使用旋转卡尺法计算坐标平面上两点间的最大距离
- 王林转载
- 2023-09-12 09:33:04607浏览
在 C++ 中,我们有一个预定义函数 sqrt,它返回任何数字的平方根。旋转卡尺法是用于求解算法或计算几何的技术。
旋转卡尺方法的视觉表示
手部旋转显示了旋转卡尺图的真实示例,每当手部旋转时,都会显示垂直方向。我们还可以通过使用多边形来理解这个概念。
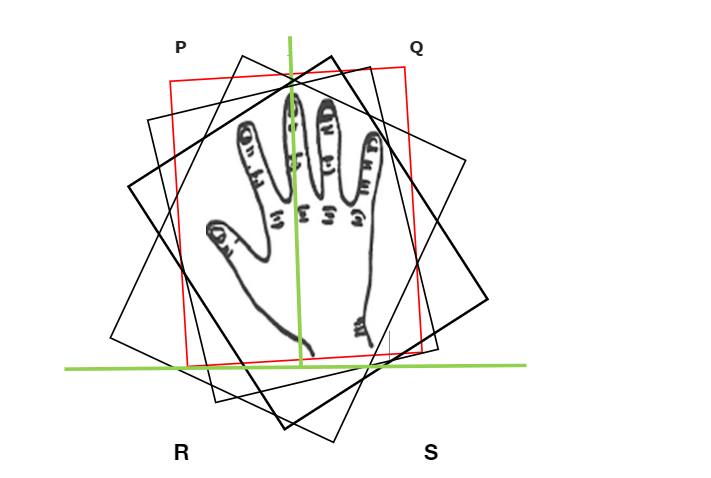
在本文中,我们将使用旋转卡尺法求出两个坐标点的最大距离。跨度>
语法
程序中使用以下语法 -
vector<datatype> name
参数
向量 - 我们从关键字向量开始,同时在 C++ 中初始化向量。
datatype - 由向量表示的数据元素的类型。
name - 向量的名称。
算法
我们将使用头文件iostream、vector和cmath来启动程序。
我们正在创建结构名称点,它将存储 x 和 y 的坐标。
我们正在定义一个 double 数据类型的函数定义 distance() 来计算两个坐标点之间的距离。这里,Points p1和Point p2是接受坐标值并使用预定义函数 sqrt 和距离公式返回距离的参数。
我们正在定义一个名为 CP() 的函数定义,其双精度数据类型接受参数 Point p1、Point p2 和 Point p3 b> 计算叉积向量,即 p2-p1 和 p3-p1 w.r.t x 和 y 坐标。
现在我们正在创建一个双精度数据类型的函数定义 rotatingCaliper(),它将参数作为点向量并最大化任意两个坐标平面之间的距离。
我们将变量result初始化为0,它将跟踪以满足最大距离的计算。为了找到点的大小,它将使用名为 size() 的预定义函数并将其存储在变量 n 中。
我们将两个变量 j 和 k 初始化为 1 并执行以下操作 -
我们正在将 j 移动到多边形中的下一个点以及当前边 'points[i]、points[ 的叉积 CP i+1] % n'且下一条边'points[j]'小于当前边'points[i]'的叉积CP,points[ (i + 1) % n]' 和下一个点'点[(j + 1) % n]'之后的边缘。这将验证当前边缘是否垂直于下一个边缘。
我们将 k 移动到多边形中的下一个点,直到当前点 'point[i]' 与下一个点 ' 之间的距离point[k]' 小于当前点 'point[i]' 与下一个点 'points[(k+1)%n] 之后的点之间的距离'。这将验证下一个点距离当前点最远。
现在我们正在计算点 j, k, 与当前点 'point[i]' 之间的距离,将所有这些点相乘,然后我们将获得 result 变量中的最大值。
我们启动主函数并将坐标平面的值应用到“向量
点” 变量。最后,我们调用函数名称 rotatingCaliper() 并将 'points' 值作为参数传递,以获取旋转卡尺图的最大距离.
示例
在这个程序中,我们将使用旋转卡尺方法来执行坐标平面中两点之间的最大距离。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
struct Point {
double x, y;
};
// In this function we are calculating the distance between two coordinate point.
double distance(Point p1, Point p2) {
return sqrt((p2.x - p1.x) * (p2.x - p1.x) + (p2.y - p1.y) * (p2.y - p1.y));
}
// In this function we are calculating the cross-product of two vector
double CP(Point p1, Point p2, Point p3) // CP: cross-product {
return (p2.x - p1.x) * (p3.y - p1.y) - (p2.y - p1.y) * (p3.x - p1.x);
}
// In this function we are calculating the Rotating Caliper
double rotatingCalipers(vector<Point> points) {
double result = 0;
int n = points.size();
int j = 1, k = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (CP(points[i], points[(i + 1) % n], points[j]) < CP(points[i], points[(i + 1) % n], points[(j + 1) % n]))
{
j = (j + 1) % n;
}
while (distance(points[i], points[k]) < distance(points[i], points[(k + 1) % n])) {
k = (k + 1) % n;
}
// calculate the max distance
result = max(result, distance(points[i], points[j]) * distance(points[i], points[k]));
}
return result;
}
int main() {
vector<Point> points = {{0, 0}, {1, 1}, {1, 2}, {2, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 3}, {3, 4}, {4, 4}, {4, 5}, {5, 5},{5,6}};
cout << "Maximum distance between two coordinate points: "<<rotatingCalipers(points) << endl;
return 0;
}
输出
Maximum distance between two coordinate points: 39.0512
结论
我们通过计算两个坐标点之间的最大距离来了解旋转卡尺法的概念。该方法的实际应用如孔径角优化、机器学习分类等。
以上是使用旋转卡尺法计算坐标平面上两点间的最大距离的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

