Linux中计算特定CPU使用率的方法:首先从【/proc/stat】中获取 t1时刻系统总体的值;然后从【/proc/stat】中获取t2时刻系统总的值;最后计算t2与t1之间系统总的CPU使用情况。

【相关学习推荐:linux视频教程】
Linux中计算特定CPU使用率的方法:
1. 背景知识
在/proc/stat中可以查看每一个CPU的使用情况的,如下图:
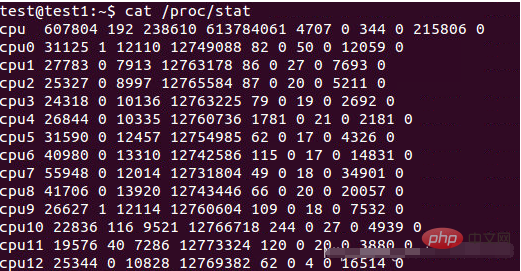
其中cpu(0/1/2/…)后面的那十个数字含义如下:
/proc/stat
kernel/system statistics. Varies with architecture.
Common entries include:
user nice system idle iowait irq softirq steal guest guest_nice
cpu 4705 356 584 3699 23 23 0 0 0 0
cpu0 1393280 32966 572056 13343292 6130 0 17875 0 23933 0
The amount of time, measured in units of USER_HZ
(1/100ths of a second on most architectures, use
sysconf(_SC_CLK_TCK) to obtain the right value), that
the system ("cpu" line) or the specific CPU ("cpuN"
line) spent in various states:
user (1) Time spent in user mode.
nice (2) Time spent in user mode with low priority
(nice).
system (3) Time spent in system mode.
idle (4) Time spent in the idle task. This value
should be USER_HZ times the second entry in the
/proc/uptime pseudo-file.
iowait (since Linux 2.5.41)
(5) Time waiting for I/O to complete. This
value is not reliable, for the following rea‐
sons:
1. The CPU will not wait for I/O to complete;
iowait is the time that a task is waiting for
I/O to complete. When a CPU goes into idle
state for outstanding task I/O, another task
will be scheduled on this CPU.
2. On a multi-core CPU, the task waiting for I/O
to complete is not running on any CPU, so the
iowait of each CPU is difficult to calculate.
3. The value in this field may decrease in cer‐
tain conditions.
irq (since Linux 2.6.0-test4)
(6) Time servicing interrupts.
softirq (since Linux 2.6.0-test4)
(7) Time servicing softirqs.
steal (since Linux 2.6.11)
(8) Stolen time, which is the time spent in
other operating systems when running in a virtu‐
alized environment
guest (since Linux 2.6.24)
(9) Time spent running a virtual CPU for guest
operating systems under the control of the Linux
kernel.
guest_nice (since Linux 2.6.33)
(10) Time spent running a niced guest (virtual
CPU for guest operating systems under the con‐
trol of the Linux kernel).2.计算具体CPU使用率
有了上面的背景知识,接下来我们就可以计算具体CPU的使用情况了。具体计算方式如下:
Total CPU time since boot = user+nice+system+idle+iowait+irq+softirq+steal Total CPU Idle time since boot = idle + iowait Total CPU usage time since boot = Total CPU time since boot - Total CPU Idle time since boot Total CPU percentage = Total CPU usage time since boot/Total CPU time since boot * 100%
有了上面的计算公式,计算某一CPU使用率或者系统总的CPU占用率也就是不难了。
示例:计算系统整体CPU占用情况
首先从/proc/stat中获取 t1时刻系统总体的user、nice、system、idle、iowait、irq、softirq、steal、guest、guest_nice的值,得到此时Total CPU time since boot(记为total1)和 Total CPU idle time since boot(记为idle1)。
其次,从/proc/stat中获取t2时刻系统总的Total CPU time since boot(记为total2)和Total CPU idle time since boot(记为idle2)。(方法同上一步)
最后,计算t2与t1之间系统总的CPU使用情况。也就是:
CPU percentage between t1 and t2 = ((total2-total1)-(idle2-idle1))/(total2-total1)* 100%
其中, ((total2-total1)-(idle2-idle1))实际上就是t1与t2时刻之间系统CPU被占用的时间(总时间 - 空闲时间)。
下面是一段计算时间段内CPU被占用情况的脚本:
#!/bin/bash
# by Paul Colby (http://colby.id.au), no rights reserved ;)
PREV_TOTAL=0
PREV_IDLE=0
while true; do
# Get the total CPU statistics, discarding the 'cpu ' prefix.
CPU=(`sed -n 's/^cpu\s//p' /proc/stat`)
IDLE=${CPU[3]} # Just the idle CPU time.
# Calculate the total CPU time.
TOTAL=0
for VALUE in "${CPU[@]}"; do
let "TOTAL=$TOTAL+$VALUE"
done
# Calculate the CPU usage since we last checked.
let "DIFF_IDLE=$IDLE-$PREV_IDLE"
let "DIFF_TOTAL=$TOTAL-$PREV_TOTAL"
let "DIFF_USAGE=(1000*($DIFF_TOTAL-$DIFF_IDLE)/$DIFF_TOTAL+5)/10"
echo -en "\rCPU: $DIFF_USAGE% \b\b"
# Remember the total and idle CPU times for the next check.
PREV_TOTAL="$TOTAL"
PREV_IDLE="$IDLE"
# Wait before checking again.
sleep 1
done以上是Linux中如何计算特定CPU使用率的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 Linux操作:系统管理和维护Apr 15, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Linux操作:系统管理和维护Apr 15, 2025 am 12:10 AMLinux系统管理和维护的关键步骤包括:1)掌握基础知识,如文件系统结构和用户管理;2)进行系统监控与资源管理,使用top、htop等工具;3)利用系统日志进行故障排查,借助journalctl等工具;4)编写自动化脚本和任务调度,使用cron工具;5)实施安全管理与防护,通过iptables配置防火墙;6)进行性能优化与最佳实践,调整内核参数和养成良好习惯。
 了解Linux的维护模式:必需品Apr 14, 2025 am 12:04 AM
了解Linux的维护模式:必需品Apr 14, 2025 am 12:04 AMLinux维护模式通过在启动时添加init=/bin/bash或single参数进入。1.进入维护模式:编辑GRUB菜单,添加启动参数。2.重新挂载文件系统为读写模式:mount-oremount,rw/。3.修复文件系统:使用fsck命令,如fsck/dev/sda1。4.备份数据并谨慎操作,避免数据丢失。
 Debian如何提升Hadoop数据处理速度Apr 13, 2025 am 11:54 AM
Debian如何提升Hadoop数据处理速度Apr 13, 2025 am 11:54 AM本文探讨如何在Debian系统上提升Hadoop数据处理效率。优化策略涵盖硬件升级、操作系统参数调整、Hadoop配置修改以及高效算法和工具的运用。一、硬件资源强化确保所有节点硬件配置一致,尤其关注CPU、内存和网络设备性能。选择高性能硬件组件对于提升整体处理速度至关重要。二、操作系统调优文件描述符和网络连接数:修改/etc/security/limits.conf文件,增加系统允许同时打开的文件描述符和网络连接数上限。JVM参数调整:在hadoop-env.sh文件中调整
 Debian syslog如何学习Apr 13, 2025 am 11:51 AM
Debian syslog如何学习Apr 13, 2025 am 11:51 AM本指南将指导您学习如何在Debian系统中使用Syslog。Syslog是Linux系统中用于记录系统和应用程序日志消息的关键服务,它帮助管理员监控和分析系统活动,从而快速识别并解决问题。一、Syslog基础知识Syslog的核心功能包括:集中收集和管理日志消息;支持多种日志输出格式和目标位置(例如文件或网络);提供实时日志查看和过滤功能。二、安装和配置Syslog(使用Rsyslog)Debian系统默认使用Rsyslog。您可以通过以下命令安装:sudoaptupdatesud
 Debian中Hadoop版本怎么选Apr 13, 2025 am 11:48 AM
Debian中Hadoop版本怎么选Apr 13, 2025 am 11:48 AM选择适合Debian系统的Hadoop版本,需要综合考虑以下几个关键因素:一、稳定性与长期支持:对于追求稳定性和安全性的用户,建议选择Debian稳定版,例如Debian11(Bullseye)。该版本经过充分测试,拥有长达五年的支持周期,能够确保系统稳定运行。二、软件包更新速度:如果您需要使用最新的Hadoop功能和特性,则可以考虑Debian的不稳定版(Sid)。但需注意,不稳定版可能存在兼容性问题和稳定性风险。三、社区支持与资源:Debian拥有庞大的社区支持,可以提供丰富的文档和
 Debian上TigerVNC共享文件方法Apr 13, 2025 am 11:45 AM
Debian上TigerVNC共享文件方法Apr 13, 2025 am 11:45 AM本文介绍如何在Debian系统上使用TigerVNC共享文件。你需要先安装TigerVNC服务器,然后进行配置。一、安装TigerVNC服务器打开终端。更新软件包列表:sudoaptupdate安装TigerVNC服务器:sudoaptinstalltigervnc-standalone-servertigervnc-common二、配置TigerVNC服务器设置VNC服务器密码:vncpasswd启动VNC服务器:vncserver:1-localhostno
 Debian邮件服务器防火墙配置技巧Apr 13, 2025 am 11:42 AM
Debian邮件服务器防火墙配置技巧Apr 13, 2025 am 11:42 AM配置Debian邮件服务器的防火墙是确保服务器安全性的重要步骤。以下是几种常用的防火墙配置方法,包括iptables和firewalld的使用。使用iptables配置防火墙安装iptables(如果尚未安装):sudoapt-getupdatesudoapt-getinstalliptables查看当前iptables规则:sudoiptables-L配置
 Debian邮件服务器SSL证书安装方法Apr 13, 2025 am 11:39 AM
Debian邮件服务器SSL证书安装方法Apr 13, 2025 am 11:39 AM在Debian邮件服务器上安装SSL证书的步骤如下:1.安装OpenSSL工具包首先,确保你的系统上已经安装了OpenSSL工具包。如果没有安装,可以使用以下命令进行安装:sudoapt-getupdatesudoapt-getinstallopenssl2.生成私钥和证书请求接下来,使用OpenSSL生成一个2048位的RSA私钥和一个证书请求(CSR):openss


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

SecLists
SecLists是最终安全测试人员的伙伴。它是一个包含各种类型列表的集合,这些列表在安全评估过程中经常使用,都在一个地方。SecLists通过方便地提供安全测试人员可能需要的所有列表,帮助提高安全测试的效率和生产力。列表类型包括用户名、密码、URL、模糊测试有效载荷、敏感数据模式、Web shell等等。测试人员只需将此存储库拉到新的测试机上,他就可以访问到所需的每种类型的列表。

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) 是一个PHP/MySQL的Web应用程序,非常容易受到攻击。它的主要目标是成为安全专业人员在合法环境中测试自己的技能和工具的辅助工具,帮助Web开发人员更好地理解保护Web应用程序的过程,并帮助教师/学生在课堂环境中教授/学习Web应用程序安全。DVWA的目标是通过简单直接的界面练习一些最常见的Web漏洞,难度各不相同。请注意,该软件中

适用于 Eclipse 的 SAP NetWeaver 服务器适配器
将Eclipse与SAP NetWeaver应用服务器集成。





