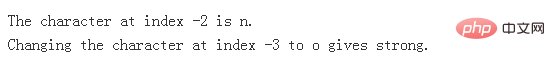php字符串有哪几种定义方式
- 青灯夜游原创
- 2022-06-30 19:06:034564浏览
有4种定义方式:1、用单引号包裹字符,语法“'字符内容'”;2、用双引号包裹字符,语法“"字符内容"”;3、用heredoc结构,语法“a816c5f037e8c22aaff6b1429c85e43c 结构是用来声明大段的不用解析的文本类似,nowdoc 结构也有相同的特征。
一个 nowdoc 结构也用和 heredocs 结构一样的标记 <<<, 但是跟在后面的标识符要用单引号括起来,即 <<<'EOT'。Heredoc 结构的所有规则也同样适用于 nowdoc 结构,尤其是结束标识符的规则。
示例:
<?php echo <<<'EOD' Example of string spanning multiple lines using nowdoc syntax. Backslashes are always treated literally, e.g. \\ and \'. EOD;
<?php /* 含有变量的更复杂的示例 */ class foo { public $foo; public $bar; function __construct() { $this->foo = 'Foo'; $this->bar = array('Bar1', 'Bar2', 'Bar3'); } } $foo = new foo(); $name = 'MyName'; echo <<<'EOT' My name is "$name". I am printing some $foo->foo. Now, I am printing some {$foo->bar[1]}. This should not print a capital 'A': \x41 EOT; ?>
注意:
Nowdoc 结构是在 PHP 5.3.0 中加入的。
扩展知识:变量解析
当字符串用双引号或 heredoc 结构定义时,其中的变量将会被解析。
这里共有两种语法规则:一种简单规则,一种复杂规则。简单的语法规则是最常用和最方便的,它可以用最少的代码在一个 string 中嵌入一个变量,一个 array 的值,或一个 object 的属性。
复杂规则语法的显著标记是用花括号包围的表达式。
简单语法
当 PHP 解析器遇到一个美元符号($)时,它会和其它很多解析器一样,去组合尽量多的标识以形成一个合法的变量名。可以用花括号来明确变量名的界线。
<?php $juice = "apple"; echo "He drank some $juice juice.".PHP_EOL; // Invalid. "s" is a valid character for a variable name, but the variable is $juice. echo "He drank some juice made of $juices."; // Valid. Explicitly specify the end of the variable name by enclosing it in braces: echo "He drank some juice made of ${juice}s."; ?>
类似的,一个 array 索引或一个 object 属性也可被解析。数组索引要用方括号(])来表示索引结束的边际,对象属性则是和上述的变量规则相同。
<?php $juices = array("apple", "orange", "koolaid1" => "purple"); echo "He drank some $juices[0] juice.".PHP_EOL; echo "He drank some $juices[1] juice.".PHP_EOL; echo "He drank some $juices[koolaid1] juice.".PHP_EOL; class people { public $john = "John Smith"; public $jane = "Jane Smith"; public $robert = "Robert Paulsen"; public $smith = "Smith"; } $people = new people(); echo "$people->john drank some $juices[0] juice.".PHP_EOL; echo "$people->john then said hello to $people->jane.".PHP_EOL; echo "$people->john's wife greeted $people->robert.".PHP_EOL; echo "$people->robert greeted the two $people->smiths."; // Won't work ?>
从 PHP 7.1.0 起,还支持负数字索引。
<?php $string = 'string'; echo "The character at index -2 is $string[-2].", PHP_EOL; $string[-3] = 'o'; echo "Changing the character at index -3 to o gives $string.", PHP_EOL; ?>
如果想要表达更复杂的结构,请用复杂语法。
复杂(花括号)语法
复杂语法不是因为其语法复杂而得名,而是因为它可以使用复杂的表达式。
任何具有 string 表达的标量变量,数组单元或对象属性都可使用此语法。 表达式的书写方式与在 string 以外的方式相同, 然后用花括号 { 和 } 把它括起来即可。由于 { 无法被转义,只有 $ 紧挨着 { 时才会被识别。可以用 {\$ 来表达 {$。下面的示例可以更好的解释:
<?php // 显示所有错误 error_reporting(E_ALL); $great = 'fantastic'; // 无效,输出: This is { fantastic} echo "This is { $great}"; // 有效,输出: This is fantastic echo "This is {$great}"; // 有效 echo "This square is {$square->width}00 centimeters broad."; // 有效,只有通过花括号语法才能正确解析带引号的键名 echo "This works: {$arr['key']}"; // 有效 echo "This works: {$arr[4][3]}"; // 这是错误的表达式,因为就象 $foo[bar] 的格式在字符串以外也是错的一样。 // 换句话说,只有在 PHP 能找到常量 foo 的前提下才会正常工作;这里会产生一个 // E_NOTICE (undefined constant) 级别的错误。 echo "This is wrong: {$arr[foo][3]}"; // 有效,当在字符串中使用多重数组时,一定要用括号将它括起来 echo "This works: {$arr['foo'][3]}"; // 有效 echo "This works: " . $arr['foo'][3]; echo "This works too: {$obj->values[3]->name}"; echo "This is the value of the var named $name: {${$name}}"; echo "This is the value of the var named by the return value of getName(): {${getName()}}"; echo "This is the value of the var named by the return value of \$object->getName(): {${$object->getName()}}"; // 无效,输出: This is the return value of getName(): {getName()} echo "This is the return value of getName(): {getName()}"; // 无效, 输出: C:\folder\{fantastic}.txt echo "C:\folder\{$great}.txt" // 有效, 输出: C:\folder\fantastic.txt echo "C:\\folder\\{$great}.txt" ?>也可以在字符串中用此语法通过变量来调用类的属性。
<?php class foo { var $bar = 'I am bar.'; } $foo = new foo(); $bar = 'bar'; $baz = array('foo', 'bar', 'baz', 'quux'); echo "{$foo->$bar}\n"; echo "{$foo->{$baz[1]}}\n"; ?>
注意:
函数、方法、静态类变量和类常量可使用 {$} ,在该字符串被定义的命名空间中将其值作为变量名来访问。只单一使用花括号 ({}) 无法处理从函数或方法的返回值或者类常量以及类静态变量的值。
推荐学习:《PHP视频教程》
以上是php字符串有哪几种定义方式的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!