nginx流量拷贝功能介绍
- 王林转载
- 2021-03-12 10:38:593784浏览

1、我们为什么要将生产环境的流量拷贝到预上线环境或测试环境呢?
这样做得好处有以下几点:
可以验证功能是否正常,以及服务的性能;
用真实有效的流量请求去验证,又不用造数据,不影响线上正常访问;
这跟灰度发布还不太一样,镜像流量不会影响真实流量;
可以用来排查线上问题;
重构,假如服务做了重构,这也是一种测试方式;
为了实现流量拷贝,Nginx提供了ngx_http_mirror_module模块
2、安装Nginx
首页,设置yum仓库。为此,创建一个文件/etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo
将以下内容写入文件
[nginx-stable] name=nginx stable repo baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/$releasever/$basearch/ gpgcheck=1 enabled=1 gpgkey=https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key module_hotfixes=true [nginx-mainline] name=nginx mainline repo baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/mainline/centos/$releasever/$basearch/ gpgcheck=1 enabled=0 gpgkey=https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key module_hotfixes=true
yum安装nginx
yum install nginx
默认情况下,nginx配置文件是nginx.conf
一般情况下,nginx.conf文件在 /usr/local/nginx/conf 或者 /etc/nginx 或者 /usr/local/etc/nginx 目录下
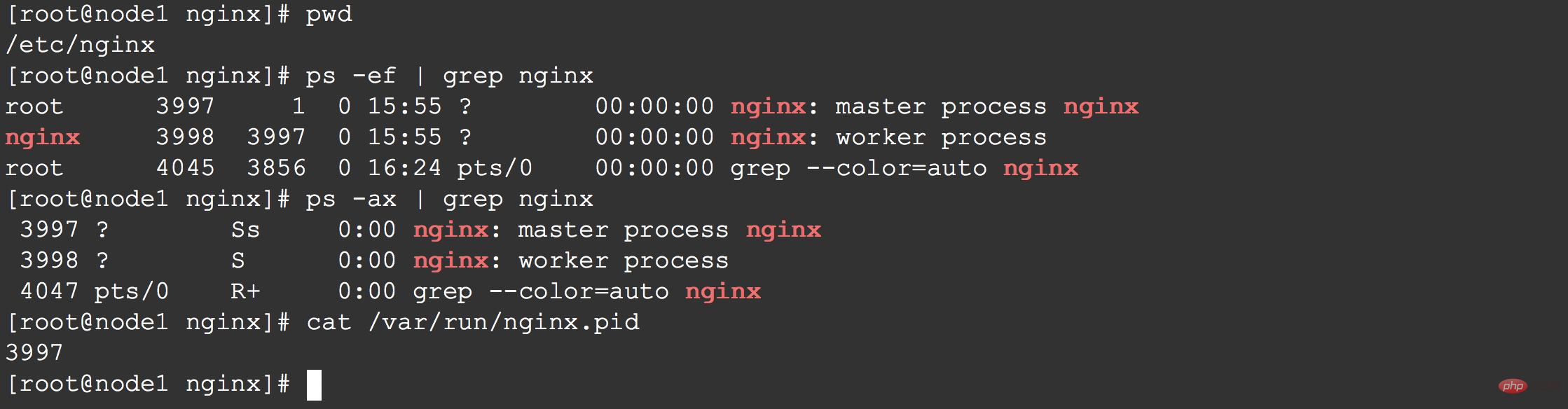
为了启动nginx,直接在命令行里输入nginx回车即可
# 启动nginx nginx # fast shutdown nginx -s stop # graceful shutdown nginx -s quit # reloading the configuration file nginx -s reload # reopening the log files nginx -s reopen # list of all running nginx processes ps -ax | grep nginx
一旦master进程接收到重新加载配置的信号,它将检查新配置文件的语法是否正确,并尝试应用其中提供的配置。如果成功,master进程将启动新的worker进程,并发送消息给旧的worker进程,要求他们shutdown。否则,master进程将回滚所做的更改,并继续使用旧配置。旧的worker进程在接收到关闭命令后,停止接受新的连接,直到所有之前已经接受的连接全部处理完为止。之后,旧的worker进程退出。
(免费学习视频分享:php视频教程)
nginx的master进程的进程ID,默认情况下,放在nginx.pid文件中,该文件所在的目录一般是/usr/local/nginx/logs 或者 /var/run
还可以这样停止nginx
kill -s QUIT 3997
初始配置文件长这样:
user nginx;
worker_processes 1;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn;
pid /var/run/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
}3、ngx_http_mirror_module
The ngx_http_mirror_module module (1.13.4) implements mirroring of an original request by creating background mirror subrequests. Responses to mirror subrequests are ignored.
我是这样理解的,这里,mirror本意是镜子、镜像,这里可以理解就像一个镜像站点一样,将所有的请求都收集起来,这个镜像就代表了所有真实有效的原始请求。有了这个镜像,后续我们才可能用这个镜像去做一些事情,比如重现一下所有的请求,这就实现了把线上的流程复制到别的地方。
官网给出的示例倒是很简单,如下:
location / {
mirror /mirror;
proxy_pass http://backend;
}
location = /mirror {
internal;
proxy_pass http://test_backend$request_uri;
}如果请求体被镜像,那么在创建子请求之前会先读取请求体
location / {
mirror /mirror;
mirror_request_body off;
proxy_pass http://backend;
}
location = /mirror {
internal;
proxy_pass http://log_backend;
proxy_pass_request_body off;
proxy_set_header Content-Length "";
proxy_set_header X-Original-URI $request_uri;
}前面我们安装了Nginx,但是里面没有包含我们所需的ngx_http_mirror_module模块,因此,真正要使用的时候最好还是采用自定义安装,即从源码构建
首先,下载源码 http://nginx.org/en/download.html
接下来,编译安装,例如:
./configure
--sbin-path=/usr/local/nginx/nginx
--conf-path=/usr/local/nginx/nginx.conf
--pid-path=/usr/local/nginx/nginx.pid
--with-http_ssl_module
--without-http_limit_req_module
--without-http_mirror_module
--with-pcre=../pcre-8.43
--with-zlib=../zlib-1.2.11
--add-module=/path/to/ngx_devel_kit
--add-module=/path/to/lua-nginx-modulemake & make install
配置
upstream api.abc.com {
server 127.0.0.1:8080;
}
upstream tapi.abc.com {
server 127.0.0.1:8081;
}
server {
listen 80;
# 源站点
location /api {
proxy_pass http://api.cjs.com;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
# 流量复制
mirror /newapi;
mirror /mirror2;
mirror /mirror3;
# 复制请求体
mirror_request_body on;
}
# 镜像站点
location /tapi {
proxy_pass http://tapi.cjs.com$request_uri;
proxy_pass_request_body on;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
}相关推荐:nginx教程
以上是nginx流量拷贝功能介绍的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

