golang怎么实现文件监控
- 青灯夜游原创
- 2023-02-20 10:15:374953浏览
在golang中,可以利用fsnotify来实现文件监控。fsnotify是go语言跨平台文件系统监控工具,实现了一个基于channel的、跨平台的实时监听接口;golang通过fsnotify可监控文件,并通过文件变化重启程序。

本教程操作环境:windows10系统、GO 1.18版本、Dell G3电脑。
在golang中,可以利用fsnotify来实现文件监控。
golang 通过fsnotify监控文件,并通过文件变化重启程序。
go语言跨平台文件系统监控工具 — fsnotify
在 linux 内核中,Inotify 是一种用于通知用户空间程序文件系统变化的机制。它监控文件系统的变化,如文件新建、修改、删除等,并可以将相应的事件通知给应用程序。
Inotify 既可以监控文件,也可以监控目录。当监控目录时,它可以同时监控目录及目录中的各子目录及文件。Golang 的标准库 syscall 实现了该机制。
为了进一步扩展和抽象, github.com/fsnotify/fsnotify 包实现了一个基于 channel 的、跨平台的实时监听接口。
fsnotify工具的使用
一、下载我们需要的包
go get github.com/fsnotify/fsnotify
二、使用fsnotify监控文件
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 |
|
监控文件fsnotify3.go代码如下:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 |
|
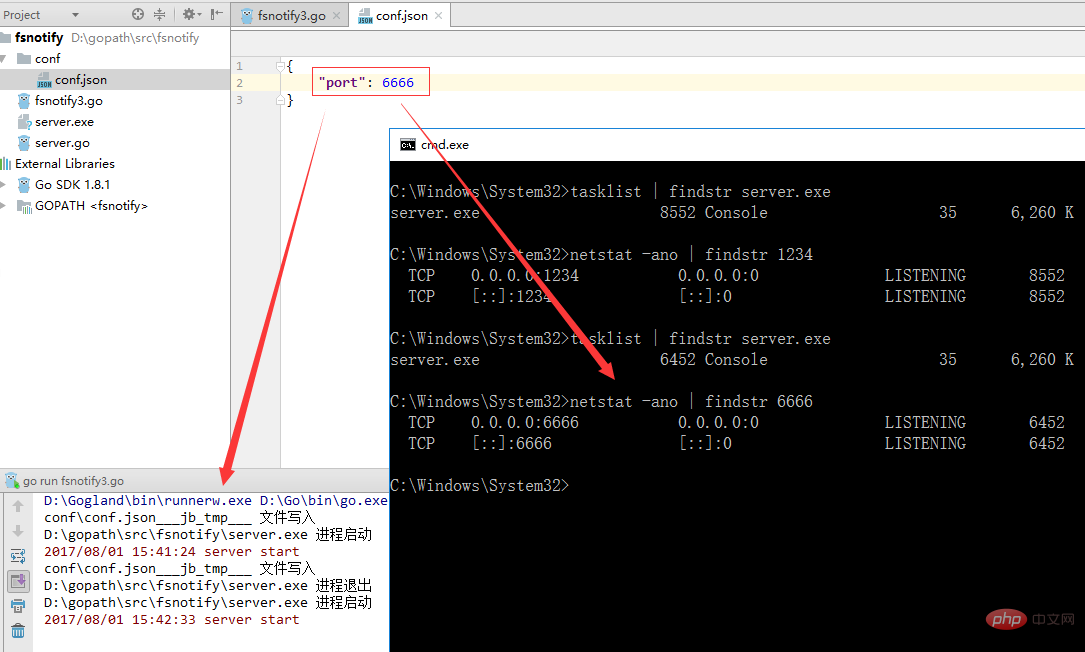
我们运行fsnotify3.go文件来监控我们的配置文件
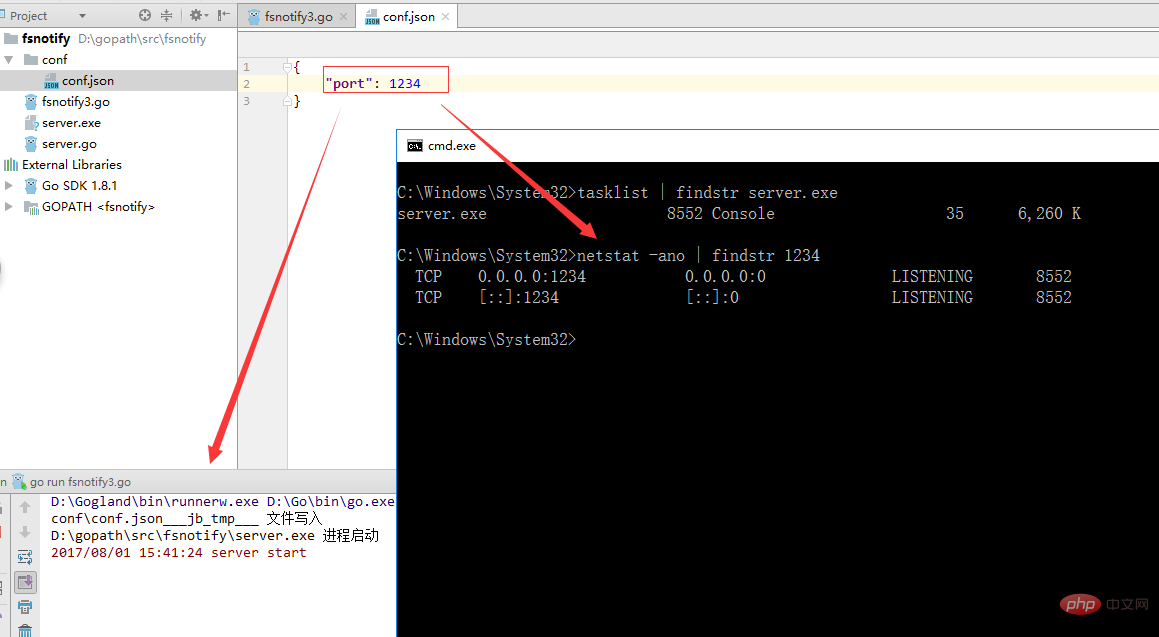
通过上面的图可以看到,当我们修改配置文件中的端口号时,会先kill掉进程,然后再启动一个进程。
推荐学习:Golang教程
以上是golang怎么实现文件监控的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

