部署到webapps目录启动
本文使用的Spring版本为Spring6,SpringBoot版本为3,JDK为17,可能会和之前有细微不同,但整体流程差不太大。
如果部署应用到tomcat webapps目录下面启动,则需要在项目中配置web.xml文件
web.xml文件
配置Spring应用上下文
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/application-context.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>context-param
在Web应用程序的上下文范围内,可以使用context-param标签来设置初始化参数。这些参数可以在整个Web应用程序中使用,并且可以通过ServletContext对象的getInitParameter()方法获取。
ContextLoaderListener
ContextLoaderListener实现了ServletContextListener接口,这个接口是tomcat留给应用程序初始化上下文环境的接口,用于在Web应用程序启动时加载ApplicationContext。
ServletContextListener有两个默认方法
// 在所有的servlet和filter初始化之前被调用
default public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
}
// 在所有的servlet和filter销毁之后被调用
default public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
}ContextLoaderListener还继承了ContextLoader类,所有的context操作都在此类进行。
ContextLoaderListener实现contextInitialized方法,然后调用父类ContextLoader的initWebApplicationContext方法,把ServletContext传进去。
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}初始化Spring Context。
initWebApplicationContext方法关键代码
...
if (this.context == null) {
// 创建ApplicationContext
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
...
// 刷新ApplicationContext
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
...
// 将当前ApplicationContext添加到ServletContext的属性中,后面有用再说
// String ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ".ROOT";
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
...创建ApplicationContext
在createWebApplicationContext方法中,先调用determineContextClass方法确定使用哪个ApplicationContext,找到之后,实例化。
determineContextClass这个方法,主要是确定使用的ApplicationContext,首先从web.xml中加载,如果用户有定义,直接使用用户自定义的。
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM);
web.xml中配置如下,
<context-param>
<param-name>contextClass</param-name>
<param-value>com.xxx.XxxContext</param-value>
</context-param>如果没有配置,则使用Spring默认的XmlWebApplicationContext类。
这个类在ContextLoader同路径包下面的ContextLoader.properties文件中定义。
org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext=org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
配置和刷新ApplicationContext
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext关键代码
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac,ServletContext sc) {
// ...
// 获取web.xml中配置的contextConfigLocation参数
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
// ...
// 刷新上下文
wac.refresh();
}至此Tomcat已经启动Spring环境了,后续就是Spring的初始化流程,这里不再叙述。
初始化DispatcherServlet
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/dispatcher-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>此处的contextConfigLocation属于DispatcherServlet的父类FrameworkServlet,主要用来加载SpringMVC相关的配置,示例如下:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-4.3.xsd">
<!-- 扫描控制器和其他组件 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.example.controller" />
<!-- 配置视图解析器 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/views/" />
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
</bean>
<!-- 启用Spring MVC注解支持 -->
<mvc:annotation-driven />
</beans>DispatcherServlet类图
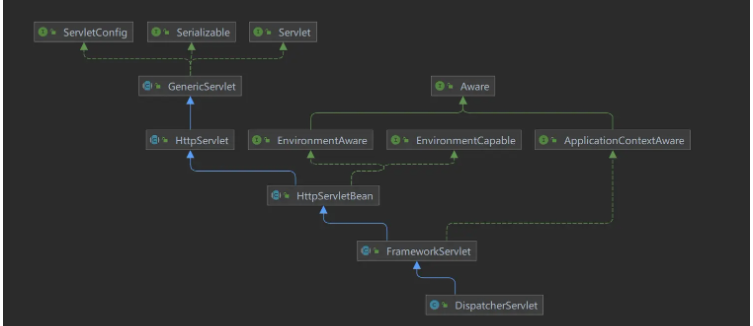
可以看到DispatcherServlet实现了Servlet接口,Servlet接口中有init方法,SpringMVC的配置就是在初始化的时候被加载的。
关键代码在HttpServletBean.init()和FrameworkServlet.initServletBean()方法中。
HttpServletBean.init()
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();
}FrameworkServlet.initServletBean()
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
...
// 在这里初始化ApplicationContext
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
// 初始化servlet
initFrameworkServlet();
}FrameworkServlet.initWebApplicationContext()
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
// 此处获取根容器,就是Spring初始化的XmlWebApplicationContext,
// 在上面把它添加到了ServletContext的属性中,标记根容器,这里把它获取出来
// String ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ".ROOT";
// servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
// 此时webApplicationContext还是null,因为DispatchServlet是被tomcat创建的,需要无参构造器
// 构造器中没有设置webApplicationContext的代码,所以此时webApplicationContext还是null
// 注意:在SpringBoot使用嵌入式Tomcat时,这个webApplicationContext不为null,因为FrameworkServlet还
// 实现了ApplicationContextAware接口,所以当SpringBoot的上下文准备好之后,会回调setApplicationContext方法
// 注入ApplicationContext,后面在细说
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac && !cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
// 此处主要是获取web.xml配置的WebApplicationContext
// 可以通过设置参数contextAttribute来设置加载SpringMVC的ApplicationContext
// 比如下面这样。除非项目中有多个WebApplicationContext,需要使用其他WebApplicationContext才会用到
// 一般都是null
// <context-param>
// <param-name>contextAttribute</param-name>
// <param-value>myWebApplicationContext</param-value>
// </context-param>
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// 现在进入到创建SpringMVC的ApplicationContext流程
// 也就是加载contextConfigLocation定义的xml文件
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
// 初始化策略对象
// 比如:HandlerMapping,HandlerAdapter,ViewResolver等等
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
// SpringMVC所使用的contextClass,可以在<servlet>标签下设置
// <init-param>
// <param-name>contextClass</param-name>
// <param-value>org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext</param-value>
// </init-param>
// 默认为XmlWebApplicationContext
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
// 实例化ApplicationContext
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
// 设置环境参数
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
// 设置父容器为Spring的ApplicationContext
wac.setParent(parent);
// 获取SpringMVC的contextConfigLocation文件
String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation();
if (configLocation != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation);
}
// 配置并刷新ApplicationContext
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}DispatchServlet初始化完成
为什么需要父子容器
父子容器的作用主要是划分框架边界和实现bean的复用。
在J2EE三层架构中,在service层我们一般使用Spring框架,而在web层则有多种选择,如Spring MVC、Struts等。为了让web层能够使用service层的bean,我们需要将service层的容器作为web层容器的父容器,这样就可以实现框架的整合。
父子容器的作用在于,当我们尝试从子容器(Servlet WebApplicationContext)中获取一个bean时,如果找不到,则会委派给父容器(Root WebApplicationContext)进行查找。重复定义相同的bean在各个子容器中被避免,从而提高了代码的复用性和可维护性。
接收请求
请求先进入doService,然后调用doDispatch进行处理。
doDispatch关键代码
...
// 首先根据当前请求HttpServletRequest,遍历所有的HandlerMapping执行handle方法,返回可用的HandlerExecutionChain对象。
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
// 然后根据handler获取支持的适配器
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// 执行HandlerInterceptor.preHandle,在controller的方法被调用前执行
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// 执行controller方法
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
// 执行HandlerInterceptor.postHandle,在controller的方法被调用后执行
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
// 渲染结果到视图
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);HandlerMapping是request与handler object之间的映射,它能根据request找到对应的handler。handler object可以是任意类型,比如@Controller注解的类,或者实现了Controller接口的类,或者实现了HttpRequestHandler接口的类等。
HandlerExecutionChain是handler执行链,它包装了handler object和一组HandlerInterceptor。HandlerInterceptor是拦截器,它可以在handler执行前后进行一些额外的操作,比如权限检查,日志记录等。
HandlerAdapter是handler的适配器,它能处理不同类型的handler object,并调用其对应的方法,返回ModelAndView对象。HandlerAdapter可以根据handler object的类型,进行参数绑定,返回值处理等操作。
HandlerInterceptor使用
定义一个拦截器类,实现HandlerInterceptor接口或者继承HandlerInterceptorAdapter类,重写preHandle,postHandle和afterCompletion三个方法。
在preHandle方法中,可以获取请求和响应对象,进行预处理,比如检查请求头中的token,或者判断请求的url是否有权限访问等。如果返回true,则继续执行后续的拦截器或者处理器;如果返回false,则中断请求,不再执行后续的拦截器或者处理器。
在postHandle方法中,可以获取请求和响应对象,以及处理器返回的ModelAndView对象,进行后处理,比如修改模型数据或者视图信息等。只有在preHandle方法返回true并且处理器成功执行后,该方法才会被调用。
在afterCompletion方法中,可以获取请求和响应对象,以及处理器抛出的异常对象(如果有的话),进行清理资源或者异常处理等。只有当preHandle方法返回true时,无论处理器是否成功执行,该方法才会被调用。
在SpringMVC配置文件中,需注册拦截器类并指定拦截的URL模式。可以注册多个拦截器,并指定顺序。拦截器会按照顺序执行preHandle方法,然后按照逆序执行postHandle和afterCompletion方法。
HandlerInterceptor和Filter的区别
HandlerInterceptor利用Java反射机制实现,而Filter则通过函数回调方式实现。HandlerInterceptor可以利用Spring的AOP技术,实现更灵活的拦截逻辑,而Filter只能在请求前后进行简单的处理。
HandlerInterceptor不依赖于Servlet容器,而Filter依赖于Servlet容器。HandlerInterceptor是SpringMVC框架提供的,可以在任何情况下使用,而Filter是Servlet规范的一部分,只能在Web应用中使用。
HandlerInterceptor的执行由SpringMVC框架控制,而Filter的执行由Servlet容器控制。HandlerInterceptor可以通过IoC容器来管理,可以注入其他的Bean,而Filter则需要在web.xml中配置,或者使用@WebFilter注解,并且需要@ServletComponentScan扫描。
HandlerInterceptor只能拦截DispatcherServlet处理的请求,而Filter可以拦截任何请求。HandlerInterceptor只能对Controller方法进行拦截,而Filter可以对静态资源、JSP页面等进行拦截。
HandlerInterceptor有三个方法:preHandle,postHandle和afterCompletion,分别在请求处理前后和视图渲染前后执行,而Filter只有一个方法:doFilter,在请求处理前后执行。
处理controller返回结果
对于被controller方法,使用的适配器是RequestMappingHandlerAdapter,在handlerAdapter.handle方法执行时,会去执行对应的controller方法,处理controller方法返回的结果。
invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle
// 执行controller方法
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
...
// 处理返回数据,会判断是不是有@ResponseBody注解,如果有,会使用RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor来处理返回值
// 然后会解析请求头等等,判断应该返回什么类型的数据,然后使用对应的HttpMessageConverter写入输出流
this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(
returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);SpringBoot Jar启动
SpringBoot使用嵌入式Servlet容器启动应用,有Tomcat,Jetty,Undertow。
选择Servlet容器
SpringBoot默认使用Tomcat,可以在配置文件中看出。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>web模块自动引入了tomcat
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId> </dependency>
如果不使用Tomcat可以排除,引入其他服务器。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<!-- 剔除Tomcat -->
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!-- 使用jetty -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId>
</dependency>如果没有排除Tomcat,直接引入其他服务器,比如下面。
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> <!-- 没有排除Tomcat --> </dependency> <!-- 引入jetty --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId> </dependency>
如果项目中同时引入了Tomcat和其他服务器的依赖,那么SpringBoot会按照以下顺序来选择启动的服务器。
Tomcat > Jetty > Undertow
也就是说,如果有Tomcat,就优先使用Tomcat,如果没有Tomcat,就看有没有Jetty,如果有Jetty,就使用Jetty,以此类推。这个顺序是在SpringBoot的ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration类中定义的。
// 只展示必要代码
class ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration {
// 当Servlet、Tomcat、UpgradeProtocol类在类路径存在时
// 并且ServletWebServerFactory类存在,则会创建tomcatServletWebServerFactory bean。
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Tomcat.class, UpgradeProtocol.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ServletWebServerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
static class EmbeddedTomcat {
@Bean
TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcatServletWebServerFactory(
... 代码省略
}
}
// 当Servlet、Server、WebAppContext类在类路径存在时
// 并且ServletWebServerFactory类型的Bean不存在时,则会创建JettyServletWebServerFactory bean。
// ServletWebServerFactory是TomcatServletWebServerFactory、JettyServletWebServerFactory、
// UndertowServletWebServerFactory的父类
// 所以如果Tomcat被引入,上面的tomcatServletWebServerFactory就会被创建,这里的条件就不满足,不会被创建。
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Server.class, Loader.class, WebAppContext.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ServletWebServerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
static class EmbeddedJetty {
@Bean
JettyServletWebServerFactory JettyServletWebServerFactory(
... 代码省略
}
}
// 分析同上
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Undertow.class, SslClientAuthMode.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ServletWebServerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
static class EmbeddedUndertow {
@Bean
UndertowServletWebServerFactory undertowServletWebServerFactory(
... 代码省略
}
}下面继续以Tomcat为例
Tomcat配置、启动
Tomcat是在Spring容器启动的时候启动的
SpringApplication.run方法
首先创建一个ConfigurableApplicationContext对象,并调用其refresh()方法,这个对象一般是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext。
context = createApplicationContext(); -> refreshContext(context); -> refresh(context); -> applicationContext.refresh();
refresh()方法会调用其父类ServletWebServerApplicationContext的refresh()方法,在父类的refresh()中再次调用父类AbstractApplicationContext的refresh()方法,主要在onRefresh阶段,会进行服务器的配置。
... refresh()代码简略 // 这里会初始化Tomcat配置 onRefresh(); // 这里会启动Tomcat finishRefresh(); ...
回到ServletWebServerApplicationContext类的onRefresh()方法,会调用createWebServer()方法,创建web服务器。
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
// 创建服务器
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}private void createWebServer() {
... 代码简略
// 获取工厂类,这里获取的就是在配置类中生效的那一个,这里为TomcatServletWebServerFactory
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
createWebServer.tag("factory", factory.getClass().toString());
// 获取服务器
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
}TomcatServletWebServerFactory.getWebServer
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
if (this.disableMBeanRegistry) {
Registry.disableRegistry();
}
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory : createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
for (LifecycleListener listener : this.serverLifecycleListeners) {
tomcat.getServer().addLifecycleListener(listener);
}
// 设置Connector,对应与Tomcat Server.xml 中的<Connector></Connector>
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
connector.setThrowOnFailure(true);
// 对应于Server.xml 中
// <Service name="Catalina">
// <Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
// connectionTimeout="20000"
// redirectPort="8443" relaxedQueryChars="[|]"/>
// </Service>
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
// 准备好Context组件
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}// 创建Tomcat服务器
protected TomcatWebServer getTomcatWebServer(Tomcat tomcat) {
return new TomcatWebServer(tomcat, getPort() >= 0, getShutdown());
}至此,Tomcat配置已经初始化完成,准备启动。
在finishRefresh()方法中,会启动Tomcat
getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh(); > DefaultLifecycleProcessor.startBeans(true); > LifecycleGroup::start > doStart(this.lifecycleBeans, member.name, this.autoStartupOnly); > bean.start(); > WebServerStartStopLifecycle.start > TomcatWebServer.start();
private void startBeans(boolean autoStartupOnly) {
Map<String, Lifecycle> lifecycleBeans = getLifecycleBeans();
Map<Integer, LifecycleGroup> phases = new TreeMap<>();
lifecycleBeans.forEach((beanName, bean) -> {
if (!autoStartupOnly || (bean instanceof SmartLifecycle smartLifecycle && smartLifecycle.isAutoStartup())) {
int phase = getPhase(bean);
phases.computeIfAbsent(
phase,
p -> new LifecycleGroup(phase, this.timeoutPerShutdownPhase, lifecycleBeans, autoStartupOnly)
).add(beanName, bean);
}
});
if (!phases.isEmpty()) {
phases.values().forEach(LifecycleGroup::start);
}
}public void start() {
this.webServer.start();
this.running = true;
this.applicationContext
.publishEvent(new ServletWebServerInitializedEvent(this.webServer, this.applicationContext));
}DispatchServlet配置
ServletContextInitializer
在prepareContext方法中,有一个方法configureContext
configureContext(context, initializersToUse);
configureContext方法,在这里面创建了一个TomcatStarter对象,这个类实现了ServletContainerInitializer接口,所以在容器启动过程中会被调用。
TomcatStarter starter = new TomcatStarter(initializers); context.addServletContainerInitializer(starter, NO_CLASSES);
initializers是Spring自己定义的初始化接口ServletContextInitializer,传入TomcatStarter之后,在onStartup方法中循环调用onStartup方法。
public void onStartup(Set<Class<?>> classes, ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
try {
for (ServletContextInitializer initializer : this.initializers) {
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
...
}需要注意的是,这里的initializers有些传过来的时候是一个函数式接口,在上面的factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());这里传进来的,就是一个函数式接口
private org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletContextInitializer getSelfInitializer() {
return this::selfInitialize;
}实际调用在下面这个方法
private void selfInitialize(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
prepareWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
registerApplicationScope(servletContext);
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(getBeanFactory(), servletContext);
for (ServletContextInitializer beans : getServletContextInitializerBeans()) {
beans.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}在此处绕过所有ServletContextInitializer,随后执行它们的onStartup方法。
其中有一个DispatcherServletRegistrationBean,这个类实现了ServletContextInitializer接口,主要是用来添加DispatchServlet。
DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration配置类中有DispatcherServlet,DispatcherServletRegistrationBean两个Bean。
protected static class DispatcherServletRegistrationConfiguration {
@Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_REGISTRATION_BEAN_NAME)
@ConditionalOnBean(value = DispatcherServlet.class, name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME)
public DispatcherServletRegistrationBean dispatcherServletRegistration(DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet,
WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties, ObjectProvider<MultipartConfigElement> multipartConfig) {
// 创建DispatcherServletRegistrationBean,并把dispatcherServlet传进去
DispatcherServletRegistrationBean registration = new DispatcherServletRegistrationBean(dispatcherServlet,
webMvcProperties.getServlet().getPath());
registration.setName(DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME);
registration.setLoadOnStartup(webMvcProperties.getServlet().getLoadOnStartup());
multipartConfig.ifAvailable(registration::setMultipartConfig);
return registration;
}
}
protected static class DispatcherServletConfiguration {
@Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME)
public DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet(WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties) {
// 创建DispatcherServlet
DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet = new DispatcherServlet();
dispatcherServlet.setDispatchOptionsRequest(webMvcProperties.isDispatchOptionsRequest());
dispatcherServlet.setDispatchTraceRequest(webMvcProperties.isDispatchTraceRequest());
dispatcherServlet.setThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound(webMvcProperties.isThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound());
dispatcherServlet.setPublishEvents(webMvcProperties.isPublishRequestHandledEvents());
dispatcherServlet.setEnableLoggingRequestDetails(webMvcProperties.isLogRequestDetails());
return dispatcherServlet;
}
}ServletContextInitializer.onStartup方法由子类RegistrationBean实现
public final void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
String description = getDescription();
if (!isEnabled()) {
logger.info(StringUtils.capitalize(description) + " was not registered (disabled)");
return;
}
// register是一个抽象方法,由子类DynamicRegistrationBean实现
register(description, servletContext);
}
protected abstract void register(String description, ServletContext servletContext);DynamicRegistrationBean.register
protected final void register(String description, ServletContext servletContext) {
// addRegistration是一个抽象方法,由子类ServletRegistrationBean实现
D registration = addRegistration(description, servletContext);
if (registration == null) {
logger.info(StringUtils.capitalize(description) + " was not registered (possibly already registered?)");
return;
}
// Servlet被添加到Context后,这里对Servlet进行配置,如拦截路径
configure(registration);
}
protected abstract D addRegistration(String description, ServletContext servletContext);ServletRegistrationBean.addRegistration,作用类似下面
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>protected ServletRegistration.Dynamic addRegistration(String description, ServletContext servletContext) {
String name = getServletName();
// 添加Servlet到Context中,这里的servlet就是DispatchServlet。
return servletContext.addServlet(name, this.servlet);
}ServletRegistrationBean.configure,作用类似下面
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>protected void configure(ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration) {
super.configure(registration);
String[] urlMapping = StringUtils.toStringArray(this.urlMappings);
if (urlMapping.length == 0 && this.alwaysMapUrl) {
// DEFAULT_MAPPINGS默是“/”
urlMapping = DEFAULT_MAPPINGS;
}
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(urlMapping)) {
// 设置mapping
registration.addMapping(urlMapping);
}
registration.setLoadOnStartup(this.loadOnStartup);
if (this.multipartConfig != null) {
registration.setMultipartConfig(this.multipartConfig);
}
}至此,DispatchServlet已配置好,后续流程和web.xml配置调用流程基本相同。
FrameworkServlet.initWebApplicationContext()
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
// 此处获取根容器,就是Spring初始化的XmlWebApplicationContext,
// 在上面把它添加到了ServletContext的属性中,标记根容器,这里把它获取出来
// String ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ".ROOT";
// servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);
// ===========上面为使用web.xml时的分析,下面为SpringBoot嵌入式Tomcat分析============
// 同样是获取根容器,不过一般为AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
// 此时webApplicationContext还是null,因为DispatchServlet是被tomcat创建的,需要无参构造器
// 构造器中没有设置webApplicationContext的代码,所以此时webApplicationContext还是null
// ===========上面为使用web.xml时的分析,下面为SpringBoot嵌入式Tomcat分析============
// 注意:在SpringBoot使用嵌入式Tomcat时,这个webApplicationContext不为null,因为FrameworkServlet还
// 实现了ApplicationContextAware接口,所以当SpringBoot的上下文准备好之后,会回调setApplicationContext方法
// 注入ApplicationContext,后面在细说
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac && !cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
// 此处主要是获取web.xml配置的WebApplicationContext
// 可以通过设置参数contextAttribute来设置加载SpringMVC的ApplicationContext
// 比如下面这样。除非项目中有多个WebApplicationContext,需要使用其他WebApplicationContext才会用到
// 一般都是null
// <context-param>
// <param-name>contextAttribute</param-name>
// <param-value>myWebApplicationContext</param-value>
// </context-param>
// ===========上面为使用web.xml时的分析,下面为SpringBoot嵌入式Tomcat分析
// 因为wac此时不为null,这里不会进入
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// 现在进入到创建SpringMVC的ApplicationContext流程
// 也就是加载contextConfigLocation定义的xml文件
// ===========上面为使用web.xml时的分析,下面为SpringBoot嵌入式Tomcat分析
// 因为wac此时不为null,这里不会进入,所以没有SpringMVC的容器,也就是没有父子容器之分,SpringBoot项目中只有一个容器
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
// 初始化策略对象
// 比如:HandlerMapping,HandlerAdapter,ViewResolver等等
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}以上是web.xml SpringBoot打包可执行Jar运行SpringMVC的方法是什么的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 Java开发的哪些方面取决于平台?Apr 26, 2025 am 12:19 AM
Java开发的哪些方面取决于平台?Apr 26, 2025 am 12:19 AMJavadevelovermentIrelyPlatForm-DeTueTososeVeralFactors.1)JVMVariationsAffectPerformanceNandBehaviorAcroSsdifferentos.2)Nativelibrariesviajnijniiniininiinniinindrododerplatefform.3)
 在不同平台上运行Java代码时是否存在性能差异?为什么?Apr 26, 2025 am 12:15 AM
在不同平台上运行Java代码时是否存在性能差异?为什么?Apr 26, 2025 am 12:15 AMJava代码在不同平台上运行时会有性能差异。1)JVM的实现和优化策略不同,如OracleJDK和OpenJDK。2)操作系统的特性,如内存管理和线程调度,也会影响性能。3)可以通过选择合适的JVM、调整JVM参数和代码优化来提升性能。
 Java平台独立性有什么局限性?Apr 26, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Java平台独立性有什么局限性?Apr 26, 2025 am 12:10 AMJava'splatFormentenceHaslimitations不包括PerformanceOverhead,versionCompatibilityIsissues,挑战WithnativelibraryIntegration,Platform-SpecificFeatures,andjvminstallation/jvminstallation/jvmintenance/jeartenance.therefactorscomplicatorscomplicatethe“ writeOnce”
 解释平台独立性和跨平台发展之间的差异。Apr 26, 2025 am 12:08 AM
解释平台独立性和跨平台发展之间的差异。Apr 26, 2025 am 12:08 AMPlatformIndependendecealLowsProgramStormonanyPlograwsStormanyPlatFormWithOutModification,而LileCross-PlatFormDevelopmentRequiredquiresMomePlatform-specificAdjustments.platFormIndependence,EneblesuniveByjava,EnablesuniversUniversAleversalexecutionbutmayCotutionButMayComproMisePerformance.cross.cross.cross-platformd
 即时(JIT)汇编如何影响Java的性能和平台独立性?Apr 26, 2025 am 12:02 AM
即时(JIT)汇编如何影响Java的性能和平台独立性?Apr 26, 2025 am 12:02 AMJITcompilationinJavaenhancesperformancewhilemaintainingplatformindependence.1)Itdynamicallytranslatesbytecodeintonativemachinecodeatruntime,optimizingfrequentlyusedcode.2)TheJVMremainsplatform-independent,allowingthesameJavaapplicationtorunondifferen
 为什么Java是开发跨平台桌面应用程序的流行选择?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:23 AM
为什么Java是开发跨平台桌面应用程序的流行选择?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:23 AMjavaispopularforcross-platformdesktopapplicationsduetoits“ writeonce,runanywhere”哲学。1)itusesbytbytybytecebytecodethatrunsonanyjvm-platform.2)librarieslikeslikeslikeswingingandjavafxhelpcreatenative-lookingenative-lookinguisis.3)
 讨论可能需要在Java中编写平台特定代码的情况。Apr 25, 2025 am 12:22 AM
讨论可能需要在Java中编写平台特定代码的情况。Apr 25, 2025 am 12:22 AM在Java中编写平台特定代码的原因包括访问特定操作系统功能、与特定硬件交互和优化性能。1)使用JNA或JNI访问Windows注册表;2)通过JNI与Linux特定硬件驱动程序交互;3)通过JNI使用Metal优化macOS上的游戏性能。尽管如此,编写平台特定代码会影响代码的可移植性、增加复杂性、可能带来性能开销和安全风险。
 与平台独立性相关的Java开发的未来趋势是什么?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:12 AM
与平台独立性相关的Java开发的未来趋势是什么?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:12 AMJava将通过云原生应用、多平台部署和跨语言互操作进一步提升平台独立性。1)云原生应用将使用GraalVM和Quarkus提升启动速度。2)Java将扩展到嵌入式设备、移动设备和量子计算机。3)通过GraalVM,Java将与Python、JavaScript等语言无缝集成,增强跨语言互操作性。


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

SecLists
SecLists是最终安全测试人员的伙伴。它是一个包含各种类型列表的集合,这些列表在安全评估过程中经常使用,都在一个地方。SecLists通过方便地提供安全测试人员可能需要的所有列表,帮助提高安全测试的效率和生产力。列表类型包括用户名、密码、URL、模糊测试有效载荷、敏感数据模式、Web shell等等。测试人员只需将此存储库拉到新的测试机上,他就可以访问到所需的每种类型的列表。

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

VSCode Windows 64位 下载
微软推出的免费、功能强大的一款IDE编辑器

螳螂BT
Mantis是一个易于部署的基于Web的缺陷跟踪工具,用于帮助产品缺陷跟踪。它需要PHP、MySQL和一个Web服务器。请查看我们的演示和托管服务。

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器






