1、使用 Math.random()可以生成一个double类型的 [ 0.0,1.0)的随机数(实际上的取值是 【0.0,0.9999999】)
假设我们要生成一个【20,80】的随机数,20可以取到,80也可以取到。
生成【min,max】范围内的随机整数
公式:
(int)( min + Math.random() * ( max - min + 1))
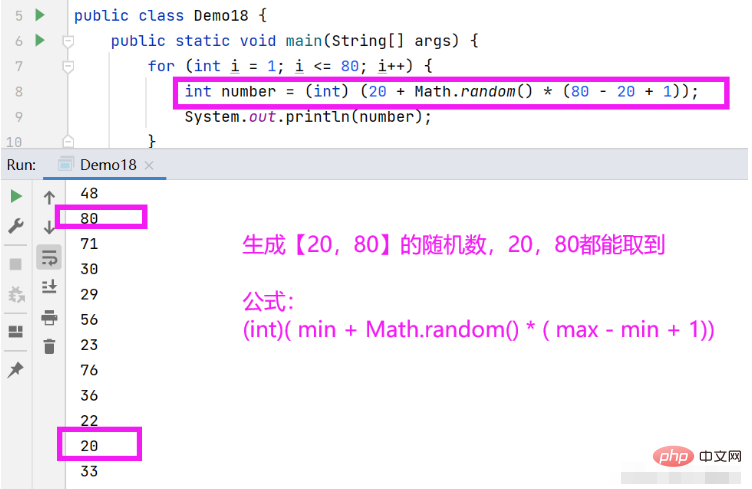
测试案例:生成一个【20,80】的随机整数
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 80; i++) {
int number = (int) (20 + Math.random() * (80 - 20 + 1));
System.out.println(number);
}
}可以多打印几次测试结果。
2、创建Random类对象,调用nextInt()方法生成随机数
需求:生成 0-10的随机数,包含0和10
Random random = new Random(); int num = random.nextInt(10); //这样写的话,生成[ 0,9]的随机整数数。
如果我们要包含0和10,应该这样写
int num = random.nextInt(10+1);
即是说括号里面的那个最大范围数实际上是取不到的,所以我们要在括号里面+1。
nextInt()生成随机整数规律公式:
需求:生成【min,max】范围内的随机整数,包含min和max
Random random = new Random(); int num = min + random.nextInt( max - min + 1);
参照需求生成【0,10】的随机整数套用公式:
//生成【0,10】的随机整数 Random random = new Random(); int num = 0 + random.nextInt( 10 - 0 + 1); // int num = random.nextInt(11);
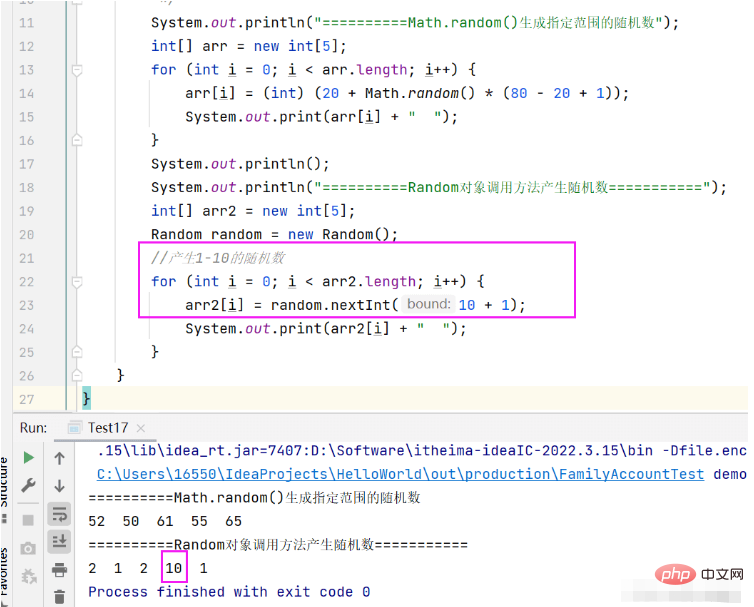
测试案例代码:
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("==========Random对象调用方法产生随机数===========");
int[] arr2 = new int[5];
Random random = new Random();
//产生【1-10】的随机数
for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
arr2[i] = random.nextInt(10 + 1);
System.out.print(arr2[i] + " ");
}
}随机打印测试的数据(结果有随机性,可以多运行几次观察结果)
猜数字大小的游戏
系统随机生成【1,100】一个随机数,用户从控制台输入一个数,两者比较大小,若不相等,就提示用户,他输入的数字比系统生成的随机数大还是小。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo18 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int randomNumber = (int) (1 + Math.random() * (100 - 1 + 1));
int userNumber;
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入您猜测的数字[1,100]:");
userNumber = sc.nextInt();
if (userNumber == randomNumber) {
System.out.println("恭喜您猜对了");
System.out.println("系统生成的随机数:" + randomNumber);
break;
} else if (userNumber > randomNumber) {
System.out.println("您猜的数字偏大");
} else {
System.out.println("您猜的数字偏小");
}
}
System.out.println("游戏结束!");
}
}以上是Java怎么生成指定范围内的一个随机整数的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 带你搞懂Java结构化数据处理开源库SPLMay 24, 2022 pm 01:34 PM
带你搞懂Java结构化数据处理开源库SPLMay 24, 2022 pm 01:34 PM本篇文章给大家带来了关于java的相关知识,其中主要介绍了关于结构化数据处理开源库SPL的相关问题,下面就一起来看一下java下理想的结构化数据处理类库,希望对大家有帮助。
 Java集合框架之PriorityQueue优先级队列Jun 09, 2022 am 11:47 AM
Java集合框架之PriorityQueue优先级队列Jun 09, 2022 am 11:47 AM本篇文章给大家带来了关于java的相关知识,其中主要介绍了关于PriorityQueue优先级队列的相关知识,Java集合框架中提供了PriorityQueue和PriorityBlockingQueue两种类型的优先级队列,PriorityQueue是线程不安全的,PriorityBlockingQueue是线程安全的,下面一起来看一下,希望对大家有帮助。
 完全掌握Java锁(图文解析)Jun 14, 2022 am 11:47 AM
完全掌握Java锁(图文解析)Jun 14, 2022 am 11:47 AM本篇文章给大家带来了关于java的相关知识,其中主要介绍了关于java锁的相关问题,包括了独占锁、悲观锁、乐观锁、共享锁等等内容,下面一起来看一下,希望对大家有帮助。
 一起聊聊Java多线程之线程安全问题Apr 21, 2022 pm 06:17 PM
一起聊聊Java多线程之线程安全问题Apr 21, 2022 pm 06:17 PM本篇文章给大家带来了关于java的相关知识,其中主要介绍了关于多线程的相关问题,包括了线程安装、线程加锁与线程不安全的原因、线程安全的标准类等等内容,希望对大家有帮助。
 详细解析Java的this和super关键字Apr 30, 2022 am 09:00 AM
详细解析Java的this和super关键字Apr 30, 2022 am 09:00 AM本篇文章给大家带来了关于Java的相关知识,其中主要介绍了关于关键字中this和super的相关问题,以及他们的一些区别,下面一起来看一下,希望对大家有帮助。
 Java基础归纳之枚举May 26, 2022 am 11:50 AM
Java基础归纳之枚举May 26, 2022 am 11:50 AM本篇文章给大家带来了关于java的相关知识,其中主要介绍了关于枚举的相关问题,包括了枚举的基本操作、集合类对枚举的支持等等内容,下面一起来看一下,希望对大家有帮助。
 java中封装是什么May 16, 2019 pm 06:08 PM
java中封装是什么May 16, 2019 pm 06:08 PM封装是一种信息隐藏技术,是指一种将抽象性函式接口的实现细节部分包装、隐藏起来的方法;封装可以被认为是一个保护屏障,防止指定类的代码和数据被外部类定义的代码随机访问。封装可以通过关键字private,protected和public实现。
 归纳整理JAVA装饰器模式(实例详解)May 05, 2022 pm 06:48 PM
归纳整理JAVA装饰器模式(实例详解)May 05, 2022 pm 06:48 PM本篇文章给大家带来了关于java的相关知识,其中主要介绍了关于设计模式的相关问题,主要将装饰器模式的相关内容,指在不改变现有对象结构的情况下,动态地给该对象增加一些职责的模式,希望对大家有帮助。


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

PhpStorm Mac 版本
最新(2018.2.1 )专业的PHP集成开发工具

Dreamweaver Mac版
视觉化网页开发工具

SecLists
SecLists是最终安全测试人员的伙伴。它是一个包含各种类型列表的集合,这些列表在安全评估过程中经常使用,都在一个地方。SecLists通过方便地提供安全测试人员可能需要的所有列表,帮助提高安全测试的效率和生产力。列表类型包括用户名、密码、URL、模糊测试有效载荷、敏感数据模式、Web shell等等。测试人员只需将此存储库拉到新的测试机上,他就可以访问到所需的每种类型的列表。

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) 是一个PHP/MySQL的Web应用程序,非常容易受到攻击。它的主要目标是成为安全专业人员在合法环境中测试自己的技能和工具的辅助工具,帮助Web开发人员更好地理解保护Web应用程序的过程,并帮助教师/学生在课堂环境中教授/学习Web应用程序安全。DVWA的目标是通过简单直接的界面练习一些最常见的Web漏洞,难度各不相同。请注意,该软件中

MinGW - 适用于 Windows 的极简 GNU
这个项目正在迁移到osdn.net/projects/mingw的过程中,你可以继续在那里关注我们。MinGW:GNU编译器集合(GCC)的本地Windows移植版本,可自由分发的导入库和用于构建本地Windows应用程序的头文件;包括对MSVC运行时的扩展,以支持C99功能。MinGW的所有软件都可以在64位Windows平台上运行。






