linux有内核级线程么
- 青灯夜游原创
- 2022-11-11 14:20:322639浏览
linux有内核级线程,linux支持内核级的多线程。Linux内核可以看作服务进程(管理软硬件资源,响应用户进程的各种进程);内核需要多个执行流并行,为了防止可能的阻塞,支持多线程。内核线程就是内核的一个分身,可以用以处理一件特定事情,内核线程的调度由内核负责,一个内核线程的处于阻塞状态时不影响其他的内核线程。

本教程操作环境:linux7.3系统、Dell G3电脑。
线程通常被定义为一个进程中代码的不同执行路线。从实现方式上划分,线程有两种类型:“用户级线程”和“内核级线程”。
用户线程指不需要内核支持而在用户程序中实现的线程,其不依赖于操作系统核心,应用进程利用线程库提供创建、同步、调度和管理线程的函数来控制用户线程。这种线程甚至在象 DOS 这样的操作系统中也可实现,但线程的调度需要用户程序完成,这有些类似 Windows 3.x 的协作式多任务。
另外一种则需要内核的参与,由内核完成线程的调度。其依赖于操作系统核心,由内核的内部需求进行创建和撤销,这两种模型各有其好处和缺点。
用户线程不需要额外的内核开支,并且用户态线程的实现方式可以被定制或修改以适应特殊应用的要求,但是当一个线程因 I/O 而处于等待状态时,整个进程就会被调度程序切换为等待状态,其他线程得不到运行的机会;而内核线程则没有各个限制,有利于发挥多处理器的并发优势,但却占用了更多的系统开支。
Windows NT和OS/2支持内核线程。Linux 支持内核级的多线程。
linux中的内核级线
1.内核线程概述
Linux内核可以看作服务进程(管理软硬件资源,响应用户进程的各种进程)
内核需要多个执行流并行,为了防止可能的阻塞,支持多线程。
内核线程就是内核的一个分身,可以用以处理一件特定事情,内核线程的调度由内核负责,一个内核线程的处于阻塞状态时不影响其他的内核线程。
内核线程是直接由内核本身启动的进程。内核线程实际上是将内核函数委托给独立的进程执行,它与内核中的其他“进程”并行执行。内核线程经常被称之为内核守护进程。当前的内核中,内核线程就负责下面的工作:
- 周期性地将修改的内存页与页来源块设备同步
- 实现文件系统的事务日志
内核线程由内核创建,所以内核线程在内核态执行,只能访问内核虚拟地址空间,不能访问用户空间。
在linux所有的线程都当作进程来实现,也没有单独为线程定义调度算法以及数据结构,一个进程相当于包含一个线程,就是自身,多线程,原本的线程称为主线程,他们一起构成线程组。
进程拥有自己的地址空间,所以每个进程都有自己的页表,而线程却没有,只能和其它线程共享主线程的地址空间和页表
2.三个数据结构
每个进程或线程由三个重要的数据结构,分别是struct thread_info, struct task_struct 和内核栈。
thread_info对象存放的进程/线程的基本信息,它和进程/线程的内核栈存放在内核空间里的一段2倍页长空间中。其中thread_info结构存放在地址段的末尾,其余空间作为内核栈。内核使用伙伴系统分配这段空间。
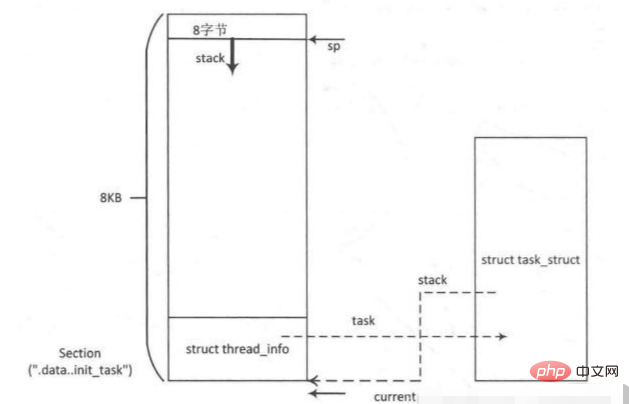
struct thread_info {
int preempt_count; /* 0 => preemptable, <0 => bug */
struct task_struct *task; /* main task structure */
__u32 cpu; /* cpu */};thread_info结构体中有一个struct task_struct *task,task指向该线程或者进程的task_struct对象,task_struct也叫做任务描述符:
struct task_struct {
pid_t pid;
pid_t tgid;
void *stack;
struct mm_struct *mm, *active_mm;
/* filesystem information */
struct fs_struct *fs;
/* open file information */
struct files_struct *files;};#define task_thread_info(task) ((struct thread_info *)(task)->stack)- stack:是指向进程或者线程的thread_info
- mm:对象用来管理该进程/线程的页表以及虚拟内存区
- active_mm:主要用于内核线程访问主内核页全局目录
- pid:每个task_struct都会有一个不同的id,就是pid
- tgid:线程组领头线程的PID,就是主线程的pid
linux系统上虚拟地址空间分为两个部分:供用户态程序访问的虚拟地址空间和供内核访问的内核空间。每当内核执行上下文切换时,虚拟地址空间的用户层部分都会切换,以便匹配运行的进程,内核空间的部分是不会切换的。
3.内核线程创建
在内核版本linux-3.x以后,内核线程的创建被延后执行,并且交给名为kthreadd 2号线程执行创建过程,但是kthreadd本身是怎么创建的呢?过程如下:
pid_t kernel_thread(int (*fn)(void *), void *arg, unsigned long flags)
{
return do_fork(flags|CLONE_VM|CLONE_UNTRACED, (unsigned long)fn,
(unsigned long)arg, NULL, NULL);
}
pid = kernel_thread(kthreadd, NULL, CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES);kthreadadd本身最终是通过do_fork实现的,do_fork通过传入不同的参数,可以分别用于创建用户态进程/线程,内核线程等。当kthreadadd被创建以后,内核线程的创建交给它实现。
内核线程的创建分为创建和启动两个部分,kthread_run作为统一的接口,可以同时实现,这两个功能:
#define kthread_run(threadfn, data, namefmt, ...) \
({ \
struct task_struct *__k \
= kthread_create(threadfn, data, namefmt, ## __VA_ARGS__); \
if (!IS_ERR(__k)) \
wake_up_process(__k); \
__k; \
})
#define kthread_create(threadfn, data, namefmt, arg...) \
kthread_create_on_node(threadfn, data, -1, namefmt, ##arg)
struct task_struct *kthread_create_on_node(int (*threadfn)(void *data),
void *data, int node,
const char namefmt[],
...)
{
DECLARE_COMPLETION_ONSTACK(done);
struct task_struct *task;
/*分配kthread_create_info空间*/
struct kthread_create_info *create = kmalloc(sizeof(*create),
GFP_KERNEL);
if (!create)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
create->threadfn = threadfn;
create->data = data;
create->node = node;
create->done = &done;
/*加入到kthread_creta_list列表中,等待ktherad_add中断线程去创建改线程*/
spin_lock(&kthread_create_lock);
list_add_tail(&create->list, &kthread_create_list);
spin_unlock(&kthread_create_lock);
wake_up_process(kthreadd_task);
/*
* Wait for completion in killable state, for I might be chosen by
* the OOM killer while kthreadd is trying to allocate memory for
* new kernel thread.
*/
if (unlikely(wait_for_completion_killable(&done))) {
/*
* If I was SIGKILLed before kthreadd (or new kernel thread)
* calls complete(), leave the cleanup of this structure to
* that thread.
*/
if (xchg(&create->done, NULL))
return ERR_PTR(-EINTR);
/*
* kthreadd (or new kernel thread) will call complete()
* shortly.
*/
wait_for_completion(&done);
}
task = create->result;
.
.
.
kfree(create);
return task;
}kthread_create_on_node函数中:
- 首先利用kmalloc分配kthread_create_info变量create,利用函数参数初始化create
- 将create加入kthread_create_list链表中,然后唤醒kthreadd内核线程创建当前线程
- 唤醒kthreadd后,利用completion等待内核线程创建完成,completion完成后,释放create空间
下面来看下kthreadd的处理过程:
int kthreadd(void *unused)
{
struct task_struct *tsk = current;
/* Setup a clean context for our children to inherit. */
set_task_comm(tsk, "kthreadd");
ignore_signals(tsk);
set_cpus_allowed_ptr(tsk, cpu_all_mask);
set_mems_allowed(node_states[N_MEMORY]);
current->flags |= PF_NOFREEZE;
for (;;) {
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
if (list_empty(&kthread_create_list))
schedule();
__set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
spin_lock(&kthread_create_lock);
while (!list_empty(&kthread_create_list)) {
struct kthread_create_info *create;
create = list_entry(kthread_create_list.next,
struct kthread_create_info, list);
list_del_init(&create->list);
spin_unlock(&kthread_create_lock);
create_kthread(create);
spin_lock(&kthread_create_lock);
}
spin_unlock(&kthread_create_lock);
}
return 0;
}kthreadd利用for(;;)一直驻留在内存中运行:主要过程如下:
- 检查kthread_create_list为空时,kthreadd让出cpu的执行权
- kthread_create_list不为空时,利用while循环遍历kthread_create_list链表
- 每取下一个链表节点后调用create_kthread,创建内核线程
static void create_kthread(struct kthread_create_info *create)
{
int pid;
/* We want our own signal handler (we take no signals by default). */
pid = kernel_thread(kthread, create, CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES | SIGCHLD);
if (pid < 0) {
/* If user was SIGKILLed, I release the structure. */
struct completion *done = xchg(&create->done, NULL);
if (!done) {
kfree(create);
return;
}
create->result = ERR_PTR(pid);
complete(done);
}
}可以看到内核线程的创建最终还是和kthreadd一样,调用kernel_thread实现。
static int kthread(void *_create)
{
.
.
.
.
/* If user was SIGKILLed, I release the structure. */
done = xchg(&create->done, NULL);
if (!done) {
kfree(create);
do_exit(-EINTR);
}
/* OK, tell user we're spawned, wait for stop or wakeup */
__set_current_state(TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE);
create->result = current;
complete(done);
schedule();
ret = -EINTR;
if (!test_bit(KTHREAD_SHOULD_STOP, &self.flags)) {
__kthread_parkme(&self);
ret = threadfn(data);
}
/* we can't just return, we must preserve "self" on stack */
do_exit(ret);
}kthread以struct kthread_create_info 类型的create为参数,create中带有创建内核线程的回调函数,以及函数的参数。kthread中,完成completion信号量的处理,然后schedule让出cpu的执行权,等待下次返回 时,执行回调函数threadfn(data)。
4.内核线程的退出
线程一旦启动起来后,会一直运行,除非该线程主动调用do_exit函数,或者其他的进程调用kthread_stop函数,结束线程的运行。
int kthread_stop(struct task_struct *k)
{
struct kthread *kthread;
int ret;
trace_sched_kthread_stop(k);
get_task_struct(k);
kthread = to_live_kthread(k);
if (kthread) {
set_bit(KTHREAD_SHOULD_STOP, &kthread->flags);
__kthread_unpark(k, kthread);
wake_up_process(k);
wait_for_completion(&kthread->exited);
}
ret = k->exit_code;
put_task_struct(k);
trace_sched_kthread_stop_ret(ret);
return ret;
}如果线程函数正在处理一个非常重要的任务,它不会被中断的。当然如果线程函数永远不返回并且不检查信号,它将永远都不会停止。在执行kthread_stop的时候,目标线程必须没有退出,否则会Oops。所以在创建thread_func时,可以采用以下形式:
thread_func()
{
// do your work here
// wait to exit
while(!thread_could_stop())
{
wait();
}
}
exit_code()
{
kthread_stop(_task); //发信号给task,通知其可以退出了
}如果线程中在等待某个条件满足才能继续运行,所以只有满足了条件以后,才能调用kthread_stop杀掉内核线程。
5.内核线程使用
#include "test_kthread.h"
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
static struct task_struct *test_thread = NULL;
unsigned int time_conut = 5;
int test_thread_fun(void *data)
{
int times = 0;
while(!kthread_should_stop())
{
printk("\n printk %u\r\n", times);
times++;
msleep_interruptible(time_conut*1000);
}
printk("\n test_thread_fun exit success\r\n\n");
return 0;
}
void register_test_thread(void)
{
test_thread = kthread_run(test_thread_fun , NULL, "test_kthread" );
if (IS_ERR(test_thread)){
printk(KERN_INFO "create test_thread failed!\n");
}
else {
printk(KERN_INFO "create test_thread ok!\n");
}
}
static ssize_t kthread_debug_start(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
register_test_thread();
return 0;
}
static ssize_t kthread_debug_stop(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
kthread_stop(test_thread);
return 0;
}
static DEVICE_ATTR(kthread_start, S_IRUSR, kthread_debug_start,NULL);
static DEVICE_ATTR(kthread_stop, S_IRUSR, kthread_debug_stop,NULL);
struct attribute * kthread_group_info_attrs[] =
{
&dev_attr_kthread_start.attr,
&dev_attr_kthread_stop.attr,
NULL,
};
struct attribute_group kthread_group =
{
.name = "kthread",
.attrs = kthread_group_info_attrs,
};
相关推荐:《Linux视频教程》
以上是linux有内核级线程么的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

