SpringBoot启动并初始化执行sql脚本
如果我们想在项目启动的时候去执行一些sql脚本该怎么办呢,SpringBoot给我们提供了这个功能,可以在启动SpringBoot的项目时,执行脚本,下面我们来看一下。
我们先看一下源码
boolean createSchema() {
//会从application.properties或application.yml中获取sql脚本列表
List<Resource> scripts = this.getScripts("spring.datasource.schema", this.properties.getSchema(), "schema");
if (!scripts.isEmpty()) {
if (!this.isEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Initialization disabled (not running DDL scripts)");
return false;
}
String username = this.properties.getSchemaUsername();
String password = this.properties.getSchemaPassword();
//运行sql脚本
this.runScripts(scripts, username, password);
}
return !scripts.isEmpty();
}
private List<Resource> getScripts(String propertyName, List<String> resources, String fallback) {
if (resources != null) {
//如果配置文件中配置,则加载配置文件
return this.getResources(propertyName, resources, true);
} else {
//指定schema要使用的Platform(mysql、oracle),默认为all
String platform = this.properties.getPlatform();
List<String> fallbackResources = new ArrayList();
//如果配置文件中没配置,则会去类路径下找名称为schema或schema-platform的文件
fallbackResources.add("classpath*:" + fallback + "-" + platform + ".sql");
fallbackResources.add("classpath*:" + fallback + ".sql");
return this.getResources(propertyName, fallbackResources, false);
}
}
private List<Resource> getResources(String propertyName, List<String> locations, boolean validate) {
List<Resource> resources = new ArrayList();
Iterator var5 = locations.iterator();
while(var5.hasNext()) {
String location = (String)var5.next();
Resource[] var7 = this.doGetResources(location);
int var8 = var7.length;
for(int var9 = 0; var9 < var8; ++var9) {
Resource resource = var7[var9];
//验证文件是否存在
if (resource.exists()) {
resources.add(resource);
} else if (validate) {
throw new InvalidConfigurationPropertyValueException(propertyName, resource, "The specified resource does not exist.");
}
}
}
return resources;
}从源码观察,大致知道是什么意思了,SpringBoot默认会从类路径下去找脚本文件,但是类路径下只能放规定名称为schema或schema-platform的脚本文件,如果我们想要分好多个脚本文件,那么这种方式就不合适了,那么就需要我们在application.properties或application.yml中去配置脚本列表,那么这个初始化脚本操作能不能在配置文件中控制呢,可以的,有一个initialization-mode属性,可以设置三个值,always为始终执行初始化,embedded只初始化内存数据库(默认值),如h3等,never为不执行初始化。
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: liuzhenyu199577
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbc
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
initialization-mode: always下面我们验证一下这两种方式
1.默认放置schema或schema-platform的脚本文件
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS department (ID VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL, NAME VARCHAR(100), PRIMARY KEY (ID));
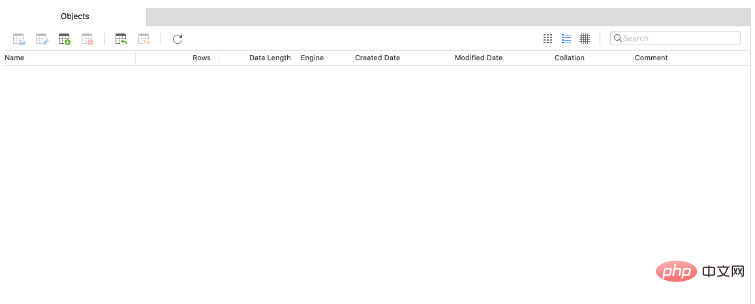
查看数据库没有department这个表,接下来我们启动程序
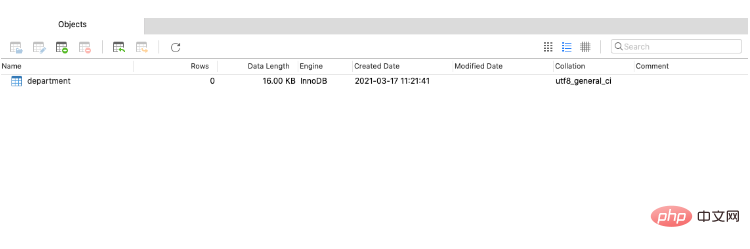
启动之后,我们再看一下,就执行了
2.配置文件中指定多个sql脚本
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: liuzhenyu199577
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbc
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
initialization-mode: always
schema:
- classpath:department.sql
- classpath:department2.sql
- classpath:department3.sql
三个sql脚本都是插入语句
INSERT INTO department (ID,NAME) VALUES ('1','2') INSERT INTO department (ID,NAME) VALUES ('2','3') INSERT INTO department (ID,NAME) VALUES ('3','4')
现在表中无任何数据,接下来我们启动程序
启动之后,我们再看一下,表中就有了三条数据
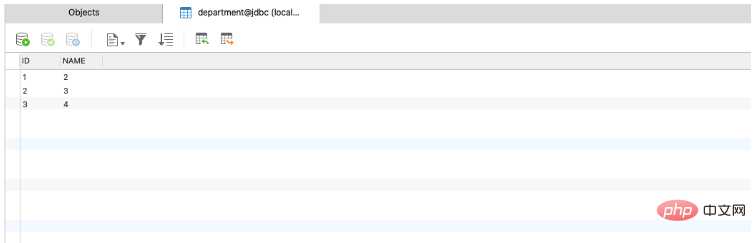
就是SpringBoot启动并初始化sql脚本的步骤
SpringBoot项目在启动时执行指定sql文件
1. 启动时执行
当有在项目启动时先执行指定的sql语句的需求时,可以在resources文件夹下添加需要执行的sql文件,文件中的sql语句可以是DDL脚本或DML脚本,然后在配置加入相应的配置即可,如下:
spring:
datasource:
schema: classpath:schema.sql # schema.sql中一般存放的是DDL脚本,即通常为创建或更新库表的脚本 data: classpath:data.sql # data.sql中一般是DML脚本,即通常为数据插入脚本2. 执行多个sql文件
spring.datasource.schema和spring.datasource.data都是支持接收一个列表,所以当需要执行多个sql文件时,可以使用如下配置:
spring:
datasource:
schema: classpath:schema_1.sql, classpath:schema_2.sql data: classpath:data_1.sql, classpath:data_2.sql 或 spring: datasource: schema: - classpath:schema_1.sql - classpath:schema_2.sql data: - classpath:data_1.sql - classpath:data_2.sql3. 不同运行环境执行不同脚本
一般情况下,都会有多个运行环境,比如开发、测试、生产等。而不同运行环境通常需要执行的sql会有所不同。为解决这个问题,可以使用通配符来实现。
创建不同环境的文件夹
在resources文件夹创建不同环境对应的文件夹,如dev/、sit/、prod/。
配置
application.yml
spring:
datasource:
schema: classpath:${spring.profiles.active:dev}/schema.sql
data: classpath:${spring.profiles.active:dev}/data.sql注:${}通配符支持缺省值。如上面的配置中的${spring.profiles.active:dev},其中分号前是取属性spring.profiles.active的值,而当该属性的值不存在,则使用分号后面的值,即dev。
bootstrap.yml
spring:
profiles:
active: dev # dev/sit/prod等。分别对应开发、测试、生产等不同运行环境。提醒:spring.profiles.active属性一般在bootstrap.yml或bootstrap.properties中配置。
4. 支持不同数据库
因为不同数据库的语法有所差异,所以要实现同样的功能,不同数据库的sql语句可能会不一样,所以可能会有多份不同的sql文件。当需要支持不同数据库时,可以使用如下配置:
spring:
datasource:
schema: classpath:${spring.profiles.active:dev}/schema-${spring.datasource.platform}.sql
data: classpath:${spring.profiles.active:dev}/data-${spring.datasource.platform}.sql
platform: mysql提醒:platform属性的默认值是'all',所以当有在不同数据库切换的情况下才使用如上配置,因为默认值的情况下,spring boot会自动检测当前使用的数据库。
注:此时,以dev允许环境为例,resources/dev/文件夹下必须存在如下文件:schema-mysql.sql和data-mysql.sql。
5. 避坑
5.1 坑
当在执行的sql文件中存在存储过程或函数时,在启动项目时会报错。
比如现在有这样的需求:项目启动时,扫描某张表,当表记录数为0时,插入多条记录;大于0时,跳过。
schema.sql文件脚本如下:
-- 当存储过程`p1`存在时,删除。 drop procedure if exists p1; -- 创建存储过程`p1` create procedure p1() begin declare row_num int; select count(*) into row_num from `t_user`; if row_num = 0 then INSERT INTO `t_user`(`username`, `password`) VALUES ('zhangsan', '123456'); end if; end; -- 调用存储过程`p1` call p1(); drop procedure if exists p1;
启动项目,报错,原因如下:
Caused by: com.mysql.jdbc.exceptions.jdbc4.MySQLSyntaxErrorException: You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near 'create procedure p1() begin declare row_num int' at line 1
大致的意思是:'create procedure p1() begin declare row_num int'这一句出现语法错误。刚看到这一句,我一开始是懵逼的,吓得我赶紧去比对mysql存储过程的写法,对了好久都发现没错,最后看到一篇讲解spring boot配置启动时执行sql脚本的文章,发现其中多了一项配置:spring.datasource.separator=$$。然后看源码发现,spring boot在解析sql脚本时,默认是以';'作为断句的分隔符的。看到这里,不难看出报错的原因,即:spring boot把'create procedure p1() begin declare row_num int'当成是一条普通的sql语句。而我们需要的是创建一个存储过程。
5.2 解决方案
修改sql脚本的断句分隔符。如:spring.datasource.separator=$$。然后把脚本改成:
-- 当存储过程`p1`存在时,删除。 drop procedure if exists p1;$$ -- 创建存储过程`p1` create procedure p1() begin declare row_num int; select count(*) into row_num from `t_user`; if row_num = 0 then INSERT INTO `t_user`(`username`, `password`) VALUES ('zhangsan', '123456'); end if; end;$$ -- 调用存储过程`p1` call p1();$$ drop procedure if exists p1;$$
5.3 不足
因为sql脚本的断句分隔符从';'变成'$$',所以可能需要在DDL、DML语句的';'后加'$$',不然可能会出现将整个脚本当成一条sql语句来执行的情况。比如:
-- DDL CREATE TABLE `table_name` ( -- 字段定义 ... ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;$$ -- DML INSERT INTO `table_name` VALUE(...);$$
以上是SpringBoot如何启动并初始化执行sql脚本的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 在平台独立性的平台独立性上使用字节码优于本机代码的优点是什么?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:24 AM
在平台独立性的平台独立性上使用字节码优于本机代码的优点是什么?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:24 AMByteCodeachievesPlatFormIndenceByByByByByByExecutedBoviratualMachine(VM),允许CodetorunonanyplatformwithTheApprepreprepvm.Forexample,Javabytecodecodecodecodecanrunonanydevicewithajvm
 Java真的100%独立于平台吗?为什么或为什么不呢?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Java真的100%独立于平台吗?为什么或为什么不呢?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:18 AMJava不能做到100%的平台独立性,但其平台独立性通过JVM和字节码实现,确保代码在不同平台上运行。具体实现包括:1.编译成字节码;2.JVM的解释执行;3.标准库的一致性。然而,JVM实现差异、操作系统和硬件差异以及第三方库的兼容性可能影响其平台独立性。
 Java的平台独立性如何支持代码可维护性?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Java的平台独立性如何支持代码可维护性?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:15 AMJava通过“一次编写,到处运行”实现平台独立性,提升代码可维护性:1.代码重用性高,减少重复开发;2.维护成本低,只需一处修改;3.团队协作效率高,方便知识共享。
 为新平台创建JVM面临哪些挑战?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:15 AM
为新平台创建JVM面临哪些挑战?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:15 AM在新平台上创建JVM面临的主要挑战包括硬件兼容性、操作系统兼容性和性能优化。1.硬件兼容性:需要确保JVM能正确使用新平台的处理器指令集,如RISC-V。2.操作系统兼容性:JVM需正确调用新平台的系统API,如Linux。3.性能优化:需进行性能测试和调优,调整垃圾回收策略以适应新平台的内存特性。
 Javafx库如何试图解决GUI开发中的平台不一致?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Javafx库如何试图解决GUI开发中的平台不一致?Apr 30, 2025 am 12:01 AMjavafxeffectife addressEddressEndressInconSiscies uningies uningusing inaplatform-agnosticsCenegraphandCssStyling.1)itabstractsplactsplatsplatsplatsplatformsthercensthascenegenceenceNaSceneGraph,确保ConsistSistEntertRenderingRenderingRenderingRenderingAccomWindows,MacOs,MacOS,MacOS,andlinux.2)
 说明JVM如何充当Java代码和基础操作系统之间的中介。Apr 29, 2025 am 12:23 AM
说明JVM如何充当Java代码和基础操作系统之间的中介。Apr 29, 2025 am 12:23 AMJVM的工作原理是将Java代码转换为机器码并管理资源。1)类加载:加载.class文件到内存。2)运行时数据区:管理内存区域。3)执行引擎:解释或编译执行字节码。4)本地方法接口:通过JNI与操作系统交互。
 解释Java虚拟机(JVM)在Java平台独立性中的作用。Apr 29, 2025 am 12:21 AM
解释Java虚拟机(JVM)在Java平台独立性中的作用。Apr 29, 2025 am 12:21 AMJVM使Java实现跨平台运行。1)JVM加载、验证和执行字节码。2)JVM的工作包括类加载、字节码验证、解释执行和内存管理。3)JVM支持高级功能如动态类加载和反射。
 您将采取哪些步骤来确保Java应用程序在不同的操作系统上正确运行?Apr 29, 2025 am 12:11 AM
您将采取哪些步骤来确保Java应用程序在不同的操作系统上正确运行?Apr 29, 2025 am 12:11 AMJava应用可通过以下步骤在不同操作系统上运行:1)使用File或Paths类处理文件路径;2)通过System.getenv()设置和获取环境变量;3)利用Maven或Gradle管理依赖并测试。Java的跨平台能力依赖于JVM的抽象层,但仍需手动处理某些操作系统特定的功能。


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

安全考试浏览器
Safe Exam Browser是一个安全的浏览器环境,用于安全地进行在线考试。该软件将任何计算机变成一个安全的工作站。它控制对任何实用工具的访问,并防止学生使用未经授权的资源。

EditPlus 中文破解版
体积小,语法高亮,不支持代码提示功能

SublimeText3 Linux新版
SublimeText3 Linux最新版

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)

PhpStorm Mac 版本
最新(2018.2.1 )专业的PHP集成开发工具






