golang与java语法上的区别
- 王林原创
- 2019-12-07 10:45:222888浏览

变量声明与赋值
Java:
int i; // 声明 int j = 1; // 声明+赋值
Go:
var i int // 声明 i := 1 // 声明+赋值
1、变量声明:var是关键字,格式:var 变量名称 变量类型
2、变量声明与赋值: := 符号支持自动推导类型
异常处理
Java:

Go:
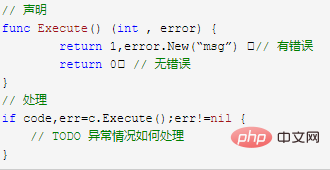
go的异常是做为函数返回值的,通过判断是否存在error,来判断异常。 (不能够像Java一样抛出异常)
go的if语句支持初始条件,即先执行if之后的语句(分号之前),再执行分号之后的判断语句,此语句经常用于异常处理。
go的大括号必须在行末go函数或者变量为”公有”,首字母大写,”私有”则小写。
参数传递
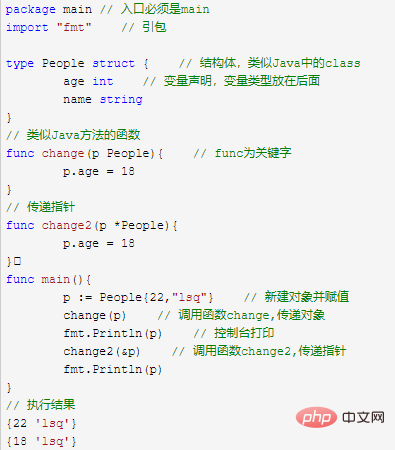
change函数是传递的对象,函数调用的时候,会拿到对象的拷贝。
change2函数是传递的指针,函数调用的时候,会拿到一个指向改对象的指针。
go没有引用传递
多态
此例有点长,是一个求面积的问题,针对与圆形和矩形两种类型
java:
java.lang.Math;public class Polymorphism{
public static class Rectangle implements Areable{ //矩形 double width;
double height;
public Rectangle(double width,double height){
this.width = width;
this.height = height;}
public double area(){
return width * height;}
}
public static class Circle implements Areable{ // 圆形 double radius;
public Circle(double radius){
this.radius = radius;}
public double area(){
return radius * radius * Math.PI;}
} public static interface Areable{
double area();
}public static void main(String[] args){
Areable arear = new Rectangle(5.0,5.0);
Areable areac = new Circle(2.5);
System.out.println(arear.area());
System.out.println(areac.area());
}
}Go:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math"
)
type Rectangle struct { // 矩形
width float64
height float64
}
type Circle struct { // 圆形
radius float64
}
type Areable interface{ // 接口:一组method签名的组合,通过interface来定义对象的一组行为。
// 只要是实现了interface中的所有的method的结构体,就可以认为是这个interface的实例,Duck typing
area() float64
}
func (r Rectangle) /* 函数的接受者Receiver */ area() float64 /* 返回值类型*/ {
return r.width * r.height
}
func (c Circle) /* 函数的另一个接受者Receiver */ area() float64 /* 返回值类型*/{
return c.radius * c.radius * math.Pi
}
func main(){
ra := Rectangle{5,5}
ca := Circle{2.5}
fmt.Println(ra.area())
fmt.Println(ca.area())
}相关文章教程:golang教程
以上是golang与java语法上的区别的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
声明:
本文内容由网友自发贡献,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有涉嫌抄袭侵权的内容,请联系admin@php.cn

