默认布局与元素类型
文档布局流
position:static静态定位
默认情况下,元素布局的完整流程
1.把内容(匿名文本)放到一个独立的盒模型,如div
2.为盒子添加上padding/border/margin
3.盒子的种类
3.1 块级
属性:display:block/table/table-cell,td/list-item/form/p/h1-h6
宽度:占据父级全部宽度
高低:由内容决定且可自定义
排列:垂直
3.2 内联(行内)
用来描述块级元素内部的内容(文本)
宽度:内容宽度
高度:内容高度
排列:水平排不下则换行显示
宽高不能自定义,padding有效,margin只有左右有效
使用displau:block可将内联元素转为快级,使宽高生效,但后面的其他元素
如果不想让后面的其他元素换行显示,可使用display:inline-block将它转为
3.3 内联块(行内块):即像内联一样水平排列,又像块级一样可设置宽高
定位原理与演示
1.静态定位:position:static
2.相对定位:position:relative
需设置top:/left:/right:/bottom:
参照物:相对元素自身在文档流张的原始位置进行偏移
3.绝对定位:position:absolute
隐藏:visibility:hidden源码有,页面有但看不见
删除:display:none源码有,页面没有
参照物:具有定位属性的包含块(定位父级)
初始包含块:根元素的父级
4.固定定位:position:fixed
永远相对于视口定位,是绝对定位的一个特例,
5.粘性定位:position:sticky
粘性定位=静态定位+固定定位
案例:
<body><div class="box parent"><div class="box child one">相对定位</div><div class="box child two">绝对定位</div><div class="box child three">固定定位</div></div><style>.box{border: 1px solid ;}.box.parent{width: 400px;height:400px;background-color:lightcyan;}.box.child{padding: 20px;}.box.child.one{background-color:aqua;}.box.child.two{background-color:aquamarine;}.box.child.three{background-color: cadetblue;}.box.child.one{display: none;}
相对于.box.parent定位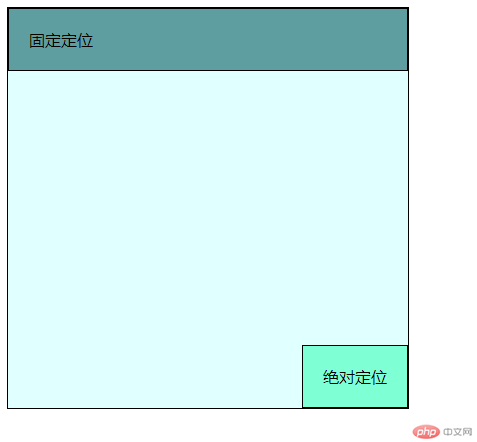
.box.parent{position:relative;}.box.child.two{right: 0;bottom: 0;}
相对于body定位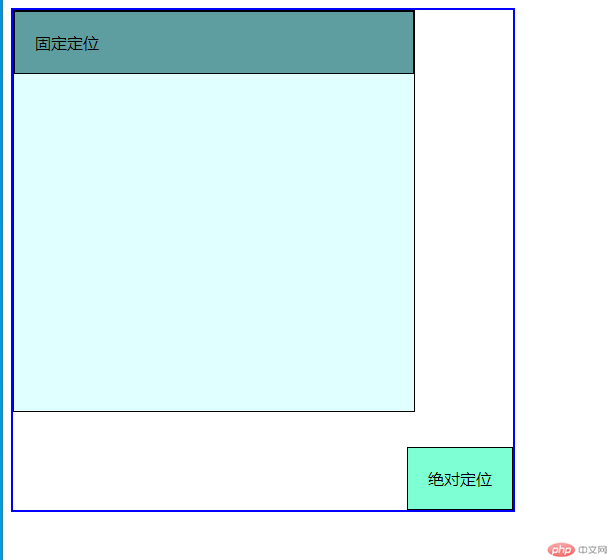
body{height: 500px;width: 500px;border: 2px solid blue;}.box.parent{position: static;}body{position: relative;}
相对于html定位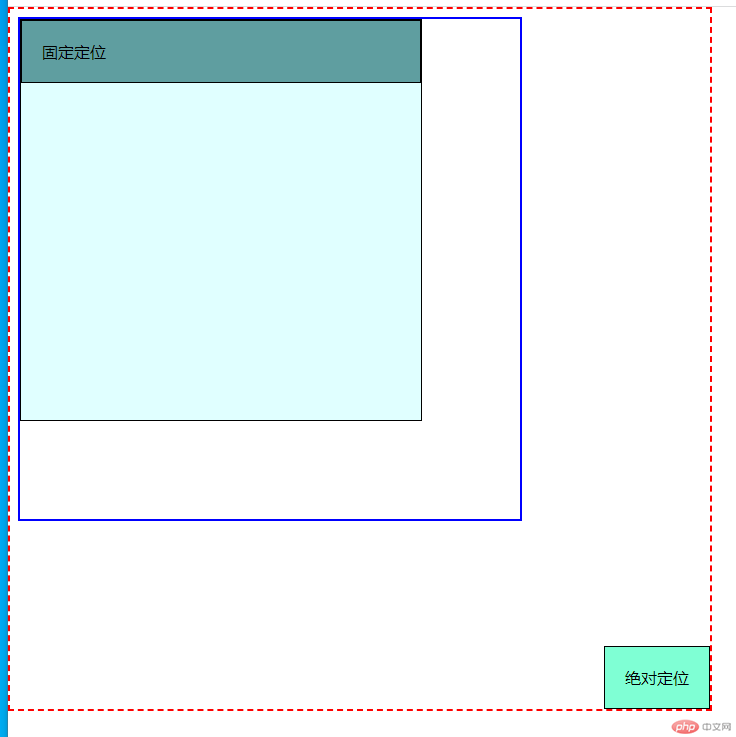
html{width: 700px;height: 700px;border: 2px dashed red;}body{position: static;}html{position: relative;}

