Nginx如何实现轮询算法
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWB转载
- 2023-05-21 21:43:131744浏览
简单轮询算法
这种算法比较简单,举个例子就是你有三台服务器
| 第一台服务器 | 192.168.1.1 |
| 第二台服务器 | 192.168.1.2 |
| 第三台服务器 | 192.168.1.3 |
第一个请求过来之后默认访问第一台,第二个请求过来访问第二台,第三次请求过来访问第三台,第四次请求过来访问第一台,以此类推。以下是我代码实现简单得算法:
public class simplepolling {
/**
* key是ip
*/
public static list <string> ipservice = new linkedlist <>();
static {
ipservice.add("192.168.1.1");
ipservice.add("192.168.1.2");
ipservice.add("192.168.1.3");
}
public static int pos = 0;
public static string getip(){
if(pos >= ipservice.size()){
//防止索引越界
pos = 0;
}
string ip = ipservice.get(pos);
pos ++;
return ip;
}
public static void main(string[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
system.out.println(getip());
}
}
}模拟执行4次执行结果是
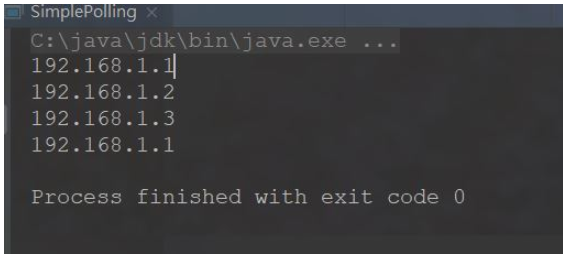
此时如果我有一台服务器性能比较好(比如192.168.1.1),我想让这台服务器处理多一点请求,此时就涉及到了权重得概率,这种算法就不能实现,请看我后面描述的轮询升级版算法。
加权轮询算法
此时我需要把我前面3台服务器都设置权重,比如第一台设置5,第二台设置1,第三台设置1
| 第一台服务器 | 192.168.1.1 | 5 |
| 第二台服务器 | 192.168.1.2 | 1 |
| 第三台服务器 | 192.168.1.3 | 1 |
此时前5个请求都会访问到第一台服务器,第六个请求会访问到第二台服务器,第七个请求会访问到第三台服务器。
以下是我给出的代码案例:
public class weightpolling {
/**
* key是ip,value是权重
*/
public static map<string, integer> ipservice = new linkedhashmap<>();
static {
ipservice.put("192.168.1.1", 5);
ipservice.put("192.168.1.2", 1);
ipservice.put("192.168.1.3", 1);
}
public static int requestid = 0;
public static int getandincrement() {
return requestid++;
}
public static string getip(){
//获取总的权重
int totalweight =0;
for (integer value : ipservice.values()) {
totalweight+= value;
}
//获取当前轮询的值
int andincrement = getandincrement();
int pos = andincrement% totalweight;
for (string ip : ipservice.keyset()) {
if(pos < ipservice.get(ip)){
return ip;
}
pos -= ipservice.get(ip);
}
return null;
}
public static void main(string[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
system.out.println(getip());
}
}
}此时运行结果是
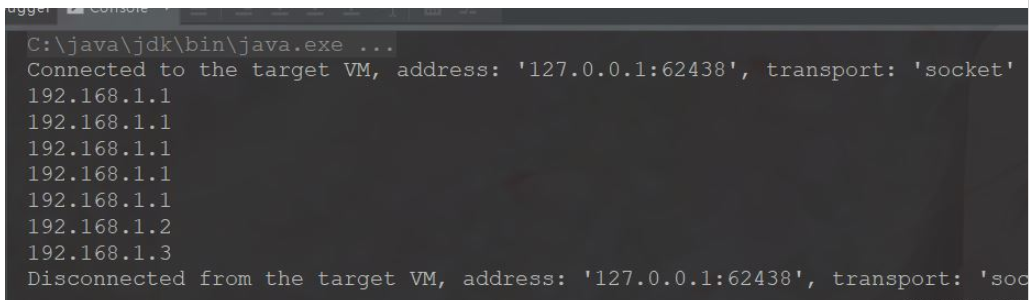
可以看的第一台服务器执行了5次,后面2台依次执行一次,依次类推。可能你觉得这种算法还不错。其实这种算法有一个缺点是,如果我第一台服务器设置权重过大可能我需要很多次请求都执行到第一台服务器上去,这样的情况分布是不均匀的,会造成某一台服务器压力过大导致崩溃。所以我后面要引入第三种算法来解决这个问题
平滑加权轮询算法
这种算法可能比较复杂,我第一次看也有点不太明白,后面看过相关资料在结合我自己的理解给大家图文解释一下,这里我举例的服务器配置和权重还是和上面一样
| 请求 | 当前权重 = 自身权重 选中后当前权重 | 总权重 | 当前最大权重 | 返回的ip | 选中后当前权重=当前最大权重-总权重 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | {5,1,1} | 7 | 5 | 192.168.1.1 | {-2,1,1} |
| 2 | {3,2,2} | 7 | 3 | 192.168.1.1 | {-4,2,2} |
| 3 | {1,3,3} | 7 | 3 | 192.168.1.2 | {1,-4,3} |
| 4 | {6,-3,4} | 7 | 6 | 192.168.1.1 | {-1,-3,4} |
| 5 | {4,-2,5} | 7 | 5 | 192.168.1.3 | {4,-2,-2} |
| 6 | {9,-1,-1} | 7 | 9 | 192.168.1.1 | {2,-1,-1} |
| 7 | {7,0,0} | 7 | 7 | 192.168.1.1 | {0,0,0} |
由上图可以看出第一台服务器虽然权重设置的是5,但并不是第五次请求过来都是第一台服务器执行,而是分散执行,调度序列是非常均匀的,且第 7 次调度时选中后当前权重又回到 {0, 0, 0},实例的状态同初始状态一致,所以后续可以一直重复调度操作。
可能有的人还不能清楚的明白上一张图表示的含义,我这里大概描述一下:
1.首先总权重不会变,默认就是当前设置的权重之和
2.在第一次请求进来的时候我默认初始化当前权重选中值是{0,0,0},所以当前权重的值就是{5 0,1 0,1 0},这里的5,1,1就是我们前面每台服务器设置的权重。
3.这里我们可以得出第一次请求过来的最大权重是5。然后返回第一台服务器ip
4.然后我们设置选中后当前权重,这里就是当前最大权重减去总权重(5-7),没有选中的权重不变,这时候得到当前权重选中权重的值{5-7,1,1}
5.在第二次请求过来的时候我们延续上面的2,3,4步骤执行.
如果这里还有不懂得我下面会提供我自己用java代码实现的算法:
public class polling {
/**
* key是ip,value是权重
*/
public static map <string,integer> ipservice = new linkedhashmap <>();
static {
ipservice.put("192.168.1.1",5);
ipservice.put("192.168.1.2",1);
ipservice.put("192.168.1.3",1);
}
private static map<string,weight> weightmap = new linkedhashmap <>();
public static string getip(){
//计算总的权重
int totalweight = 0;
for (integer value : ipservice.values()) {
totalweight+=value;
}
//首先判断weightmap是否为空
if(weightmap.isempty()){
ipservice.foreach((ip,weight)->{
weight weights = new weight(ip, weight,0);
weightmap.put(ip,weights);
});
}
//给map中得对象设置当前权重
weightmap.foreach((ip,weight)->{
weight.setcurrentweight(weight.getweight() + weight.getcurrentweight());
});
//判断最大权重是否大于当前权重,如果为空或者小于当前权重,则把当前权重赋值给最大权重
weight maxweight = null;
for (weight weight : weightmap.values()) {
if(maxweight ==null || weight.getcurrentweight() > maxweight.getcurrentweight()){
maxweight = weight;
}
}
//最后把当前最大权重减去总的权重
maxweight.setcurrentweight(maxweight.getcurrentweight() - totalweight);
//返回
return maxweight.getip();
}
public static void main(string[] args) {
//模拟轮询7次取ip
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
system.out.println(getip());
}
}
}
class weight{
/**
* ip
*/
private string ip;
/**
* 设置得权重
*/
private int weight;
/**
* 当前权重
*/
private int currentweight;
public weight(string ip, int weight,int currentweight) {
this.ip = ip;
this.weight = weight;
this.currentweight = currentweight;
}
public string getip() {
return ip;
}
public void setip(string ip) {
this.ip = ip;
}
public int getweight() {
return weight;
}
public void setweight(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public int getcurrentweight() {
return currentweight;
}
public void setcurrentweight(int currentweight) {
this.currentweight = currentweight;
}
}这里代码得执行结果是:
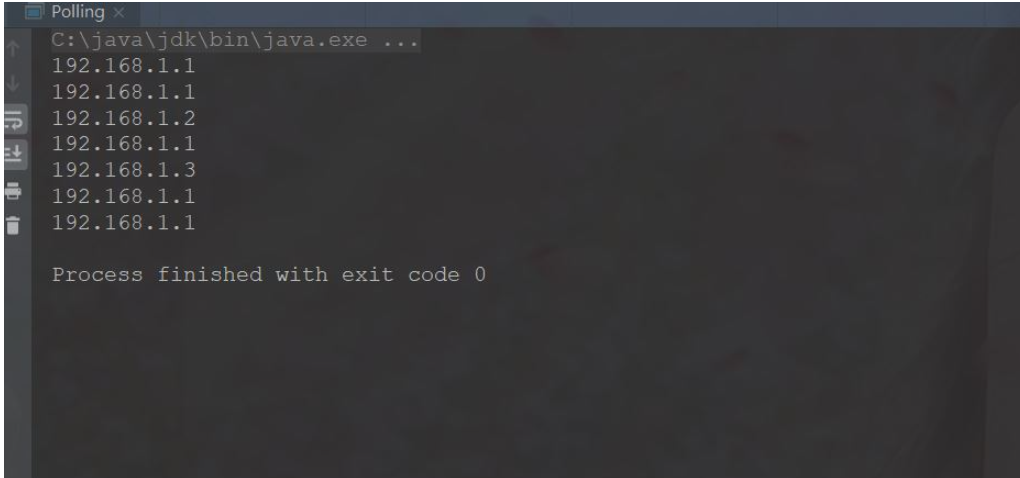
可以看出此处执行结果和表格里描述得结果一致。
以上是Nginx如何实现轮询算法的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

