数据库系列更新到现在我想大家对所有的概念都已有个大概认识了,这周我在看评论的时候我发现有个网友的提问我觉得很有意思:如何设计一个索引?你们都是怎么设计索引的?怎么设计更高效?

前言
我们知道,索引是一个基于链表实现的树状Tree结构,能够快速的检索数据,目前几乎所RDBMS数据库都实现了索引特性,比如MySQL的B+Tree索引,MongoDB的BTree索引等。
在业务开发过程中,索引设计高效与否决定了接口对应SQL的执行效率,高效的索引可以降低接口的Response Time,同时还可以降低成本,我们要现实的目标是:索引设计->降低接口响应时间->降低服务器配置->降低成本,最终要落实到成本上来,因为老板最关心的是成本。
今天就跟大家聊聊MySQL中的索引以及如何设计索引,使用索引才能提降低接口的RT,提高用户体检。
MySQL中的索引
MySQL中的InnoDB引擎使用B+Tree结构来存储索引,可以尽量减少数据查询时磁盘IO次数,同时树的高度直接影响了查询的性能,一般树的高度维持在 3~4 层。
B+Tree由三部分组成:根root、枝branch以及Leaf叶子,其中root和branch不存储数据,只存储指针地址,数据全部存储在Leaf Node,同时Leaf Node之间用双向链表链接,结构如下:
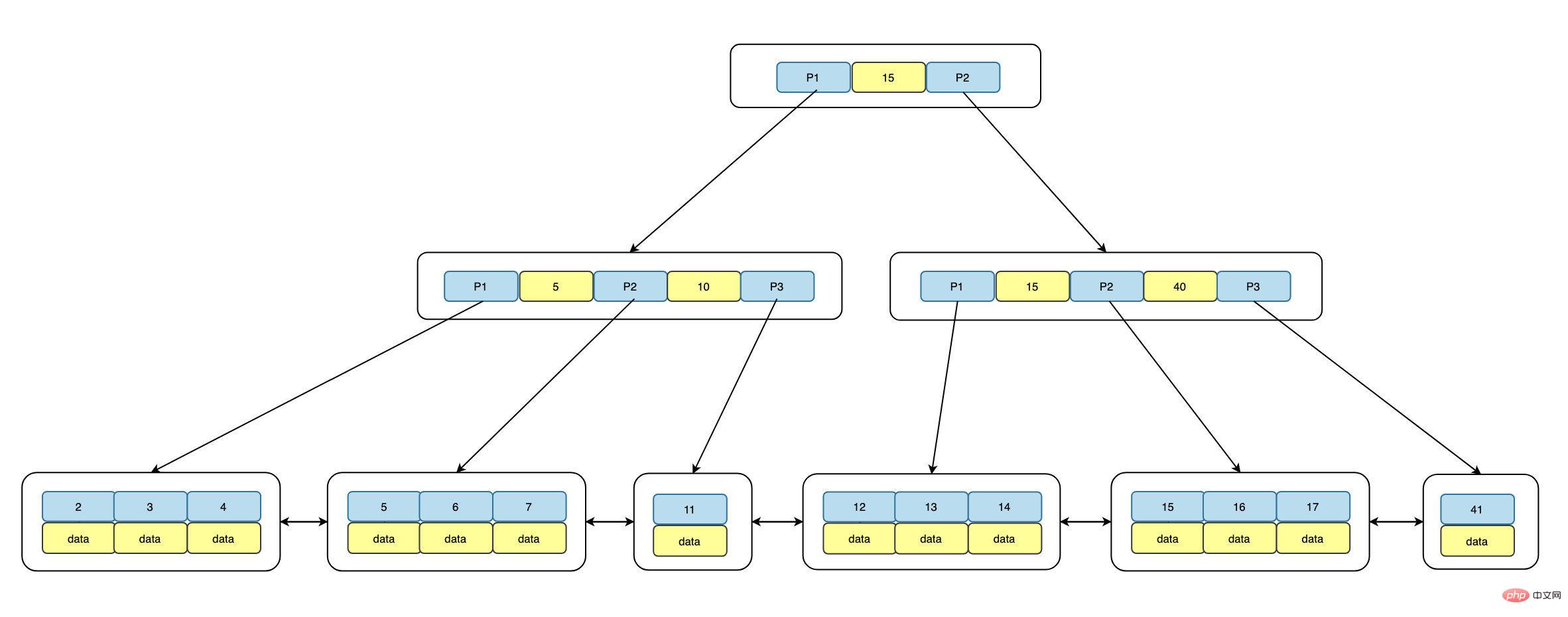
从上面可以看到,每个Leaf Node是三部分组成的,即前驱指针p_prev,数据data以及后继指针p_next,同时数据data是有序的,默认是升序ASC,分布在B+tree右边的键值总是大于左边的,同时从root到每个Leaf的距离是相等的,也就是访问任何一个Leaf Node需要的IO是一样的,即索引树的高度Level + 1次IO操作。
我们可以将MySQL中的索引可以看成一张小表,占用磁盘空间,创建索引的过程其实就是按照索引列排序的过程,先在sort_buffer_size进行排序,如果排序的数据量大,sort_buffer_size容量不下,就需要通过临时文件来排序,最重要的是通过索引可以避免排序操作(distinct,group by,order by)。
聚集索引
MySQL中的表是IOT(Index Organization Table,索引组织表),数据按照主键id顺序存储(逻辑上是连续,物理上不连续),而且主键id是聚集索引(clustered index),存储着整行数据,如果没有显示的指定主键,MySQL会将所有的列组合起来构造一个row_id作为primary key,例如表users(id, user_id, user_name, phone, primary key(id)),id是聚集索引,存储了id, user_id, user_name, phone整行的数据。
辅助索引
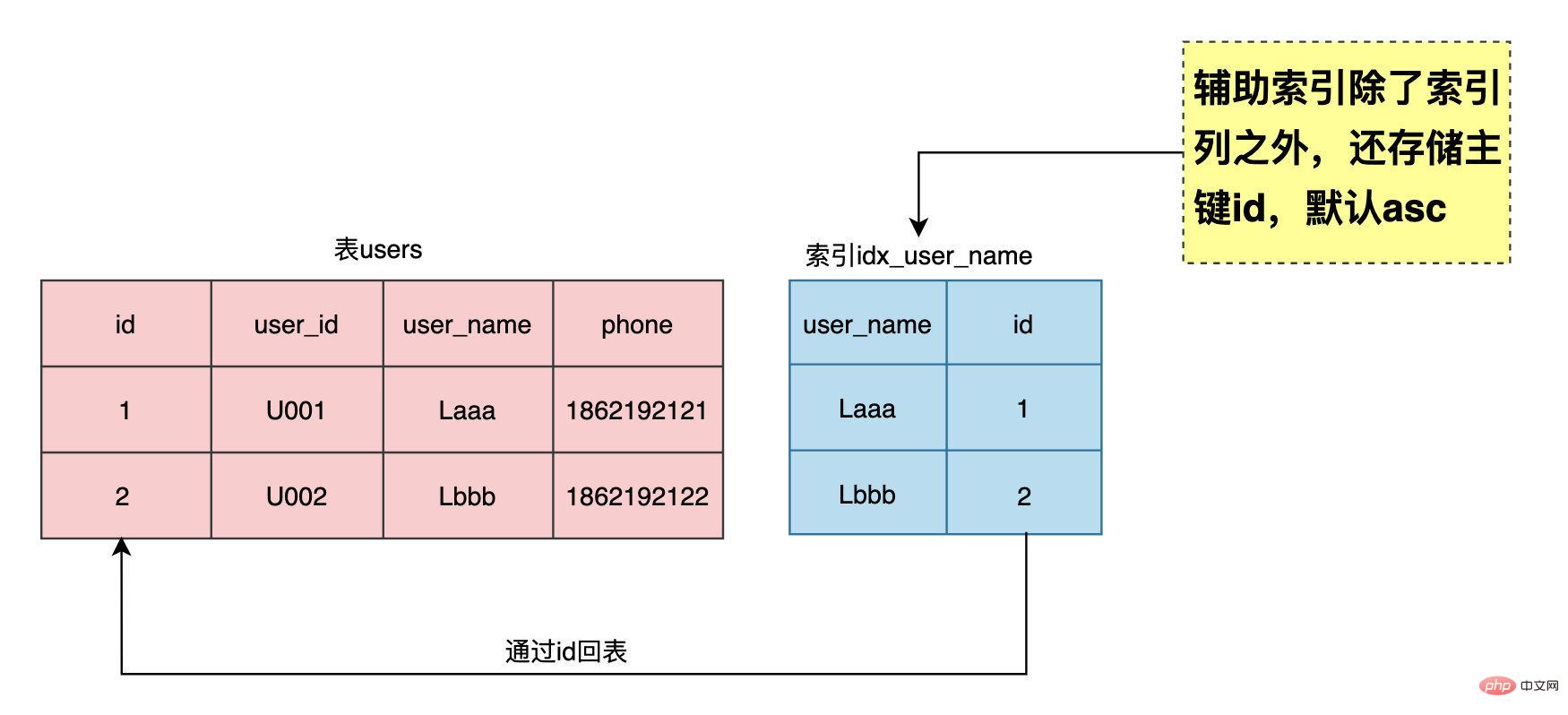
辅助索引也称为二级索引,索引中除了存储索引列外,还存储了主键id,对于user_name的索引idx_user_name(user_name)而言,其实等价于idx_user_name(user_name, id),MySQL会自动在辅助索引的最后添加上主键id,熟悉Oracle数据库的都知道,索引里除了索引列还存储了row_id(代表数据的物理位置,由四部分组成:对象编号+数据文件号+数据块号+数据行号),我们在创建辅助索引也可以显示添加主键id。
-- 创建user_name列上的索引 mysql> create index idx_user_name on users(user_name); -- 显示添加主键id创建索引 mysql> create index idx_user_name_id on users(user_name,id); -- 对比两个索引的统计数据 mysql> select a.space as tbl_spaceid, a.table_id, a.name as table_name, row_format, space_type, b.index_id , b.name as index_name, n_fields, page_no, b.type as index_type from information_schema.INNODB_TABLES a left join information_schema.INNODB_INDEXES b on a.table_id =b.table_id where a.name = 'test/users'; +-------------+----------+------------+------------+------------+----------+------------------+----------+------ | tbl_spaceid | table_id | table_name | row_format | space_type | index_id | index_name | n_fields | page_no | index_type | +-------------+----------+------------+------------+------------+----------+------------------+----------+------ | 518 | 1586 | test/users | Dynamic | Single | 1254 | PRIMARY | 9 | 4 | 3 | | 518 | 1586 | test/users | Dynamic | Single | 4003 | idx_user_name | 2 | 5 | 0 | | 518 | 1586 | test/users | Dynamic | Single | 4004 | idx_user_name_id | 2 | 45 | 0 | mysql> select index_name, last_update, stat_name, stat_value, stat_description from mysql.innodb_index_stats where index_name in ('idx_user_name','idx_user_name_id'); +------------------+---------------------+--------------+------------+-----------------------------------+ | index_name | last_update | stat_name | stat_value | stat_description | +------------------+---------------------+--------------+------------+-----------------------------------+ | idx_user_name | 2021-01-02 17:14:48 | n_leaf_pages | 1358 | Number of leaf pages in the index | | idx_user_name | 2021-01-02 17:14:48 | size | 1572 | Number of pages in the index | | idx_user_name_id | 2021-01-02 17:14:48 | n_leaf_pages | 1358 | Number of leaf pages in the index | | idx_user_name_id | 2021-01-02 17:14:48 | size | 1572 | Number of pages in the index |
对比一下两个索引的结果,n_fields表示索引中的列数,n_leaf_pages表示索引中的叶子页数,size表示索引中的总页数,通过数据比对就可以看到,辅助索引中确实包含了主键id,也说明了这两个索引时完全一致。
| Index_name | n_fields | n_leaf_pages | size |
|---|---|---|---|
| idx_user_name | 2 | 1358 | 1572 |
| idx_user_name_id | 2 | 1358 | 1572 |
索引回表
上面证明了辅助索引包含主键id,如果通过辅助索引列去过滤数据有可能需要回表,举个例子:业务需要通过用户名user_name去查询用户表users的信息,业务接口对应的SQL:
select user_id, user_name, phone from users where user_name = 'Laaa';
我们知道,对于索引idx_user_name而言,其实就是一个小表idx_user_name(user_name, id),如果只查询索引中的列,只需要扫描索引就能获取到所需数据,是不需要回表的,如下SQL语句:
SQL 1: select id, user_name from users where user_name = 'Laaa';
SQL 2: select id from users where user_name = 'Laaa';
mysql> explain select id, name from users where name = 'Laaa'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------------+---------+-------+------+------- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------------+---------+-------+------+------- | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | ref | idx_user_name | idx_user_name | 82 | const | 1 | 100.00 | Using index | mysql> explain select id from users where name = 'Laaa'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------------+---------+-------+------+------- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------------+---------+-------+------+------- | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | ref | idx_user_name | idx_user_name | 82 | const | 1 | 100.00 | Using index |
SQL 1和SQL 2的执行计划中的Extra=Using index 表示使用覆盖索引扫描,不需要回表,再来看上面的业务SQL:
select user_id, user_name, phone from users where user_name = 'Laaa';
可以看到select后面的user_id,phone列不在索引idx_user_name中,就需要通过主键id进行回表查找,MySQL内部分如下两个阶段处理:
Section 1: select **id** from users where user_name = 'Laaa' //id = 100101
Section 2: select user_id, user_name, phone from users where id = 100101;
将Section 2的操作称为回表,即通过辅助索引中的主键id去原表中查找数据。
索引高度
MySQL的索引时B+tree结构,即使表里有上亿条数据,索引的高度都不会很高,通常维持在3-4层左右,我来计算下索引idx_name的高度,从上面知道索引信息:index_id = 4003, page_no = 5,它的偏移量offset就是page_no x innodo_page_size + 64 = 81984,通过hexdump进行查看
$hexdump -s 81984 -n 10 /usr/local/var/mysql/test/users.ibd 0014040 00 02 00 00 00 00 00 00 0f a3 001404a
其中索引的PAGE_LEVEL为00,即idx_user_name索引高度为1,0f a3 代表索引编号,转换为十进制是4003,正是index_id。
数据扫描方式
全表扫描
从左到右依次扫描整个B+Tree获取数据,扫描整个表数据,IO开销大,速度慢,锁等严重,影响MySQL的并发。
对于OLAP的业务场景,需要扫描返回大量数据,这时候全表扫描的顺序IO效率更高。
索引扫描
通常来讲索引比表小,扫描的数据量小,消耗的IO少,执行速度块,几乎没有锁等,能够提高MySQL的并发。
对于OLTP系统,希望所有的SQL都能命中合适的索引总是美好的。
主要区别就是扫描数据量大小以及IO的操作,全表扫描是顺序IO,索引扫描是随机IO,MySQL对此做了优化,增加了change buffer特性来提高IO性能。
索引优化案例
分页查询优化
业务要根据时间范围查询交易记录,接口原始的SQL如下:
select * from trade_info where status = 0 and create_time >= '2020-10-01 00:00:00' and create_time <= '2020-10-07 23:59:59' order by id desc limit 102120, 20;
表trade_info上有索引idx_status_create_time(status,create_time),通过上面分析知道,等价于索引**(status,create_time,id)**,对于典型的分页limit m, n来说,越往后翻页越慢,也就是m越大会越慢,因为要定位m位置需要扫描的数据越来越多,导致IO开销比较大,这里可以利用辅助索引的覆盖扫描来进行优化,先获取id,这一步就是索引覆盖扫描,不需要回表,然后通过id跟原表trade_info进行关联,改写后的SQL如下:
select * from trade_info a , (select id from trade_info where status = 0 and create_time >= '2020-10-01 00:00:00' and create_time <= '2020-10-07 23:59:59' order by id desc limit 102120, 20) as b //这一步走的是索引覆盖扫描,不需要回表 where a.id = b.id;
很多同学只知道这样写效率高,但是未必知道为什么要这样改写,理解索引特性对编写高质量的SQL尤为重要。
分而治之总是不错的
营销系统有一批过期的优惠卷要失效,核心SQL如下:
-- 需要更新的数据量500w update coupons set status = 1 where status =0 and create_time >= '2020-10-01 00:00:00' and create_time <= '2020-10-07 23:59:59';
在Oracle里更新500w数据是很快,因为可以利用多个cpu core去执行,但是MySQL就需要注意了,一个SQL只能使用一个cpu core去处理,如果SQL很复杂或执行很慢,就会阻塞后面的SQL请求,造成活动连接数暴增,MySQL CPU 100%,相应的接口Timeout,同时对于主从复制架构,而且做了业务读写分离,更新500w数据需要5分钟,Master上执行了5分钟,binlog传到了slave也需要执行5分钟,那就是Slave延迟5分钟,在这期间会造成业务脏数据,比如重复下单等。
优化思路:先获取where条件中的最小id和最大id,然后分批次去更新,每个批次1000条,这样既能快速完成更新,又能保证主从复制不会出现延迟。
优化如下:
- 先获取要更新的数据范围内的最小id和最大id(表没有物理delete,所以id是连续的)
mysql> explain select min(id) min_id, max(id) max_id from coupons where status =0 and create_time >= '2020-10-01 00:00:00' and create_time <= '2020-10-07 23:59:59'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+--- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+--- | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | range | idx_status_create_time | idx_status_create_time | 6 | NULL | 180300 | 100.00 | Using where; Using index |
Extra=Using where; Using index使用了索引idx_status_create_time,同时需要的数据都在索引中能找到,所以不需要回表查询数据。
- 以每次1000条commit一次进行循环update,主要代码如下:
current_id = min_id; for current_id < max_id do update coupons set status = 1 where id >=current_id and id <= current_id + 1000; //通过主键id更新1000条很快 commit; current_id += 1000; done
这两个案例告诉我们,要充分利用辅助索引包含主键id的特性,先通过索引获取主键id走覆盖索引扫描,不需要回表,然后再通过id去关联操作是高效的,同时根据MySQL的特性使用分而治之的思想既能高效完成操作,又能避免主从复制延迟产生的业务数据混乱。
MySQL索引设计
熟悉了索引的特性之后,就可以在业务开发过程中设计高质量的索引,降低接口的响应时间。
前缀索引
对于使用REDUNDANT或者COMPACT格式的InnoDB表,索引键前缀长度限制为767字节。如果TEXT或VARCHAR列的列前缀索引超过191个字符,则可能会达到此限制,假定为utf8mb4字符集,每个字符最多4个字节。
可以通过设置参数innodb_large_prefix来开启或禁用索引前缀长度的限制,即是设置为OFF,索引虽然可以创建成功,也会有一个警告,主要是因为index size会很大,效率大量的IO的操作,即使MySQL优化器命中了该索引,效率也不会很高。
-- 设置innodb_large_prefix=OFF禁用索引前缀限制,虽然可以创建成功,但是有警告。 mysql> create index idx_nickname on users(nickname); // `nickname` varchar(255) Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 1 mysql> show warnings; +---------+------+---------------------------------------------------------+ | Level | Code | Message | +---------+------+---------------------------------------------------------+ | Warning | 1071 | Specified key was too long; max key length is 767 bytes |
业务发展初期,为了快速实现功能,对一些数据表字段的长度定义都比较宽松,比如用户表users的昵称nickname定义为varchar(128),而且有业务接口需要通过nickname查询,系统运行了一段时间之后,查询users表最大的nickname长度为30,这个时候就可以创建前缀索引来减小索引的长度提升性能。
-- `nickname` varchar(128) DEFAULT NULL定义的执行计划 mysql> explain select * from users where nickname = 'Laaa'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------------+---------+-------+------+-------- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------------+---------+-------+------+-------- | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | ref | idx_nickname | idx_nickname | 515 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
key_len=515,由于表和列都是utf8mb4字符集,每个字符占4个字节,变长数据类型+2Bytes,允许NULL额外+1Bytes,即128 x 4 + 2 + 1 = 515Bytes。创建前缀索引,前缀长度也可以不是当前表的数据列最大值,应该是区分度最高的那部分长度,一般能达到90%以上即可,例如email字段存储都是类似这样的值xxxx@yyy.com,前缀索引的最大长度可以是xxxx这部分的最大长度即可。
-- 创建前缀索引,前缀长度为30 mysql> create index idx_nickname_part on users(nickname(30)); -- 查看执行计划 mysql> explain select * from users where nickname = 'Laaa'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+--------------------------------+-------------------+---------+- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+--------------------------------+-------------------+---------+- | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | ref | idx_nickname_part,idx_nickname | idx_nickname_part | 123 | const | 1 | 100.00 | Using where |
可以看到优化器选择了前缀索引,索引长度为123,即30 x 4 + 2 + 1 = 123 Bytes,大小不到原来的四分之。
前缀索引虽然可以减小索引的大小,但是不能消除排序。
mysql> explain select gender,count(*) from users where nickname like 'User100%' group by nickname limit 10; +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+--------------------------------+--------------+---------+----- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+--------------------------------+--------------+---------+----- | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | range | idx_nickname_part,idx_nickname | idx_nickname | 515 | NULL | 899 | 100.00 | Using index condition | --可以看到Extra= Using index condition表示使用了索引,但是需要回表查询数据,没有发生排序操作。 mysql> explain select gender,count(*) from users where nickname like 'User100%' group by nickname limit 10; +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+-------------------+-------------------+---------+------+------ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+-------------------+-------------------+---------+------+------ | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | range | idx_nickname_part | idx_nickname_part | 123 | NULL | 899 | 100.00 | Using where; Using temporary | --可以看到Extra= Using where; Using temporaryn表示在使用了索引的情况下,需要回表去查询所需的数据,同时发生了排序操作。
复合索引
在单列索引不能很好的过滤数据的时候,可以结合where条件中其他字段来创建复合索引,更好的去过滤数据,减少IO的扫描次数,举个例子:业务需要按照时间段来查询交易记录,有如下的SQL:
select * from trade_info where status = 1 and create_time >= '2020-10-01 00:00:00' and create_time <= '2020-10-07 23:59:59';
开发同学根据以往复合索引的设计的经验:唯一值多选择性好的列作为复合索引的前导列,所以创建复合索idx_create_time_status是高效的,因为create_time是一秒一个值,唯一值很多,选择性很好,而status只有离散的6个值,所以认为这样创建是没问题的,但是这个经验只适合于等值条件过滤,不适合有范围条件过滤的情况,例如idx_user_id_status(user_id,status)这个是没问题的,但是对于包含有create_time范围的复合索引来说,就不适应了,我们来看下这两种不同索引顺序的差异,即idx_status_create_time和idx_create_time_status。
-- 分别创建两种不同的复合索引 mysql> create index idx_status_create_time on trade_info(status, create_time); mysql> create index idx_create_time_status on trade_info(create_time,status); -- 查看SQL的执行计划 mysql> explain select * from users where status = 1 and create_time >='2021-10-01 00:00:00' and create_time <= '2021-10-07 23:59:59'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+-----------------------------------------------+--------------- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+-----------------------------------------------+--------------- | 1 | SIMPLE | trade_info | NULL | range | idx_status_create_time,idx_create_time_status | idx_status_create_time | 6 | NULL | 98518 | 100.00 | Using index condition |
从执行计划可以看到,两种不同顺序的复合索引都存在的情况,MySQL优化器选择的是idx_status_create_time索引,那为什么不选择idx_create_time_status,我们通过optimizer_trace来跟踪优化器的选择。
-- 开启optimizer_trace跟踪 mysql> set session optimizer_trace="enabled=on",end_markers_in_json=on; -- 执行SQL语句 mysql> select * from trade_info where status = 1 and create_time >='2021-10-01 00:00:00' and create_time <= '2021-10-07 23:59:59'; -- 查看跟踪结果 mysql>SELECT trace FROM information_schema.OPTIMIZER_TRACE\G;
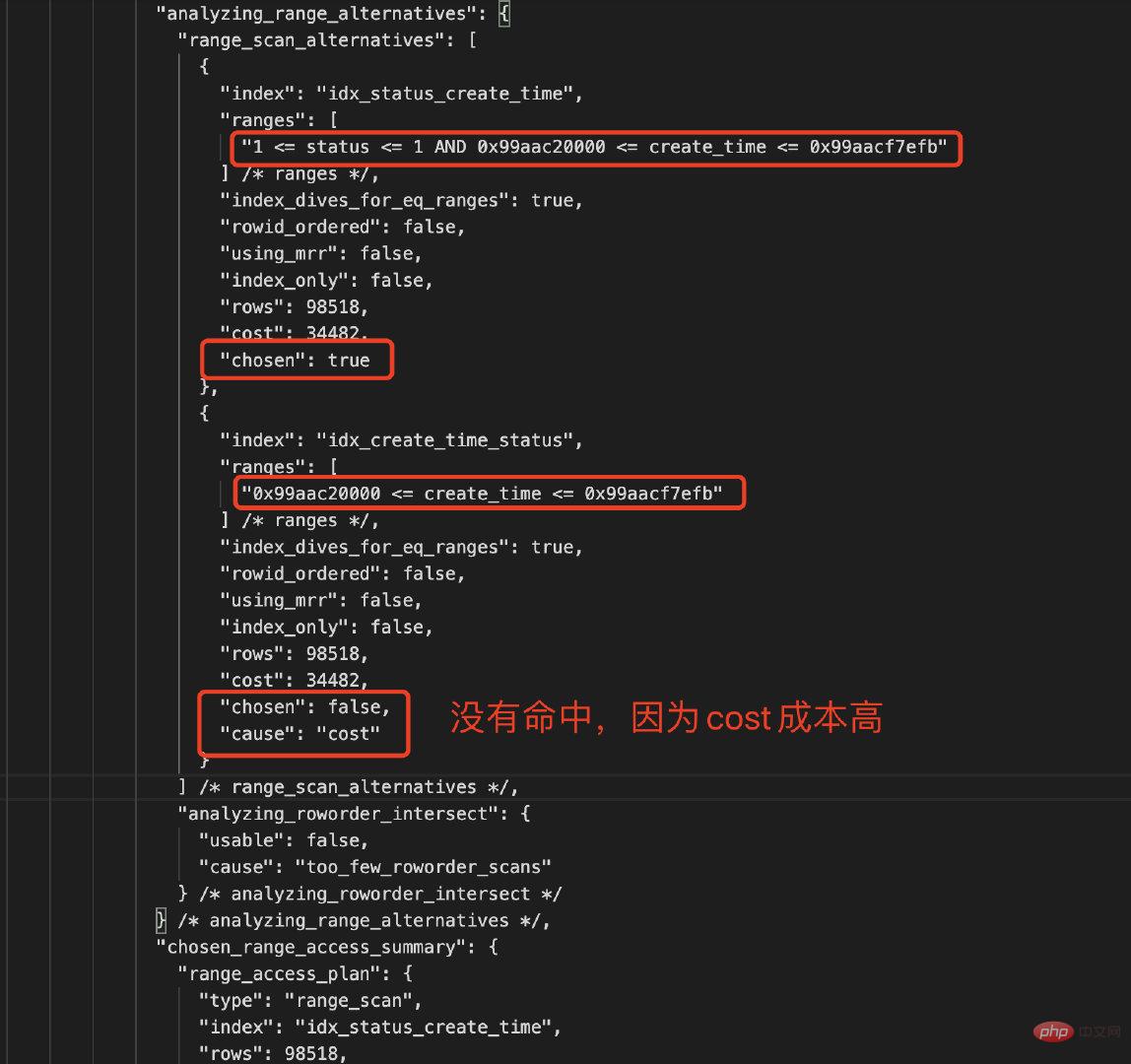
对比下两个索引的统计数据,如下所示:
| 复合索引 | Type | Rows | 参与过滤索引列 | Chosen | Cause |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| idx_status_create_time | Index Range Scan | 98518 | status AND create_time | True | Cost低 |
| idx_create_time_status | Index Range Scan | 98518 | create_time | False | Cost高 |
MySQL优化器是基于Cost的,COST主要包括IO_COST和CPU_COST,MySQL的CBO(Cost-Based Optimizer基于成本的优化器)总是选择Cost最小的作为最终的执行计划去执行,从上面的分析,CBO选择的是复合索引idx_status_create_time,因为该索引中的status和create_time都能参与了数据过滤,成本较低;而idx_create_time_status只有create_time参数数据过滤,status被忽略了,其实CBO将其简化为单列索引idx_create_time,选择性没有复合索引idx_status_create_time好。
复合索引设计原则
将范围查询的列放在复合索引的最后面,例如idx_status_create_time。
列过滤的频繁越高,选择性越好,应该作为复合索引的前导列,适用于等值查找,例如idx_user_id_status。
这两个原则不是矛盾的,而是相辅相成的。
跳跃索引
一般情况下,如果表users有复合索引idx_status_create_time,我们都知道,单独用create_time去查询,MySQL优化器是不走索引,所以还需要再创建一个单列索引idx_create_time。用过Oracle的同学都知道,是可以走索引跳跃扫描(Index Skip Scan),在MySQL 8.0也实现Oracle类似的索引跳跃扫描,在优化器选项也可以看到skip_scan=on。
| optimizer_switch |use_invisible_indexes=off,skip_scan=on,hash_join=on |
适合复合索引前导列唯一值少,后导列唯一值多的情况,如果前导列唯一值变多了,则MySQL CBO不会选择索引跳跃扫描,取决于索引列的数据分表情况。
mysql> explain select id, user_id,status, phone from users where create_time >='2021-01-02 23:01:00' and create_time <= '2021-01-03 23:01:00'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+---- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+---- | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | range | idx_status_create_time | idx_status_create_time | NULL | NULL | 15636 | 11.11 | Using where; Using index for skip scan|
也可以通过optimizer_switch='skip_scan=off’来关闭索引跳跃扫描特性。
总结
本位为大家介绍了MySQL中的索引,包括聚集索引和辅助索引,辅助索引包含了主键id用于回表操作,同时利用覆盖索引扫描可以更好的优化SQL。
同时也介绍了如何更好做MySQL索引设计,包括前缀索引,复合索引的顺序问题以及MySQL 8.0推出的索引跳跃扫描,我们都知道,索引可以加快数据的检索,减少IO开销,会占用磁盘空间,是一种用空间换时间的优化手段,同时更新操作会导致索引频繁的合并分裂,影响索引性能,在实际的业务开发中,如何根据业务场景去设计合适的索引是非常重要的,今天就聊这么多,希望对大家有所帮助。
相关推荐:《mysql教程》
以上是MySQL让索引更高效的方法是什么?的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 MySQL的位置:数据库和编程Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL的位置:数据库和编程Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AMMySQL在数据库和编程中的地位非常重要,它是一个开源的关系型数据库管理系统,广泛应用于各种应用场景。1)MySQL提供高效的数据存储、组织和检索功能,支持Web、移动和企业级系统。2)它使用客户端-服务器架构,支持多种存储引擎和索引优化。3)基本用法包括创建表和插入数据,高级用法涉及多表JOIN和复杂查询。4)常见问题如SQL语法错误和性能问题可以通过EXPLAIN命令和慢查询日志调试。5)性能优化方法包括合理使用索引、优化查询和使用缓存,最佳实践包括使用事务和PreparedStatemen
 MySQL:从小型企业到大型企业Apr 13, 2025 am 12:17 AM
MySQL:从小型企业到大型企业Apr 13, 2025 am 12:17 AMMySQL适合小型和大型企业。1)小型企业可使用MySQL进行基本数据管理,如存储客户信息。2)大型企业可利用MySQL处理海量数据和复杂业务逻辑,优化查询性能和事务处理。
 幻影是什么读取的,InnoDB如何阻止它们(下一个键锁定)?Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
幻影是什么读取的,InnoDB如何阻止它们(下一个键锁定)?Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AMInnoDB通过Next-KeyLocking机制有效防止幻读。1)Next-KeyLocking结合行锁和间隙锁,锁定记录及其间隙,防止新记录插入。2)在实际应用中,通过优化查询和调整隔离级别,可以减少锁竞争,提高并发性能。
 mysql:不是编程语言,而是...Apr 13, 2025 am 12:03 AM
mysql:不是编程语言,而是...Apr 13, 2025 am 12:03 AMMySQL不是一门编程语言,但其查询语言SQL具备编程语言的特性:1.SQL支持条件判断、循环和变量操作;2.通过存储过程、触发器和函数,用户可以在数据库中执行复杂逻辑操作。
 MySQL:世界上最受欢迎的数据库的简介Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL:世界上最受欢迎的数据库的简介Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AMMySQL是一种开源的关系型数据库管理系统,主要用于快速、可靠地存储和检索数据。其工作原理包括客户端请求、查询解析、执行查询和返回结果。使用示例包括创建表、插入和查询数据,以及高级功能如JOIN操作。常见错误涉及SQL语法、数据类型和权限问题,优化建议包括使用索引、优化查询和分表分区。
 MySQL的重要性:数据存储和管理Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL的重要性:数据存储和管理Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AMMySQL是一个开源的关系型数据库管理系统,适用于数据存储、管理、查询和安全。1.它支持多种操作系统,广泛应用于Web应用等领域。2.通过客户端-服务器架构和不同存储引擎,MySQL高效处理数据。3.基本用法包括创建数据库和表,插入、查询和更新数据。4.高级用法涉及复杂查询和存储过程。5.常见错误可通过EXPLAIN语句调试。6.性能优化包括合理使用索引和优化查询语句。
 为什么要使用mysql?利益和优势Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
为什么要使用mysql?利益和优势Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM选择MySQL的原因是其性能、可靠性、易用性和社区支持。1.MySQL提供高效的数据存储和检索功能,支持多种数据类型和高级查询操作。2.采用客户端-服务器架构和多种存储引擎,支持事务和查询优化。3.易于使用,支持多种操作系统和编程语言。4.拥有强大的社区支持,提供丰富的资源和解决方案。
 描述InnoDB锁定机制(共享锁,独家锁,意向锁,记录锁,间隙锁,下一键锁)。Apr 12, 2025 am 12:16 AM
描述InnoDB锁定机制(共享锁,独家锁,意向锁,记录锁,间隙锁,下一键锁)。Apr 12, 2025 am 12:16 AMInnoDB的锁机制包括共享锁、排他锁、意向锁、记录锁、间隙锁和下一个键锁。1.共享锁允许事务读取数据而不阻止其他事务读取。2.排他锁阻止其他事务读取和修改数据。3.意向锁优化锁效率。4.记录锁锁定索引记录。5.间隙锁锁定索引记录间隙。6.下一个键锁是记录锁和间隙锁的组合,确保数据一致性。


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

安全考试浏览器
Safe Exam Browser是一个安全的浏览器环境,用于安全地进行在线考试。该软件将任何计算机变成一个安全的工作站。它控制对任何实用工具的访问,并防止学生使用未经授权的资源。

螳螂BT
Mantis是一个易于部署的基于Web的缺陷跟踪工具,用于帮助产品缺陷跟踪。它需要PHP、MySQL和一个Web服务器。请查看我们的演示和托管服务。

适用于 Eclipse 的 SAP NetWeaver 服务器适配器
将Eclipse与SAP NetWeaver应用服务器集成。

SublimeText3 英文版
推荐:为Win版本,支持代码提示!

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)






