CSS3 3D Transformation
3D Transforms
CSS3 allows you to use 3D transforms to format elements.
In this chapter, you will learn some of these 3D transformation methods:
rotateX()
rotateY( )
Click on the elements below to see the differences between 2D conversion and 3D conversion:
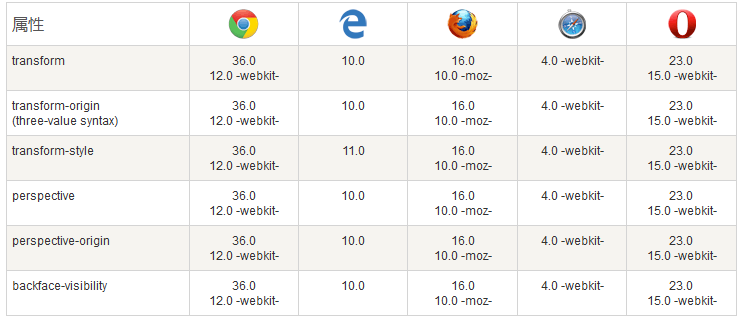
Browser support
The number in the table indicates the first browser version number that supports this attribute.
The number immediately before -webkit-, -ms- or -moz- is the first browser version number that supports this prefix attribute.
rotateX() method
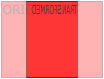
rotateX() method rotates an element around its X-axis by a given degree.
Instance
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>php中文网(php.cn)</title>
<style>
div
{
width:100px;
height:75px;
background-color:red;
border:1px solid black;
}
div#div2
{
transform:rotateX(120deg);
-webkit-transform:rotateX(120deg); /* Safari and Chrome */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p><b>注意:</b> Internet Explorer 9 (以及更早版本的浏览器) 和 Opera 不支持 rotateX 方法.</p>
<div>Hello. This is a DIV element.</div>
<div id="div2">Hello. This is a DIV element.</div>
</body>
</html>Run instance»
Click the "Run instance" button to view the online instance
rotateY() method

rotateY() method rotates an element around its Y-axis by a given degree.
Instance
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>php中文网(php.cn)</title>
<style>
div
{
width:100px;
height:75px;
background-color:red;
border:1px solid black;
}
div#div2
{
transform:rotateY(130deg);
-webkit-transform:rotateY(130deg); /* Safari and Chrome */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p><b>注意:</b> Internet Explorer 9 (以及更早版本的浏览器) 和 Opera 不支持 rotateY方法.</p>
<div>Hello. This is a DIV element.</div>
<div id="div2">Hello. This is a DIV element.</div>
</body>
</html>Run instance»
Click the "Run instance" button to view the online instance
Conversion Properties
The following table lists all conversion properties:
| Properties | Description | CSS |
|---|---|---|
| transform | Apply a 2D or 3D transform to an element. | 3 |
| transform-origin | Allows you to change the position of the element being transformed. | 3 |
| transform-style | Specifies how nested elements are displayed in 3D space. | 3 |
| perspective | Specifies the perspective effect of 3D elements. | 3 |
| perspective-origin | Specifies the bottom position of the 3D element. | 3 |
| backface-visibility | Defines whether the element is visible when not facing the screen. | 3 |
3D conversion method
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| matrix3d(n ,n,n,n,n,n, n,n,n,n,n,n,n, n,n,n) | Define the 3D transformation, using a 4x4 matrix of 16 values. |
| translate3d(x,y,z) | Define 3D transformation. |
| translateX(x) | Define a 3D translation, using only the values used for the X-axis. |
| translateY(y) | Define a 3D translation, using only the values used for the Y axis. |
| translateZ(z) | Define a 3D translation, using only the value used for the Z axis. |
| scale3d(x,y,z) | Define the 3D scaling transformation. |
| scaleX(x) | Defines a 3D scaling transformation, given an X-axis value. |
| scaleY(y) | Define the 3D scaling transformation by giving a Y-axis value. |
| scaleZ(z) | Defines a 3D scaling transformation, given a Z-axis value. |
| rotate3d(x,y,z,angle) | Define 3D rotation. |
| rotateX(angle) | Defines a 3D rotation along the X-axis. |
| rotateY(angle) | Defines a 3D rotation along the Y axis. |
| rotateZ(angle) | Defines a 3D rotation along the Z axis. |
| perspective(n) | Defines the perspective view of a 3D transformed element. |








