需求描述
有时候,我们的数据是带有层级的,比如常见的省市区三级联动,就是一层套着一层,如下图:
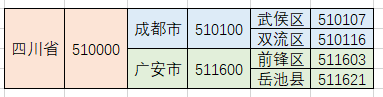
而我们在数据库存放数据的时候,往往是列表形式的,如下图:
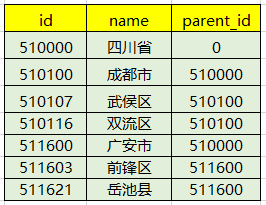
那么当我们从数据库查询出来,返回给前端的时候,前端又需要给出树形层级的时候,这个时候可能就需要递归处理为树形结构了,因此下面这个工具或许就可以用得上了。
使用示例
我们按照上面定义一个Place对象,打上工具注解:
@TreeKey 标识唯一
@TreeParentKey 标识父节点标识
@TreeChildren 标识子孙节点集合
@Data
@Data
public class Place {
@TreeKey
private String id;
@TreeParentKey
private String parentId;
private String name;
@TreeChildren
private List<Place> children;
public Place(String id, String name, String parentId) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.parentId = parentId;
}
}测试:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Place> places = new ArrayList<>();
places.add(new Place("510000", "四川省", "0"));
places.add(new Place("510100", "成都市", "510000"));
places.add(new Place("510107", "武侯区", "510100"));
places.add(new Place("510116", "双流区", "510100"));
places.add(new Place("511600", "广安市", "510000"));
places.add(new Place("511603", "前锋区", "511600"));
places.add(new Place("511621", "岳池县", "511600"));
List<Place> treeList = TreeUtils.getTree(places, "0");
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(treeList));
}
}最终效果:

工具代码
@TreeKey
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface TreeKey {
}@TreeParentKey
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface TreeParentKey {
}@TreeChildren
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface TreeChildren {
}@TreeUtils
package com.csd.utils.tree;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* 递归求树形工具类
*
* @author Yuanqiang.Zhang
* @since 2023/3/8
*/
public class TreeUtils {
/**
* 集合转化为树形
*
* @param list 集合
* @param highestParentKey 最高层父节点值
* @param <T> 泛型
* @return 树形
*/
public static <T> List<T> getTree(List<T> list, Object highestParentKey) {
if (Objects.isNull(list) || list.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
Field key = null;
Field parentKey = null;
Field children = null;
Field[] fields = list.get(0).getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
if (Objects.isNull(key)) {
TreeKey treeKey = field.getAnnotation(TreeKey.class);
if (Objects.nonNull(treeKey)) {
key = field;
continue;
}
}
if (Objects.isNull(parentKey)) {
TreeParentKey treeParentKey = field.getAnnotation(TreeParentKey.class);
if (Objects.nonNull(treeParentKey)) {
parentKey = field;
continue;
}
}
if (Objects.isNull(children)) {
TreeChildren treeChildren = field.getAnnotation(TreeChildren.class);
if (Objects.nonNull(treeChildren)) {
children = field;
continue;
}
}
}
if (Objects.isNull(key) || Objects.isNull(parentKey) || Objects.isNull(children)) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
key.setAccessible(true);
parentKey.setAccessible(true);
children.setAccessible(true);
// 获取最高层数据
List<T> highs = new ArrayList<>();
try {
for (T t : list) {
Object pk = parentKey.get(t);
if (getString(pk).equals(getString(highestParentKey))) {
highs.add(t);
}
}
// 获取最高层子孙节点
for (T t : highs) {
setChildren(list, t, key, parentKey, children);
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return highs;
}
/**
* 获取子孙节点
*
* @param list 集合
* @param parent 父节点对象
* @param key 唯一属性
* @param parentKey 父唯一属性
* @param children 节点
* @param <T> 泛型
* @return 带有子孙集合的父节点对象
* @throws IllegalAccessException
*/
private static <T> T setChildren(List<T> list, T parent, Field key, Field parentKey, Field children) throws IllegalAccessException {
Object k = key.get(parent);
List<T> tempList = new ArrayList<>();
for (T t : list) {
Object pk = parentKey.get(t);
if (getString(k).equals(getString(pk))) {
tempList.add(setChildren(list, t, key, parentKey, children));
}
}
children.set(parent, tempList);
return parent;
}
/**
* 获取字符串
*
* @param o 值
* @return 字符串
*/
private static String getString(Object o) {
return Objects.isNull(o) ? "" : o.toString();
}
}以上是Java怎么用递归实现树形结构的工具类的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 在Java应用程序中缓解平台特定问题的策略是什么?May 01, 2025 am 12:20 AM
在Java应用程序中缓解平台特定问题的策略是什么?May 01, 2025 am 12:20 AMJava如何缓解平台特定的问题?Java通过JVM和标准库来实现平台无关性。1)使用字节码和JVM抽象操作系统差异;2)标准库提供跨平台API,如Paths类处理文件路径,Charset类处理字符编码;3)实际项目中使用配置文件和多平台测试来优化和调试。
 Java的平台独立性与微服务体系结构之间有什么关系?May 01, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Java的平台独立性与微服务体系结构之间有什么关系?May 01, 2025 am 12:16 AMjava'splatformentenceenhancesenhancesmicroservicesharchitecture byferingDeploymentFlexible,一致性,可伸缩性和便携性。1)DeploymentFlexibilityAllowsibilityAllowsOllowsOllowSorlowsOllowsOllowsOllowSeStorunonAnyPlatformwithajvM.2)penterencyCrossServAccAcrossServAcrossServiCessImplifififiesDeevelopmentandeDe
 GRAALVM与Java的平台独立目标有何关系?May 01, 2025 am 12:14 AM
GRAALVM与Java的平台独立目标有何关系?May 01, 2025 am 12:14 AMGraalVM通过三种方式增强了Java的平台独立性:1.跨语言互操作,允许Java与其他语言无缝互操作;2.独立的运行时环境,通过GraalVMNativeImage将Java程序编译成本地可执行文件;3.性能优化,Graal编译器生成高效的机器码,提升Java程序的性能和一致性。
 您如何测试Java应用程序的平台兼容性?May 01, 2025 am 12:09 AM
您如何测试Java应用程序的平台兼容性?May 01, 2025 am 12:09 AM效率testjavaapplicationsforplatformcompatibility oftheSesteps:1)setUpautomatedTestingTestingActingAcrossMultPlatFormSusingCitoolSlikeSlikeJenkinSorgithUbactions.2)contuctualtemualtemalualTesteTESTENRETESTINGINREALHARTWARETOLEALHARDOELHARDOLEATOCATCHISSUSESUSEUSENINCIENVIRENTMENTS.3)schictcross.3)schoscross.3)
 Java编译器(Javac)在实现平台独立性中的作用是什么?May 01, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Java编译器(Javac)在实现平台独立性中的作用是什么?May 01, 2025 am 12:06 AMJava编译器通过将源代码转换为平台无关的字节码,实现了Java的平台独立性,使得Java程序可以在任何安装了JVM的操作系统上运行。
 在平台独立性的平台独立性上使用字节码优于本机代码的优点是什么?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:24 AM
在平台独立性的平台独立性上使用字节码优于本机代码的优点是什么?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:24 AMByteCodeachievesPlatFormIndenceByByByByByByExecutedBoviratualMachine(VM),允许CodetorunonanyplatformwithTheApprepreprepvm.Forexample,Javabytecodecodecodecodecanrunonanydevicewithajvm
 Java真的100%独立于平台吗?为什么或为什么不呢?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Java真的100%独立于平台吗?为什么或为什么不呢?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:18 AMJava不能做到100%的平台独立性,但其平台独立性通过JVM和字节码实现,确保代码在不同平台上运行。具体实现包括:1.编译成字节码;2.JVM的解释执行;3.标准库的一致性。然而,JVM实现差异、操作系统和硬件差异以及第三方库的兼容性可能影响其平台独立性。
 Java的平台独立性如何支持代码可维护性?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Java的平台独立性如何支持代码可维护性?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:15 AMJava通过“一次编写,到处运行”实现平台独立性,提升代码可维护性:1.代码重用性高,减少重复开发;2.维护成本低,只需一处修改;3.团队协作效率高,方便知识共享。


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

mPDF
mPDF是一个PHP库,可以从UTF-8编码的HTML生成PDF文件。原作者Ian Back编写mPDF以从他的网站上“即时”输出PDF文件,并处理不同的语言。与原始脚本如HTML2FPDF相比,它的速度较慢,并且在使用Unicode字体时生成的文件较大,但支持CSS样式等,并进行了大量增强。支持几乎所有语言,包括RTL(阿拉伯语和希伯来语)和CJK(中日韩)。支持嵌套的块级元素(如P、DIV),

适用于 Eclipse 的 SAP NetWeaver 服务器适配器
将Eclipse与SAP NetWeaver应用服务器集成。

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)

MinGW - 适用于 Windows 的极简 GNU
这个项目正在迁移到osdn.net/projects/mingw的过程中,你可以继续在那里关注我们。MinGW:GNU编译器集合(GCC)的本地Windows移植版本,可自由分发的导入库和用于构建本地Windows应用程序的头文件;包括对MSVC运行时的扩展,以支持C99功能。MinGW的所有软件都可以在64位Windows平台上运行。






