1.盒模型的常用属性
- 宽度 width: 200px;
- 高度 height: 200px;
- 内边距 padding: 10px;
- 背景色 background-color: cadetblue;
- 边框 border: 1px solid #000;
- 规定背景的绘制区域background-clip: content-box;
/* border-box 背景被裁剪到边框盒。 *//* padding-box 背景被裁剪到内边距框。 *//* content-box 背景被裁剪到内容框。 */
- 外边距 margin: 1px 2px 3px 4px 顺序为上右下左
定位 position
- 相对定位position:relative,生成相对定位的元素,相对于其正常位置进行定位。
因此,”left:20” 会向元素的 LEFT 位置添加 20 像素。 - 绝对定位position:absolute,相对于 static 定位以外的第一个父元素进行定位。
元素的位置通过 “left”, “top”, “right” 以及 “bottom” 属性进行规定。 - 固定定位 position: fixed;相对于浏览器窗口进行定位。元素的位置通过 “left”, “top”, “right” 以及 “bottom” 属性进行规定。
- position:static 默认值。没有定位,元素出现在正常的流中(忽略 top, bottom, left, right 或者 z-index 声明)。
- 相对定位position:relative,生成相对定位的元素,相对于其正常位置进行定位。
实际测试案例
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta charset="utf-8" /><style>.box {/* 元素的宽度 */width: 200px;/* 元素的高度 */height: 200px;}.box-1 {/* 内边距 */padding: 10px;/* 背景色 */background-color: cadetblue;/* 边框 */border: 1px solid #000;/* 规定背景的绘制区域: *//* border-box 背景被裁剪到边框盒。 *//* padding-box 背景被裁剪到内边距框。 *//* content-box 背景被裁剪到内容框。 */background-clip: content-box;/* 设置下外边距 */margin-bottom: 10px;}.box-2 {/* 内边距 */padding: 10px;/* 背景色 */background-color: chartreuse;/* 边框 */border: 1px solid #000;/* 规定背景的绘制区域: *//* border-box 背景被裁剪到边框盒。 *//* padding-box 背景被裁剪到内边距框。 *//* content-box 背景被裁剪到内容框。 */background-clip: content-box;margin-bottom: 10px;}.boxx {width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: rgb(218, 8, 8);/* 相对定位 */position: relative;}.box3 {height: 100px;width: 100px;background: cornflowerblue;/* 绝对定位 */position: absolute;top: 20px;left: 15px;}.guding {width: 110px;height: 110px;background-color: fuchsia;/* 固定定位 */position: fixed;top: 50px;left: 500px;}</style><title>06.盒模型常用属性</title></head><body><div class="box box-1"></div><div class="box box-2"></div><hr /><div class="boxx"><div class="box3"></div></div><hr /><div class="guding"></div></body></html>

2. 理解元素大小的重新计算: box-sizing的用法,并举例
默认情况下,元素的宽度与高度计算方式如下:
width(宽) + padding(内边距) + border(边框) = 元素实际宽度
height(高) + padding(内边距) + border(边框) = 元素实际高度在盒子内无内容时,这么计算是没有问题的,但是当盒子内的padding值改变时,盒子的大小也跟着改变了。
示例如下:
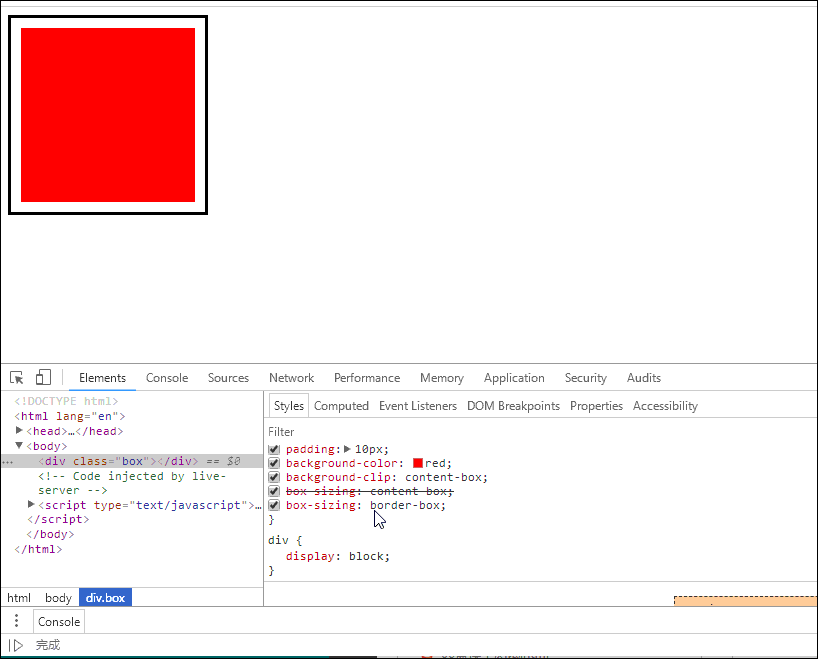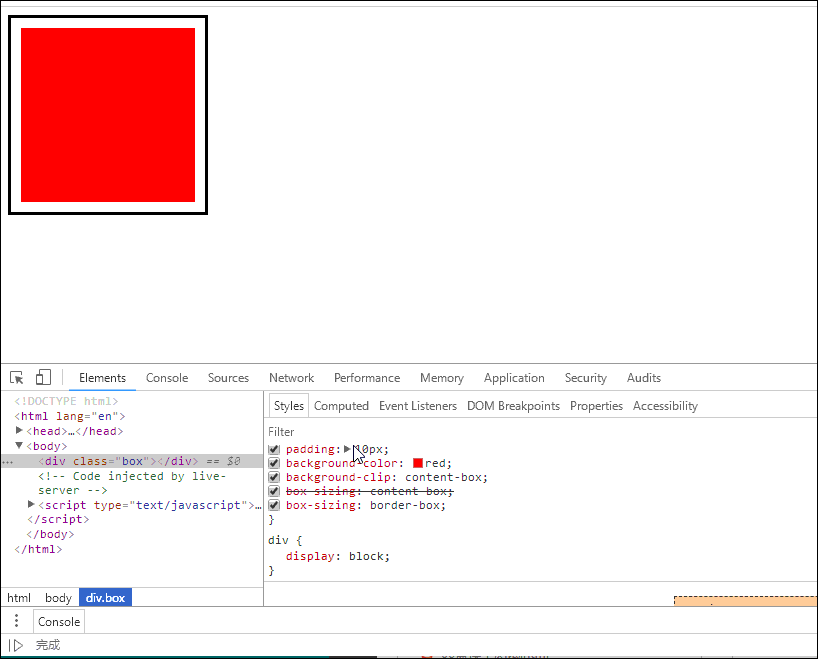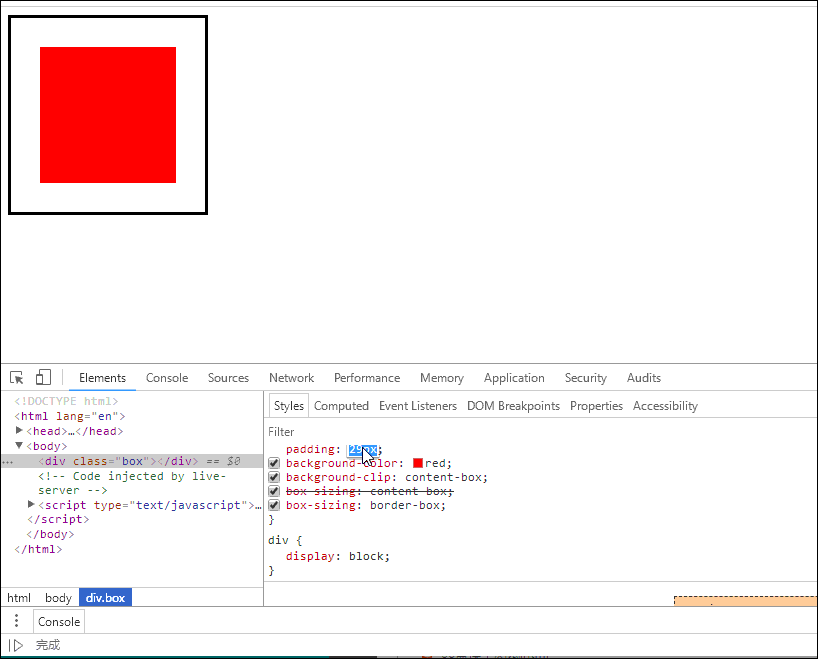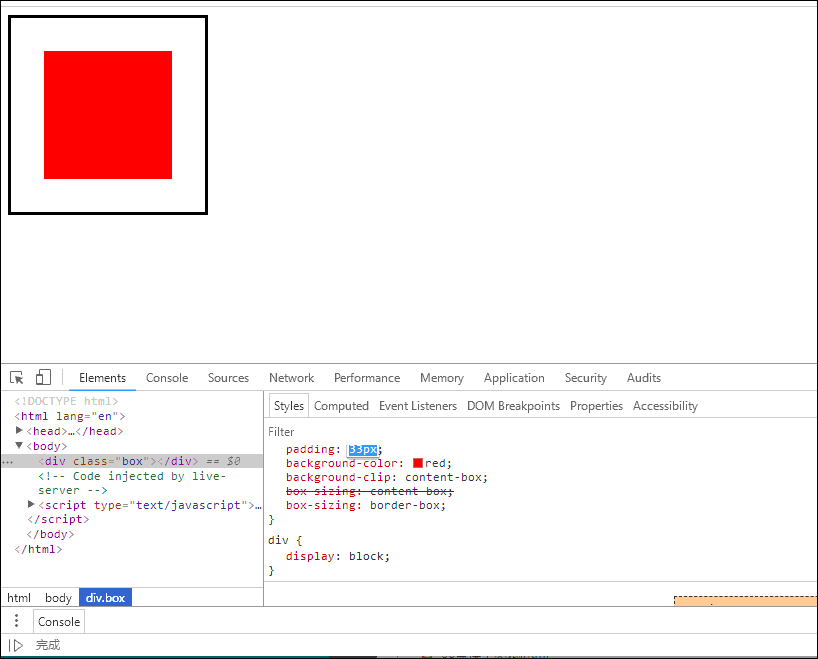
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>用户自定义元素大小的计算方式</title><style>.box {width: 200px;height: 200px;border: 3px solid #000;padding: 10px;background-color: pink;background-clip: content-box;}</style></head><body><div class="box"></div></body></html>
- 效果如下
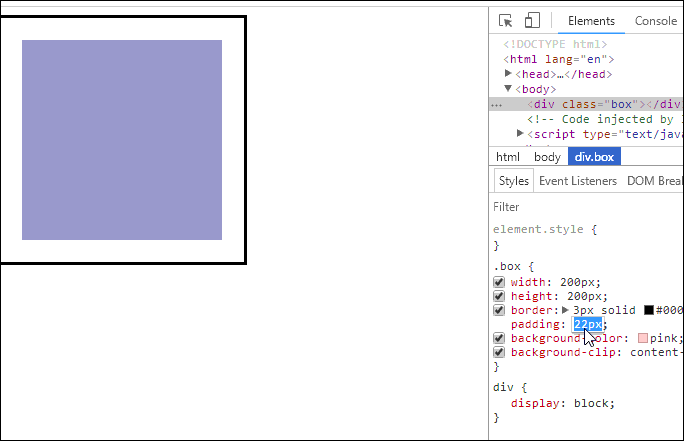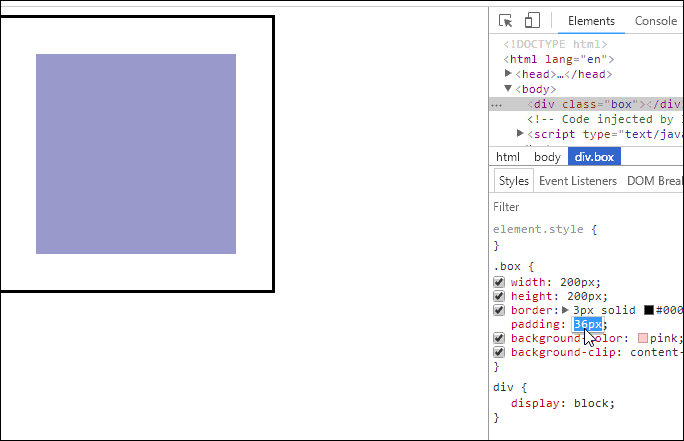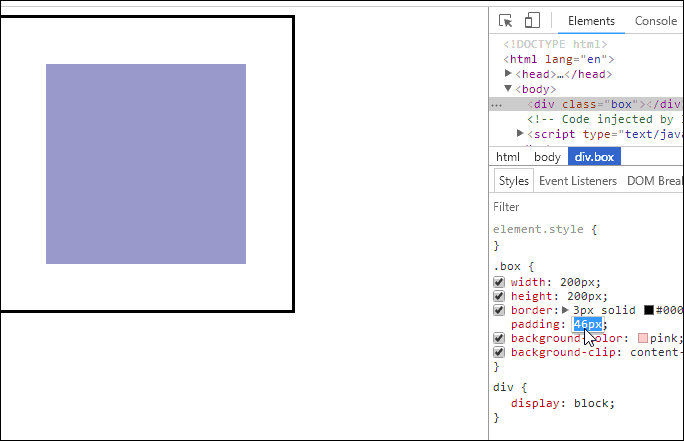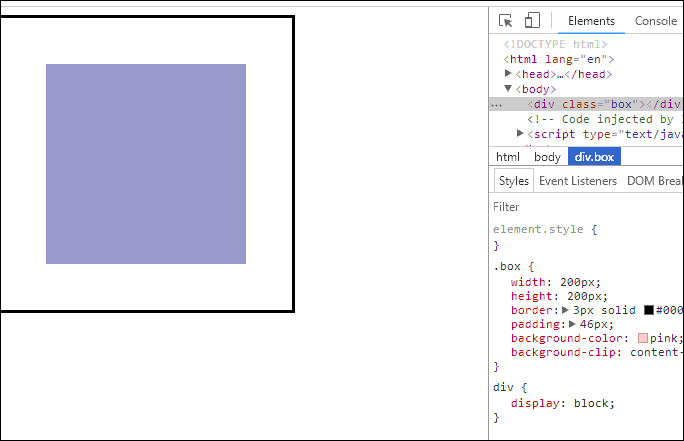
- 这意味着当你调整一个元素的宽度和高度时需要时刻注意到这个元素的边框和内边距。
box-sizing 属性可以被用来调整这些表现:
content-box 是默认值。如果你设置一个元素的宽为100px,那么这个元素的内容区会有100px 宽,并且任何边框和内边距的宽度都会被增加到最后绘制出来的元素宽度中。
border-box 告诉浏览器:你想要设置的边框和内边距的值是包含在width内的。
示例如下:
- 这意味着当你调整一个元素的宽度和高度时需要时刻注意到这个元素的边框和内边距。
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>用户自定义元素大小的计算方式</title><style>.box {width: 200px;height: 200px;border: 3px solid #000;padding: 10px;background-color: red;/* 属性规定背景的绘制区域为盒子部内部 */background-clip: content-box;/* 重新计算盒大小,宽和高只用在内容区部分 */box-sizing: content-box;/* 将边框包含在内容区的宽和高 */box-sizing: border-box;}</style></head><body><div class="box"></div></body></html>
元素的水平于垂直对齐
1.文本在div中的水平与垂直对齐
- 文本的水平居中可以使用 text-align: center;
- 文本的垂直居中可以使用line-height 来设置
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>盒子水平居中于垂直居中</title><style>.box {width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: #999;/* 设置相对定位属性 */position: relative;}.box .box1 {width: 150px;height: 150px;background-color: coral;/* 水平居中 */margin: auto;/* 设置绝对定位属性 */position: absolute;/* 左上上角开始 */top: 0;left: 0;/* 右下角结束 */right: 0;bottom: 0;/* 设置文字水平居中 */text-align: center;/* 设置文字在盒子中的垂直居中-等于盒子的高度*/line-height: 150px;}</style></head><body><div class="box"><div class="box1">你好我是box1</div></div></body></html>
- 效果如下

2.块级元素的居中与对齐
块级元素的水平对齐通常使用margin:auto;让浏览器自动计算左右外边距来实现水平居中。
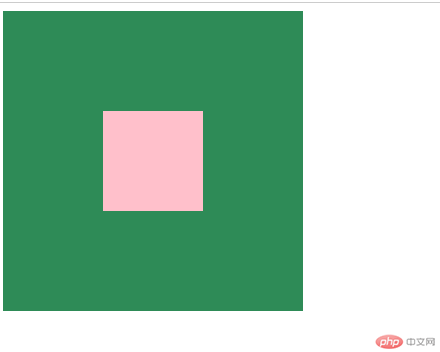
- 水平居中对齐
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><style>.box {height: 300px;width: 300px;background-color: seagreen;}.box1 {height: 100px;width: 100px;background-color: pink;margin: auto;}</style><title>块级元素的水平对齐</title></head><body><div class="box"><div class="box1"></div></div></body></html>
垂直居中对齐,要实现垂直居中,我们可以通过定位来实现。通过设置父级容器的top、bottom、left、right值为0
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><style>.box {height: 300px;width: 300px;background-color: seagreen;position: relative;}.box1 {height: 100px;width: 100px;background-color: pink;margin: auto;position: absolute;left: 0;top: 0;right: 0;bottom: 0;}</style><title>块级元素的垂直对齐</title></head><body><div class="box"><div class="box1"></div></div></body></html>