我正在学习Python,不过遇到一些问题,想请教
OS模块中的os.path.dirname(__file__)和os.path.abspath(__file__)
运行os.path.dirname(__file__)时候,为什么返回的是空白呢?是不是因为他运行的是相对路径???
如果是的话:
1:我怎么能够知道,括号内的文件是以相对路径还是绝对路径被运行的?
2:为什么我运行下面例子脚本的时候,这个文件是以相对路径被运行的呢?
比如我下面的例子
import os
print (os.path.dirname(__file__))
print (os.path.abspath(__file__))
print (os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)))
print (os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
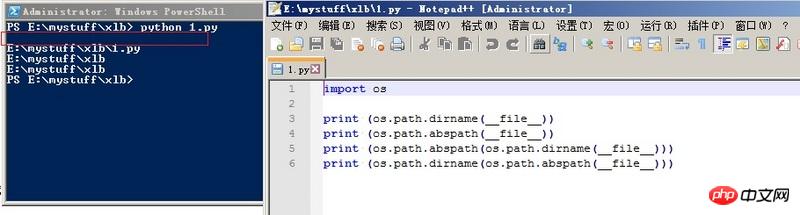
PS:附加问题
os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__))和os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))性质是否一样呢?
迷茫2017-04-18 09:19:06
建议你稍微浏览一下Python doc:os.path,你就会理解啰:
我放上重庆相关的几个入境问题:
os.path.abspath(path)os.path.abspath(path)
Return a normalized absolutized version of the pathname path. On most platforms, this is equivalent to calling the function normpath() as follows: normpath(join(os.getcwd(), path)).
os.path.normpath(path)
Normalize a pathname by collapsing redundant separators and up-level references so that A//B, A/B/, A/./B and A/foo/../B all become A/B. This string manipulation may change the meaning of a path that contains symbolic links. On Windows, it converts forward slashes to backward slashes. To normalize case, use normcase().
os.path.dirname(path)
Return the directory name of pathname path. This is the first element of the pair returned by passing path to the function split().
os.path.split(path)
Split the pathname path into a pair, (head, tail) where tail is the last pathname component and head is everything leading up to that. The tail part will never contain a slash; if path ends in a slash, tail will be empty. If there is no slash in path, head will be empty. If path is empty, both head and tail are empty. Trailing slashes are stripped from head unless it is the root (one or more slashes only). In all cases, join(head, tail) returns a path to the same location as path (but the strings may differ). Also see the functions dirname() and basename().
我們做以下觀察:
test.py
import os
print(__file__)
print(os.path.dirname(__file__))
print(os.path.abspath(__file__))
print(os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)))
print(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))運行:
$ pwd
/home/dokelung
$ python test.py結果:
test.py
/home/dokelung/test.py
/home/dokelung
/home/dokelung首先 __file__ 的值其實就是在命令列上 invoke Python 時給的 script 名稱:
$ python test.py # 此時 __file__ 是 test.py
$ python ../test.py # 此時 __file__ 是 ../test.py
$ python hello/../test.py # 此時 __file__ 是 hello/../test.py在這裡, 因為 __file__ 的值為 test.py, 所以 print(__file__) 的結果是 test.py 也就不意外了。
接著, os.path.dirname(__file__)之所以得出空白(空字串), 是因為 __file__ 就只是一個單純的名稱(非路徑) 且 dirname 也只是很單純的利用 os.path.split() 來切割這個名稱(這當然沒甚麼好切的, 連路徑分割符都沒有):
>>> import os
>>> os.path.split('test.py')
('', 'test.py')
>>> os.path.split('test.py')[0]
''我分會發現切出來的 head 是空字串, 所以 dirname 的結果是空白。
abspath 動用了 os.getcwd() 所以即便給定的是單純的名稱, 也能返回路徑:
>>> os.getcwd()
'/home/dokelung'
>>> os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'test.py')
'/home/dokelung/test.py'
>>> os.path.normpath(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'test.py'))
'/home/dokelung/test.py'而 os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)) 的結果就等於是 os.getcwd() 的結果去接上 dirname 得到的空字串:
>>> os.path.dirname('test.py')
''
>>> os.path.join(os.getcwd(), os.path.dirname('test.py'))
'/home/dokelung/'最後, os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
os.path.normpath(path)🎜
🎜🎜🎜通过折叠冗余分隔符和上层引用来标准化路径名,以便 A//B、A/B/、A/./B 和 A/foo/../B 全部变为 A/B。此字符串操作可能会更改包含符号链接的路径的含义。在 Windows 上,它将正斜杠转换为反斜杠。要标准化大小写,请使用normcase()。🎜
🎜
🎜os.path.dirname(路径)🎜
🎜🎜🎜返回pathname路径的目录名。这是通过将路径传递给函数 split() 返回的对的第一个元素。🎜
🎜
🎜os.path.split(path)🎜
🎜🎜🎜将路径名路径分成一对(head,tail),其中tail是最后一个路径名组件,head是导致该路径名的所有内容。尾部永远不会包含斜线;如果路径以斜杠结尾,则 tail 将为空。如果路径中没有斜杠,则 head 将为空。如果路径为空,则头部和尾部都为空。尾部斜杠将从头部剥离,除非它是根(仅一个或多个斜杠)。在所有情况下, join(head, tail) 返回与 path 相同位置的路径(但字符串可能不同)。另请参阅函数 dirname() 和 basename()。🎜
🎜我们做以下观察:🎜
🎜test.py🎜
雷雷
🎜运行:🎜
雷雷
🎜结果:🎜
雷雷
🎜首先 __file__ 的值其实就是在命令列上调用 Python 时给的脚本名称:🎜
雷雷
🎜在这里,因为 __file__ 的值为 test.py,所以 print(__file__) 的结果是 test.py 也不满意了。🎜
🎜连接, os.path.dirname(__file__) 那么此时空白(空字串), 是因为 __file__ 就只是一个无聊的名称(非路径)且dirname 也只是很简单的利用 os.path.split() 来切割这个名称(这当然没什么好切的,连路径分割符都没有):🎜
雷雷
🎜我分会发现切出来的 head 是空字串,所以 dirname 的结果是空白。🎜
🎜abspath动用了os.getcwd()所以祭祀给定了简单的名称,也能返回路径:🎜
雷雷
🎜而 os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)) 的结果就等于 os.getcwd() 的结果去接上 dirname 得到的空字串:🎜
雷雷
🎜最后, os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)) 的结果是这么来的:🎜
雷雷
🎜希望讲到这里能让你明白!🎜结论
现在简要的回答你的问题
-
为什么 dirname 出现空白?dirname 出現空白?
因為你運行的時候給的是單純的名稱, 所以 __file__ 是單純的名字非路徑
-
我怎么能够知道,括号内的文件是以相对路径还是绝对路径被运行的?
很簡單, 就看你怎麼運行 Python 的
-
为什么我运行下面例子脚本的时候,这个文件是以相对路径被运行的呢?
因為 $ python 1.py 你自己給了相對路徑
-
os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)) 和 os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
- 因为你运行的时候给的是单纯的名称, 所以
__file__ 是单纯的名字非路径
我怎么能够知道,括号内的文件是以相对路径还是绝对路径被运行的?
很简单, 就看你怎么运行 Python 的
🎜🎜
🎜
🎜
🎜为什么我运行下面例子脚本的时候,这个文件是以相对路径被运行的呢? 🎜
🎜🎜🎜因为 $ python 1.py 你自己给了相对路径🎜🎜🎜
🎜
🎜
🎜os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)) 和os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)) 性质是否一样呢? 🎜
🎜🎜🎜基本上一样🎜🎜🎜
🎜
🎜
🎜
🎜🎜我回答过的问题🎜: Python-QA🎜回复0