1、读取xlsx表格:pd.read_excel()
原始内容如下:
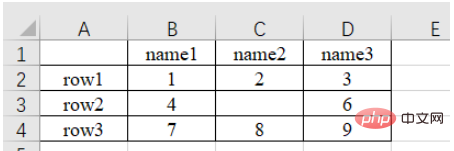
a)读取第n个Sheet(子表,在左下方可以查看或增删子表)的数据
import pandas as pd # 每次都需要修改的路径 path = "test.xlsx" # sheet_name默认为0,即读取第一个sheet的数据 sheet = pd.read_excel(path, sheet_name=0) print(sheet) """ Unnamed: 0 name1 name2 name3 0 row1 1 2.0 3 1 row2 4 NaN 6 2 row3 7 8.0 9 """
可以注意到,原始表格左上角没有填入内容,读取的结果是“Unnamed: 0” ,这是由于read_excel函数会默认把表格的第一行为列索引名。另外,对于行索引名来说,默认从第二行开始编号(因为默认第一行是列索引名,所以默认第一行不是数据),如果不特意指定,则自动从0开始编号,如下。
sheet = pd.read_excel(path) # 查看列索引名,返回列表形式 print(sheet.columns.values) # 查看行索引名,默认从第二行开始编号,如果不特意指定,则自动从0开始编号,返回列表形式 print(sheet.index.values) """ ['Unnamed: 0' 'name1' 'name2' 'name3'] [0 1 2] """
b)列索引名还可以自定义,如下:
sheet = pd.read_excel(path, names=['col1', 'col2', 'col3', 'col4']) print(sheet) # 查看列索引名,返回列表形式 print(sheet.columns.values) """ col1 col2 col3 col4 0 row1 1 2.0 3 1 row2 4 NaN 6 2 row3 7 8.0 9 ['col1' 'col2' 'col3' 'col4'] """
c)也可以指定第n列为行索引名,如下:
# 指定第一列为行索引
sheet = pd.read_excel(path, index_col=0)
print(sheet)
"""
name1 name2 name3
row1 1 2.0 3
row2 4 NaN 6
row3 7 8.0 9
"""d)读取时跳过第n行的数据
# 跳过第2行的数据(第一行索引为0) sheet = pd.read_excel(path, skiprows=[1]) print(sheet) """ Unnamed: 0 name1 name2 name3 0 row2 4 NaN 6 1 row3 7 8.0 9 """
2、获取表格的数据大小:shape
path = "test.xlsx"
# 指定第一列为行索引
sheet = pd.read_excel(path, index_col=0)
print(sheet)
print('==========================')
print('shape of sheet:', sheet.shape)
"""
name1 name2 name3
row1 1 2.0 3
row2 4 NaN 6
row3 7 8.0 9
==========================
shape of sheet: (3, 3)
"""3、索引数据的方法:[ ] / loc[] / iloc[]
1、直接加方括号索引
可以使用方括号加列名的方式 [col_name] 来提取某列的数据,然后再用方括号加索引数字 [index] 来索引这列的具体位置的值。这里索引名为name1的列,然后打印位于该列第1行(索引是1)位置的数据:4,如下:
sheet = pd.read_excel(path) # 读取列名为 name1 的列数据 col = sheet['name1'] print(col) # 打印该列第二个数据 print(col[1]) # 4 """ 0 1 1 4 2 7 Name: name1, dtype: int64 4 """
2、iloc方法,按整数编号索引
使用 sheet.iloc[ ] 索引,方括号内为行列的整数位置编号(除去作为行索引的那一列和作为列索引的哪一行后,从 0 开始编号)。
a)sheet.iloc[1, 2] :提取第2行第3列数据。第一个是行索引,第二个是列索引
b)sheet.iloc[0: 2] :提取前两行数据
c)sheet.iloc[0:2, 0:2] :通过分片的方式提取 前两行 的 前两列 数据
# 指定第一列数据为行索引
sheet = pd.read_excel(path, index_col=0)
# 读取第2行(row2)的第3列(6)数据
# 第一个是行索引,第二个是列索引
data = sheet.iloc[1, 2]
print(data) # 6
print('================================')
# 通过分片的方式提取 前两行 数据
data_slice = sheet.iloc[0:2]
print(data_slice)
print('================================')
# 通过分片的方式提取 前两行 的 前两列 数据
data_slice = sheet.iloc[0:2, 0:2]
print(data_slice)
"""
6
================================
name1 name2 name3
row1 1 2.0 3
row2 4 NaN 6
================================
name1 name2
row1 1 2.0
row2 4 NaN
"""3、loc方法,按行列名称索引
使用 sheet.loc[ ] 索引,方括号内为行列的名称字符串。具体使用方式同 iloc ,只是把 iloc 的整数索引替换成了行列的名称索引。这种索引方式用起来更直观。
注意:iloc[1: 2] 是不包含2的,但是 loc['row1': 'row2'] 是包含 'row2' 的。
# 指定第一列数据为行索引
sheet = pd.read_excel(path, index_col=0)
# 读取第2行(row2)的第3列(6)数据
# 第一个是行索引,第二个是列索引
data = sheet.loc['row2', 'name3']
print(data) # 1
print('================================')
# 通过分片的方式提取 前两行 数据
data_slice = sheet.loc['row1': 'row2']
print(data_slice)
print('================================')
# 通过分片的方式提取 前两行 的 前两列 数据
data_slice1 = sheet.loc['row1': 'row2', 'name1': 'name2']
print(data_slice1)
"""
6
================================
name1 name2 name3
row1 1 2.0 3
row2 4 NaN 6
================================
name1 name2
row1 1 2.0
row2 4 NaN
"""4、判断数据为空:np.isnan() / pd.isnull()
1、使用 numpy 库的 isnan() 或 pandas 库的 isnull() 方法判断是否等于 nan 。
sheet = pd.read_excel(path) # 读取列名为 name1 的列数据 col = sheet['name2'] print(np.isnan(col[1])) # True print(pd.isnull(col[1])) # True """ True True """
2、使用 str() 转为字符串,判断是否等于 'nan' 。
sheet = pd.read_excel(path)
# 读取列名为 name1 的列数据
col = sheet['name2']
print(col)
# 打印该列第二个数据
if str(col[1]) == 'nan':
print('col[1] is nan')
"""
0 2.0
1 NaN
2 8.0
Name: name2, dtype: float64
col[1] is nan
"""5、查找符合条件的数据
下面的代码意会一下吧
# 提取name1 == 1 的行
mask = (sheet['name1'] == 1)
x = sheet.loc[mask]
print(x)
"""
name1 name2 name3
row1 1 2.0 3
"""6、修改元素值:replace()
sheet['name2'].replace(2, 100, inplace=True) :把 name2 列的元素 2 改为元素 100,原位操作。
sheet['name2'].replace(2, 100, inplace=True)
print(sheet)
"""
name1 name2 name3
row1 1 100.0 3
row2 4 NaN 6
row3 7 8.0 9
"""sheet['name2'].replace(np.nan, 100, inplace=True) :把 name2 列的空元素(nan)改为元素 100,原位操作。
import numpy as np
sheet['name2'].replace(np.nan, 100, inplace=True)
print(sheet)
print(type(sheet.loc['row2', 'name2']))
"""
name1 name2 name3
row1 1 2.0 3
row2 4 100.0 6
row3 7 8.0 9
"""7、增加数据:[ ]
增加列,直接使用中括号 [ 要添加的名字 ] 添加。
sheet['name_add'] = [55, 66, 77] :添加名为 name_add 的列,值为[55, 66, 77]
path = "test.xlsx"
# 指定第一列为行索引
sheet = pd.read_excel(path, index_col=0)
print(sheet)
print('====================================')
# 添加名为 name_add 的列,值为[55, 66, 77]
sheet['name_add'] = [55, 66, 77]
print(sheet)
"""
name1 name2 name3
row1 1 2.0 3
row2 4 NaN 6
row3 7 8.0 9
====================================
name1 name2 name3 name_add
row1 1 2.0 3 55
row2 4 NaN 6 66
row3 7 8.0 9 77
"""8、删除数据:del() / drop()
a)del(sheet['name3']) :使用 del 方法删除
sheet = pd.read_excel(path, index_col=0)
# 使用 del 方法删除 'name3' 的列
del(sheet['name3'])
print(sheet)
"""
name1 name2
row1 1 2.0
row2 4 NaN
row3 7 8.0
"""b)sheet.drop('row1', axis=0)
使用 drop 方法删除 row1 行,删除列的话对应的 axis=1。
当 inplace 参数为 True 时,不会返回参数,直接在原数据上删除
当 inplace 参数为 False (默认)时不会修改原数据,而是返回修改后的数据
sheet.drop('row1', axis=0, inplace=True)
print(sheet)
"""
name1 name2 name3
row2 4 NaN 6
row3 7 8.0 9
"""c)sheet.drop(labels=['name1', 'name2'], axis=1)
使用 label=[ ] 参数可以删除多行或多列
# 删除多列,默认 inplace 参数位 False,即会返回结果
print(sheet.drop(labels=['name1', 'name2'], axis=1))
"""
name3
row1 3
row2 6
row3 9
"""9、保存到excel文件:to_excel()
1、把 pandas 格式的数据另存为 .xlsx 文件
names = ['a', 'b', 'c'] scores = [99, 100, 99] result_excel = pd.DataFrame() result_excel["姓名"] = names result_excel["评分"] = scores # 写入excel result_excel.to_excel('test3.xlsx')
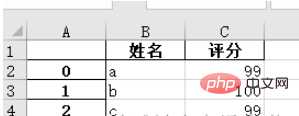
2、把改好的 excel 文件另存为 .xlsx 文件。
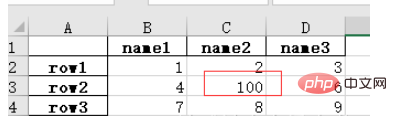
比如修改原表格中的 nan 为 100 后,保存文件:
import numpy as np # 指定第一列为行索引 sheet = pd.read_excel(path, index_col=0) sheet['name2'].replace(np.nan, 100, inplace=True) sheet.to_excel('test2.xlsx')
打开 test2.xlsx 结果如下:
以上是如何用Python的Pandas库处理Excel数据?的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 Python:编译器还是解释器?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python:编译器还是解释器?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AMPython是解释型语言,但也包含编译过程。1)Python代码先编译成字节码。2)字节码由Python虚拟机解释执行。3)这种混合机制使Python既灵活又高效,但执行速度不如完全编译型语言。
 python用于循环与循环时:何时使用哪个?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
python用于循环与循环时:何时使用哪个?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMuseeAforloopWheniteratingOveraseQuenceOrforAspecificnumberoftimes; useAwhiLeLoopWhenconTinuingUntilAcIntiment.ForloopSareIdeAlforkNownsences,而WhileLeleLeleLeleLoopSituationSituationSituationsItuationSuationSituationswithUndEtermentersitations。
 Python循环:最常见的错误May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Python循环:最常见的错误May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMpythonloopscanleadtoerrorslikeinfiniteloops,modifyingListsDuringteritation,逐个偏置,零indexingissues,andnestedloopineflinefficiencies
 对于循环和python中的循环时:每个循环的优点是什么?May 13, 2025 am 12:01 AM
对于循环和python中的循环时:每个循环的优点是什么?May 13, 2025 am 12:01 AMforloopsareadvantageousforknowniterations and sequests,供应模拟性和可读性;而LileLoopSareIdealFordyNamicConcitionSandunknowniterations,提供ControloperRoverTermination.1)forloopsareperfectForeTectForeTerToratingOrtratingRiteratingOrtratingRitterlistlistslists,callings conspass,calplace,cal,ofstrings ofstrings,orstrings,orstrings,orstrings ofcces
 Python:深入研究汇编和解释May 12, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python:深入研究汇编和解释May 12, 2025 am 12:14 AMpythonisehybridmodelofcompilationand interpretation:1)thepythoninterspretercompilesourcececodeintoplatform- interpententbybytecode.2)thepytythonvirtualmachine(pvm)thenexecuteCutestestestesteSteSteSteSteSteSthisByTecode,BelancingEaseofuseWithPerformance。
 Python是一种解释或编译语言,为什么重要?May 12, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python是一种解释或编译语言,为什么重要?May 12, 2025 am 12:09 AMpythonisbothinterpretedAndCompiled.1)它的compiledTobyTecodeForportabilityAcrosplatforms.2)bytecodeisthenInterpreted,允许fordingfordforderynamictynamictymictymictymictyandrapiddefupment,尽管Ititmaybeslowerthananeflowerthanancompiledcompiledlanguages。
 对于python中的循环时循环与循环:解释了关键差异May 12, 2025 am 12:08 AM
对于python中的循环时循环与循环:解释了关键差异May 12, 2025 am 12:08 AM在您的知识之际,而foroopsareideal insinAdvance中,而WhileLoopSareBetterForsituations则youneedtoloopuntilaconditionismet
 循环时:实用指南May 12, 2025 am 12:07 AM
循环时:实用指南May 12, 2025 am 12:07 AMForboopSareSusedwhenthentheneMberofiterationsiskNownInAdvance,而WhileLoopSareSareDestrationsDepportonAcondition.1)ForloopSareIdealForiteratingOverSequencesLikelistSorarrays.2)whileLeleLooleSuitableApeableableableableableableforscenarioscenarioswhereTheLeTheLeTheLeTeLoopContinusunuesuntilaspecificiccificcificCondond


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

EditPlus 中文破解版
体积小,语法高亮,不支持代码提示功能

PhpStorm Mac 版本
最新(2018.2.1 )专业的PHP集成开发工具

SublimeText3 Linux新版
SublimeText3 Linux最新版

WebStorm Mac版
好用的JavaScript开发工具

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境






