
最近看 Vue 相关的知识点,看到 KeepAlive 组件时比较好奇它是怎么做到组件间切换时不重新渲染的,于是便稍微深入的了解了一下。(学习视频分享:vue视频教程)
如果你也有兴趣想要了解一下具体内部怎么实现的或者说有一定的了解但是不够熟悉,那么正好你也可以一起巩固下
Tips: 这样面试的时候你就可以大声的问别人这个知识点了?。
KeepAlive 是什么
53f0c36d9619adcda0d52683f186ae16 是一个内置组件,它的功能是在多个组件间动态切换时缓存被移除的组件实例。
KeepAlive 功能
KeepAlive 一词借鉴于 HTTP 协议,在 HTTP 协议里面 KeepAlive 又称持久连接,作用是允许多个请求/响应共用同一个 HTTP 连接,解决了频繁的销毁和创建 HTTP 连接带来的额外性能开销。而同理 Vue 里的 KeepAlive 组件也是为了避免一个组件被频繁的销毁/重建,避免了性能上的开销。
// App.vue <Test :msg="curTab" v-if="curTab === 'Test'"></Test> <HelloWorld :msg="curTab" v-if="curTab === 'HelloWorld'"></HelloWorld> <div @click="toggle">toggle</div>
上述代码可以看到,如果我们频繁点击 toggle 时会频繁的渲染 Test/HelloWorld 组件,当用户频繁的点击时 Test 组件需要频繁的销毁/渲染,这就造成很大的渲染性能损失。
所以为了解决这种性能开销,你需要知道是时候使用 KeepAlive 组件。
<KeepAlive> <component :is="curTab === 'Test' ? Test : HelloWorld" :msg="curTab"></component> </KeepAlive> <div @click="toggle">toggle</div>
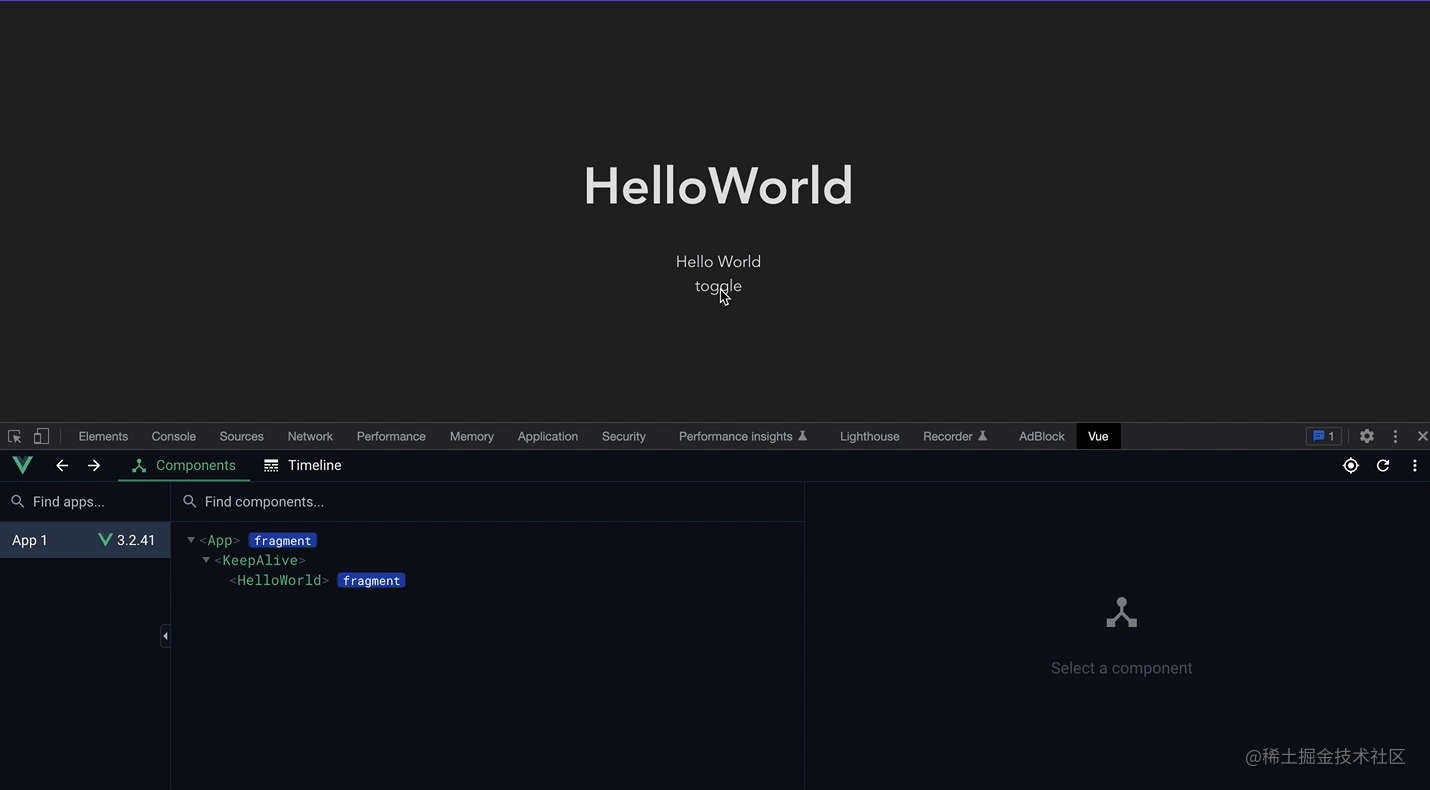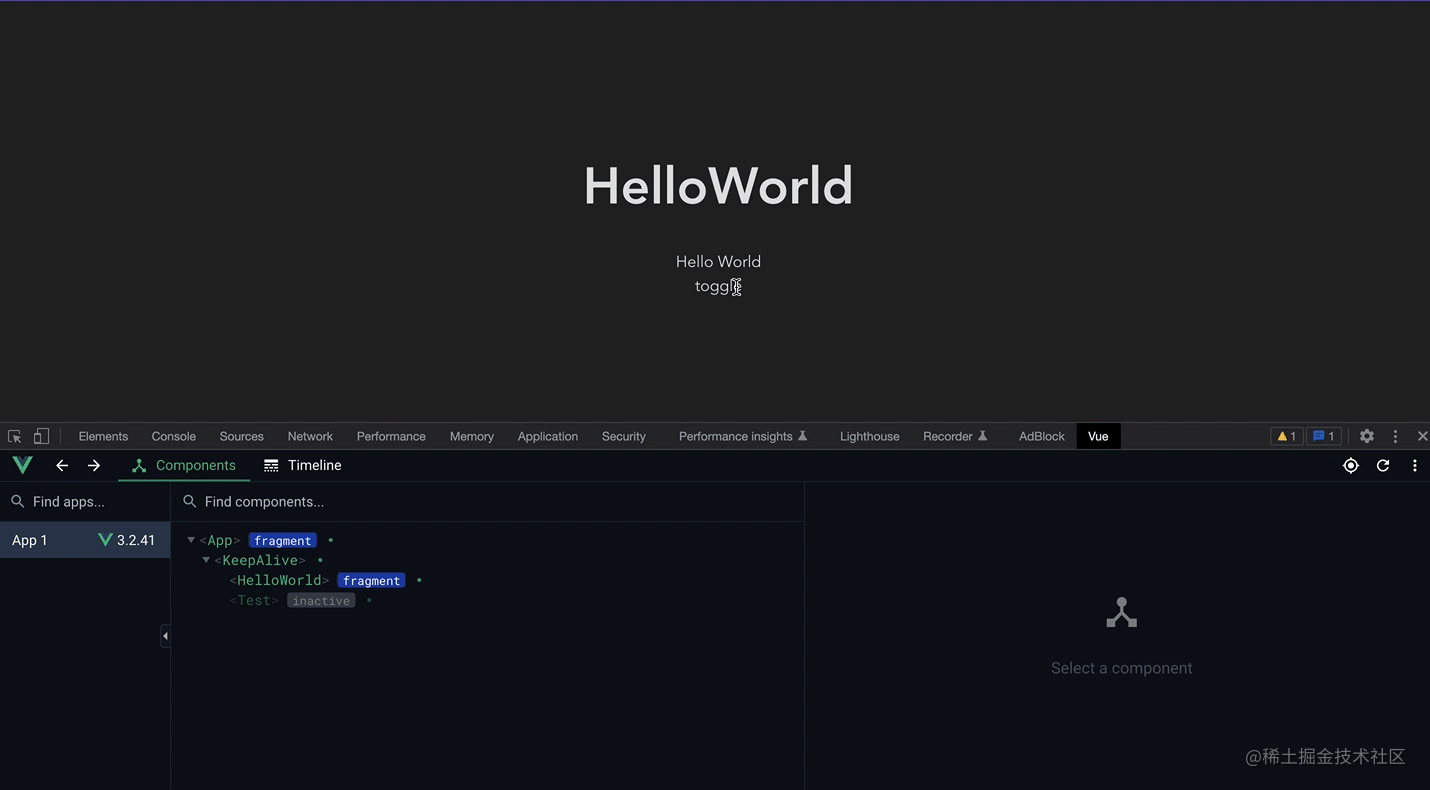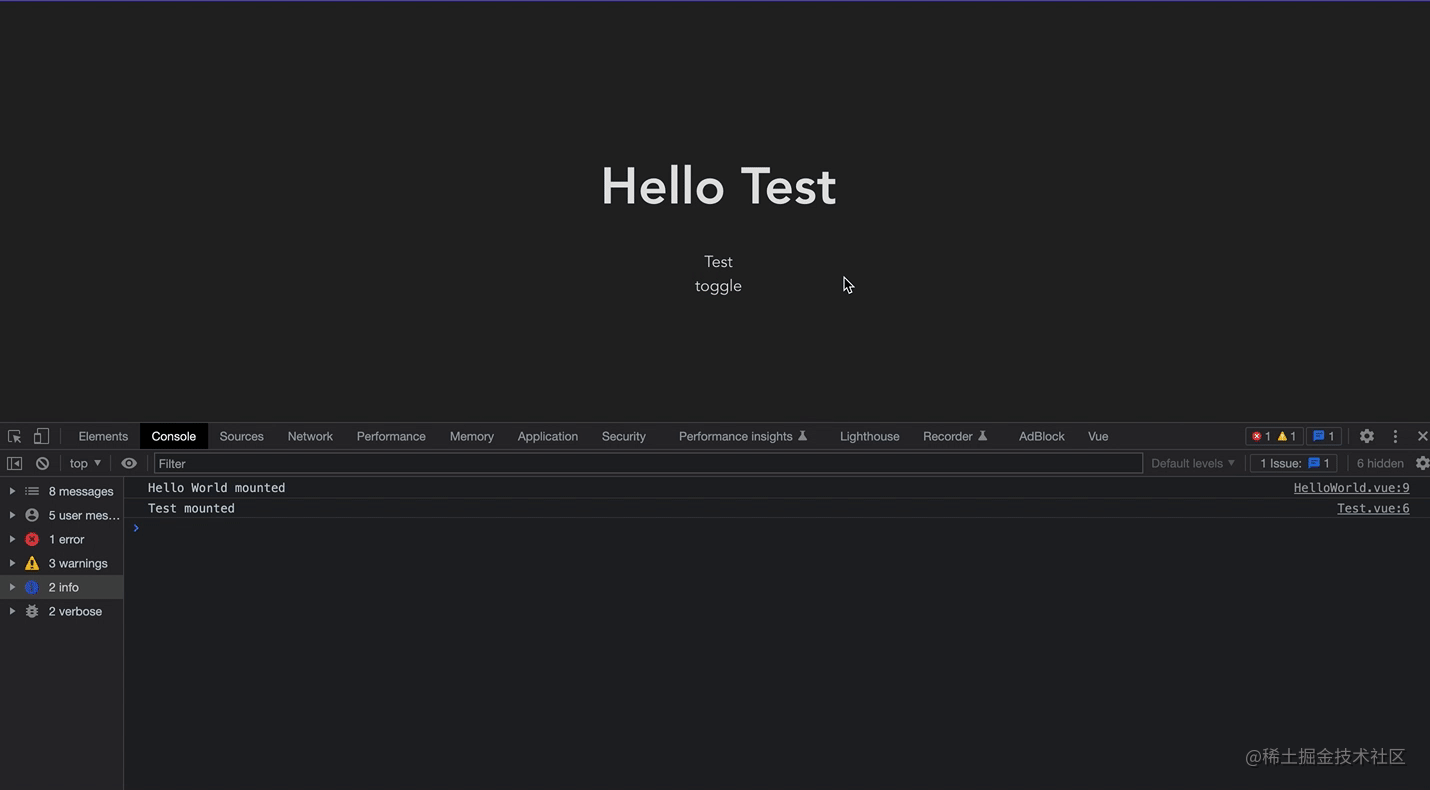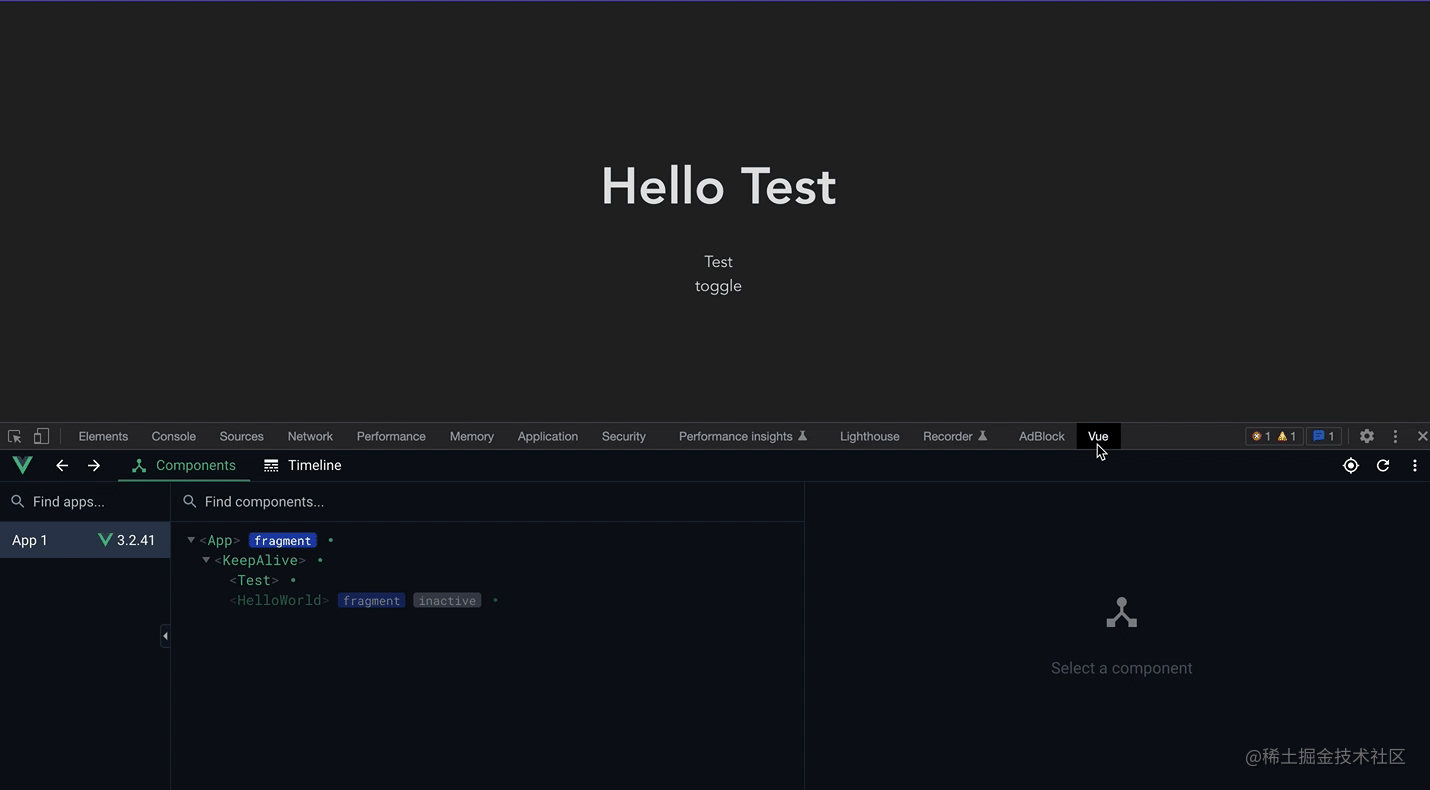
可以看这个录屏,在首次加载后再次频繁的切换并没有重新销毁与挂载,而仅仅是将组件进行了失活(而不是销毁),渲染时只需要重新激活就可以,而不需重新挂载,如果要渲染的组件很大,那就能有不错的性能优化。
想要体验的话可以去看看这个例子?官方demo,其中数据会被缓存这个也需要在开发使用中去注意到的
如何实现
实现原理其实很简单,其实就是缓存管理和特定的销毁和渲染逻辑,使得它不同于其他组件。
KeepAlive 组件在卸载组件时并不能真的将其卸载,而是将其放到一个隐藏的容器里面,当被激活时再从隐藏的容器中拿出来挂载到真正的 dom 上就行,这也就对应了 KeepAlive 的两个独特的生命周期activated和deactivated。
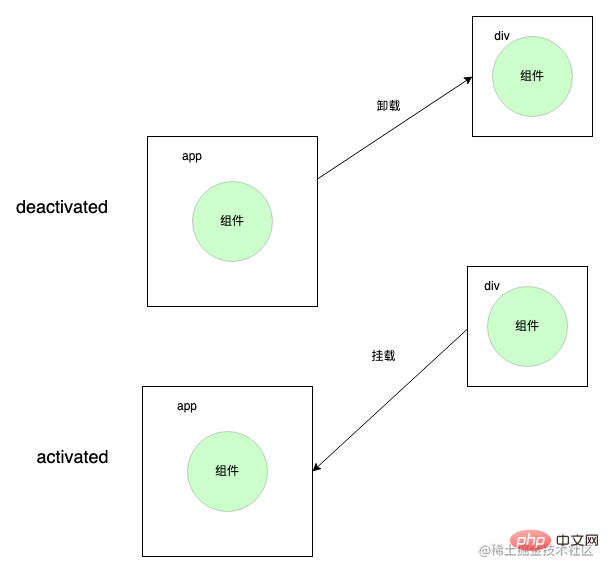
先来简单了解下组件的挂载过程
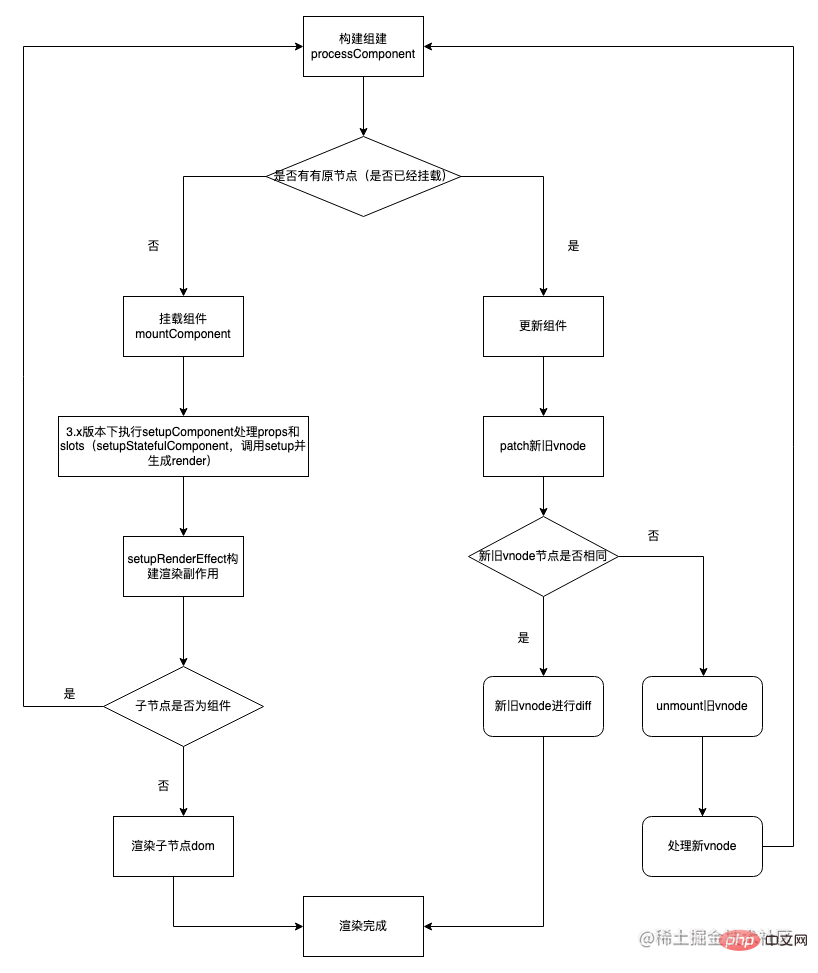 所以在 KeepAlive 内的子组件在 mount 和 unmount 的时候会执行特定的渲染逻辑,从而不会去走挂载和销毁逻辑
所以在 KeepAlive 内的子组件在 mount 和 unmount 的时候会执行特定的渲染逻辑,从而不会去走挂载和销毁逻辑
具体实现(实现一个小而简单的 KeepAlive)
KeepAlive 组件的属性
const KeepAliveImpl: ComponentOptions = {
name: "KeepAlive",
// 标识这是一个 KeepAlive 组件
__isKeepAlive: true,
// props
props: {
exclude: [String, Array, RegExp],
include: [String, Array, RegExp],
max: [String, Number]
}
}
// isKeepAlive
export const isKeepAlive = (vnode: VNode): boolean =>
(vnode.type as any).__isKeepAliveKeepAlive 组件的 setup 逻辑以及渲染逻辑(重点看)
// setup 接着上面的代码
// 获取到当前 KeepAlive 组件实例
const instance = getCurrentInstance()! as any;
// 拿到 ctx
const sharedContext = instance.ctx as KeepAliveContext;
// cache 缓存
// key: vnode.key | vnode.type value: vnode
const cache: Cache = new Map()
// 需要拿到某些的 renderer 操作函数,需要自己特定执行渲染和卸载逻辑
const { renderer: { p: patch, m: move, um: _unmount, o: { createElement } } } = sharedContext
// 隐藏的容器,用来存储需要隐藏的 dom
const storeageContainer = createElement('div')
// 存储当前的子组件的缓存 key
let pendingKey: CacheKey | null = null
sharedContext.activate = (vnode, container, anchor) => {
// KeepAlive 下组件激活时执行的 move 逻辑
move(vnode, container, anchor, 0 /* ENTER */)
}
sharedContext.deactivate = (vnode) => {
// KeepAlive 下组件失活时执行的 move 逻辑
move(vnode, storeageContainer, null, 1 /* LEAVE */)
}
return () => {
// 没有子组件
if (!slots.default) {
return null;
}
const children = slots.default() as VNode[];
const rawNode = children[0];
let vnode = rawNode;
const comp = vnode.type as ConcreteComponent;
const name = comp.displayName || comp.name
const { include, exclude } = props;
// 没有命中的情况
if (
(include && (!name || !matches(include, name))) ||
(exclude && name && matches(exclude, name))
) {
// 直接渲染子组件
return rawNode;
}
// 获取子组件的 vnode key
const key = vnode.key == null ? comp : vnode.key;
// 获取子组件缓存的 vnode
const cachedVNode = cache.get(key);
pendingKey = key;
// 命中缓存
if (cachedVNode) {
vnode.el = cachedVNode.el;
// 继承组件实例
vnode.component = cachedVNode.component;
// 在 vnode 上更新 shapeFlag,标记为 COMPONENT_KEPT_ALIVE 属性,防止渲染器重新挂载
vnode.shapeFlag |= ShapeFlags.COMPONENT_KEPT_ALIVE
} else {
// 没命中将其缓存
cache.set(pendingKey, vnode)
}
// 在 vnode 上更新 shapeFlag,标记为 COMPONENT_SHOULD_KEEP_ALIVE 属性,防止渲染器将组件卸载了
vnode.shapeFlag |= ShapeFlags.COMPONENT_SHOULD_KEEP_ALIVE
// 渲染组件 vnode
return vnode;
}KeepAlive组件 mount 时挂载 renderer 到 ctx 上
在 KeepAlive 组件内会从 sharedContext 上的 renderer 上拿到一些方法比如 move、createElement 等
function mountComponent() {
// ...
if (isKeepAlive(initialVNode)) {
;(instance.ctx as KeepAliveContext).renderer = internals
}
}子组件执行特定的销毁和渲染逻辑
首先从上面可以看到,在渲染 KeepAlive 组件时会对其子组件的 vnode 上增加对应的 shapeFlag 标志
比如COMPONENT_KEPT_ALIVE标志,组件挂载的时候告诉渲染器这个不需要 mount 而需要特殊处理
const processComponent = (
n1: VNode | null,
n2: VNode,
container: RendererElement,
anchor: RendererNode | null,
) => {
if (n1 == null) {
// 在 KeepAlive 组件渲染时会对子组件增加 COMPONENT_KEPT_ALIVE 标志
// 挂载子组件时会判断是否 COMPONENT_KEPT_ALIVE ,如果是不会调用 mountComponent 而是直接执行 activate 方法
if (n2.shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.COMPONENT_KEPT_ALIVE) {
;(parentComponent!.ctx as KeepAliveContext).activate(
n2,
container,
anchor
)
}
// ...
}
}同理COMPONENT_SHOULD_KEEP_ALIVE标志也是用来在组件卸载的时候告诉渲染器这个不需要 unmount 而需要特殊处理。
const unmount: UnmountFn = (vnode) => {
// ...
// 在 KeepAlive 组件渲染时会对子组件增加 COMPONENT_SHOULD_KEEP_ALIVE 标志
// 然后在子组件卸载时并不会真实的卸载而是调用 KeepAlive 的 deactivate 方法
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.COMPONENT_SHOULD_KEEP_ALIVE) {
;(parentComponent!.ctx as KeepAliveContext).deactivate(vnode)
return
}
}如何挂载
activated和deactivated生命周期(生命周期相关可以不用重点看)
首先这两个生命周期是在 KeepAlive 组件内独特声明的,是直接导出使用的。
export function onActivated(
hook: Function,
target?: ComponentInternalInstance | null
) {
// 注册 activated 的回调函数到当前的 instance 的钩子函数上
registerKeepAliveHook(hook, LifecycleHooks.ACTIVATED, target)
}
export function onDeactivated(
hook: Function,
target?: ComponentInternalInstance | null
) {
// 注册 deactivated 的回调函数到当前的 instance 的钩子函数上
registerKeepAliveHook(hook, LifecycleHooks.DEACTIVATED, target)
}然后因为这两个生命周期会注册在 setup 里面,所以只要执行 setup 就会将两个生命周期的回调函数注册到当前的 instance 实例上
// renderer.ts
// mount 函数逻辑
const mountComponent = (initialVNode,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
optimized
) => {
// ...
const instance: ComponentInternalInstance =
compatMountInstance ||
(initialVNode.component = createComponentInstance(
initialVNode,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense
))
// 执行 setup
setupComponent(instance)
}
// setupcomponent 处理 setup 函数值
export function setupComponent(
instance: ComponentInternalInstance,
isSSR = false
) {
// ...
const isStateful = isStatefulComponent(instance)
// ...
const setupResult = isStateful
// setupStatefulComponent 函数主要功能是设置当前的 instance
? setupStatefulComponent(instance, isSSR)
: undefined
// ...
}
function setupStatefulComponent(
instance: ComponentInternalInstance
){
if (setup) {
//设置当前实例
setCurrentInstance(instance)
// 执行组件内 setup 函数,执行 onActivated 钩子函数进行回调函数收集
const setupResult = callWithErrorHandling(
setup,
instance,
ErrorCodes.SETUP_FUNCTION,
[__DEV__ ? shallowReadonly(instance.props) : instance.props, setupContext]
)
// currentInstance = null;
unsetCurrentInstance()
}
}最后在执行sharedContext.activate和sharedContext.deactivate的时候将注册在实例上的回调函数取出来直接执行就OK了,执行时机在 postRender 之后
sharedContext.activate = (vnode, container, anchor) => {
// KeepAlive 下组件激活时执行的 move 逻辑
move(vnode, container, anchor, 0 /* ENTER */)
// 把回调推入到 postFlush 的异步任务队列中去执行
queuePostRenderEffect(() => {
if (instance.a) {
// a是 activated 钩子的简称
invokeArrayFns(instance.a)
}
})
}
sharedContext.activate = (vnode, container, anchor) => {
// KeepAlive 下组件失活时执行的 move 逻辑
move(vnode, container, anchor, 0 /* ENTER */)
queuePostRenderEffect(() => {
if (instance.da) {
// da是 deactivated 钩子的简称
invokeArrayFns(instance.da)
}
})
}
export const enum LifecycleHooks {
// ... 其他生命周期声明
DEACTIVATED = 'da',
ACTIVATED = 'a',
}
export interface ComponentInternalInstance {
// ... 其他生命周期
[LifecycleHooks.ACTIVATED]: Function[]
[LifecycleHooks.DEACTIVATED]: Function[]
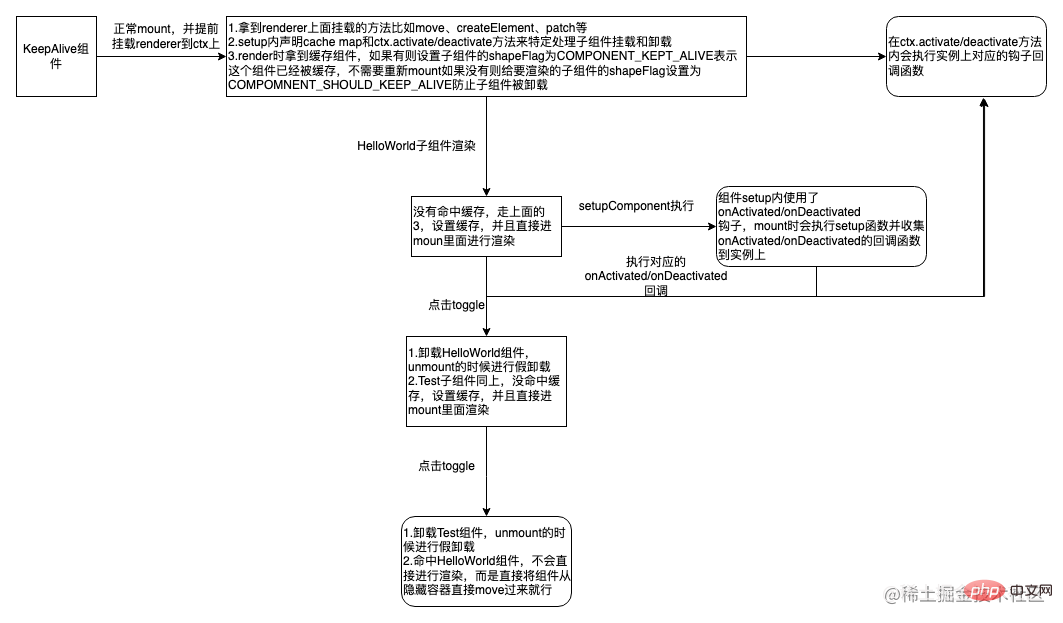
}以下是关于上述demo如何实现的简化流程图
需要注意的知识点
1、什么时候缓存
KeepAlive 组件的onMounted和onUpdated生命周期时进行缓存
2、什么时候取消缓存
缓存数量超过设置的 max 时
- 监听 include 和 exclude 修改的时候,会读取缓存中的知进行判断是否需要清除缓存
修剪缓存的时候也要 unmount(如果该缓存不是当前组件)或者 resetShapeFlag 将标志为从 KeepAlive 相关 shapeFlag 状态重置为 STATEFUL_COMPONENT 状态(如果该缓存是当前组件,但是被exclude了),当然 unmount 函数内包含 resetShapeFlag 操作
3、缓存策略
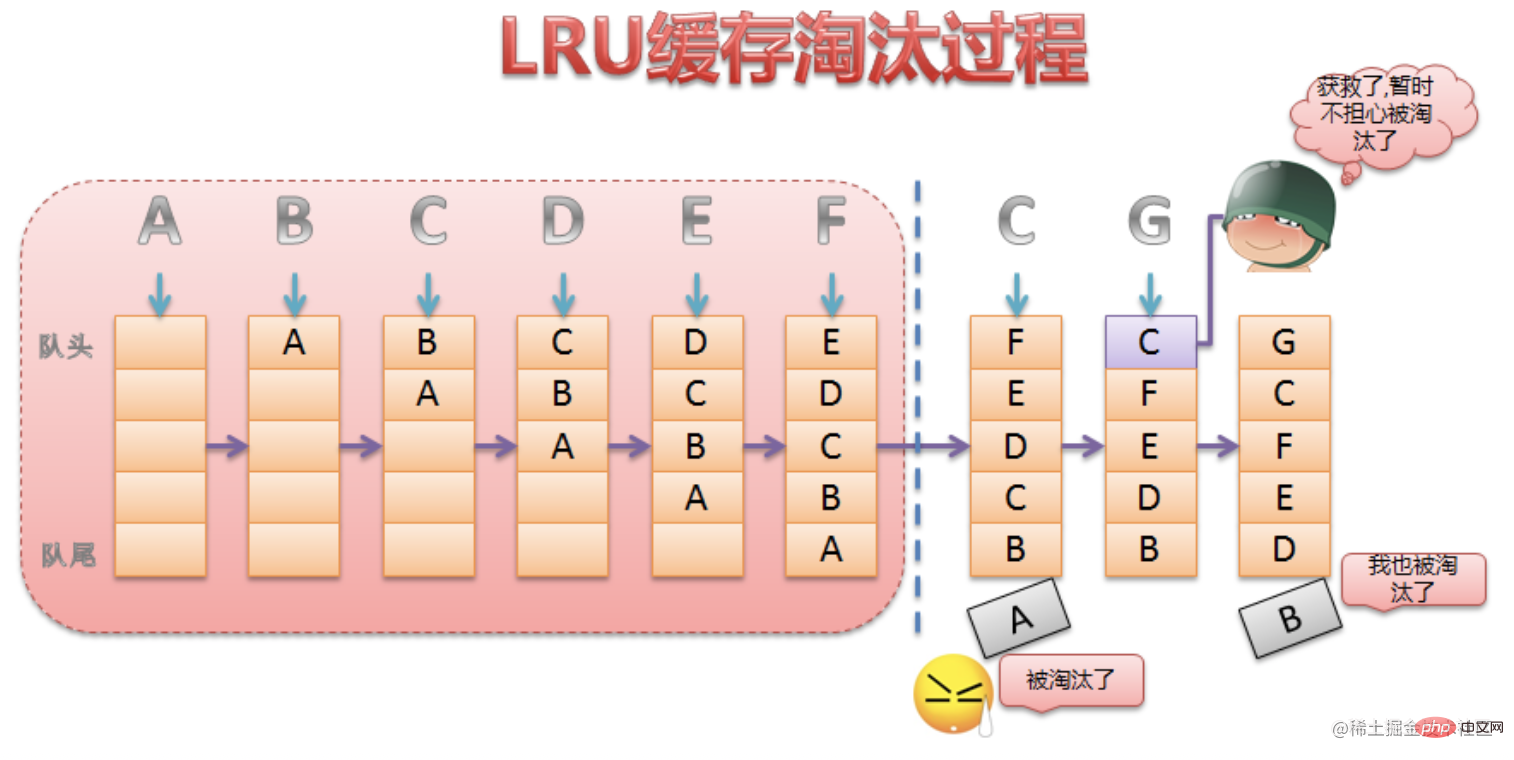
KeepAlive 组件的缓存策略是 LRU(last recently used)缓存策略
核心思想在于需要把当前访问或渲染的组件作为最新一次渲染的组件,并且该组件在缓存修剪过程中始终是安全的,即不会被修剪。
看下面的图更加直观,图片来源一篇讲keepAlive 缓存优化的文章
4、如何添加到 vue devtools 组件树上
sharedContext.activate = (vnode, container, anchor) => {
// instance 是子组件实例
const instance = vnode.component!
// ...
// dev环境下设置, 自己模拟写的
devtools.emit('component:added', instance.appContext.app, instance.uid, instance.parent ? instance.parent.uid: undefined, instance)
// 官方添加
if (__DEV__ || __FEATURE_PROD_DEVTOOLS__) {
// Update components tree
devtoolsComponentAdded(instance)
}
}
// 同理 sharedContext.deactivates 上也要添加,不然不会显示在组件树上5、缓存的子组件 props 更新处理
当子组件有 prop 更新时是需要重新去 patch 的,所以在 activate 的时候需要重新执行 patch 进行子组件更新
sharedContext.activate = (vnode, container, anchor) => {
// ...
// props 改变需要重新 patch(update)
patch(
instance.vnode,
vnode,
container,
anchor,
instance,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
vnode.slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
}以上是一文聊聊Vue中的KeepAlive组件的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 vue.js和React:了解关键差异Apr 10, 2025 am 09:26 AM
vue.js和React:了解关键差异Apr 10, 2025 am 09:26 AMVue.js适合小型到中型项目,而React更适用于大型、复杂应用。1.Vue.js的响应式系统通过依赖追踪自动更新DOM,易于管理数据变化。2.React采用单向数据流,数据从父组件流向子组件,提供明确的数据流向和易于调试的结构。
 vue.js vs.反应:特定于项目的考虑因素Apr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AM
vue.js vs.反应:特定于项目的考虑因素Apr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AMVue.js适合中小型项目和快速迭代,React适用于大型复杂应用。1)Vue.js易于上手,适用于团队经验不足或项目规模较小的情况。2)React的生态系统更丰富,适合有高性能需求和复杂功能需求的项目。
 vue怎么a标签跳转Apr 08, 2025 am 09:24 AM
vue怎么a标签跳转Apr 08, 2025 am 09:24 AM实现 Vue 中 a 标签跳转的方法包括:HTML 模板中使用 a 标签指定 href 属性。使用 Vue 路由的 router-link 组件。使用 JavaScript 的 this.$router.push() 方法。可通过 query 参数传递参数,并在 router 选项中配置路由以进行动态跳转。
 vue怎么实现组件跳转Apr 08, 2025 am 09:21 AM
vue怎么实现组件跳转Apr 08, 2025 am 09:21 AMVue 中实现组件跳转有以下方法:使用 router-link 和 <router-view> 组件进行超链接跳转,指定 :to 属性为目标路径。直接使用 <router-view> 组件显示当前路由渲染的组件。使用 router.push() 和 router.replace() 方法进行程序化导航,前者保存历史记录,后者替换当前路由不留记录。
 vue的div怎么跳转Apr 08, 2025 am 09:18 AM
vue的div怎么跳转Apr 08, 2025 am 09:18 AMVue 中 div 元素跳转的方法有两种:使用 Vue Router,添加 router-link 组件。添加 @click 事件监听器,调用 this.$router.push() 方法跳转。
 vue引入方式怎么跳转Apr 08, 2025 am 09:12 AM
vue引入方式怎么跳转Apr 08, 2025 am 09:12 AMVue.js提供了三种跳转方式:原生 JavaScript API:使用 window.location.href 进行跳转。Vue Router:使用 <router-link> 标签或 this.$router.push() 方法进行跳转。VueX:通过 dispatch action 或 commit mutation 来触发路由跳转。
 vue怎么设置跳转页面Apr 08, 2025 am 09:09 AM
vue怎么设置跳转页面Apr 08, 2025 am 09:09 AM在 Vue 中设置页面跳转有多种方法,包括:使用 router-link 组件创建可点击链接。使用 router.push() 方法手动添加新路由到历史记录堆栈。使用 router.replace() 方法替换当前路由。直接使用 location.href 重定向到新页面。


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

SecLists
SecLists是最终安全测试人员的伙伴。它是一个包含各种类型列表的集合,这些列表在安全评估过程中经常使用,都在一个地方。SecLists通过方便地提供安全测试人员可能需要的所有列表,帮助提高安全测试的效率和生产力。列表类型包括用户名、密码、URL、模糊测试有效载荷、敏感数据模式、Web shell等等。测试人员只需将此存储库拉到新的测试机上,他就可以访问到所需的每种类型的列表。

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

Atom编辑器mac版下载
最流行的的开源编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用







