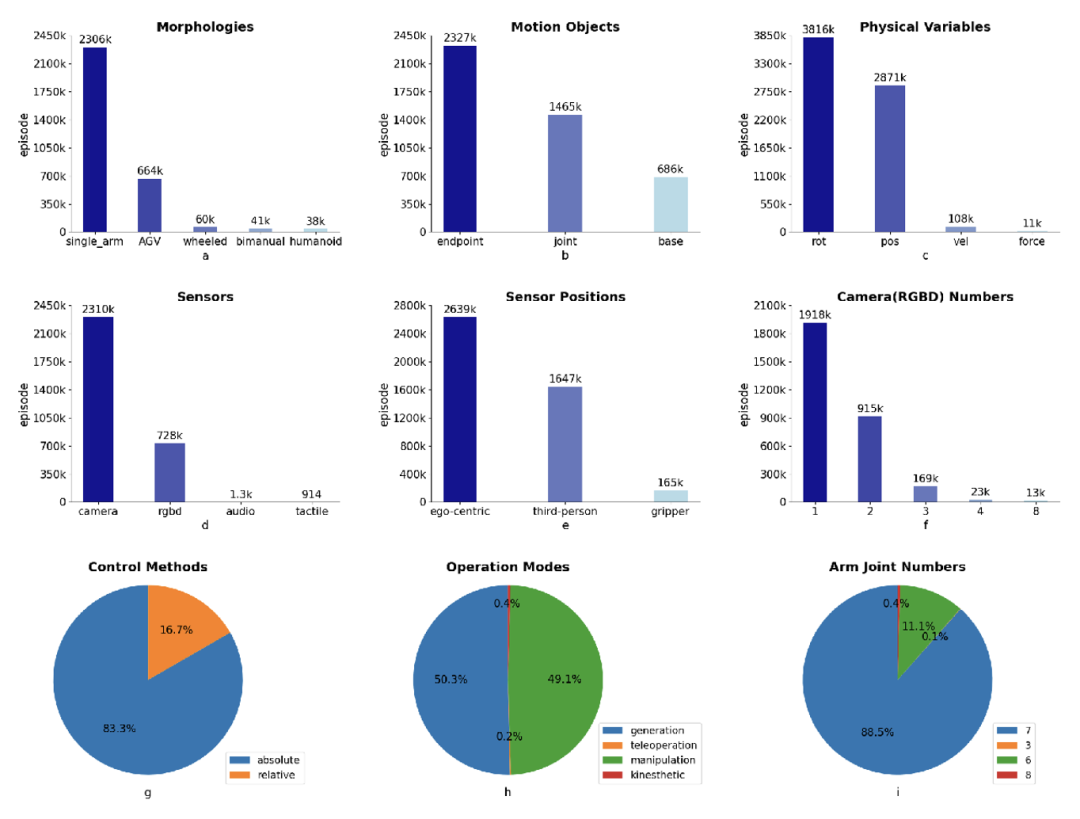
In addition to scenarios and skills, ARIO data can also conduct statistical analysis from the perspective of the robot itself, and learn about some of the current development trends of the robot industry. The ARIO data set provides statistical data on the robot shape, moving objects, physical control variables, sensor types and installation locations, the number of visual sensors, the proportion of control methods, the proportion of data collection methods, and the proportion of the number of degrees of freedom of the robotic arm, corresponding to Figures a-i below. 
Take Figure a below as an example. From it, we can find that most of the current data comes from single-arm robots. There are very few open source data for humanoid robots, and they mainly come from real collection and simulation generation of Pengcheng Laboratory.

Original paper and project homepage.
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonEs wird immer gesagt, dass verkörperte Geheimdienstdaten zu teuer sind. Das Pengcheng-Labor hat einen millionenschweren standardisierten Datensatz als Open-Source-Quelle bereitgestellt. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!
Stellungnahme:Der Inhalt dieses Artikels wird freiwillig von Internetnutzern beigesteuert und das Urheberrecht liegt beim ursprünglichen Autor. Diese Website übernimmt keine entsprechende rechtliche Verantwortung. Wenn Sie Inhalte finden, bei denen der Verdacht eines Plagiats oder einer Rechtsverletzung besteht, wenden Sie sich bitte an admin@php.cn


 MUJOCO simulation data collection example video
MUJOCO simulation data collection example video 

 Example video of simulation data generation based on the platform
Example video of simulation data generation based on the platform