Heim >Technologie-Peripheriegeräte >KI >Der Simultandolmetscher-Agent für große Modelle von Byte verfügt von Anfang an über ein Niveau an Simultandolmetschen, das mit dem von Menschen vergleichbar ist.
Der Simultandolmetscher-Agent für große Modelle von Byte verfügt von Anfang an über ein Niveau an Simultandolmetschen, das mit dem von Menschen vergleichbar ist.
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOriginal
- 2024-07-25 17:53:431090Durchsuche
Ob es sich um Zungenbrecher mit superschneller Sprache und komplexer Aussprache, exquisites klassisches Chinesisch oder lockere Chats voller Impromptu und Inspiration handelt, das Modell kann reibungslos und natürlich genaue und authentische Übersetzungsergebnisse liefern.
In den letzten Jahren entwickelt sich die künstliche Intelligenz (KI), insbesondere die KI, die durch große Sprachmodelle (LLMs) repräsentiert wird, in alarmierendem Tempo. Diese Modelle haben bei einer Vielzahl von Aufgaben zur Verarbeitung natürlicher Sprache bewiesen. Doch trotz Durchbrüchen in vielen Bereichen ist das Simultandolmetschen (Simultaneous Interpretation, SI), das die höchste Ebene der menschlichen Sprache darstellt, immer noch ein Problem, das nicht vollständig gelöst wurde.
Traditionelle Simultandolmetschersoftware auf dem Markt verwendet normalerweise die Kaskadenmodellmethode, d. h. zuerst wird die automatische Spracherkennung (ASR) und dann die maschinelle Übersetzung (MT) durchgeführt. Bei diesem Ansatz gibt es ein erhebliches Problem – die Fehlerausbreitung. Fehler im ASR-Prozess wirken sich direkt auf die spätere Übersetzungsqualität aus und führen zu einer schwerwiegenden Fehlerhäufigkeit. Darüber hinaus verwenden herkömmliche Simultandolmetschersysteme aufgrund der begrenzten Anforderungen an eine geringe Latenz normalerweise nur kleine Modelle mit schlechter Leistung, was zu Engpässen bei der Bewältigung komplexer und veränderlicher praktischer Anwendungsszenarien führt.
Forscher des ByteDance Research-Teams haben einen End-to-End-Simultandolmetscher auf den Markt gebracht: Cross Language Agent – Simultandolmetschen, CLASI. Seine Wirkung kommt der professionellen Simultandolmetschen auf künstlicher Ebene nahe und zeigt großes Potenzial und fortschrittliche technische Fähigkeiten. CLASI verwendet eine End-to-End-Architektur, um das Problem der Fehlerausbreitung im Kaskadenmodell zu vermeiden. Es stützt sich auf die Sprachverständnisfähigkeiten des großen Bohnenbeutel-Basismodells und der Sprachgruppe des großen Bohnenbeutels Wissen von außen erwerben und schließlich ein Simultandolmetschersystem bilden, das mit menschlicher Leistung vergleichbar ist.

Papieradresse: https://byteresearchcla.github.io/clasi/technical_report.pdf Anzeigeseite: https://byteresearchcla.github.io/clasi/
Effekt Show
Video-Demo: Nutzen Sie zunächst ein paar spontane Videos, um die Wirkung von CLASI zu erleben. Alle Untertitel werden in Echtzeit aufgezeichnet und ausgegeben. Wir können sehen, dass das Modell präzise und authentische Übersetzungsergebnisse reibungslos und natürlich liefern kann, egal ob es sich um Zungenbrecher mit schneller Sprache und komplexer Aussprache, exquisites klassisches Chinesisch oder lockere Chats voller Improvisation und Inspiration handelt. Ganz zu schweigen davon, dass sich CLASI in seiner Spezialität auszeichnet – der Übersetzung von Konferenzszenen.
Impromptu Konversation-Aufstellung Lesen-Chibi Fu
Lesen-Chibi Fu Zungenbrecher
Zungenbrecher
Für weitere Videos klicken Sie bitte auf „Originaltext lesen“, um sie anzusehen
Quantitativer Vergleich: Die Forscher luden professionelle Simultandolmetscher ein, manuelle Bewertungen in vier verschiedenen Bereichen im Hinblick auf Chinesisch-Englisch- und Englisch-Chinesisch-Übersetzungen durchzuführen, und verwendeten einen Bewertungsindex, der mit dem manuellen Simultandolmetschen übereinstimmt: den Anteil effektiver Informationen (Prozentsystem). . Wie in der Abbildung zu sehen ist, ist das CLASI-System allen kommerziellen Systemen und Open-Source-SOTA-Systemen deutlich voraus und erreicht oder übertrifft bei einigen Testsätzen sogar das Niveau der menschlichen Simultanübersetzung (allgemein wird davon ausgegangen, dass es sich um das durchschnittliche Niveau menschlicher Simultanübersetzung handelt). Simultandolmetschen liegt bei ca. 80 %).

Systemarchitektur
In terms of system architecture, CLASI adopts an architecture based on LLM agents (left in the figure below), which defines simultaneous interpretation as a series of simple and coordinated operations, including reading audio streams, retrieval (optional), and reading memory , update memory, output, etc. The entire process is autonomously controlled by a large language model, thus achieving an efficient balance between real-time performance and translation quality. The system can flexibly adjust the processing strategies of each link according to actual needs, ensuring that the accuracy and coherence of the translated content are maintained while efficiently transmitting information. The underlying model of CLASI is an Encoder-conditioned LLM, pre-trained on massive amounts of unsupervised and supervised data. The system architecture of the CLASI model is shown in the figure below.
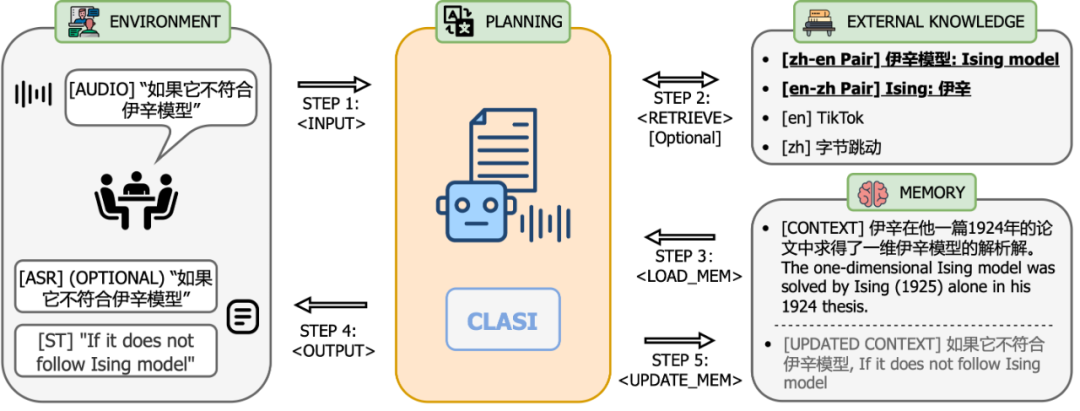
Figure 1: Diagram showing the overall operating process of CLASI. In step 1, CLASI processes the currently input audio data. The searcher is then activated (optional) to retrieve relevant information from the user-defined knowledge base. In this example, using the translation pair "Ising model: Ising model" in the knowledge base can help the model output the correct translation. In step 3, CLASI loads the transcription (optional) and translation from memory from the previous round. Next (steps 4 and 5), CLASI may enable the Chain of Thoughts (CoT) to output the transliteration (optional) and translation results, and then update its memory. Finally, return to step 1 to process the next round of speech.
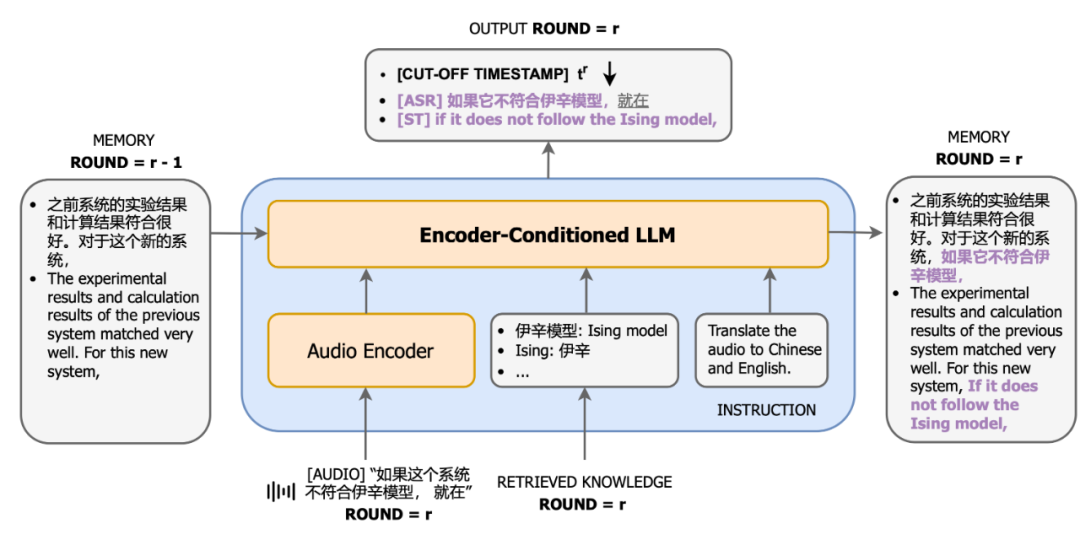
Figure 2: Structural diagram of CLASI. In round r, CLASI takes as input the current audio stream, the previous memory (r-1), and the retrieved knowledge (if any). CLASI outputs a response based on the given instructions and then updates the memory. At the same time, CLASI will also output the deadline timestamp of the last semantic fragment as of now. For the given example, what comes before the phrase "just before" is considered a complete semantic fragment, so the cutoff timestamp is just before this phrase.
Experimental results
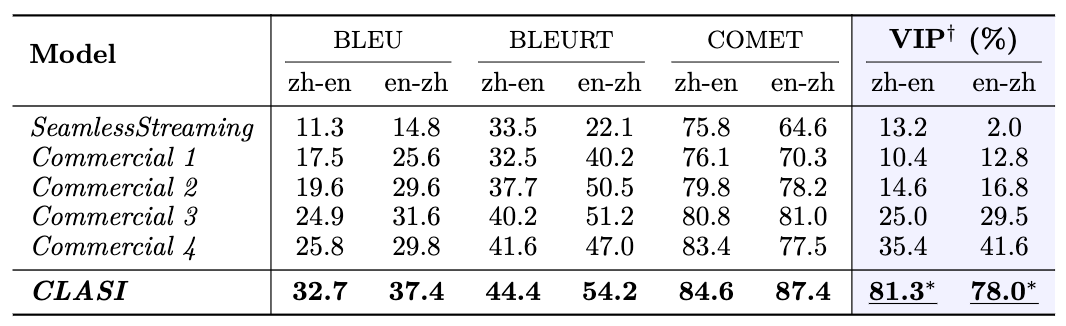
Table 1: In the manual evaluation of valid field proportion (Valid Information Proportion, VIP), the CLASI system significantly surpassed all other competing products, and in both language directions An accuracy of over 78% was achieved. Generally speaking, the accuracy of human simultaneous interpretation can be considered to be above 70%, and ideally can reach 95%, with researchers using 80% accuracy as the average standard for high-level human translators.
Example analysis
Chinese to English: 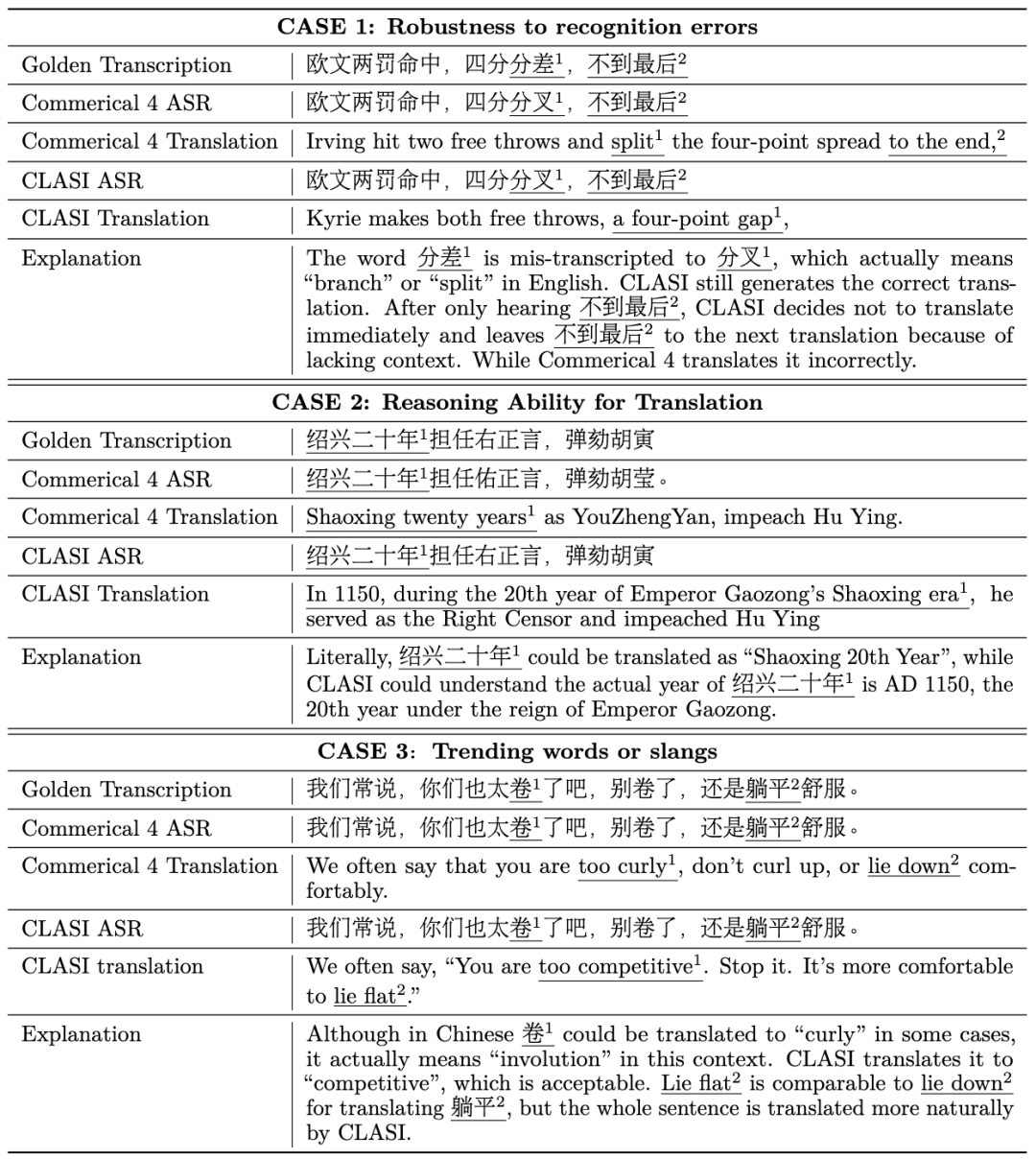
English to Chinese:
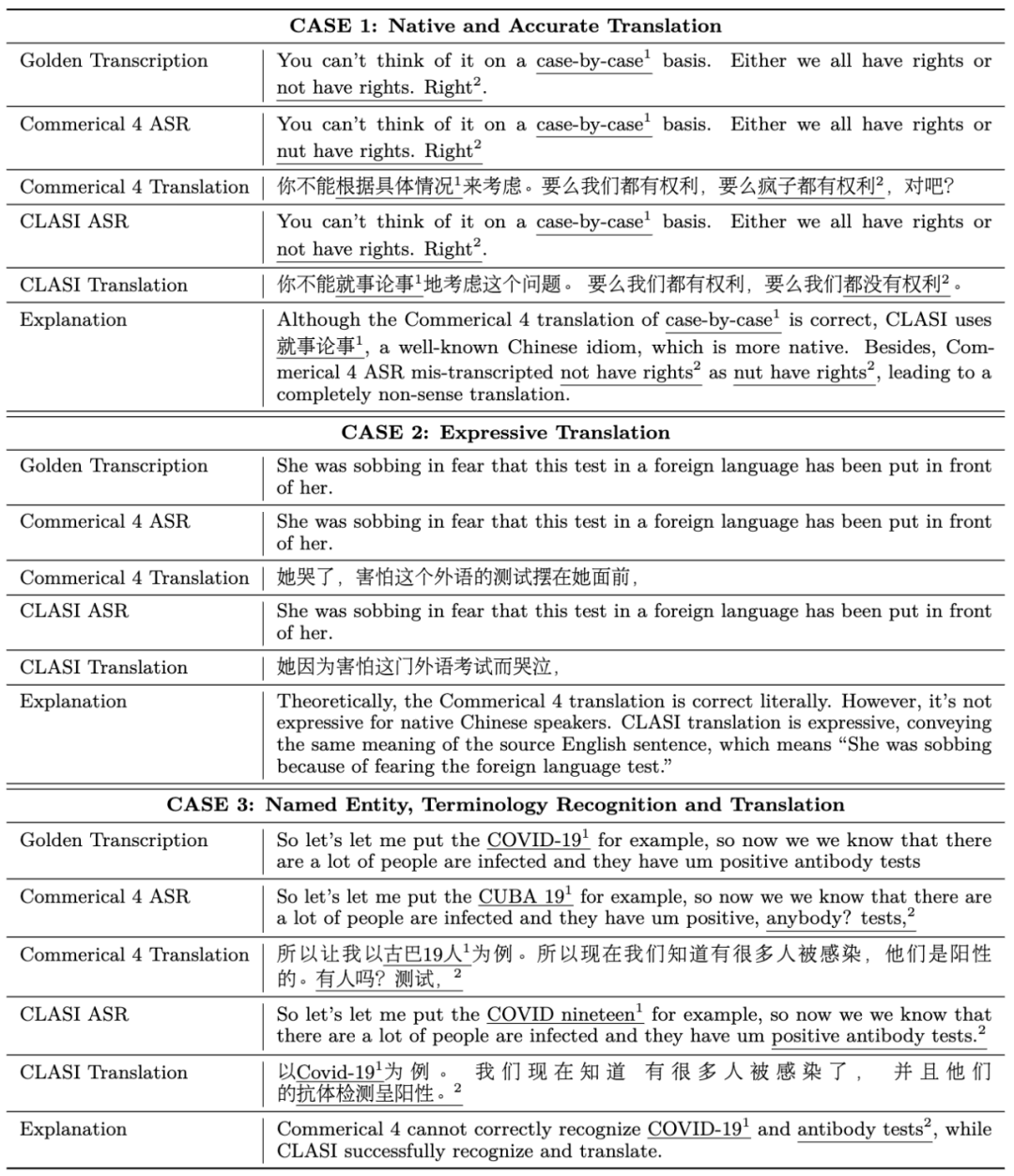
It can be seen that the translation of CLASI is significantly better than commercial systems in many aspects.
Summary
Researchers from the ByteDance Research team proposed a simultaneous interpretation agent based on the Beanbao large model: CLASI. Thanks to large-scale pre-training and imitation learning, CLASI significantly outperforms the performance of existing automatic simultaneous interpretation systems in human evaluation, almost reaching the level of human simultaneous interpretation.
1. Researchers propose a data-driven literacy strategy that mimics professional human translators. This strategy easily balances translation quality and latency without requiring complex human pre-design. Unlike most commercial systems that frequently rewrite output during translation to improve quality, this strategy guarantees that all output is deterministic while maintaining high quality.
2. Human translators generally need to prepare simultaneous interpretation content in advance. Inspired by this, researchers introduced a multi-modal retrieval-augmented generation (MM-RAG) process to enable LLM to have domain-specific knowledge in real time. The proposed module further improves translation quality with minimal computational overhead during inference.
3. Researchers worked closely with professional human simultaneous interpreters to develop a new manual evaluation strategy "Valid Information Proportion" (VIP) and published detailed guidelines. At the same time, a multi-domain manual annotation test set for long speech translation that is closer to real-life scenarios was also released.
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonDer Simultandolmetscher-Agent für große Modelle von Byte verfügt von Anfang an über ein Niveau an Simultandolmetschen, das mit dem von Menschen vergleichbar ist.. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!
In Verbindung stehende Artikel
Mehr sehen- Technologietrends, die Sie im Jahr 2023 im Auge behalten sollten
- Wie künstliche Intelligenz Rechenzentrumsteams neue Alltagsaufgaben beschert
- Können künstliche Intelligenz oder Automatisierung das Problem der geringen Energieeffizienz in Gebäuden lösen?
- OpenAI-Mitbegründer im Interview mit Huang Renxun: Die Argumentationsfähigkeiten von GPT-4 haben noch nicht die Erwartungen erfüllt
- Dank der OpenAI-Technologie übertrifft Bing von Microsoft Google im Suchverkehr

