
java继承与合成基本概念
继承:可以基于已经存在的类构造一个新类。继承已经存在的类就可以复用这些类的方法和域。在此基础上,可以添加新的方法和域,从而扩充了类的功能。
合成:在新类里创建原有的对象称为合成。这种方式可以重复利用现有的代码而不更改它的形式。
相关视频教程推荐:java视频教程
1.继承的语法
关键字extends表明新类派生于一个已经存在的类。已存在的类称为父类或基类,新类称为子类或派生类。例如:
class Student extends Person {
}类Student继承了Person,Person类称为父类或基类,Student类称为子类或派生类。
2.合成的语法
合成比较简单,就是在一个类中创建一个已经存在的类。
class Student {
Dog dog;
}上溯造型
1.基本概念
继承的作用在于代码的复用。由于继承意味着父类的所有方法亦可在子类中使用,所以发给父类的消息亦可发给衍生类。如果Person类中有一个eat方法,那么Student类中也会有这个方法,这意味着Student对象也是Person的一种类型。
class Person {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("eat");
}
static void show(Person p) {
p.eat();
}
}
public class Student extends Person{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student();
Person.show(s); // ①
}
}【运行结果】:
eat
在Person中定义的show方法是用来接收Person句柄的,但是在①处接收的却是Student对象的引用。这是因为Student对象也是Person对象。在show方法中,传入的句柄(对象的引用)可以是Person对象以及Person的衍生类对象。这种将Student句柄转换成Person句柄的行为成为上溯造型。
2.为什么要上溯造型
为什么在调用eat是要有意忽略调用它的对象类型呢?如果让show方法简单地获取Student句柄似乎更加直观易懂,但是那样会使衍生自Person类的每一个新类都要实现专属自己的show方法:
class Value {
private int count = 1;
private Value(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
public static final Value
v1 = new Value(1),
v2 = new Value(2),
v3 = new Value(3);
}
class Person {
public void eat(Value v) {
System.out.println("Person.eat()");
}
}
class Teacher extends Person {
public void eat(Value v) {
System.out.println("Teacher.eat()");
}
}
class Student extends Person {
public void eat(Value v) {
System.out.println("Student.eat()");
}
}
public class UpcastingDemo {
public static void show(Student s) {
s.eat(Value.v1);
}
public static void show(Teacher t) {
t.eat(Value.v1);
}
public static void show(Person p) {
p.eat(Value.v1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student();
Teacher t = new Teacher();
Person p = new Person();
show(s);
show(t);
show(p);
}
}这种做法一个很明显的缺陷就是必须为每一个Person类的衍生类定义与之紧密相关的方法,产生了很多重复的代码。另一方面,对于如果忘记了方法的重载也不会报错。上例中的三个show方法完全可以合并为一个:
public static void show(Person p) {
p.eat(Value.v1);
}动态绑定
当执行show(s)时,输出结果是Student.eat(),这确实是希望得到的结果,但是似乎没有按照我们希望的形式来执行,再来看一下show方法:
public static void show(Person p) {
p.eat(Value.v1);
}它接收的是Person句柄,当执行show(s)时,它是如何知道Person句柄指向的是一个Student对象而不是Teacher对象呢?编译器是无从得知的,这涉及到接下来要说明的绑定问题。
1.方法调用的绑定
将一个方法同一个方法主体连接在一起就称为绑定(Binding)。若在运行运行前执行绑定,就称为“早期绑定”。上面的例子中,在只有一个Person句柄的情况下,编译器不知道具体调用哪个方法。Java实现了一种方法调用机制,可在运行期间判断对象的类型,然后调用相应的方法,这种在运行期间进行,以对象的类型为基础的绑定称为动态绑定。除非一个方法被声明为final,Java中的所有方法都是动态绑定的。
用一张图表示上溯造型的继承关系:
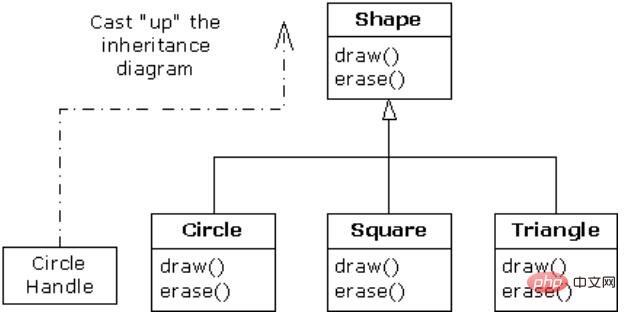
用代码概括为:
Shape s = new Shape();
按照继承关系,将创建的Circle对象句柄赋给一个Shape是合法的,因为Circle属于Shape的一种。
当调用其中一个基础类方法时:
Shape s = new Shape();
此时,调用的是Circle.draw(),这是由于动态绑定的原因。
class Person {
void eat() {}
void speak() {}
}
class Boy extends Person {
void eat() {
System.out.println("Boy.eat()");
}
void speak() {
System.out.println("Boy.speak()");
}
}
class Girl extends Person {
void eat() {
System.out.println("Girl.eat()");
}
void speak() {
System.out.println("Girl.speak()");
}
}
public class Persons {
public static Person randPerson() {
switch ((int)(Math.random() * 2)) {
default:
case 0:
return new Boy();
case 1:
return new Girl();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person[] p = new Person[4];
for (int i = 0; i < p.length; i++) {
p[i] = randPerson(); // 随机生成Boy或Girl
}
for (int i = 0; i < p.length; i++) {
p[i].eat();
}
}
}对所有从Person衍生出来的类,Person建立了一个通用接口,所有衍生的类都有eat和speak两种行为。衍生类覆盖了这些定义,重新定义了这两种行为。
在主类中,randPerson随机选择Person对象的句柄。**上诉造型是在return语句里发生的。**return语句取得一个Boy或Girl的句柄并将其作为Person类型返回,此时并不知道具体是什么类型,只知道是Person对象句柄。
在main方法中调用randPerson方法为数组填入Person对象,但不知具体情况。当调用数组每个元素的eat方法时,动态绑定的作用就是执行对象的重新定义了的方法。
然而,动态绑定是有前提的,绑定的方法必须存在于基类中,否则无法编译通过。
class Person {
void eat() {
System.out.println("Person.eat()");
}
}
class Boy extends Person {
void eat() {
System.out.println("Boy.eat()");
}
void speak() {
System.out.println("Boy.speak()");
}
}
public class Persons {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Boy();
p.eat();
p.speak(); // The method speak() is undefined for the type Person
}
}如果子类中没有定义覆盖方法,则会调用父类中的方法:
class Person {
void eat() {
System.out.println("Person.eat()");
}
}
class Boy extends Person {
}
public class Persons {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Boy();
p.eat();
}
}【运行结果】:
Person.eat()
2.静态方法的绑定
将上面的方法都加上static关键字,变成静态方法:
class Person {
static void eat() {
System.out.println("Person.eat()");
}
static void speak() {
System.out.println("Person.speak()");
}
}
class Boy extends Person {
static void eat() {
System.out.println("Boy.eat()");
}
static void speak() {
System.out.println("Boy.speak()");
}
}
class Girl extends Person {
static void eat() {
System.out.println("Girl.eat()");
}
static void speak() {
System.out.println("Girl.speak()");
}
}
public class Persons {
public static Person randPerson() {
switch ((int)(Math.random() * 2)) {
default:
case 0:
return new Boy();
case 1:
return new Girl();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person[] p = new Person[4];
for (int i = 0; i < p.length; i++) {
p[i] = randPerson(); // 随机生成Boy或Girl
}
for (int i = 0; i < p.length; i++) {
p[i].eat();
}
}
}【运行结果】:
Person.eat() Person.eat() Person.eat() Person.eat()
观察结果,对于静态方法而言,不管父类引用指向的什么子类对象,调用的都是父类的方法。
更多java相关文章请关注java基础教程栏目。
以上是Java中继承图文详解的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

安全考试浏览器
Safe Exam Browser是一个安全的浏览器环境,用于安全地进行在线考试。该软件将任何计算机变成一个安全的工作站。它控制对任何实用工具的访问,并防止学生使用未经授权的资源。

SublimeText3 Linux新版
SublimeText3 Linux最新版

螳螂BT
Mantis是一个易于部署的基于Web的缺陷跟踪工具,用于帮助产品缺陷跟踪。它需要PHP、MySQL和一个Web服务器。请查看我们的演示和托管服务。

WebStorm Mac版
好用的JavaScript开发工具




