1.CSS简单基本选择器
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>基本CSS选择器</title> <style> body { background-color: lightcyan; } /* 类选择器: 根据元素的class值来去选择,将其改变样式 */ .container { width: 300px; height: 300px; display: grid; /* 网格布局 */ grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr 1fr; /* 有几列? 每列有多大 如: 我有3列 每列1ft */ grid-template-rows: 60px 60px 60px; /* 有几行? 每行有多大 如: 我有3行 每行16px */ gap: 10px; /* .container下面的元素 gap:行和列为10px cloums-gap:列间距; rows-gap:行间距 */ } /* 类选择器: 选择class为item的元素,将其改变以下样式 */ .item { background-color: #CCC; font-size: 2rem; display: flex; /* 弹性布局 */ justify-content: center; /* 垂直居中 */ align-items: center; /* 左右居中 */ } /* 多个类选择器: 一个元素只能有一个class属性,但class可以有多个值例如: clsss="value1 value2 n..." */ .item.center { background-color: lightgreen; } /* id选择器: 选择id属性值为first的元素,将其改变样式 */ #first { background-color: lime; } /* id,class可以添加到任何元素上,前面的元素限定符默认就是*, 所以可以省略 */ /* 选择div的id属性为first值的元素 */ div#first { background-color: #ccc; } /* 类选择器的优先级比元素选择器优先级大,所以会覆盖元素选择器设置的样式 */ .item#first { background-color: red; } /* id选择器比类选择器和元素选择器要大, 所以会覆盖类选择器或元素选择器的样式 */ #first.item { background-color: violet; } /* 属性选择器: 属性选择器优先级比id,class,元素选择器要底 */ .item[name='tom'] { background-color: #000; } .item[title='php']{ background-color: red; } /* 多组选择器:可以按照id,class,元素,属性选择器选择多少用逗号分隔开 */ /* 下面将id为first, class为item center, title属性为hello world 设置为绿色*/ *#first, .item.center, .item[title="hello world"] { background-color: green } </style></head><body> <div class="container"> <div class="item" id="first" name="tom">1</div> <div class="item" id="first" title="tag">2</div> <div class="item" title="php">3</div> <div class="item">4</div> <div class="item center">5</div> <div class="item" title="hello world">6</div> <div class="item">7</div> <div class="item">8</div> <div class="item" title="hello world">9</div> </div></body></html>
- 效果图
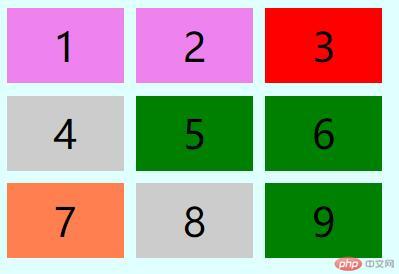
上述总结:
- 通过以下表格的总结内容可以看出非常简单使用css选择器
| 名称 |
选择器 |
实例 |
描述说明 |
| 类选择器 |
class |
<div class="container"></div> |
选择所有container的元素, 将其写入css代码改变样式 |
| 多类选择器 |
class |
<div class="item center"></div> |
一个元素只能有一个class属性,但class可以有多个值例如: clsss=”value1 value2 n…” |
| id选择器 |
id |
<div id="first"></div> |
选择所有id属性值为first的元素, 在html文档中id值是可以重复的, 但不建议id值有重复 |
| 元素选择器 |
element |
<p></p> <div></div> |
根据标签名称来去选择 如: 标签名 {} |
| id选择器的优先级 |
#first |
<div id="first"></div> |
id选择器比类选择器和元素选择器要大, 所以会覆盖类选择器或元素选择器的样式 |
| 属性选择器 |
.item[属性名=’属性值’] |
<div class="item" name="tom"></div> |
属性选择器优先级比id,class,element选择器要底 |
| 内联 |
style |
<div style="background-color: coral;"></div> |
所有标签的style属性上的css优先级是最高的,会覆盖class,id,element,attribute选择器 |
| 群组选择器 |
#first, .item.center, .item[title=”hello world” |
#first, .item.center, .item[title="hello world"] {} |
下面用逗号分隔开将id为first, class为item center, title属性为hello world 选中 |
2. CSS的上下文选择器
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>上下文选择器</title> <style> body { background-color: #f2f2f2; } .container { width: 300px; height: 300px; display: grid; grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr 1fr; margin-top: 50px; margin-left: 50px; } .item { font-size: 2rem; display: flex; justify-content: center; align-items: center; background-color: #ccc; } /* 后代选择器 */ .container div { margin: 5px; border: 4px dotted coral; } /* 父子选择器 */ body > div { border: 3px dashed green; } /* 同级相邻选择器 */ .item.center + .item { /* background-color: lightgreen; */ } /* 同级所有选择器 */ .item.center ~ .item { background-color: red; } </style></head><body> <div class="container"> <div class="item">1</div> <div class="item">2</div> <div class="item">3</div> <div class="item">4</div> <div class="item center">5</div> <div class="item">6</div> <div class="item">7</div> <div class="item">8</div> <div class="item">9</div> </div></body> </html>
- 效果图
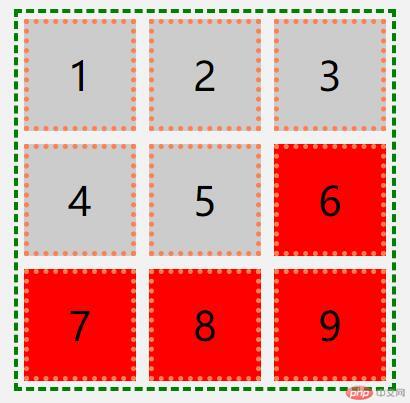
上述总结:
| 名称 |
实例 |
描述说明 |
| 后代选择器 |
.container div |
选择container元素内所有的div元素 |
| 父子选择器 |
body > div |
选择父级是body元素的所有div元素 |
| 同级相邻选择器 |
.item.center + .item |
选择与第5个格子右相邻的格子,即后面的 “一个” 元素, 若然有多个就用 + 号连接 例如: .item.center + .item + .item + n... |
| 同级所有选择器 |
.item.center ~ .item |
选择第5个格子(不含第5个)后面的,有共同父级的所有兄弟元素即: 跟着第5个格子的元素全选中 |
3. 伪类选择器
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>伪类选择器</title> <style> * {margin: 0;padding: 0;} body { background-color: #ccc; } .container { width: 300px; height: 300px; display: grid; grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr 1fr; grid-template-rows: 2fr 2fr 2fr; gap: 5px; margin-top: 10px; margin-left: 10px; } /* 类选择器 */ .item { font-size: 2rem; background-color: #fff; display: flex; /* 左右居中 */ justify-content: center; /* 上下居中 */ align-items: center; } .container > :first-child { background-color: lightcoral; } .container > :last-child { background-color: lightsalmon; } .container > :nth-child(2) { background-color: lightpink; } .container > :nth-child(even) { background-color: red; } .container > :nth-child(odd) { background-color: blue; } .container > :nth-child(-n + 4) { background-color: orange; } .container > :nth-last-child(2) { background-color: green; } .container > :nth-child(n + 6) { background-color: lightyellow; } </style></head><body> <div class="container"> <div class="item">1</div> <div class="item">2</div> <div class="item">3</div> <div class="item">4</div> <div class="item">5</div> <div class="item">6</div> <div class="item">7</div> <div class="item">8</div> <div class="item">9</div> </div></body> </html>
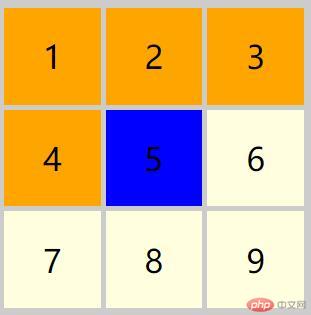
伪类选择器总结_1:
| 名称 |
实例 |
描述说明 |
| :first-child |
.container > :first-child {} |
为了防止递归, 应该在具体的父级元素上调用伪类,选择父级元素下面的第一个子元素 |
| :last-child |
.container > :last-child {} |
选择父级元素下面的最后一个子元素 |
| :nth-child() |
.container > :nth-child(2) {} |
在父级元素中匹配任意一个子元素,索引是从1开始计算 (1就是匹配第一个, 2就是匹配第二个, 如此类推) |
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>伪类选择器</title> <style> * {margin: 0;padding: 0;} body { background-color: #ccc; } .container { width: 300px; height: 300px; display: grid; grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr 1fr; grid-template-rows: 2fr 2fr 2fr; gap: 5px; margin-top: 10px; margin-left: 10px; } .container span, .container div { display: flex; font-weight: bolder; justify-content: center; align-items: center; border: 2px dashed; } .container > span:first-of-type { background-color: red; } .container > span:last-of-type { background-color: blue; } .container > div:nth-of-type(-n + 2) { background-color: lightcoral; } .container > div:nth-last-of-type(-n + 2) { background-color: lightgreen; } </style></head><body> <div class="container"> <span>flex-start</span> <span>center</span> <span>flex-end</span> <div>1</div> <div>2</div> <div>3</div> </div></body> </html>
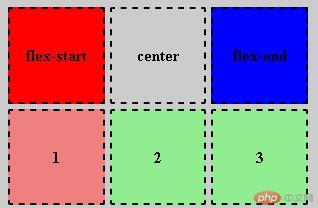
伪类选择器总结_2:
| 名称 |
实例 |
描述说明 |
| :first-of-type |
.container > span:first-of-type {} |
选中父元素的第一个span元素 |
| :last-of-type |
.container > span:last-of-type {} |
选中父元素的最后一个span元素 |
| :nth-of-type(-n + 2) |
.container > div:nth-of-type(-n + 2) {} |
选中父元素下面从索引1开始的2个div子元素 |
| :nth-last-of-type |
.container > div:nth-last-of-type(-n + 2) {} |
选中父元素下面从索引倒数开始的2个div子元素(逆向: 从最后那个子元素开始选中2个) |
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title></title> <style> input:enabled { background-color: red; } input:disabled { background-color: yellow; } input:required { background-color: blue; } </style></head><body> <input type="text" value="enabled"> <hr> <input type="text" disabled value="disabled"> <hr> <input type="text" required value="required"></body> </html>
- 效果图
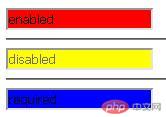
伪类选择器总结_3:
| 名称 |
实例 |
描述说明 |
| :enabled |
input:enabled {} |
选择所有有效的input元素, input默认是enabled |
| :disabled |
input:disabled {} |
选择带有disabled属性的input元素 |
| :required |
input:required {} |
选择带有必选项required属性的input元素 |






