怎么利用angular Material做统计表格?下面本篇文章给大家介绍一下用angular Material 做统计表格的方法,希望对大家有所帮助!

用angular Material 做统计表格
安装 Angular Material、组件开发工具 (CDK) 和 Angular 动画库,并运行代码原理图
ng add @angular/material
表格原理图将创建一个组件,它可以渲染出一个预置了可排序、可分页数据源的 Angular Material。【相关教程推荐:《angular教程》】
ng generate @angular/material:table texe1
然后在这的基础上进行修改。
该组件的html文件
<div class="mat-elevation-z8">
<table mat-table class="full-width-table" matSort aria-label="Elements">
<!-- Id Column -->
<ng-container matColumnDef="id">
<th mat-header-cell *matHeaderCellDef mat-sort-header>序号</th>
<td mat-cell *matCellDef="let row">{{row.id}}</td>
</ng-container>
<!-- Name Column -->
<ng-container matColumnDef="name">
<th mat-header-cell *matHeaderCellDef mat-sort-header> 岩土名</th>
<td mat-cell *matCellDef="let row">{{row.name}}</td>
</ng-container>
<!-- num1 Column -->
<ng-container matColumnDef="num1">
<th mat-header-cell *matHeaderCellDef mat-sort-header> 期望数量</th>
<td mat-cell *matCellDef="let row">{{row.num1}}</td>
</ng-container>
<!-- num2 Column -->
<ng-container matColumnDef="num2">
<th mat-header-cell *matHeaderCellDef mat-sort-header> 当前数量</th>
<td mat-cell *matCellDef="let row">{{row.num2}}</td>
</ng-container>
<tr mat-header-row *matHeaderRowDef="displayedColumns"></tr>
<tr mat-row *matRowDef="let row; columns: displayedColumns;"></tr>
</table>
<!-- 控制表格数据的显示长度 -->
<mat-paginator #paginator
[length]="dataSource?.data?.length"
[pageIndex]="0"
[pageSize]="10"
[pageSizeOptions]="[5, 10, 17]"
aria-label="Select page">
</mat-paginator>
</div>该组件的texe1-datasource.ts文件
import { DataSource } from '@angular/cdk/collections';
import { MatPaginator } from '@angular/material/paginator';
import { MatSort } from '@angular/material/sort';
import { map } from 'rxjs/operators';
import { Observable, of as observableOf, merge } from 'rxjs';
// TODO: Replace this with your own data model type
export interface Texe1Item {
name: string;
id: number;
num1: number;
num2: number;
}
// TODO: replace this with real data from your application
const EXAMPLE_DATA: Texe1Item[] = [
{id: 1, name: '粉质粘土', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 2, name: '淤泥质粉质粘土', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 3, name: '粘土', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 4, name: '粘质粉土', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 5, name: '淤泥质粘土', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 6, name: '圆砾(角砾)', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 7, name: '中砂', num1:1000, num2:1000,},
{id: 8, name: '有机质土', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 9, name: '泥炭质土A', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 10, name: '泥炭质土B', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 11, name: '砂质粉土', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 12, name: '粉砂', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 13, name: '细砂', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 14, name: '粗砂', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 15, name: '砾砂', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 16, name: '卵石(碎石)', num1:1000, num2:100,},
{id: 17, name: '漂石(块石)', num1:1000, num2:100,},
];
/**
* Data source for the Texe1 view. This class should
* encapsulate all logic for fetching and manipulating the displayed data
* (including sorting, pagination, and filtering).
*/
export class Texe1DataSource extends DataSource<Texe1Item> {
data: Texe1Item[] = EXAMPLE_DATA;
paginator: MatPaginator | undefined;
sort: MatSort | undefined;
constructor() {
super();
}
/**
* Connect this data source to the table. The table will only update when
* the returned stream emits new items.
* @returns A stream of the items to be rendered.
*/
connect(): Observable<Texe1Item[]> {
if (this.paginator && this.sort) {
// Combine everything that affects the rendered data into one update
// stream for the data-table to consume.
return merge(observableOf(this.data), this.paginator.page, this.sort.sortChange)
.pipe(map(() => {
return this.getPagedData(this.getSortedData([...this.data ]));
}));
} else {
throw Error('Please set the paginator and sort on the data source before connecting.');
}
}
/**
* Called when the table is being destroyed. Use this function, to clean up
* any open connections or free any held resources that were set up during connect.
*/
disconnect(): void {}
/**
* Paginate the data (client-side). If you're using server-side pagination,
* this would be replaced by requesting the appropriate data from the server.
*/
private getPagedData(data: Texe1Item[]): Texe1Item[] {
if (this.paginator) {
const startIndex = this.paginator.pageIndex * this.paginator.pageSize;
return data.splice(startIndex, this.paginator.pageSize);
} else {
return data;
}
}
/**
* Sort the data (client-side). If you're using server-side sorting,
* this would be replaced by requesting the appropriate data from the server.
*/
private getSortedData(data: Texe1Item[]): Texe1Item[] {
if (!this.sort || !this.sort.active || this.sort.direction === '') {
return data;
}
return data.sort((a, b) => {
const isAsc = this.sort?.direction === 'asc';
switch (this.sort?.active) {
case 'name': return compare(a.name, b.name, isAsc);
case 'id': return compare(+a.id, +b.id, isAsc);
default: return 0;
}
});
}
}
/** Simple sort comparator for example ID/Name columns (for client-side sorting). */
function compare(a: string | number, b: string | number, isAsc: boolean): number {
return (a < b ? -1 : 1) * (isAsc ? 1 : -1);
}该组件的texe1.component.ts文件
import { AfterViewInit, Component, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { MatPaginator } from '@angular/material/paginator';
import { MatSort } from '@angular/material/sort';
import { MatTable } from '@angular/material/table';
import { Texe1DataSource, Texe1Item } from './texe1-datasource';
@Component({
selector: 'app-texe1',
templateUrl: './texe1.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./texe1.component.css']
})
export class Texe1Component implements AfterViewInit {
@ViewChild(MatPaginator) paginator!: MatPaginator;
@ViewChild(MatSort) sort!: MatSort;
@ViewChild(MatTable) table!: MatTable<Texe1Item>;
dataSource: Texe1DataSource;
/** Columns displayed in the table. Columns IDs can be added, removed, or reordered. */
displayedColumns = ['id', 'name','num1','num2'];
constructor() {
this.dataSource = new Texe1DataSource();
}
ngAfterViewInit(): void {
this.dataSource.sort = this.sort;
this.dataSource.paginator = this.paginator;
this.table.dataSource = this.dataSource;
}
}最后再app.component.html文件中进行显示。
<app-texe1></app-texe1>
效果图: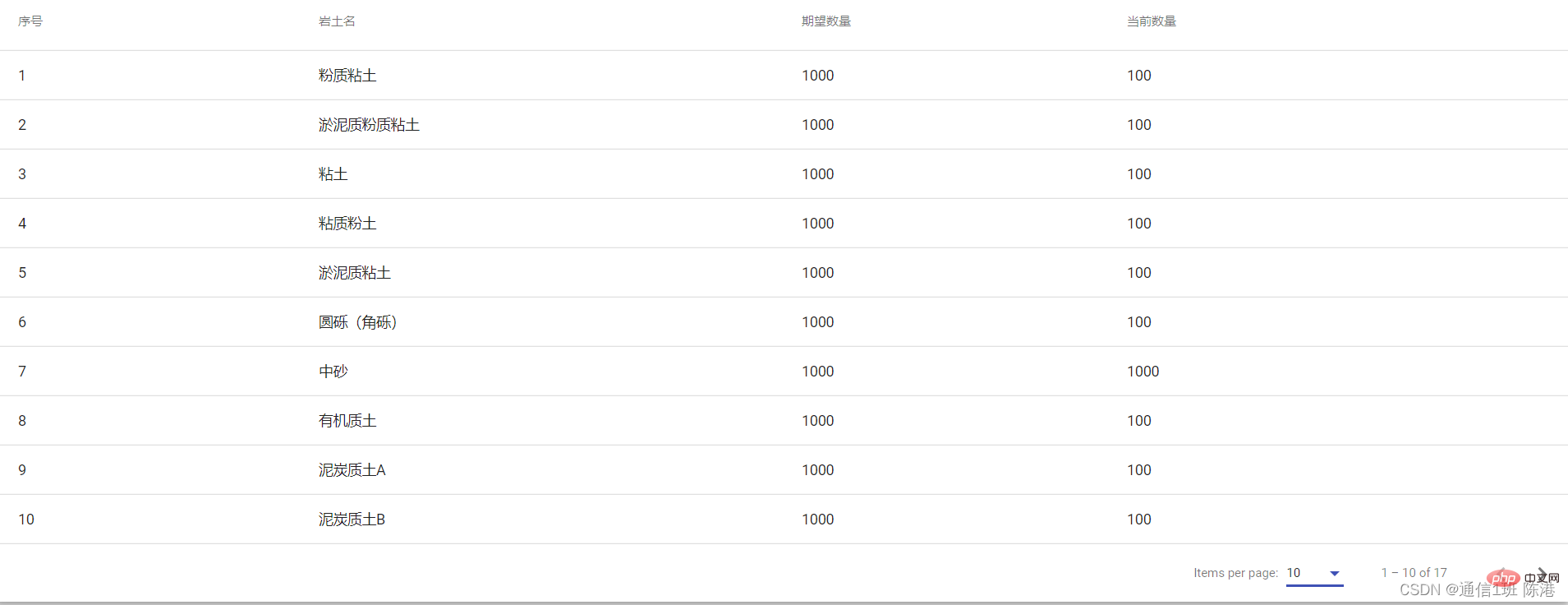
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程视频!!
以上是聊聊怎么利用angular Material做统计表格的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 JavaScript数据类型:浏览器和nodejs之间是否有区别?May 14, 2025 am 12:15 AM
JavaScript数据类型:浏览器和nodejs之间是否有区别?May 14, 2025 am 12:15 AMJavaScript核心数据类型在浏览器和Node.js中一致,但处理方式和额外类型有所不同。1)全局对象在浏览器中为window,在Node.js中为global。2)Node.js独有Buffer对象,用于处理二进制数据。3)性能和时间处理在两者间也有差异,需根据环境调整代码。
 JavaScript评论:使用//和 / * * / * / * /May 13, 2025 pm 03:49 PM
JavaScript评论:使用//和 / * * / * / * /May 13, 2025 pm 03:49 PMJavaScriptusestwotypesofcomments:single-line(//)andmulti-line(//).1)Use//forquicknotesorsingle-lineexplanations.2)Use//forlongerexplanationsorcommentingoutblocksofcode.Commentsshouldexplainthe'why',notthe'what',andbeplacedabovetherelevantcodeforclari
 Python vs. JavaScript:开发人员的比较分析May 09, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:开发人员的比较分析May 09, 2025 am 12:22 AMPython和JavaScript的主要区别在于类型系统和应用场景。1.Python使用动态类型,适合科学计算和数据分析。2.JavaScript采用弱类型,广泛用于前端和全栈开发。两者在异步编程和性能优化上各有优势,选择时应根据项目需求决定。
 Python vs. JavaScript:选择合适的工具May 08, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:选择合适的工具May 08, 2025 am 12:10 AM选择Python还是JavaScript取决于项目类型:1)数据科学和自动化任务选择Python;2)前端和全栈开发选择JavaScript。Python因其在数据处理和自动化方面的强大库而备受青睐,而JavaScript则因其在网页交互和全栈开发中的优势而不可或缺。
 Python和JavaScript:了解每个的优势May 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python和JavaScript:了解每个的优势May 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMPython和JavaScript各有优势,选择取决于项目需求和个人偏好。1.Python易学,语法简洁,适用于数据科学和后端开发,但执行速度较慢。2.JavaScript在前端开发中无处不在,异步编程能力强,Node.js使其适用于全栈开发,但语法可能复杂且易出错。
 JavaScript的核心:它是在C还是C上构建的?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript的核心:它是在C还是C上构建的?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AMjavascriptisnotbuiltoncorc; saninterpretedlanguagethatrunsonenginesoftenwritteninc.1)javascriptwasdesignedAsalightweight,解释edganguageforwebbrowsers.2)Enginesevolvedfromsimpleterterterpretpreterterterpretertestojitcompilerers,典型地提示。
 JavaScript应用程序:从前端到后端May 04, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript应用程序:从前端到后端May 04, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript可用于前端和后端开发。前端通过DOM操作增强用户体验,后端通过Node.js处理服务器任务。1.前端示例:改变网页文本内容。2.后端示例:创建Node.js服务器。
 Python vs. JavaScript:您应该学到哪种语言?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:您应该学到哪种语言?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM选择Python还是JavaScript应基于职业发展、学习曲线和生态系统:1)职业发展:Python适合数据科学和后端开发,JavaScript适合前端和全栈开发。2)学习曲线:Python语法简洁,适合初学者;JavaScript语法灵活。3)生态系统:Python有丰富的科学计算库,JavaScript有强大的前端框架。


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

Dreamweaver Mac版
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 英文版
推荐:为Win版本,支持代码提示!





