一.box-sizing 功能
示图
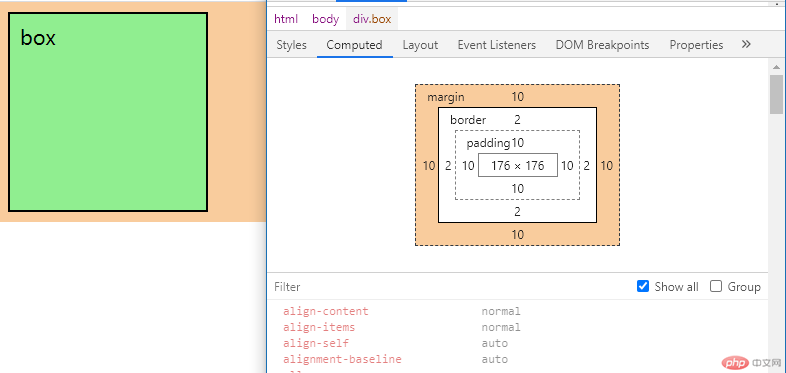
html 代码
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh_CN"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>box-sizing</title><style>/* 初始化代码 */* {margin: 0;padding: 0;/* 考虑将w3c的标准盒子转为IE的盒子 *//* 将盒子的padding和border计算在width,height内 */box-sizing: border-box;/* 再转为标准盒子 *//* box-sizing: content-box; *//* 背景裁切到内容区 *//* background-clip: content-box; */}/* :root === html */:root {/* font-size: 16px; */font-size: 10px;}/* em,rem *//* em:根据元素的上下文来确定它的值 默认一个em等于16像素*//* rem:根据根元素的自豪来设置 */.box {font-size: 20px;/* width: 200px; *//* width: 12.5em; */width: 20rem;/* height: 200px; *//* height: 12.5em; */height: 20rem;border: 2px solid;background-color: lightgreen;padding: 1rem;margin: 1rem;}</style></head><body><div class="box">box</div></body></html>
二.相对定位与绝对定位
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh_CN"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>定位</title><style>/* html {border: 1px solid;} */.box {background-color: lightcoral;width: 20em;height: 20em;/* 默认:静态定位,就是没有定位 *//* position: static; *//* 相对定位:自动的转为定位元素 *//* 定位元素:只要这个元素上有非static的定位属性,就是定位元素 *//* position: relative; *//* 只要是定位元素,定位偏移量有效 *//* 相对于它在文档流中的原始位置进行定位 *//* top: 3em;left: 5em; *//* 绝对定位 */position: absolute;/* 绝对定位元素脱离了文档流 *//* 相对于它在文档流中的原始位置进行定位 */top: 3em;left: 5em;}.parent {border: 1px solid;/* 转为定位元素,做为绝对定位元素的定位父级/定位参考/定位包含块 */position: relative;top: 3em;left: 4em;min-height: 30em;}</style></head><body><div class="parent"><div class="box"></div></div></body></html>

