python中,yield关键字的作用:1、将一个函数修改为生成器,利用生成器可以有效地节约系统资源,避免不必要的内存占用;2、用于定义上下文管理器;3、协程;4、配合from形成yield from用于消费子生成器并传递消息。

yield 的用法有以下四种常见的情况:
-
一个是生成器,
概括的话就是:生成器内部的代码执行到yield会返回,返回的内容为yield后的表达式。下次再执行生成器的内部代码时将从上次的状态继续开始。通过yield关键字,我们可以很方便的将一个函数修改为生成器。
二是用于定义上下文管理器,
三是协程,
四是配合 from 形成 yield from 用于消费子生成器并传递消息。
这四种用法,其实都源于 yield 所具有的暂停的特性,也就说程序在运行到 yield 所在的位置 result = yield expr 时,先执行 yield expr 将产生的值返回给调用生成器的 caller,然后暂停,等待 caller 再次激活并恢复程序的执行。而根据恢复程序使用的方法不同,yield expr 表达式的结果值 result 也会跟着变化。如果使用 __next()__ 来调用,则 yield 表达式的值 result 是 None;如果使用 send() 来调用,则 yield 表达式的值 result 是通过 send 函数传送的值。下面是官方文档介绍 yield 表达式时的一个例子[1],能够很好地说明关键字 yield 的特性和用法:
>>> def echo(value=None):
... print("Begin...")
... try:
... while True:
... try:
... value = (yield value)
... except Exception as e:
... value = e
... finally:
... print("Clean up!!!")
...
>>> generator = echo(1)
>>> print(next(generator))
Begin...
1
>>> print(next(generator))
None
>>> print(generator.send(2))
2
>>> generator.throw(TypeError, "spam")
TypeError('spam')
>>> generator.close()
Clean up!!!上面这段代码的说明如下图所示:
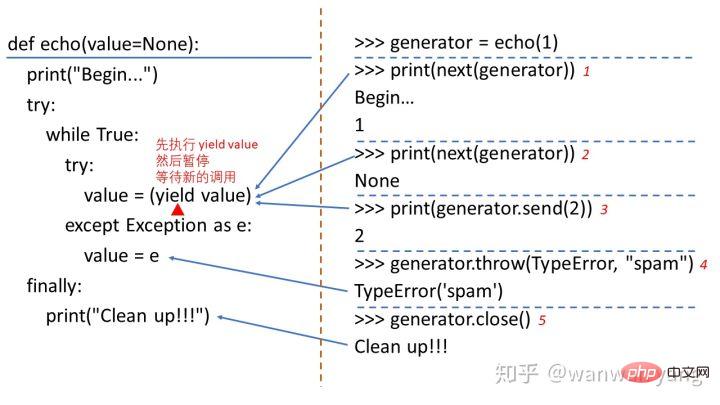
执行第一个 next(generator) 的时候,也就是预激活生成器,生成器开始执行,打印 Begin... 字符串,执行到 value = (yield value) 的位置时,首先调用 yield value 产生数字 1,然后生成器在 yield 的位置暂停。
接着调用第 2 个 next(generator) 的时候,生成器恢复执行,由于使用 next() 来调用生成器函数, value 的值会变成 None ,因此生成器函数继续执行到 yield value 时,会将 value 的值 None 返回给解释器,然后再次暂停。
接着使用 send(2) 方法继续调用生成器,value 接收到传入的数字 2,继续到执行 value = (yield value) ,将数字 2 返回给解释器后暂停。
此后,解释器再次通过 throw(TypeError, "spam") 方法调用,生成器恢复执行,并抛出异常,生成器捕获到异常,并将异常 TypeError('spam') 赋值给变量 value,然后程序再次执行到 value = (yield value) ,将 TypeError('spam') 返回给解释器。
最后,程序调用 close() 方法,在生成器函数的位置抛出 GeneratorExit ,异常被抛出,生成器正常退出,并最终执行最外层 try 语句对应的 finally 分支,打印输出 Clean up。
python中有一个非常有用的语法叫做生成器,所利用到的关键字就是yield。有效利用生成器这个工具可以有效地节约系统资源,避免不必要的内存占用。
生成器
不出意外,你最先遇到 yield 一定会是一个生成器函数里面。生成器是一个用于不断生成数字或者其他类型的值的函数,可以通过 for 循环或者 next() 函数逐一调用。这里需要强调的是,生成器包含的是一个没有赋值的 yield 表达式,所以下面两种形式是等价的[2]:
def integers_1():
for i in range(4):
yield i + 1def integers_2():
for i in range(4):
value = yield i + 1这里之所以强调第二种形式,是为了在理解通过 send() 方法发送 value 时,能够更好地理解 yield。同时,也能够更正确地说明,调用生成器返回的值是 yield 关键字右边的表达式 i + 1 的值,而不是 yield 表达式本身的结果值。
我们试着调用一下:
>>> for n in integers_1(): ... print(n) ... 1 2 3 4 >>> for n in integers_2(): ... print(n) ... 1 2 3 4
上下文管理器
配合 Python 的 contexlib 模块里的 @contextmanager 装饰器,yield 也可以用于定义上下文管理器,下面是 Python Tricks 书中的一个例子[3]:
from contextlib import contextmanager
@contextmanager
def managed_file(name):
try:
f = open(name, 'w')
yield f
finally:
f.close()上面通过装饰器和 yield 关键字定义的上下文管理器和下面类的方法定义等同:
class ManagedFile:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
def __enter__(self):
self.file = open(self.name, 'w')
return self.file
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb):
if self.file:
self.file.close()可以利用下面的方法分别进行调用:
>>> with ManagedFile('hello.txt') as f: ... f.write('hello, world!') ... f.write('bye now') >>> with managed_file('hello.txt') as f: ... f.write('hello, world!') ... f.write('bye now')
协程
协程的概念充满了美感,非常符合人的办事模式,想要完全掌握却还是需要花费一些功夫。不过这些功夫是值得的,因为有时多线程所带来的麻烦会远远比协程多。下面是 Python Cookbook 中的一个只用 yield 表达式编写的协程实例[4]:
from collections import deque
# Two simple generator functions
def countdown(n):
while n > 0:
print('T-minus', n)
yield
n -= 1
print('Blastoff!')
def countup(n):
x = 0
while x < n:
print('Counting up', x)
yield
x += 1
class TaskScheduler:
def __init__(self):
self._task_queue = deque()
def new_task(self, task):
'''
Admit a newly started task to the scheduler
'''
self._task_queue.append(task)
def run(self):
'''
Run until there are no more tasks
'''
while self._task_queue:
task = self._task_queue.popleft()
try:
# Run until the next yield statement
next(task)
self._task_queue.append(task)
except StopIteration:
# Generator is no longer executing
pass
# Example use
sched = TaskScheduler()
sched.new_task(countdown(2))
sched.new_task(countup(5))
sched.run()运行上面的脚本,可以得到以下输出:
T-minus 2 Counting up 0 T-minus 1 Counting up 1 Blastoff! Counting up 2 Counting up 3 Counting up 4
countdown 和 countup 两个任务交替执行,主程序在执行到 countdown 函数的 yield 表达式时,暂停后将被重新附加到队列里面。然后,countup 任务从队列中取了出来,并开始执行到 yield 表达式的地方后暂停,同样将暂停后的协程附加到队列里面,接着从队列里取出最左边的任务 countdown 继续执行。重复上述过程,直到队列为空。
上面的协程可以利用 Python3.7 中的 asyncio 库改写为:
import asyncio
async def countdown(n):
while n > 0:
print('T-minus', n)
await asyncio.sleep(0)
n -= 1
print('Blastoff!')
async def countup(n):
x = 0
while x < n:
print('Counting up', x)
await asyncio.sleep(0)
x += 1
async def main():
await asyncio.gather(countdown(2), countup(5))
asyncio.run(main())可以看到利用 asyncio 库编写的协程示例比用 yield 来编写的协程要优雅地多,也简单地多,更容易被人理解。
yield from
说实话,yield from 实在有点令人费解,让人摸不着头脑。yield from 更多地被用于协程,而 await 关键字的引入会大大减少 yield from 的使用频率。yield from 一方面可以迭代地消耗生成器,另一方面则建立了一条双向通道,可以让调用者和子生成器便捷地通信,并自动地处理异常,接收子生成器返回的值。下面是 Python Cookbook 书里的一个例子,用于展开嵌套的序列[5]:
from collections.abc import Iterable
def flatten(items, ignore_types=(str, bytes)):
for x in items:
if isinstance(x, Iterable) and not isinstance(x, ignore_types):
yield from flatten(x)
else:
yield x
items = [1, 2, [3, 4, [5, 6], 7], 8]
# Produces 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
for x in flatten(items):
print(x)而 yield from 用于建立双向通道的用法则可以参考 Fluent Python 里例子[6],这里就不详细地解释这段代码:
# BEGIN YIELD_FROM_AVERAGER
from collections import namedtuple
Result = namedtuple('Result', 'count average')
# the subgenerator
def averager():
total = 0.0
count = 0
average = None
while True:
term = yield
if term is None:
break
total += term
count += 1
average = total/count
return Result(count, average)
# the delegating generator
def grouper(results, key):
while True:
results[key] = yield from averager()
# the client code, a.k.a. the caller
def main(data):
results = {}
for key, values in data.items():
group = grouper(results, key)
next(group)
for value in values:
group.send(value)
group.send(None)
report(results)
# output report
def report(results):
for key, result in sorted(results.items()):
group, unit = key.split(';')
print(f'{result.count:2} {group:5} averaging {result.average:.2f}{unit}')
data = {
'girls;kg':
[40.9, 38.5, 44.3, 42.2, 45.2, 41.7, 44.5, 38.0, 40.6, 44.5],
'girls;m':
[1.6, 1.51, 1.4, 1.3, 1.41, 1.39, 1.33, 1.46, 1.45, 1.43],
'boys;kg':
[39.0, 40.8, 43.2, 40.8, 43.1, 38.6, 41.4, 40.6, 36.3],
'boys;m':
[1.38, 1.5, 1.32, 1.25, 1.37, 1.48, 1.25, 1.49, 1.46],
}
if __name__ == '__main__':
main(data)可能对于熟练掌握 Python 的程序员来说,yield 和 yield from 相关的语法充满了美感。但对于刚入门的我来说,除了生成器语法让我感觉到了美感,其他的语法都让我理解起来很是费解。不过还好,asyncio 库融入了 Python 的标准库里,关键字 async 和 await 的引入,将会让我们更少地在编写协程时去使用 yield 和 yield from。 但不管怎么样,yield 都是 Python 里非常特别的一个关键字,值得花时间好好掌握了解。
以上是Python中关键字yield有什么作用的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 Python中的合并列表:选择正确的方法May 14, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Python中的合并列表:选择正确的方法May 14, 2025 am 12:11 AMTomergelistsinpython,YouCanusethe操作员,estextMethod,ListComprehension,Oritertools
 如何在Python 3中加入两个列表?May 14, 2025 am 12:09 AM
如何在Python 3中加入两个列表?May 14, 2025 am 12:09 AM在Python3中,可以通过多种方法连接两个列表:1)使用 运算符,适用于小列表,但对大列表效率低;2)使用extend方法,适用于大列表,内存效率高,但会修改原列表;3)使用*运算符,适用于合并多个列表,不修改原列表;4)使用itertools.chain,适用于大数据集,内存效率高。
 Python串联列表字符串May 14, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Python串联列表字符串May 14, 2025 am 12:08 AM使用join()方法是Python中从列表连接字符串最有效的方法。1)使用join()方法高效且易读。2)循环使用 运算符对大列表效率低。3)列表推导式与join()结合适用于需要转换的场景。4)reduce()方法适用于其他类型归约,但对字符串连接效率低。完整句子结束。
 Python执行,那是什么?May 14, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Python执行,那是什么?May 14, 2025 am 12:06 AMpythonexecutionistheprocessoftransformingpypythoncodeintoExecutablestructions.1)InternterPreterReadSthecode,ConvertingTingitIntObyTecode,whepythonvirtualmachine(pvm)theglobalinterpreterpreterpreterpreterlock(gil)the thepythonvirtualmachine(pvm)
 Python:关键功能是什么May 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python:关键功能是什么May 14, 2025 am 12:02 AMPython的关键特性包括:1.语法简洁易懂,适合初学者;2.动态类型系统,提高开发速度;3.丰富的标准库,支持多种任务;4.强大的社区和生态系统,提供广泛支持;5.解释性,适合脚本和快速原型开发;6.多范式支持,适用于各种编程风格。
 Python:编译器还是解释器?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python:编译器还是解释器?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AMPython是解释型语言,但也包含编译过程。1)Python代码先编译成字节码。2)字节码由Python虚拟机解释执行。3)这种混合机制使Python既灵活又高效,但执行速度不如完全编译型语言。
 python用于循环与循环时:何时使用哪个?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
python用于循环与循环时:何时使用哪个?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMuseeAforloopWheniteratingOveraseQuenceOrforAspecificnumberoftimes; useAwhiLeLoopWhenconTinuingUntilAcIntiment.ForloopSareIdeAlforkNownsences,而WhileLeleLeleLeleLoopSituationSituationSituationsItuationSuationSituationswithUndEtermentersitations。
 Python循环:最常见的错误May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Python循环:最常见的错误May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMpythonloopscanleadtoerrorslikeinfiniteloops,modifyingListsDuringteritation,逐个偏置,零indexingissues,andnestedloopineflinefficiencies


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

SublimeText3 英文版
推荐:为Win版本,支持代码提示!

EditPlus 中文破解版
体积小,语法高亮,不支持代码提示功能

VSCode Windows 64位 下载
微软推出的免费、功能强大的一款IDE编辑器

Dreamweaver Mac版
视觉化网页开发工具

Atom编辑器mac版下载
最流行的的开源编辑器





