data access object pattern
The Data Access Object Pattern or DAO pattern is used to separate low-level data access APIs or operations from high-level business services. The following are the participants of the Data Access Object pattern.
Data Access Object Interface - This interface defines standard operations to be performed on a model object.
Data Access Object concrete class - This class implements the above interface. This class is responsible for obtaining data from the data source, which can be a database, xml, or other storage mechanism.
Model Object/Value Object - This object is a simple POJO that contains get/set methods to store data using the DAO class Retrieved data.
Implementation
We will create a Student object that is either a model object or a numeric object. StudentDao is the data access object interface. StudentDaoImpl is an entity class that implements the data access object interface. DaoPatternDemo, our demo class uses StudentDao to demonstrate the usage of the data access object pattern.
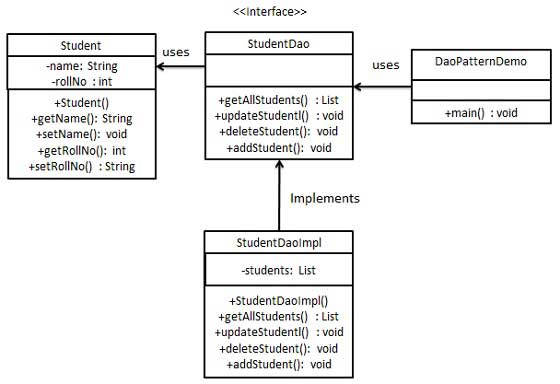
Step 1
Create a numerical object.
Student.java
public class Student {
private String name;
private int rollNo;
Student(String name, int rollNo){
this.name = name;
this.rollNo = rollNo;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getRollNo() {
return rollNo;
}
public void setRollNo(int rollNo) {
this.rollNo = rollNo;
}
}Step 2
Create the data access object interface.
StudentDao.java
import java.util.List;
public interface StudentDao {
public List<Student> getAllStudents();
public Student getStudent(int rollNo);
public void updateStudent(Student student);
public void deleteStudent(Student student);
}Step 3
Create an entity class that implements the above interface.
StudentDaoImpl.java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao {
//列表是当作一个数据库
List<Student> students;
public StudentDaoImpl(){
students = new ArrayList<Student>();
Student student1 = new Student("Robert",0);
Student student2 = new Student("John",1);
students.add(student1);
students.add(student2);
}
@Override
public void deleteStudent(Student student) {
students.remove(student.getRollNo());
System.out.println("Student: Roll No " + student.getRollNo()
+", deleted from database");
}
//从数据库中检索学生名单
@Override
public List<Student> getAllStudents() {
return students;
}
@Override
public Student getStudent(int rollNo) {
return students.get(rollNo);
}
@Override
public void updateStudent(Student student) {
students.get(student.getRollNo()).setName(student.getName());
System.out.println("Student: Roll No " + student.getRollNo()
+", updated in the database");
}
}Step 4
Use StudentDao to demonstrate the usage of the data access object pattern.
CompositeEntityPatternDemo.java
public class DaoPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDaoImpl();
//输出所有的学生
for (Student student : studentDao.getAllStudents()) {
System.out.println("Student: [RollNo : "
+student.getRollNo()+", Name : "+student.getName()+" ]");
}
//更新学生
Student student =studentDao.getAllStudents().get(0);
student.setName("Michael");
studentDao.updateStudent(student);
//获取学生
studentDao.getStudent(0);
System.out.println("Student: [RollNo : "
+student.getRollNo()+", Name : "+student.getName()+" ]");
}
}Step 5
Verify the output.
Student: [RollNo : 0, Name : Robert ] Student: [RollNo : 1, Name : John ] Student: Roll No 0, updated in the database Student: [RollNo : 0, Name : Michael ]








