今天分享几个不为人知的pandas函数,大家可能平时看到的不多,但是使用起来倒是非常的方便,也能够帮助我们数据分析人员大幅度地提高工作效率,同时也希望大家看完之后能够有所收获
items()方法items()方法iterrows()方法insert()方法assign()方法eval()方法pop()方法truncate()方法count()方法add_prefix()方法/add_suffix()方法clip()方法-
filter()🎜 first()方法first()方法isin()方法df.plot.area()方法df.plot.bar()方法df.plot.box()方法df.plot.pie()方法
iterrows() 方法🎜🎜🎜 🎜insert() 方法🎜🎜🎜🎜 分配()方法🎜🎜🎜🎜eval() 方法🎜🎜🎜🎜pop() 方法🎜🎜🎜🎜truncate() 方法🎜🎜🎜🎜count() 方法🎜🎜🎜🎜add_prefix() 方法/add_suffix() 方法🎜🎜🎜🎜clip() 方法🎜🎜🎜🎜filter() 方法🎜🎜
items()方法
items()方法可以用来遍历数据集当中的每一列,同时返回列名以及每一列当中的内容,通过以元组的形式,示例如下df = pd.DataFrame({'species': ['bear', 'bear', 'marsupial'],
'population': [1864, 22000, 80000]},
index=['panda', 'polar', 'koala'])
dfoutput
species population panda bear 1864 polar bear 22000 koala marsupial 80000
然后我们使用items()方法
for label, content in df.items():
print(f'label: {label}')
print(f'content: {content}', sep='\n')
print("=" * 50)output
label: species content: panda bear polar bear koala marsupial Name: species, dtype: object ================================================== label: population content: panda 1864 polar 22000 koala 80000 Name: population, dtype: int64 ==================================================
相继的打印出了‘species’和‘population’这两列的列名和相应的内容
iterrows()方法
iterrows() li>isin() 方法
df.plot.area() 方法🎜🎜🎜df .plot.bar()方法🎜🎜🎜df.plot.box()方法🎜🎜🎜df.plot.pie()方法🎜
items()方法
items() 方法用于遍历数据集占用的每一列,同时返回列名以及每一列贸易的内容,通过以元组的形式,示例如下🎜for label, content in df.iterrows():
print(f'label: {label}')
print(f'content: {content}', sep='\n')
print("=" * 50)🎜output🎜label: panda content: species bear population 1864 Name: panda, dtype: object ================================================== label: polar content: species bear population 22000 Name: polar, dtype: object ================================================== label: koala content: species marsupial population 80000 Name: koala, dtype: object ==================================================🎜然后我们使用
items() 方法🎜df.insert(1, "size", [2000, 3000, 4000])🎜输出🎜
species size population panda bear 2000 1864 polar bear 3000 22000 koala marsupial 4000 80000🎜表格的打印生长'物种'和'种群'这列的列名称及相应的内容🎜
iterrows()方法
iterrows() 方法而言,其功能遍历数据集里的每一行,返回每一行的索引以及带有列名的每一行的内容,示例如下🎜df.assign(size_1=lambda x: x.population * 9 / 5 + 32)🎜output🎜
label: panda content: species bear population 1864 Name: panda, dtype: object ================================================== label: polar content: species bear population 22000 Name: polar, dtype: object ================================================== label: koala content: species marsupial population 80000 Name: koala, dtype: object ==================================================
insert()方法
insert()方法主要是用于在数据集当中的特定位置处插入数据,示例如下
df.insert(1, "size", [2000, 3000, 4000])
output
species size population panda bear 2000 1864 polar bear 3000 22000 koala marsupial 4000 80000
可见在DataFrame数据集当中,列的索引也是从0开始的
assign()方法
assign()方法可以用来在数据集当中添加新的列,示例如下
df.assign(size_1=lambda x: x.population * 9 / 5 + 32)
output
species population size_1 panda bear 1864 3387.2 polar bear 22000 39632.0 koala marsupial 80000 144032.0
lambda匿名函数,在数据集当中添加一个新的列,命名为‘size_1’,当然我们也可以通过assign()方法来创建不止一个列df.assign(size_1 = lambda x: x.population * 9 / 5 + 32,
size_2 = lambda x: x.population * 8 / 5 + 10)output
species population size_1 size_2 panda bear 1864 3387.2 2992.4 polar bear 22000 39632.0 35210.0 koala marsupial 80000 144032.0 128010.0
eval()方法
eval()方法主要是用来执行用字符串来表示的运算过程的,例如
df.eval("size_3 = size_1 + size_2")output
species population size_1 size_2 size_3 panda bear 1864 3387.2 2992.4 6379.6 polar bear 22000 39632.0 35210.0 74842.0 koala marsupial 80000 144032.0 128010.0 272042.0
当然我们也可以同时对执行多个运算过程
df = df.eval(''' size_3 = size_1 + size_2 size_4 = size_1 - size_2 ''')
output
species population size_1 size_2 size_3 size_4 panda bear 1864 3387.2 2992.4 6379.6 394.8 polar bear 22000 39632.0 35210.0 74842.0 4422.0 koala marsupial 80000 144032.0 128010.0 272042.0 16022.0
pop()方法
pop()方法主要是用来删除掉数据集中特定的某一列数据
df.pop("size_3")output
panda 6379.6 polar 74842.0 koala 272042.0 Name: size_3, dtype: float64
而原先的数据集当中就没有这个‘size_3’这一例的数据了
truncate()方法
truncate()方法主要是根据行索引来筛选指定行的数据的,示例如下
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'],
'B': ['f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j'],
'C': ['k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o']},
index=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5])output
A B C 1 a f k 2 b g l 3 c h m 4 d i n 5 e j o
我们使用truncate()方法来做一下尝试
df.truncate(before=2, after=4)
output
A B C 2 b g l 3 c h m 4 d i n
before和after存在于truncate()方法中,目的就是把行索引2之前和行索引4之后的数据排除在外,筛选出剩余的数据
count()方法
count()方法主要是用来计算某一列当中非空值的个数,示例如下
df = pd.DataFrame({"Name": ["John", "Myla", "Lewis", "John", "John"],
"Age": [24., np.nan, 25, 33, 26],
"Single": [True, True, np.nan, True, False]})output
Name Age Single 0 John 24.0 True 1 Myla NaN True 2 Lewis 25.0 NaN 3 John 33.0 True 4 John 26.0 False
我们使用count()方法来计算一下数据集当中非空值的个数
df.count()
output
Name 5 Age 4 Single 4 dtype: int64
add_prefix()方法/add_suffix()方法
add_prefix()方法和add_suffix()方法分别会给列名以及行索引添加后缀和前缀,对于Series()数据集而言,前缀与后缀是添加在行索引处,而对于DataFrame()数据集而言,前缀与后缀是添加在列索引处,示例如下s = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4])
output
0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 dtype: int64
我们使用add_prefix()方法与add_suffix()方法在Series()数据集上
s.add_prefix('row_')
output
row_0 1 row_1 2 row_2 3 row_3 4 dtype: int64
又例如
s.add_suffix('_row')
output
0_row 1 1_row 2 2_row 3 3_row 4 dtype: int64
DataFrame()形式数据集而言,add_prefix()方法以及add_suffix()方法是将前缀与后缀添加在列索引处的df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3, 4], 'B': [3, 4, 5, 6]})output
A B 0 1 3 1 2 4 2 3 5 3 4 6
示例如下
df.add_prefix("column_")output
column_A column_B 0 1 3 1 2 4 2 3 5 3 4 6
又例如
df.add_suffix("_column")output
A_column B_column 0 1 3 1 2 4 2 3 5 3 4 6
clip()方法
clip()方法主要是通过设置阈值来改变数据集当中的数值,当数值超过阈值的时候,就做出相应的调整data = {'col_0': [9, -3, 0, -1, 5], 'col_1': [-2, -7, 6, 8, -5]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)output
df.clip(lower = -4, upper = 4)
output
col_0 col_1 0 4 -2 1 -3 -4 2 0 4 3 -1 4 4 4 -4
lower和upper分别代表阈值的上限与下限,数据集当中超过上限与下限的值会被替代。
filter()方法
pandas当中的filter()方法是用来筛选出特定范围的数据的,示例如下
df = pd.DataFrame(np.array(([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12])),
index=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'],
columns=['one', 'two', 'three'])output
one two three A 1 2 3 B 4 5 6 C 7 8 9 D 10 11 12
我们使用filter()方法来筛选数据
df.filter(items=['one', 'three'])
output
one three A 1 3 B 4 6 C 7 9 D 10 12
我们还可以使用正则表达式来筛选数据
df.filter(regex='e$', axis=1)
output
one three A 1 3 B 4 6 C 7 9 D 10 12
当然通过参数axis来调整筛选行方向或者是列方向的数据
df.filter(like='B', axis=0)
output
one two three B 4 5 6
first()方法
当数据集当中的行索引是日期的时候,可以通过该方法来筛选前面几行的数据
index_1 = pd.date_range('2021-11-11', periods=5, freq='2D')
ts = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]}, index=index_1)
tsoutput
A 2021-11-11 1 2021-11-13 2 2021-11-15 3 2021-11-17 4 2021-11-19 5
我们使用first()方法来进行一些操作,例如筛选出前面3天的数据
ts.first('3D')
output
A 2021-11-11 1 2021-11-13 2
isin()方法
isin()方法主要是用来确认数据集当中的数值是否被包含在给定的列表当中
df = pd.DataFrame(np.array(([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12])),
index=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'],
columns=['one', 'two', 'three'])
df.isin([3, 5, 12])output
one two three A False False True B False True False C False False False D False False True
True,否则就返回False
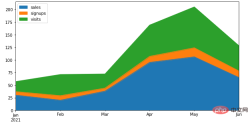
df.plot.area()方法
Pandas当中通过一行代码来绘制图表,将所有的列都通过面积图的方式来绘制df = pd.DataFrame({
'sales': [30, 20, 38, 95, 106, 65],
'signups': [7, 9, 6, 12, 18, 13],
'visits': [20, 42, 28, 62, 81, 50],
}, index=pd.date_range(start='2021/01/01', end='2021/07/01', freq='M'))
ax = df.plot.area(figsize = (10, 5))output
df.plot.bar()方法
下面我们看一下如何通过一行代码来绘制柱状图
df = pd.DataFrame({'label':['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'], 'values':[10, 30, 50, 70]})
ax = df.plot.bar(x='label', y='values', rot=20)output

当然我们也可以根据不同的类别来绘制柱状图
age = [0.1, 17.5, 40, 48, 52, 69, 88]
weight = [2, 8, 70, 1.5, 25, 12, 28]
index = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G']
df = pd.DataFrame({'age': age, 'weight': weight}, index=index)
ax = df.plot.bar(rot=0)output

当然我们也可以横向来绘制图表
ax = df.plot.barh(rot=0)
output

df.plot.box()方法
我们来看一下箱型图的具体的绘制,通过pandas一行代码来实现
data = np.random.randn(25, 3) df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=list('ABC')) ax = df.plot.box()
output

df.plot.pie()方法
接下来是饼图的绘制
df = pd.DataFrame({'mass': [1.33, 4.87 , 5.97],
'radius': [2439.7, 6051.8, 6378.1]},
index=['Mercury', 'Venus', 'Earth'])
plot = df.plot.pie(y='mass', figsize=(8, 8))output

除此之外,还有折线图、直方图、散点图等等,步骤与方式都与上述的技巧有异曲同工之妙,大家感兴趣的可以自己另外去尝试。
以上是4000字详细说明,推荐20个好用到爆的Pandas函数方法的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 Python的科学计算中如何使用阵列?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:28 AM
Python的科学计算中如何使用阵列?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:28 AMArraysinpython,尤其是Vianumpy,ArecrucialInsCientificComputingfortheireftheireffertheireffertheirefferthe.1)Heasuedfornumerericalicerationalation,dataAnalysis和Machinelearning.2)Numpy'Simpy'Simpy'simplementIncressionSressirestrionsfasteroperoperoperationspasterationspasterationspasterationspasterationspasterationsthanpythonlists.3)inthanypythonlists.3)andAreseNableAblequick
 您如何处理同一系统上的不同Python版本?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:24 AM
您如何处理同一系统上的不同Python版本?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:24 AM你可以通过使用pyenv、venv和Anaconda来管理不同的Python版本。1)使用pyenv管理多个Python版本:安装pyenv,设置全局和本地版本。2)使用venv创建虚拟环境以隔离项目依赖。3)使用Anaconda管理数据科学项目中的Python版本。4)保留系统Python用于系统级任务。通过这些工具和策略,你可以有效地管理不同版本的Python,确保项目顺利运行。
 与标准Python阵列相比,使用Numpy数组的一些优点是什么?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:21 AM
与标准Python阵列相比,使用Numpy数组的一些优点是什么?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:21 AMnumpyarrayshaveseveraladagesoverandastardandpythonarrays:1)基于基于duetoc的iMplation,2)2)他们的aremoremoremorymorymoremorymoremorymoremorymoremoremory,尤其是WithlargedAtasets和3)效率化,效率化,矢量化函数函数函数函数构成和稳定性构成和稳定性的操作,制造
 阵列的同质性质如何影响性能?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:13 AM
阵列的同质性质如何影响性能?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:13 AM数组的同质性对性能的影响是双重的:1)同质性允许编译器优化内存访问,提高性能;2)但限制了类型多样性,可能导致效率低下。总之,选择合适的数据结构至关重要。
 编写可执行python脚本的最佳实践是什么?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:11 AM
编写可执行python脚本的最佳实践是什么?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:11 AM到CraftCraftExecutablePythcripts,lollow TheSebestPractices:1)Addashebangline(#!/usr/usr/bin/envpython3)tomakethescriptexecutable.2)setpermissionswithchmodwithchmod xyour_script.3)
 Numpy数组与使用数组模块创建的数组有何不同?Apr 24, 2025 pm 03:53 PM
Numpy数组与使用数组模块创建的数组有何不同?Apr 24, 2025 pm 03:53 PMnumpyArraysareAreBetterFornumericalialoperations andmulti-demensionaldata,而learthearrayModuleSutableforbasic,内存效率段
 Numpy数组的使用与使用Python中的数组模块阵列相比如何?Apr 24, 2025 pm 03:49 PM
Numpy数组的使用与使用Python中的数组模块阵列相比如何?Apr 24, 2025 pm 03:49 PMnumpyArraySareAreBetterForHeAvyNumericalComputing,而lelethearRayModulesiutable-usemoblemory-connerage-inderabledsswithSimpleDatateTypes.1)NumpyArsofferVerverVerverVerverVersAtility andPerformanceForlargedForlargedAtatasetSetsAtsAndAtasEndCompleXoper.2)
 CTYPES模块与Python中的数组有何关系?Apr 24, 2025 pm 03:45 PM
CTYPES模块与Python中的数组有何关系?Apr 24, 2025 pm 03:45 PMctypesallowscreatingingangandmanipulatingc-stylarraysinpython.1)usectypestoInterfacewithClibrariesForperfermance.2)createc-stylec-stylec-stylarraysfornumericalcomputations.3)passarraystocfunctions foreforfunctionsforeffortions.however.however,However,HoweverofiousofmemoryManageManiverage,Pressiveo,Pressivero


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)

SecLists
SecLists是最终安全测试人员的伙伴。它是一个包含各种类型列表的集合,这些列表在安全评估过程中经常使用,都在一个地方。SecLists通过方便地提供安全测试人员可能需要的所有列表,帮助提高安全测试的效率和生产力。列表类型包括用户名、密码、URL、模糊测试有效载荷、敏感数据模式、Web shell等等。测试人员只需将此存储库拉到新的测试机上,他就可以访问到所需的每种类型的列表。

SublimeText3 英文版
推荐:为Win版本,支持代码提示!

Atom编辑器mac版下载
最流行的的开源编辑器

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境





