常规的Excel数据处理中,就是对Excel数据文件的读/写/文件对象操作。
通过对应的python非标准库xlrd/xlwt/xlutils,来实现具体的数据处理业务逻辑。
在复杂的Excel业务数据处理中,三兄弟扮演的角色缺一不可。今天我们的内容是关于如何采用xlrd/xlwt/xlutils三个模块来实现数据处理。
1、模块说明
使用该三个模块来处理Excel数据最好的地方就是他们和Excel文件对象对应的数据处理概念是一样的,能更好的便于我们理解数据对象。
首先,这三个模块都是python的非标准库,可以选择pip的方式来进行安装。
pip install xlrd pip install xlwt pip install xlutils
下面是我们为演示数据处理的过程准备的源数据内容,只是用于测试。
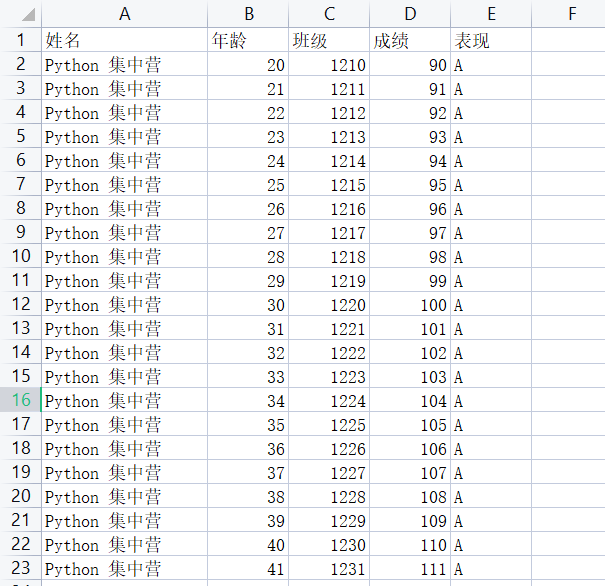
xlrd:用于读取Excle数据文件将返回的数据对象放到内存中,然后查询数据文件对象的相关信息。
xlwt:用于在内存中生成新的数据文件对象,处理完成后写入到Excel数据文件中。
xlutils:主要的作用就是copy新的文件对象,在新的数据对象中完成数据处理操作。
将xlrd/xlwt/xlutils三个模块分别都导入到待开发的代码块中提供支持。
# Importing the xlrd module. import xlrd as read # Importing the xlwt module. import xlwt as write # Copying the contents of the original workbook into a new workbook. from xlutils.copy import copy
2、xlrd处理
# Opening the workbook and assigning it to the variable `work_book`.
work_book = read.open_workbook('D:/test-data-work/test.xls')
# Assigning the sheet named 'Sheet1' to the variable `sheet`.
sheet = work_book.sheet_by_name('Sheet1')
# `row = sheet.nrows` is assigning the number of rows in the sheet to the variable `row`.
row = sheet.nrows
# `col = sheet.ncols` is assigning the number of columns in the sheet to the variable `col`.
col = sheet.ncols
print('Sheet1工作表有:{0}行,{1}列'.format(str(row), str(col)))
# Sheet1工作表有:23行,5列下面是三种常用的sheet对象的数据遍历方式,分别是按行/列的方式进行数据遍历。
for a in sheet.get_rows():
print(a)
# [text:'姓名', text:'年龄', text:'班级', text:'成绩', text:'表现']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:20.0, number:1210.0, number:90.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:21.0, number:1211.0, number:91.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:22.0, number:1212.0, number:92.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:23.0, number:1213.0, number:93.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:24.0, number:1214.0, number:94.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:25.0, number:1215.0, number:95.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:26.0, number:1216.0, number:96.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:27.0, number:1217.0, number:97.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:28.0, number:1218.0, number:98.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:29.0, number:1219.0, number:99.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:30.0, number:1220.0, number:100.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:31.0, number:1221.0, number:101.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:32.0, number:1222.0, number:102.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:33.0, number:1223.0, number:103.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:34.0, number:1224.0, number:104.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:35.0, number:1225.0, number:105.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:36.0, number:1226.0, number:106.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:37.0, number:1227.0, number:107.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:38.0, number:1228.0, number:108.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:39.0, number:1229.0, number:109.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:40.0, number:1230.0, number:110.0, text:'A']
# [text:'Python 集中营', number:41.0, number:1231.0, number:111.0, text:'A']
for b in range(row):
print(sheet.row_values(b))
# ['姓名', '年龄', '班级', '成绩', '表现']
# ['Python 集中营', 20.0, 1210.0, 90.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 21.0, 1211.0, 91.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 22.0, 1212.0, 92.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 23.0, 1213.0, 93.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 24.0, 1214.0, 94.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 25.0, 1215.0, 95.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 26.0, 1216.0, 96.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 27.0, 1217.0, 97.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 28.0, 1218.0, 98.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 29.0, 1219.0, 99.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 30.0, 1220.0, 100.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 31.0, 1221.0, 101.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 32.0, 1222.0, 102.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 33.0, 1223.0, 103.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 34.0, 1224.0, 104.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 35.0, 1225.0, 105.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 36.0, 1226.0, 106.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 37.0, 1227.0, 107.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 38.0, 1228.0, 108.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 39.0, 1229.0, 109.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 40.0, 1230.0, 110.0, 'A']
# ['Python 集中营', 41.0, 1231.0, 111.0, 'A']
for c in range(col):
print(sheet.col_values(c))
# ['姓名', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营', 'Python 集中营']
# ['年龄', 20.0, 21.0, 22.0, 23.0, 24.0, 25.0, 26.0, 27.0, 28.0, 29.0, 30.0, 31.0, 32.0, 33.0, 34.0, 35.0, 36.0, 37.0, 38.0, 39.0, 40.0, 41.0]
# ['班级', 1210.0, 1211.0, 1212.0, 1213.0, 1214.0, 1215.0, 1216.0, 1217.0, 1218.0, 1219.0, 1220.0, 1221.0, 1222.0, 1223.0, 1224.0, 1225.0, 1226.0, 1227.0, 1228.0, 1229.0, 1230.0, 1231.0]
# ['成绩', 90.0, 91.0, 92.0, 93.0, 94.0, 95.0, 96.0, 97.0, 98.0, 99.0, 100.0, 101.0, 102.0, 103.0, 104.0, 105.0, 106.0, 107.0, 108.0, 109.0, 110.0, 111.0]
# ['表现', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A']3、xlwt处理
# Creating a new workbook.
work_book_2 = write.Workbook()
# Creating a new sheet named 'Sheet4' in the workbook.
sheet_2 = work_book_2.add_sheet('Sheet4')
list = [
['姓名', '年龄', '班级', '成绩'],
['张三', '20', '1210', '89'],
['李四', '21', '1211', '90'],
['王五', '22', '1212', '91'],
]
for row_index in range(4):
for col_index in range(4):
sheet_2.write(row_index, col_index, list[row_index][col_index])
col_index += 1
row_index += 1
# Saving the workbook to the specified location.
work_book_2.save('D:/test-data-work/test2.xls')4、xlutils处理
# Opening the workbook and assigning it to the variable `work_book_3`. work_book_3 = read.open_workbook('D:/test-data-work/test.xls') # Copying the contents of the original workbook into a new workbook. work_book_3_copy = copy(work_book_3) # Saving the contents of the original workbook into a new workbook. work_book_3_copy.save('D:/test-data-work/test3.xls')
以上是Python Excel数据处理之xlrd/xlwt/xlutils模块怎么使用的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 Python:深入研究汇编和解释May 12, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python:深入研究汇编和解释May 12, 2025 am 12:14 AMpythonisehybridmodelofcompilationand interpretation:1)thepythoninterspretercompilesourcececodeintoplatform- interpententbybytecode.2)thepytythonvirtualmachine(pvm)thenexecuteCutestestestesteSteSteSteSteSteSthisByTecode,BelancingEaseofuseWithPerformance。
 Python是一种解释或编译语言,为什么重要?May 12, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python是一种解释或编译语言,为什么重要?May 12, 2025 am 12:09 AMpythonisbothinterpretedAndCompiled.1)它的compiledTobyTecodeForportabilityAcrosplatforms.2)bytecodeisthenInterpreted,允许fordingfordforderynamictynamictymictymictymictyandrapiddefupment,尽管Ititmaybeslowerthananeflowerthanancompiledcompiledlanguages。
 对于python中的循环时循环与循环:解释了关键差异May 12, 2025 am 12:08 AM
对于python中的循环时循环与循环:解释了关键差异May 12, 2025 am 12:08 AM在您的知识之际,而foroopsareideal insinAdvance中,而WhileLoopSareBetterForsituations则youneedtoloopuntilaconditionismet
 循环时:实用指南May 12, 2025 am 12:07 AM
循环时:实用指南May 12, 2025 am 12:07 AMForboopSareSusedwhenthentheneMberofiterationsiskNownInAdvance,而WhileLoopSareSareDestrationsDepportonAcondition.1)ForloopSareIdealForiteratingOverSequencesLikelistSorarrays.2)whileLeleLooleSuitableApeableableableableableableforscenarioscenarioswhereTheLeTheLeTheLeTeLoopContinusunuesuntilaspecificiccificcificCondond
 Python:它是真正的解释吗?揭穿神话May 12, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Python:它是真正的解释吗?揭穿神话May 12, 2025 am 12:05 AMpythonisnotpuroly interpred; itosisehybridablectofbytecodecompilationandruntimeinterpretation.1)PythonCompiLessourceceCeceDintobyTecode,whitsthenexecececected bytybytybythepythepythepythonvirtirtualmachine(pvm).2)
 与同一元素的Python串联列表May 11, 2025 am 12:08 AM
与同一元素的Python串联列表May 11, 2025 am 12:08 AMconcateNateListsinpythonwithTheSamelements,使用:1)operatototakeepduplicates,2)asettoremavelemavphicates,or3)listCompreanspearensionforcontroloverduplicates,每个methodhasdhasdifferentperferentperferentperforentperforentperforentperfortenceandordormplications。
 解释与编译语言:Python的位置May 11, 2025 am 12:07 AM
解释与编译语言:Python的位置May 11, 2025 am 12:07 AMpythonisanterpretedlanguage,offeringosofuseandflexibilitybutfacingperformancelanceLimitationsInCricapplications.1)drightingedlanguageslikeLikeLikeLikeLikeLikeLikeLikeThonexecuteline-by-line,允许ImmediaMediaMediaMediaMediaMediateFeedBackAndBackAndRapidPrototypiD.2)compiledLanguagesLanguagesLagagesLikagesLikec/c thresst
 循环时:您什么时候在Python中使用?May 11, 2025 am 12:05 AM
循环时:您什么时候在Python中使用?May 11, 2025 am 12:05 AMUseforloopswhenthenumberofiterationsisknowninadvance,andwhileloopswheniterationsdependonacondition.1)Forloopsareidealforsequenceslikelistsorranges.2)Whileloopssuitscenarioswheretheloopcontinuesuntilaspecificconditionismet,usefulforuserinputsoralgorit


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

Atom编辑器mac版下载
最流行的的开源编辑器

SublimeText3 英文版
推荐:为Win版本,支持代码提示!

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

EditPlus 中文破解版
体积小,语法高亮,不支持代码提示功能

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) 是一个PHP/MySQL的Web应用程序,非常容易受到攻击。它的主要目标是成为安全专业人员在合法环境中测试自己的技能和工具的辅助工具,帮助Web开发人员更好地理解保护Web应用程序的过程,并帮助教师/学生在课堂环境中教授/学习Web应用程序安全。DVWA的目标是通过简单直接的界面练习一些最常见的Web漏洞,难度各不相同。请注意,该软件中






