一、单目三维重建概述
尽管客观世界的物体是三维的,但我们获取的图像为二维,但是我们可以从这些二维图像中感知目标的三维信息。三维重建技术是以一定的方式处理图像进而得到计算机能够识别的三维信息,由此对目标进行分析。而单目三维重建则是根据单个摄像头的运动来模拟双目视觉,从而获得物体在空间中的三维视觉信息,其中,单目即指单个摄像头。
二、实现过程
在对物体进行单目三维重建的过程中,相关运行环境如下:
matplotlib 3.3.4
numpy 1.19.5
opencv-contrib-python 3.4.2.16
opencv-python 3.4.2.16
pillow 8.2.0
python 3.6.2
其重建主要包含以下步骤:
(1)相机的标定
(2)图像特征提取及匹配
(3)三维重建
接下来,我们来详细看下每个步骤的具体实现:
(1)相机的标定
在我们日常生活中有很多相机,如手机上的相机、数码相机及功能模块型相机等等,每一个相机的参数都是不同的,即相机拍出的照片的分辨率、模式等。假设我们在进行物体三维重建的时候,事先并不知道我们相机的矩阵参数,那么,我们就应当计算出相机的矩阵参数,这一个步骤就叫做相机的标定。相机标定的相关原理我就不介绍了,网上很多人都讲解的挺详细的。其标定的具体实现如下:
def camera_calibration(ImagePath):
# 循环中断
criteria = (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS + cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER, 30, 0.001)
# 棋盘格尺寸(棋盘格的交叉点的个数)
row = 11
column = 8
objpoint = np.zeros((row * column, 3), np.float32)
objpoint[:, :2] = np.mgrid[0:row, 0:column].T.reshape(-1, 2)
objpoints = [] # 3d point in real world space
imgpoints = [] # 2d points in image plane.
batch_images = glob.glob(ImagePath + '/*.jpg')
for i, fname in enumerate(batch_images):
img = cv2.imread(batch_images[i])
imgGray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# find chess board corners
ret, corners = cv2.findChessboardCorners(imgGray, (row, column), None)
# if found, add object points, image points (after refining them)
if ret:
objpoints.append(objpoint)
corners2 = cv2.cornerSubPix(imgGray, corners, (11, 11), (-1, -1), criteria)
imgpoints.append(corners2)
# Draw and display the corners
img = cv2.drawChessboardCorners(img, (row, column), corners2, ret)
cv2.imwrite('Checkerboard_Image/Temp_JPG/Temp_' + str(i) + '.jpg', img)
print("成功提取:", len(batch_images), "张图片角点!")
ret, mtx, dist, rvecs, tvecs = cv2.calibrateCamera(objpoints, imgpoints, imgGray.shape[::-1], None, None)其中,cv2.calibrateCamera函数求出的mtx矩阵即为K矩阵。
当修改好相应参数并完成标定后,我们可以输出棋盘格的角点图片来看看是否已成功提取棋盘格的角点,输出角点图如下:
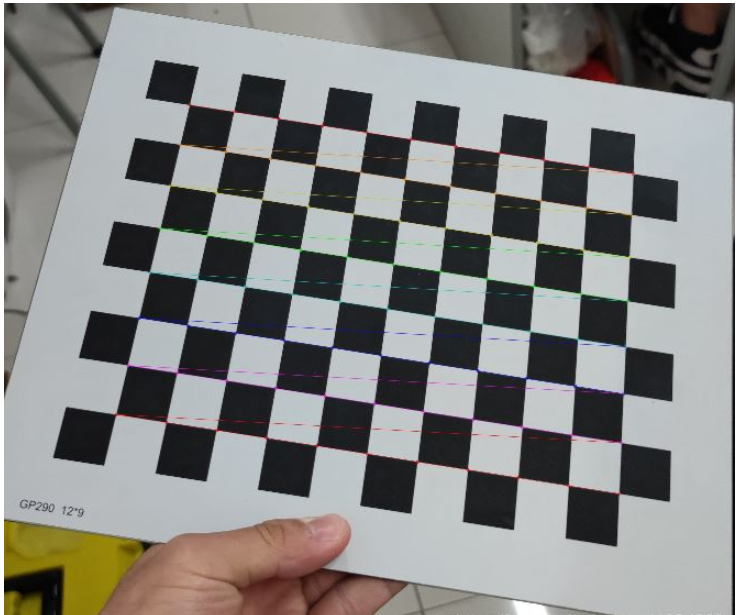
图1:棋盘格角点提取
(2)图像特征提取及匹配
在整个三维重建的过程中,这一步是最为关键的,也是最为复杂的一步,图片特征提取的好坏决定了你最后的重建效果。
在图片特征点提取算法中,有三种算法较为常用,分别为:SIFT算法、SURF算法以及ORB算法。通过综合分析对比,我们在这一步中采取SURF算法来对图片的特征点进行提取。三种算法的特征点提取效果对比如果大家感兴趣可以去网上搜来看下,在此就不逐一对比了。具体实现如下:
def epipolar_geometric(Images_Path, K):
IMG = glob.glob(Images_Path)
img1, img2 = cv2.imread(IMG[0]), cv2.imread(IMG[1])
img1_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
img2_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# Initiate SURF detector
SURF = cv2.xfeatures2d_SURF.create()
# compute keypoint & descriptions
keypoint1, descriptor1 = SURF.detectAndCompute(img1_gray, None)
keypoint2, descriptor2 = SURF.detectAndCompute(img2_gray, None)
print("角点数量:", len(keypoint1), len(keypoint2))
# Find point matches
bf = cv2.BFMatcher(cv2.NORM_L2, crossCheck=True)
matches = bf.match(descriptor1, descriptor2)
print("匹配点数量:", len(matches))
src_pts = np.asarray([keypoint1[m.queryIdx].pt for m in matches])
dst_pts = np.asarray([keypoint2[m.trainIdx].pt for m in matches])
# plot
knn_image = cv2.drawMatches(img1_gray, keypoint1, img2_gray, keypoint2, matches[:-1], None, flags=2)
image_ = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(knn_image))
image_.save("MatchesImage.jpg")
# Constrain matches to fit homography
retval, mask = cv2.findHomography(src_pts, dst_pts, cv2.RANSAC, 100.0)
# We select only inlier points
points1 = src_pts[mask.ravel() == 1]
points2 = dst_pts[mask.ravel() == 1]找到的特征点如下:
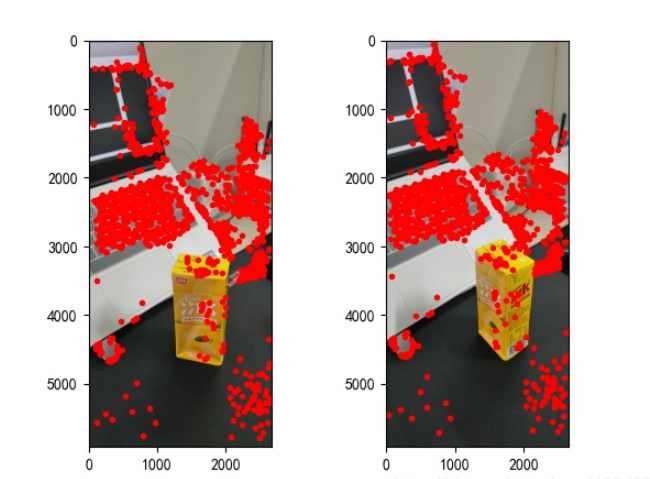
图2:特征点提取
(3)三维重建
我们找到图片的特征点并相互匹配后,则可以开始进行三维重建了,具体实现如下:
points1 = cart2hom(points1.T)
points2 = cart2hom(points2.T)
# plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2)
ax[0].autoscale_view('tight')
ax[0].imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
ax[0].plot(points1[0], points1[1], 'r.')
ax[1].autoscale_view('tight')
ax[1].imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
ax[1].plot(points2[0], points2[1], 'r.')
plt.savefig('MatchesPoints.jpg')
fig.show()
#
points1n = np.dot(np.linalg.inv(K), points1)
points2n = np.dot(np.linalg.inv(K), points2)
E = compute_essential_normalized(points1n, points2n)
print('Computed essential matrix:', (-E / E[0][1]))
P1 = np.array([[1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1, 0]])
P2s = compute_P_from_essential(E)
ind = -1
for i, P2 in enumerate(P2s):
# Find the correct camera parameters
d1 = reconstruct_one_point(points1n[:, 0], points2n[:, 0], P1, P2)
# Convert P2 from camera view to world view
P2_homogenous = np.linalg.inv(np.vstack([P2, [0, 0, 0, 1]]))
d2 = np.dot(P2_homogenous[:3, :4], d1)
if d1[2] > 0 and d2[2] > 0:
ind = i
P2 = np.linalg.inv(np.vstack([P2s[ind], [0, 0, 0, 1]]))[:3, :4]
Points3D = linear_triangulation(points1n, points2n, P1, P2)
fig = plt.figure()
fig.suptitle('3D reconstructed', fontsize=16)
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
ax.plot(Points3D[0], Points3D[1], Points3D[2], 'b.')
ax.set_xlabel('x axis')
ax.set_ylabel('y axis')
ax.set_zlabel('z axis')
ax.view_init(elev=135, azim=90)
plt.savefig('Reconstruction.jpg')
plt.show()其重建效果如下(效果一般):
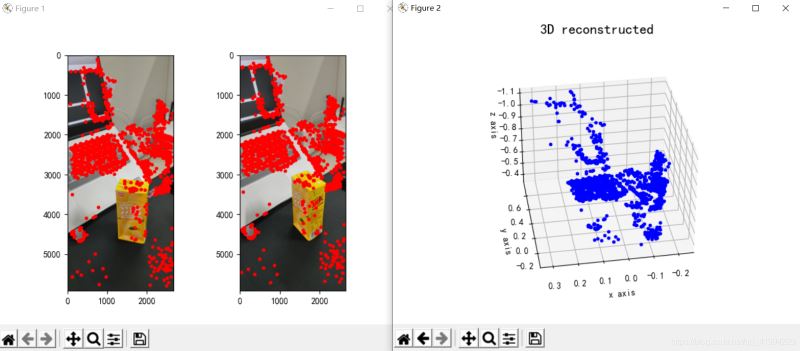
图3:三维重建
三、结论
从重建的结果来看,单目三维重建效果一般,我认为可能与这几方面因素有关:
(1)图片拍摄形式。如果是进行单目三维重建任务,在拍摄图片时最好保持平行移动相机,且最好正面拍摄,即不要斜着拍或特异角度进行拍摄;
(2)拍摄时周边环境干扰。选取拍摄的地点最好保持单一,减少无关物体的干扰;
(3)拍摄光源问题。选取的拍照场地要保证合适的亮度(具体情况要试才知道你们的光源是否达标),还有就是移动相机的时候也要保证前一时刻和此时刻的光源一致性。
事实上,单目三维重建的表现通常较差,即使在各方面条件都最佳的情况下,所得到的重建效果也不十分出色。或者我们可以考虑采用双目三维重建,双目三维重建效果肯定是要比单目的效果好的,在实现是也就麻烦一(亿)点点,哈哈。其实操作并不复杂,最麻烦的部分是要拍摄和标定两个相机,其他方面都相对容易。
四、代码
import cv2
import json
import numpy as np
import glob
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
def cart2hom(arr):
""" Convert catesian to homogenous points by appending a row of 1s
:param arr: array of shape (num_dimension x num_points)
:returns: array of shape ((num_dimension+1) x num_points)
"""
if arr.ndim == 1:
return np.hstack([arr, 1])
return np.asarray(np.vstack([arr, np.ones(arr.shape[1])]))
def compute_P_from_essential(E):
""" Compute the second camera matrix (assuming P1 = [I 0])
from an essential matrix. E = [t]R
:returns: list of 4 possible camera matrices.
"""
U, S, V = np.linalg.svd(E)
# Ensure rotation matrix are right-handed with positive determinant
if np.linalg.det(np.dot(U, V)) < 0:
V = -V
# create 4 possible camera matrices (Hartley p 258)
W = np.array([[0, -1, 0], [1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1]])
P2s = [np.vstack((np.dot(U, np.dot(W, V)).T, U[:, 2])).T,
np.vstack((np.dot(U, np.dot(W, V)).T, -U[:, 2])).T,
np.vstack((np.dot(U, np.dot(W.T, V)).T, U[:, 2])).T,
np.vstack((np.dot(U, np.dot(W.T, V)).T, -U[:, 2])).T]
return P2s
def correspondence_matrix(p1, p2):
p1x, p1y = p1[:2]
p2x, p2y = p2[:2]
return np.array([
p1x * p2x, p1x * p2y, p1x,
p1y * p2x, p1y * p2y, p1y,
p2x, p2y, np.ones(len(p1x))
]).T
return np.array([
p2x * p1x, p2x * p1y, p2x,
p2y * p1x, p2y * p1y, p2y,
p1x, p1y, np.ones(len(p1x))
]).T
def scale_and_translate_points(points):
""" Scale and translate image points so that centroid of the points
are at the origin and avg distance to the origin is equal to sqrt(2).
:param points: array of homogenous point (3 x n)
:returns: array of same input shape and its normalization matrix
"""
x = points[0]
y = points[1]
center = points.mean(axis=1) # mean of each row
cx = x - center[0] # center the points
cy = y - center[1]
dist = np.sqrt(np.power(cx, 2) + np.power(cy, 2))
scale = np.sqrt(2) / dist.mean()
norm3d = np.array([
[scale, 0, -scale * center[0]],
[0, scale, -scale * center[1]],
[0, 0, 1]
])
return np.dot(norm3d, points), norm3d
def compute_image_to_image_matrix(x1, x2, compute_essential=False):
""" Compute the fundamental or essential matrix from corresponding points
(x1, x2 3*n arrays) using the 8 point algorithm.
Each row in the A matrix below is constructed as
[x'*x, x'*y, x', y'*x, y'*y, y', x, y, 1]
"""
A = correspondence_matrix(x1, x2)
# compute linear least square solution
U, S, V = np.linalg.svd(A)
F = V[-1].reshape(3, 3)
# constrain F. Make rank 2 by zeroing out last singular value
U, S, V = np.linalg.svd(F)
S[-1] = 0
if compute_essential:
S = [1, 1, 0] # Force rank 2 and equal eigenvalues
F = np.dot(U, np.dot(np.diag(S), V))
return F
def compute_normalized_image_to_image_matrix(p1, p2, compute_essential=False):
""" Computes the fundamental or essential matrix from corresponding points
using the normalized 8 point algorithm.
:input p1, p2: corresponding points with shape 3 x n
:returns: fundamental or essential matrix with shape 3 x 3
"""
n = p1.shape[1]
if p2.shape[1] != n:
raise ValueError('Number of points do not match.')
# preprocess image coordinates
p1n, T1 = scale_and_translate_points(p1)
p2n, T2 = scale_and_translate_points(p2)
# compute F or E with the coordinates
F = compute_image_to_image_matrix(p1n, p2n, compute_essential)
# reverse preprocessing of coordinates
# We know that P1' E P2 = 0
F = np.dot(T1.T, np.dot(F, T2))
return F / F[2, 2]
def compute_fundamental_normalized(p1, p2):
return compute_normalized_image_to_image_matrix(p1, p2)
def compute_essential_normalized(p1, p2):
return compute_normalized_image_to_image_matrix(p1, p2, compute_essential=True)
def skew(x):
""" Create a skew symmetric matrix *A* from a 3d vector *x*.
Property: np.cross(A, v) == np.dot(x, v)
:param x: 3d vector
:returns: 3 x 3 skew symmetric matrix from *x*
"""
return np.array([
[0, -x[2], x[1]],
[x[2], 0, -x[0]],
[-x[1], x[0], 0]
])
def reconstruct_one_point(pt1, pt2, m1, m2):
"""
pt1 and m1 * X are parallel and cross product = 0
pt1 x m1 * X = pt2 x m2 * X = 0
"""
A = np.vstack([
np.dot(skew(pt1), m1),
np.dot(skew(pt2), m2)
])
U, S, V = np.linalg.svd(A)
P = np.ravel(V[-1, :4])
return P / P[3]
def linear_triangulation(p1, p2, m1, m2):
"""
Linear triangulation (Hartley ch 12.2 pg 312) to find the 3D point X
where p1 = m1 * X and p2 = m2 * X. Solve AX = 0.
:param p1, p2: 2D points in homo. or catesian coordinates. Shape (3 x n)
:param m1, m2: Camera matrices associated with p1 and p2. Shape (3 x 4)
:returns: 4 x n homogenous 3d triangulated points
"""
num_points = p1.shape[1]
res = np.ones((4, num_points))
for i in range(num_points):
A = np.asarray([
(p1[0, i] * m1[2, :] - m1[0, :]),
(p1[1, i] * m1[2, :] - m1[1, :]),
(p2[0, i] * m2[2, :] - m2[0, :]),
(p2[1, i] * m2[2, :] - m2[1, :])
])
_, _, V = np.linalg.svd(A)
X = V[-1, :4]
res[:, i] = X / X[3]
return res
def writetofile(dict, path):
for index, item in enumerate(dict):
dict[item] = np.array(dict[item])
dict[item] = dict[item].tolist()
js = json.dumps(dict)
with open(path, 'w') as f:
f.write(js)
print("参数已成功保存到文件")
def readfromfile(path):
with open(path, 'r') as f:
js = f.read()
mydict = json.loads(js)
print("参数读取成功")
return mydict
def camera_calibration(SaveParamPath, ImagePath):
# 循环中断
criteria = (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS + cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER, 30, 0.001)
# 棋盘格尺寸
row = 11
column = 8
objpoint = np.zeros((row * column, 3), np.float32)
objpoint[:, :2] = np.mgrid[0:row, 0:column].T.reshape(-1, 2)
objpoints = [] # 3d point in real world space
imgpoints = [] # 2d points in image plane.
batch_images = glob.glob(ImagePath + '/*.jpg')
for i, fname in enumerate(batch_images):
img = cv2.imread(batch_images[i])
imgGray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# find chess board corners
ret, corners = cv2.findChessboardCorners(imgGray, (row, column), None)
# if found, add object points, image points (after refining them)
if ret:
objpoints.append(objpoint)
corners2 = cv2.cornerSubPix(imgGray, corners, (11, 11), (-1, -1), criteria)
imgpoints.append(corners2)
# Draw and display the corners
img = cv2.drawChessboardCorners(img, (row, column), corners2, ret)
cv2.imwrite('Checkerboard_Image/Temp_JPG/Temp_' + str(i) + '.jpg', img)
print("成功提取:", len(batch_images), "张图片角点!")
ret, mtx, dist, rvecs, tvecs = cv2.calibrateCamera(objpoints, imgpoints, imgGray.shape[::-1], None, None)
dict = {'ret': ret, 'mtx': mtx, 'dist': dist, 'rvecs': rvecs, 'tvecs': tvecs}
writetofile(dict, SaveParamPath)
meanError = 0
for i in range(len(objpoints)):
imgpoints2, _ = cv2.projectPoints(objpoints[i], rvecs[i], tvecs[i], mtx, dist)
error = cv2.norm(imgpoints[i], imgpoints2, cv2.NORM_L2) / len(imgpoints2)
meanError += error
print("total error: ", meanError / len(objpoints))
def epipolar_geometric(Images_Path, K):
IMG = glob.glob(Images_Path)
img1, img2 = cv2.imread(IMG[0]), cv2.imread(IMG[1])
img1_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
img2_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# Initiate SURF detector
SURF = cv2.xfeatures2d_SURF.create()
# compute keypoint & descriptions
keypoint1, descriptor1 = SURF.detectAndCompute(img1_gray, None)
keypoint2, descriptor2 = SURF.detectAndCompute(img2_gray, None)
print("角点数量:", len(keypoint1), len(keypoint2))
# Find point matches
bf = cv2.BFMatcher(cv2.NORM_L2, crossCheck=True)
matches = bf.match(descriptor1, descriptor2)
print("匹配点数量:", len(matches))
src_pts = np.asarray([keypoint1[m.queryIdx].pt for m in matches])
dst_pts = np.asarray([keypoint2[m.trainIdx].pt for m in matches])
# plot
knn_image = cv2.drawMatches(img1_gray, keypoint1, img2_gray, keypoint2, matches[:-1], None, flags=2)
image_ = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(knn_image))
image_.save("MatchesImage.jpg")
# Constrain matches to fit homography
retval, mask = cv2.findHomography(src_pts, dst_pts, cv2.RANSAC, 100.0)
# We select only inlier points
points1 = src_pts[mask.ravel() == 1]
points2 = dst_pts[mask.ravel() == 1]
points1 = cart2hom(points1.T)
points2 = cart2hom(points2.T)
# plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2)
ax[0].autoscale_view('tight')
ax[0].imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
ax[0].plot(points1[0], points1[1], 'r.')
ax[1].autoscale_view('tight')
ax[1].imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
ax[1].plot(points2[0], points2[1], 'r.')
plt.savefig('MatchesPoints.jpg')
fig.show()
#
points1n = np.dot(np.linalg.inv(K), points1)
points2n = np.dot(np.linalg.inv(K), points2)
E = compute_essential_normalized(points1n, points2n)
print('Computed essential matrix:', (-E / E[0][1]))
P1 = np.array([[1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1, 0]])
P2s = compute_P_from_essential(E)
ind = -1
for i, P2 in enumerate(P2s):
# Find the correct camera parameters
d1 = reconstruct_one_point(points1n[:, 0], points2n[:, 0], P1, P2)
# Convert P2 from camera view to world view
P2_homogenous = np.linalg.inv(np.vstack([P2, [0, 0, 0, 1]]))
d2 = np.dot(P2_homogenous[:3, :4], d1)
if d1[2] > 0 and d2[2] > 0:
ind = i
P2 = np.linalg.inv(np.vstack([P2s[ind], [0, 0, 0, 1]]))[:3, :4]
Points3D = linear_triangulation(points1n, points2n, P1, P2)
return Points3D
def main():
CameraParam_Path = 'CameraParam.txt'
CheckerboardImage_Path = 'Checkerboard_Image'
Images_Path = 'SubstitutionCalibration_Image/*.jpg'
# 计算相机参数
camera_calibration(CameraParam_Path, CheckerboardImage_Path)
# 读取相机参数
config = readfromfile(CameraParam_Path)
K = np.array(config['mtx'])
# 计算3D点
Points3D = epipolar_geometric(Images_Path, K)
# 重建3D点
fig = plt.figure()
fig.suptitle('3D reconstructed', fontsize=16)
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
ax.plot(Points3D[0], Points3D[1], Points3D[2], 'b.')
ax.set_xlabel('x axis')
ax.set_ylabel('y axis')
ax.set_zlabel('z axis')
ax.view_init(elev=135, azim=90)
plt.savefig('Reconstruction.jpg')
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()以上是基于python怎么实现单目三维重建的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 2小时的Python计划:一种现实的方法Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM
2小时的Python计划:一种现实的方法Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM2小时内可以学会Python的基本编程概念和技能。1.学习变量和数据类型,2.掌握控制流(条件语句和循环),3.理解函数的定义和使用,4.通过简单示例和代码片段快速上手Python编程。
 Python:探索其主要应用程序Apr 10, 2025 am 09:41 AM
Python:探索其主要应用程序Apr 10, 2025 am 09:41 AMPython在web开发、数据科学、机器学习、自动化和脚本编写等领域有广泛应用。1)在web开发中,Django和Flask框架简化了开发过程。2)数据科学和机器学习领域,NumPy、Pandas、Scikit-learn和TensorFlow库提供了强大支持。3)自动化和脚本编写方面,Python适用于自动化测试和系统管理等任务。
 您可以在2小时内学到多少python?Apr 09, 2025 pm 04:33 PM
您可以在2小时内学到多少python?Apr 09, 2025 pm 04:33 PM两小时内可以学到Python的基础知识。1.学习变量和数据类型,2.掌握控制结构如if语句和循环,3.了解函数的定义和使用。这些将帮助你开始编写简单的Python程序。
 如何在10小时内通过项目和问题驱动的方式教计算机小白编程基础?Apr 02, 2025 am 07:18 AM
如何在10小时内通过项目和问题驱动的方式教计算机小白编程基础?Apr 02, 2025 am 07:18 AM如何在10小时内教计算机小白编程基础?如果你只有10个小时来教计算机小白一些编程知识,你会选择教些什么�...
 如何在使用 Fiddler Everywhere 进行中间人读取时避免被浏览器检测到?Apr 02, 2025 am 07:15 AM
如何在使用 Fiddler Everywhere 进行中间人读取时避免被浏览器检测到?Apr 02, 2025 am 07:15 AM使用FiddlerEverywhere进行中间人读取时如何避免被检测到当你使用FiddlerEverywhere...
 Python 3.6加载Pickle文件报错"__builtin__"模块未找到怎么办?Apr 02, 2025 am 07:12 AM
Python 3.6加载Pickle文件报错"__builtin__"模块未找到怎么办?Apr 02, 2025 am 07:12 AMPython3.6环境下加载Pickle文件报错:ModuleNotFoundError:Nomodulenamed...
 如何提高jieba分词在景区评论分析中的准确性?Apr 02, 2025 am 07:09 AM
如何提高jieba分词在景区评论分析中的准确性?Apr 02, 2025 am 07:09 AM如何解决jieba分词在景区评论分析中的问题?当我们在进行景区评论分析时,往往会使用jieba分词工具来处理文�...
 如何使用正则表达式匹配到第一个闭合标签就停止?Apr 02, 2025 am 07:06 AM
如何使用正则表达式匹配到第一个闭合标签就停止?Apr 02, 2025 am 07:06 AM如何使用正则表达式匹配到第一个闭合标签就停止?在处理HTML或其他标记语言时,常常需要使用正则表达式来�...


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Atom编辑器mac版下载
最流行的的开源编辑器

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

EditPlus 中文破解版
体积小,语法高亮,不支持代码提示功能






