一、简单选择器
| 选择器名 | 符号 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 元素选择器 | 某个 HTML 元素 | 比如 p、h1、em、a,甚至可以是 html 本身 |
| 类选择器 | . | 对应着 html 标签中的 class 属性 |
| id 选择器 | # | 对应着 html 标签中的 id 属性 |
代码实例:
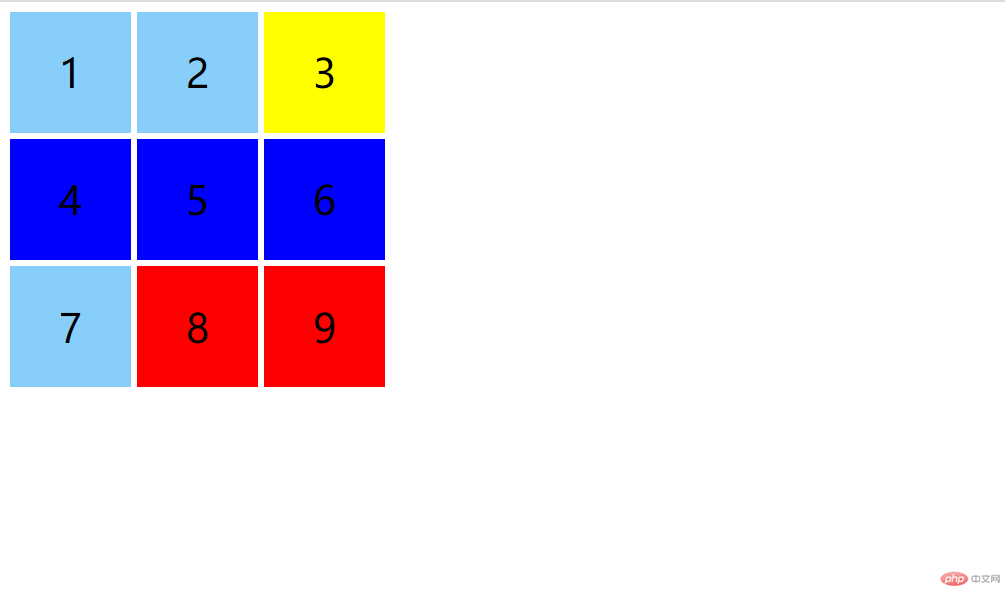
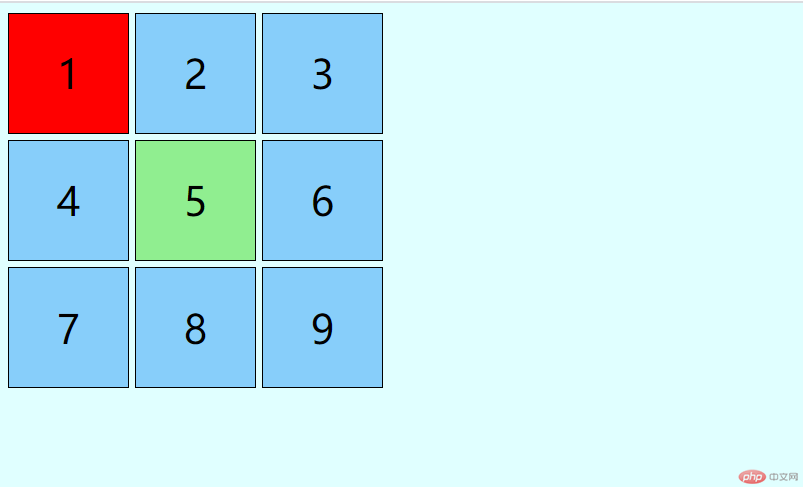
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>选择器: 简单选择器</title><style>/* 使用九宫格来演示: grid布局实现 */.container {width: 300px;height: 300px;display: grid;grid-template-columns: repeat(3, 1fr);gap: 5px;}.item {font-size: 2rem;background-color: lightskyblue;display: flex;justify-content: center;align-items: center;}/* 简单选择器 *//* 元素选择器: 标签选择器 */body {background-color: lightcyan;}/* 类选择器: 对应着html标签中的class属性 */.item {border: 1px solid #000;}/* 多个类复合应用 */.item.center {background-color: lightgreen;}/* id选择器 */.item#first {background-color: lightpink;}/* 层叠样式表, 相同元素,后面追加的样式会覆盖前面的样式 */*#first {background-color: yellow;}#first.item {background-color: red;}/* * :属于元素级别元素 < class < id *//* id,class可以添加到任何元素上,所以可以省略 *//* id 选择器的应用场景目前只有二种场景: 表单元素, 锚点 */</style></head><body><div class="container"><div class="item" id="first">1</div><div class="item">2</div><div class="item">3</div><div class="item">4</div><div class="item center">5</div><div class="item">6</div><div class="item">7</div><div class="item">8</div><div class="item">9</div></div></body></html>
效果预览:
二、上下文选择器
| 选择器名 | 符号 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 后代选择器 | 空格 | 标签 1 标签 2,获取到标签 1 的所有叫标签 2 的元素 |
| 父子选择器 | > | 标签 1 > 标签 2,标签 2 必须是标签 1 的子元素。与其他常规的上下文选择符不同,这个选择符中的标签 1 不能使标签 2 的父元素之外的其他祖先元素 |
| 同级(相邻)兄弟选择器 | + | 标签 1 + 标签 2,标签 2 必须紧跟在其同胞标签 1 的后面 |
| 同级所有选择器 | ~ | 标签 1 ~ 标签 2,标签 2 必须在(不一定紧挨着)其同胞标签 1 后面 |
代码示例:
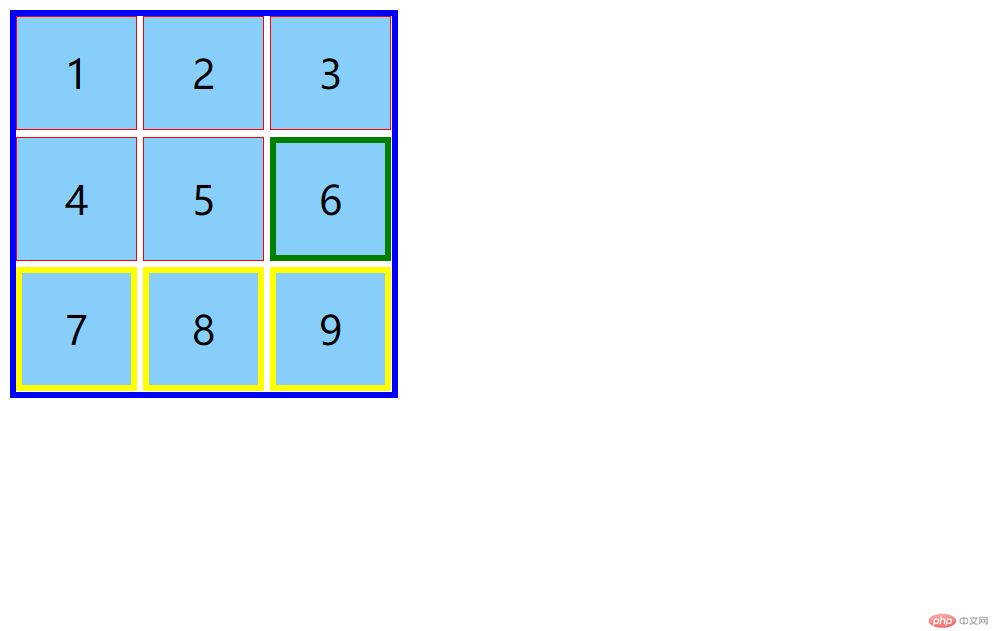
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>选择器:上下文选择器</title></head><style>/* 使用九宫格来演示: grid布局实现 */.container {width: 300px;height: 300px;display: grid;grid-template-columns: repeat(3, 1fr);gap: 5px;}.item {font-size: 2rem;background-color: lightskyblue;display: flex;justify-content: center;align-items: center;}/* 1.后代选择器 : 空格 */.container div {border: 1px solid red;}/* 2.父子选择器: > */body > div {border: 5px solid blue;}/* 3.同级相邻(兄弟)选择器 */.item.center + .item {border: 5px solid green;}/* 4.同级所有选择器 */.item.next ~ .item {border: 5px solid yellow;}</style><body><div class="container"><div class="item">1</div><div class="item">2</div><div class="item">3</div><div class="item">4</div><div class="item center">5</div><div class="item next">6</div><div class="item">7</div><div class="item">8</div><div class="item">9</div></div></body></html>
效果预览:
三、结构伪类选择器
| 不分组(不区分元素类型) | 分组(区分元素类型) |
|---|---|
| :first-child | :first-of-type |
| :last-child | :last-of-type |
| :nth-child(n) | :nth-of-type() |
| :nth-last-child(n) | :nth-last-of-tyle() |
1.结构伪类选择器:不分组(不区分元素类型)实例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>结构伪类选择器:不分组(不区分元素类型)</title></head><style>/* 使用九宫格来演示: grid布局实现 */.container {width: 300px;height: 300px;display: grid;grid-template-columns: repeat(3, 1fr);gap: 5px;}.item {font-size: 2rem;background-color: lightskyblue;display: flex;justify-content: center;align-items: center;}/* 1.匹配第一个子元素 */.container > *:first-child {/* background-color: lightgreen; */}.container > .item:first-child {/* background-color: blue; */}/* 2.匹配最后一个子元素 */.container > :last-child {/* background-color: blueviolet; */}/* 3.选第三个:索引从1开始 */.container > :nth-child(3) {/* background-color: lightgreen; */}/* n从0开始计算 *//* 4.只选择偶数单元格(4n)或(even) */.container > :nth-child(2n) {/* background-color: blue; */}/* 5.只选择奇数单元格(2n + 1)或(2n - 1)或(odd) */.container > :nth-child(odd) {/* background-color: green; */}/* 6.从指定位置(从第4个开始),选择器盛下的所有元素 */.container > .item:nth-child(n + 4) {/* background-color: greenyellow; */}/* 7.从指定位置(只取前三个),选择器盛下的所有元素 */.container > .item:nth-child(-n + 3) {/* background-color: brown; */}/* 8.从指定位置(取最后三个),选择器盛下的所有元素 */.container > .item:nth-last-child(-n + 3) {background-color: brown;}/* 9.取第8个,用倒数的方式更直观 */.container > .item:nth-last-child(2) {background-color: blue;}</style><body><div class="container"><div class="item">1</div><div class="item">2</div><div class="item">3</div><div class="item">4</div><div class="item">5</div><div class="item">6</div><div class="item">7</div><div class="item">8</div><div class="item">9</div></div></body></html>
以上代码可根据注释一个一个测试结果!p
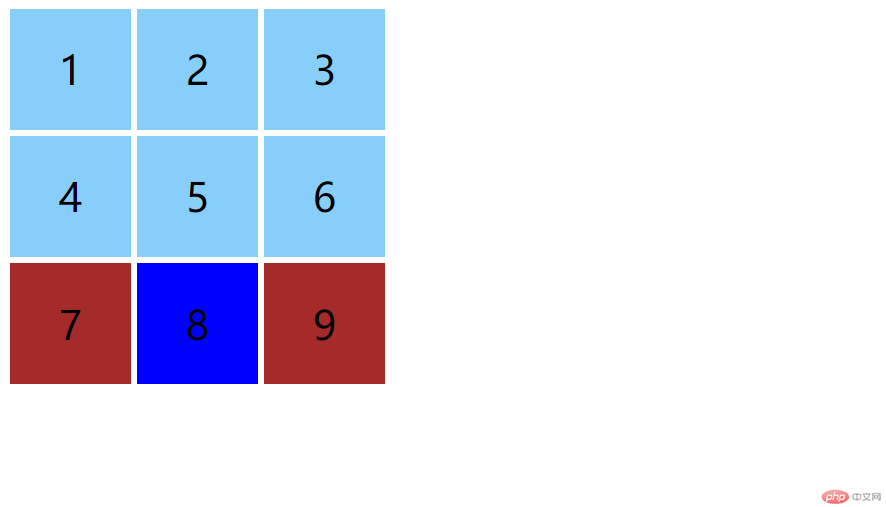
实现注释中 8,9 效果预览:
ps:优先级相同时后面的代码效果会覆盖上面的代码效果,所以我这里 8 的蓝色覆盖了原先 8 的深红色。2.结构伪类选择器:分组(区分元素类型)实例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>结构伪类选择器:分组(区分元素类型)</title></head><style>/* 使用九宫格来演示: grid布局实现 */.container {width: 300px;height: 300px;display: grid;grid-template-columns: repeat(3, 1fr);gap: 5px;}.item {font-size: 2rem;background-color: lightskyblue;display: flex;justify-content: center;align-items: center;}/* 分组结构伪类分二步1.元素按类型进行分组2.在分组中根据索引进行注释*//* 在分组中匹配最后一个 */.container div:last-of-type {background-color: yellow;}/* 在分组中匹配任何一个 */.container span:nth-of-type(3) {background-color: violet;}/* 在分组中匹配前3个 */.container span:nth-of-type(-n + 3) {background-color: blue;}/* 在分组中匹配最后2个 */.container span:nth-last-of-type(-n + 2) {background-color: red;}</style><body><div class="container"><div class="item">1</div><div class="item">2</div><div class="item">3</div><span class="item">4</span><span class="item">5</span><span class="item">6</span><span class="item">7</span><span class="item">8</span><span class="item">9</span></div></body></html>
效果预览:
四、伪类与伪元素
| 伪类 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| :target | 必须配合 id ,实现锚点操作。 |
| :focus | 选择器选取当前具有焦点的元素 |
| :not() | 选择器选取除了指定元素以外的所有元素 |
| 伪元素 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ::before | 选择器向选定的元素之前插入内容,使用 content 属性来指定要插入的内容。 |
| ::after | 选择器向选定的元素之后插入内容,使用 content 属性来指定要插入的内容。 |
| ::selection | 选择器匹配元素中被用户选中或处于高亮状态的部分,只可以应用于少数的 CSS 属性:color, background, cursor,和 outline。 |
实例代码:
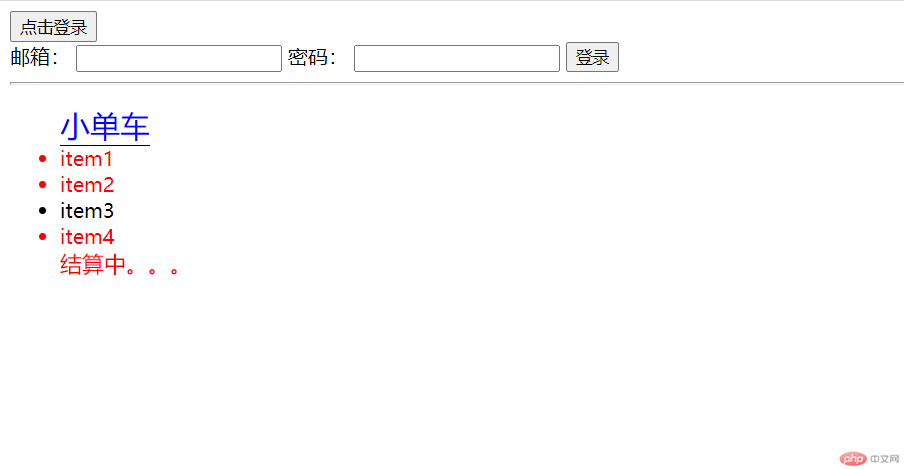
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>伪类与伪元素</title><style>#login-form {display: none;}/* :target: 必须配合id,实现锚点操作 *//* 当前#login-form的表单元素被a的锚点激活的时候执行 */#login-form:target {display: block;}/* :focus: 当前焦点的时候 */input:focus {background-color: #ccc;}/* ::selection 设置选中文本的前景色与背景色 */input::selection {color: white;background-color: red;}/* :not(): 用于选择不满足条件元素 */.list > li:not(:nth-of-type(3)) {color: red;}/* ::before */.list::before {content: "小单车";font-size: 1.5em;color: blue;border-bottom: 1px solid #000;}/* ::after */.list::after {content: "结算中。。。";font-size: 1.1em;color: red;}/* 伪元素前面双冒号,伪类前面单引号,伪元素选不中 */</style></head><body><!-- <a href="#login-form">我要登录:</a> --><button onclick="location='#login-form'">点击登录</button><form action="" method="post" id="login-form"><label for="email">邮箱:</label><input type="email" name="email" id="email" /><label for="email">密码:</label><input type="password" name="password" id="password" /><button>登录</button></form><hr /><ul class="list"><li>item1</li><li>item2</li><li>item3</li><li>item4</li></ul></body></html>
效果预览:
ps:点击登录后显示表单。