本篇文章给大家带来的内容是关于Parcel源码的详细分析(附示例),有一定的参考价值,有需要的朋友可以参考一下,希望对你有所帮助。
本篇文章是对 Parce 的源码解析,代码基本架构与执行流程,在这之前你如果对 parcel 不熟悉可以先到 Parcel官网 了解
介绍
下面是偷懒从官网抄下来的介绍:
极速零配置Web应用打包工具极速打包
Parcel 使用 worker 进程去启用多核编译。同时有文件系统缓存,即使在重启构建后也能快速再编译。
将你所有的资源打包
Parcel 具备开箱即用的对 JS, CSS, HTML, 文件 及更多的支持,而且不需要插件。
自动转换
如若有需要,Babel, PostCSS, 和 PostHTML 甚至 node_modules 包会被用于自动转换代码.
零配置代码分拆
使用动态 import() 语法, Parcel 将你的输出文件束(bundles)分拆,因此你只需要在初次加载时加载你所需要的代码。
热模块替换
Parcel 无需配置,在开发环境的时候会自动在浏览器内随着你的代码更改而去更新模块。
友好的错误日志
当遇到错误时,Parcel 会输出 语法高亮的代码片段,帮助你定位问题。
| 打包工具 | 时间 |
|---|---|
| browserify | 22.98s |
| webpack | 20.71s |
| parcel | 9.98s |
| parcel - with cache | 2.64s |
打包工具
我们常用的打包工具大致功能:
模块化(代码的拆分, 合并, Tree-Shaking 等)编译(es6,7,8 sass typescript 等)压缩 (js, css, html包括图片的压缩)HMR (热替换)
version
parcel-bundler 版本:
"version": "1.11.0"
文件架构
|-- assets 资源目录 继承自 Asset.js |-- builtins 用于最终构建 |-- packagers 打包 |-- scope-hoisting 作用域提升 Tree-Shake |-- transforms 转换代码为 AST |-- utils 工具 |-- visitors 遍历 js AST树 收集依赖等 |-- Asset.js 资源 |-- Bundle.js 用于构建 bundle 树 |-- Bundler.js 主目录 |-- FSCache.js 缓存 |-- HMRServer.js HMR服务器提供 WebSocket |-- Parser.js 根据文件扩展名获取对应 Asset |-- Pipeline.js 多线程执行方法 |-- Resolver.js 解析模块路径 |-- Server.js 静态资源服务器 |-- SourceMap.js SourceMap |-- cli.js cli入口 解析命令行参数 |-- worker.js 多线程入口
流程
说明
Parcel是面向资源的,JavaScript,CSS,HTML 这些都是资源,并不是 webpack 中 js 是一等公民,Parcel 会自动的从入口文件开始分析这些文件 和 模块中的依赖,然后构建一个 bundle 树,并对其进行打包输出到指定目录
一个简单的例子
我们从一个简单的例子开始了解 parcel 内部源码与流程
index.html |-- index.js |-- module1.js |-- module2.js
上面是我们例子的结构,入口为 index.html, 在 index.html 中我们用 script 标签引用了 src/index.js,在 index.js 中我们引入了2个子模块
执行
npx parcel index.html 或者 ./node_modules/.bin/parcel index.html,或者使用 npm script
cli
"bin": {
"parcel": "bin/cli.js"
}
查看 parcel-bundler的 package.json 找到 bin/cli.js,在cli.js里又指向 ../src/cli
const program = require('commander');
program
.command('serve [input...]') // watch build
...
.action(bundle);
program.parse(process.argv);
async function bundle(main, command) {
const Bundler = require('./Bundler');
const bundler = new Bundler(main, command);
if (command.name() === 'serve' && command.target === 'browser') {
const server = await bundler.serve();
if (server && command.open) {...启动自动打开浏览器}
} else {
bundler.bundle();
}
}
在 cli.js 中利用 commander 解析命令行并调用 bundle 方法
有 serve, watch, build 3个命令来调用 bundle 函数,执行 pracel index.html 默认为 serve,所以调用的是 bundler.serve 方法
进入 Bundler.js
bundler.serve
async serve(port = 1234, https = false, host) {
this.server = await Server.serve(this, port, host, https);
try {
await this.bundle();
} catch (e) {}
return this.server;
}
bundler.serve 方法 调用 serveStatic 起了一个静态服务指向 最终打包的文件夹
下面就是重要的 bundle 方法
bundler.bundle
async bundle() {
// 加载插件 设置env 启动多线程 watcher hmr
await this.start();
if (isInitialBundle) {
// 创建 输出目录
await fs.mkdirp(this.options.outDir);
this.entryAssets = new Set();
for (let entry of this.entryFiles) {
let asset = await this.resolveAsset(entry);
this.buildQueue.add(asset);
this.entryAssets.add(asset);
}
}
// 打包队列中的资源
let loadedAssets = await this.buildQueue.run();
// findOrphanAssets 获取所有资源中独立的没有父Bundle的资源
let changedAssets = [...this.findOrphanAssets(), ...loadedAssets];
// 因为接下来要构建 Bundle 树,先对上一次的 Bundle树 进行 clear 操作
for (let asset of this.loadedAssets.values()) {
asset.invalidateBundle();
}
// 构建 Bundle 树
this.mainBundle = new Bundle();
for (let asset of this.entryAssets) {
this.createBundleTree(asset, this.mainBundle);
}
// 获取新的最终打包文件的url
this.bundleNameMap = this.mainBundle.getBundleNameMap(
this.options.contentHash
);
// 将代码中的旧文件url替换为新的
for (let asset of changedAssets) {
asset.replaceBundleNames(this.bundleNameMap);
}
// 将改变的资源通过websocket发送到浏览器
if (this.hmr && !isInitialBundle) {
this.hmr.emitUpdate(changedAssets);
}
// 对资源打包
this.bundleHashes = await this.mainBundle.package(
this,
this.bundleHashes
);
// 将独立的资源删除
this.unloadOrphanedAssets();
return this.mainBundle;
}
我们一步步先从 this.start 看
start
if (this.farm) {
return;
}
await this.loadPlugins();
if (!this.options.env) {
await loadEnv(Path.join(this.options.rootDir, 'index'));
this.options.env = process.env;
}
if (this.options.watch) {
this.watcher = new Watcher();
this.watcher.on('change', this.onChange.bind(this));
}
if (this.options.hmr) {
this.hmr = new HMRServer();
this.options.hmrPort = await this.hmr.start(this.options);
}
this.farm = await WorkerFarm.getShared(this.options, {
workerPath: require.resolve('./worker.js')
});
start:
开头的判断 防止多次执行,也就是说 this.start 只会执行一次loadPlugins 加载插件,找到 package.json 文件 dependencies, devDependencies 中 parcel-plugin-开头的插件进行调用loadEnv 加载环境变量,利用 dotenv, dotenv-expand 包将 env.development.local, .env.development, .env.local, .env 扩展至 process.envwatch 初始化监听文件并绑定 change 回调函数,内部 child_process.fork 起一个子进程,使用 chokidar 包来监听文件改变hmr 起一个服务,WebSocket 向浏览器发送更改的资源farm 初始化多进程并指定 werker 工作文件,开启多个 child_process 去解析编译资源
接下来回到 bundle,isInitialBundle 是一个判断是否是第一次构建
fs.mkdirp 创建输出文件夹
遍历入口文件,通过 resolveAsset,内部调用 resolver 解析路径,并 getAsset 获取到对应的 asset(这里我们入口是 index.html,根据扩展名获取到的是 HTMLAsset)
将 asset 添加进队列
然后启动 this.buildQueue.run() 对资源从入口递归开始打包
PromiseQueue
这里 buildQueue 是一个 PromiseQueue 异步队列
PromiseQueue 在初始化的时候传入一个回调函数 callback,内部维护一个参数队列 queue,add 往队列里 push 一个参数,run 的时候while遍历队列 callback(...queue.shift()),队列全部执行完毕 Promise 置为完成(resolved)(可以将其理解为 Promise.all)
这里定义的回调函数是 processAsset,参数就是入口文件 index.html 的 HTMLAsset
async processAsset(asset, isRebuild) {
if (isRebuild) {
asset.invalidate();
if (this.cache) {
this.cache.invalidate(asset.name);
}
}
await this.loadAsset(asset);
}
processAsset 函数内先判断是否是 Rebuild ,是第一次构建,还是 watch 监听文件改变进行的重建,如果是重建则对资源的属性重置,并使其缓存失效
之后调用 loadAsset 加载资源编译资源
loadAsset
async loadAsset(asset) {
if (asset.processed) {
return;
}
// Mark the asset processed so we don't load it twice
asset.processed = true;
// 先尝试读缓存,缓存没有在后台加载和编译
asset.startTime = Date.now();
let processed = this.cache && (await this.cache.read(asset.name));
let cacheMiss = false;
if (!processed || asset.shouldInvalidate(processed.cacheData)) {
processed = await this.farm.run(asset.name);
cacheMiss = true;
}
asset.endTime = Date.now();
asset.buildTime = asset.endTime - asset.startTime;
asset.id = processed.id;
asset.generated = processed.generated;
asset.hash = processed.hash;
asset.cacheData = processed.cacheData;
// 解析和加载当前资源的依赖项
let assetDeps = await Promise.all(
dependencies.map(async dep => {
dep.parent = asset.name;
let assetDep = await this.resolveDep(asset, dep);
if (assetDep) {
await this.loadAsset(assetDep);
}
return assetDep;
})
);
if (this.cache && cacheMiss) {
this.cache.write(asset.name, processed);
}
}
loadAsset 在开始有个判断防止重复编译
之后去读缓存,读取失败就调用 this.farm.run 在多进程里编译资源
编译完就去加载并编译依赖的文件
最后如果是新的资源没有用到缓存,就重新设置一下缓存
下面说一下这里吗涉及的两个东西:缓存 FSCache 和 多进程 WorkerFarm
FSCache
read 读取缓存,并判断最后修改时间和缓存的修改时间
write 写入缓存
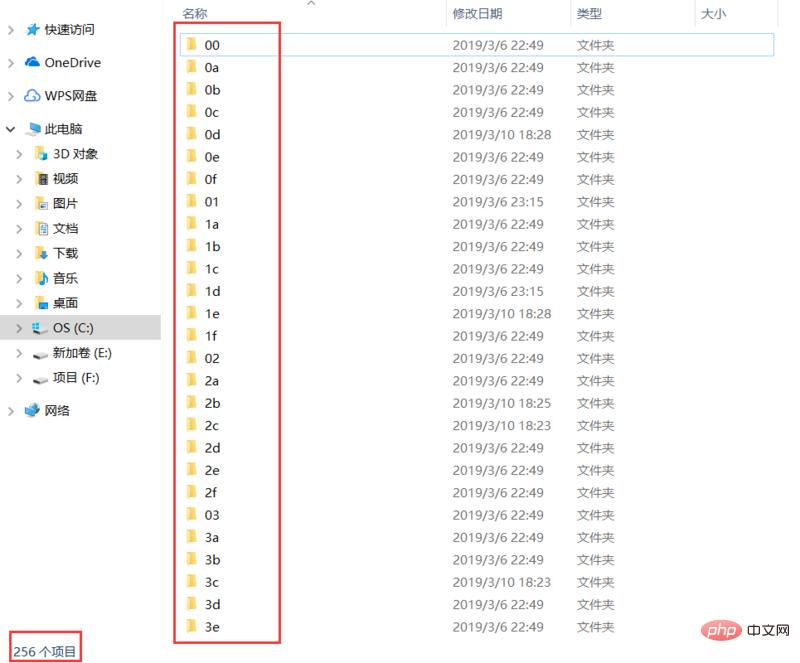
缓存目录为了加速读取,避免将所有的缓存文件放在一个文件夹里,parcel 将 16进制 两位数的 256 种可能创建为文件夹,这样存取缓存文件的时候,将目标文件路径 md5 加密转换为 16进制,然后截取前两位是目录,后面几位是文件名
WorkerFarm
在上面 start 里初始化 farm 的时候,workerPath 指向了 worker.js 文件,worker.js 里有两个函数,init 和 run
WorkerFarm.getShared 初始化的时候会创建一个 new WorkerFarm ,调用 worker.js 的 init 方法,根据 cpu 获取最大的 Worker 数,并启动一半的子进程
farm.run 会通知子进程执行 worker.js 的 run 方法,如果进程数没有达到最大会再次开启一个新的子进程,子进程执行完毕后将 Promise状态更改为完成
worker.run -> pipeline.process -> pipeline.processAsset -> asset.process
Asset.process 处理资源:
async process() {
if (!this.generated) {
await this.loadIfNeeded();
await this.pretransform();
await this.getDependencies();
await this.transform();
this.generated = await this.generate();
}
return this.generated;
}
将上面的代码内部扩展一下:
async process() {
// 已经有就不需要编译
if (!this.generated) {
// 加载代码
if (this.contents == null) {
this.contents = await this.load();
}
// 可选。在收集依赖之前转换。
await this.pretransform();
// 将代码解析为 AST 树
if (!this.ast) {
this.ast = await this.parse(this.contents);
}
// 收集依赖
await this.collectDependencies();
// 可选。在收集依赖之后转换。
await this.transform();
// 生成代码
this.generated = await this.generate();
}
return this.generated;
}
// 最后处理代码
async postProcess(generated) {
return generated
}
processAsset 中调用 asset.process 生成 generated 这个generated 不一定是最终代码 ,像 html里内联的 script ,vue 的 html, js, css,都会进行二次或多次递归处理,最终调用 asset.postProcess 生成代码
Asset
下面说几个实现
HTMLAsset:
pretransform 调用 posthtml 将 html 解析为 PostHTMLTree(如果没有设置posthtmlrc之类的不会走)
parse 调用 posthtml-parser 将 html 解析为 PostHTMLTree
collectDependencies 用 walk 遍历 ast,找到 script, img 的 src,link 的 href 等的地址,将其加入到依赖
transform htmlnano 压缩代码
generate 处理内联的 script 和 css
postProcess posthtml-render 生成 html 代码
JSAsset:
pretransform 调用 @babel/core 将 js 解析为 AST,处理 process.env
parse 调用 @babel/parser 将 js 解析为 AST
collectDependencies 用 babylon-walk 遍历 ast, 如 ImportDeclaration,import xx from 'xx' 语法,CallExpression 找到 require调用,import 被标记为 dynamic 动态导入,将这些模块加入到依赖
transform 处理 readFileSync,__dirname, __filename, global等,如果没有设置scopeHoist 并存在 es6 module 就将代码转换为 commonjs,terser 压缩代码
generate @babel/generator 获取 js 与 sourceMap 代码
VueAsset:
parse @vue/component-compiler-utils 与 vue-template-compiler 对 .vue 文件进行解析
generate 对 html, js, css 处理,就像上面说到会对其分别调用 processAsset 进行二次解析
postProcess component-compiler-utils 的 compileTemplate, compileStyle处理 html,css,vue-hot-reload-api HMR处理,压缩代码
回到 bundle 方法:
let loadedAssets = await this.buildQueue.run() 就是上面说到的PromiseQueue 和 WorkerFarm 结合起来:buildQueue.run —> processAsset -> loadAsset -> farm.run -> worker.run -> pipeline.process -> pipeline.processAsset -> asset.process,执行之后所有资源编译完毕,并返回入口资源loadedAssets就是 index.html 对应的 HTMLAsset 资源
之后是 let changedAssets = [...this.findOrphanAssets(), ...loadedAssets] 获取到改变的资源
findOrphanAssets 是从所有资源中查找没有 parentBundle 的资源,也就是独立的资源,这个 parentBundle 会在等会的构建 Bundle 树中被赋值,第一次构建都没有 parentBundle,所以这里会重复入口文件,这里的 findOrphanAssets 的作用是在第一次构建之后,文件change的时候,在这个文件 import了新的一个文件,因为新文件没有被构建过 Bundle 树,所以没有 parentBundle,这个新文件也被标记物 change
invalidateBundle 因为接下来要构建新的树所以调用重置所有资源上一次树的属性
createBundleTree 构建 Bundle 树:
首先一个入口资源会被创建成一个 bundle,然后动态的 import() 会被创建成子 bundle ,这引发了代码的拆分。
当不同类型的文件资源被引入,兄弟 bundle 就会被创建。例如你在 JavaScript 中引入了 CSS 文件,那它会被放置在一个与 JavaScript 文件对应的兄弟 bundle 中。
如果资源被多于一个 bundle 引用,它会被提升到 bundle 树中最近的公共祖先中,这样该资源就不会被多次打包。
Bundle:
type:它包含的资源类型 (例如:js, css, map, ...)
name:bundle 的名称 (使用 entryAsset 的 Asset.generateBundleName() 生成)
parentBundle:父 bundle ,入口 bundle 的父 bundle 是 null
entryAsset:bundle 的入口,用于生成名称(name)和聚拢资源(assets)
assets:bundle 中所有资源的集合(Set)
childBundles:所有子 bundle 的集合(Set)
siblingBundles:所有兄弟 bundle 的集合(Set)
siblingBundlesMap:所有兄弟 bundle 的映射 Map
offsets:所有 bundle 中资源位置的映射 Map
我们的例子会被构建成:
html ( index.html ) |-- js ( index.js, module1.js, module2.js ) |-- map ( index.js, module1.js, module2.js )
module1.js 和 module2.js 被提到了与 index.js 同级,map 因为类型不同被放到了 子bundle
一个复杂点的树:
// 资源树 index.html |-- index.css |-- bg.png |-- index.js |-- module.js
// mainBundle html ( index.html ) |-- js ( index.js, module.js ) |-- map ( index.map, module.map ) |-- css ( index.css ) |-- js ( index.css, css-loader.js bundle-url.js ) |-- map ( css-loader.js, bundle-url.js ) |-- png ( bg.png )
因为要对 css 热更新,所以新增了 css-loader.js, bundle-url.js 两个 js
replaceBundleNames替换引用:生成树之后将代码中的文件引用替换为最终打包的文件名,如果是生产环境会替换为 contentHash 根据内容生成 hash
hmr更新: 判断启用 hmr 并且不是第一次构建的情况,调用 hmr.emitUpdate 将改变的资源发送给浏览器
Bundle.package 打包
unloadOrphanedAssets 将独立的资源删除
package
package 将generated 写入到文件
有6种打包:
CSSPackager,HTMLPackager,SourceMapPackager,JSPackager,JSConcatPackager,RawPackager
当开启 scopeHoist 时用 JSConcatPackager 否则 JSPackager
图片等资源用 RawPackager
最终我们的例子被打包成 index.html, src.[hash].js, src.[hash].map 3个文件
index.html 里的 js 路径被替换成立最终打包的地址
我们看一下打包的 js:
parcelRequire = (function (modules, cache, entry, globalName) {
// Save the require from previous bundle to this closure if any
var previousRequire = typeof parcelRequire === 'function' && parcelRequire;
var nodeRequire = typeof require === 'function' && require;
function newRequire(name, jumped) {
if (!cache[name]) {
localRequire.resolve = resolve;
localRequire.cache = {};
var module = cache[name] = new newRequire.Module(name);
modules[name][0].call(module.exports, localRequire, module, module.exports, this);
}
return cache[name].exports;
function localRequire(x){
return newRequire(localRequire.resolve(x));
}
function resolve(x){
return modules[name][4][x] || x;
}
}
for (var i = 0; i < entry.length; i++) {
newRequire(entry[i]);
}
// Override the current require with this new one
return newRequire;
})({"src/module1.js":[function(require,module,exports) {
"use strict";
},{}],"src/module2.js":[function(require,module,exports) {
"use strict";
},{}],"src/index.js":[function(require,module,exports) {
"use strict";
var _module = require("./module");
var _module2 = require("./module1");
var _module3 = require("./module2");
console.log(_module.m);
},{"./module":"src/module.js","./module1":"src/module1.js","./module2":"src/module2.js","fs":"node_modules/parcel-bundler/src/builtins/_empty.js"}]
,{}]},{},["node_modules/parcel-bundler/src/builtins/hmr-runtime.js","src/index.js"], null)
//# sourceMappingURL=/src.a2b27638.map
可以看到代码被拼接成了对象的形式,接收参数 module, require 用来模块导入导出,实现了 commonjs 的模块加载机制,一个更加简化版:
parcelRequire = (function (modules, cache, entry, globalName) {
function newRequire(id){
if(!cache[id]){
let module = cache[id] = { exports: {} }
modules[id][0].call(module.exports, newRequire, module, module.exports, this);
}
return cache[id]
}
for (var i = 0; i < entry.length; i++) {
newRequire(entry[i]);
}
return newRequire;
})()
代码被拼接起来:
`(function(modules){
//...newRequire
})({` +
asset.id +
':[function(require,module,exports) {\n' +
asset.generated.js +
'\n},' +
'})'
(function(modules){
//...newRequire
})({
"src/index.js":[function(require,module,exports){
// code
}]
})
hmr-runtime
上面打包的 js 中还有个 hmr-runtime.js 太长被我省略了
hmr-runtime.js 创建一个 WebSocket 监听服务端消息
修改文件触发 onChange 方法,onChange 将改变的资源 buildQueue.add 加入构建队列,重新调用 bundle 方法,打包资源,并调用 emitUpdate 通知浏览器更新
当浏览器接收到服务端有新资源更新消息时
新的资源就会设置或覆盖之前的模块
modules[asset.id] = new Function('require', 'module', 'exports', asset.generated.js)
对模块进行更新:
function hmrAccept(id){
// dispose 回调
cached.hot._disposeCallbacks.forEach(function (cb) {
cb(bundle.hotData);
});
delete bundle.cache[id]; // 删除之前缓存
newRequire(id); // 重新此加载
// accept 回调
cached.hot._acceptCallbacks.forEach(function (cb) {
cb();
});
// 递归父模块 进行更新
getParents(global.parcelRequire, id).some(function (id) {
return hmrAccept(global.parcelRequire, id);
});
}
至此整个打包流程结束
总结
parcle index.html
进入 cli,启动Server调用 bundle,初始化配置(Plugins, env, HMRServer, Watcher, WorkerFarm),从入口资源开始,递归编译(babel, posthtml, postcss, vue-template-compiler等),编译完设置缓存,构建 Bundle 树,进行打包
如果没有 watch 监听,结束关闭 Watcher, Worker, HMR
有 watch 监听:
文件修改,触发 onChange,将修改的资源加入构建队列,递归编译,查找缓存(这一步缓存的作用就提醒出来了),编译完设置新缓存,构建 Bundle 树,进行打包,将 change 的资源发送给浏览器,浏览器接收 hmr 更新资源
以上是Parcel源码的详细分析(附示例)的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 从C/C到JavaScript:所有工作方式Apr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
从C/C到JavaScript:所有工作方式Apr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM从C/C 转向JavaScript需要适应动态类型、垃圾回收和异步编程等特点。1)C/C 是静态类型语言,需手动管理内存,而JavaScript是动态类型,垃圾回收自动处理。2)C/C 需编译成机器码,JavaScript则为解释型语言。3)JavaScript引入闭包、原型链和Promise等概念,增强了灵活性和异步编程能力。
 JavaScript引擎:比较实施Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScript引擎:比较实施Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM不同JavaScript引擎在解析和执行JavaScript代码时,效果会有所不同,因为每个引擎的实现原理和优化策略各有差异。1.词法分析:将源码转换为词法单元。2.语法分析:生成抽象语法树。3.优化和编译:通过JIT编译器生成机器码。4.执行:运行机器码。V8引擎通过即时编译和隐藏类优化,SpiderMonkey使用类型推断系统,导致在相同代码上的性能表现不同。
 超越浏览器:现实世界中的JavaScriptApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AM
超越浏览器:现实世界中的JavaScriptApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AMJavaScript在现实世界中的应用包括服务器端编程、移动应用开发和物联网控制:1.通过Node.js实现服务器端编程,适用于高并发请求处理。2.通过ReactNative进行移动应用开发,支持跨平台部署。3.通过Johnny-Five库用于物联网设备控制,适用于硬件交互。
 使用Next.js(后端集成)构建多租户SaaS应用程序Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
使用Next.js(后端集成)构建多租户SaaS应用程序Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM我使用您的日常技术工具构建了功能性的多租户SaaS应用程序(一个Edtech应用程序),您可以做同样的事情。 首先,什么是多租户SaaS应用程序? 多租户SaaS应用程序可让您从唱歌中为多个客户提供服务
 如何使用Next.js(前端集成)构建多租户SaaS应用程序Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
如何使用Next.js(前端集成)构建多租户SaaS应用程序Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM本文展示了与许可证确保的后端的前端集成,并使用Next.js构建功能性Edtech SaaS应用程序。 前端获取用户权限以控制UI的可见性并确保API要求遵守角色库
 JavaScript:探索网络语言的多功能性Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript:探索网络语言的多功能性Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AMJavaScript是现代Web开发的核心语言,因其多样性和灵活性而广泛应用。1)前端开发:通过DOM操作和现代框架(如React、Vue.js、Angular)构建动态网页和单页面应用。2)服务器端开发:Node.js利用非阻塞I/O模型处理高并发和实时应用。3)移动和桌面应用开发:通过ReactNative和Electron实现跨平台开发,提高开发效率。
 JavaScript的演变:当前的趋势和未来前景Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
JavaScript的演变:当前的趋势和未来前景Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AMJavaScript的最新趋势包括TypeScript的崛起、现代框架和库的流行以及WebAssembly的应用。未来前景涵盖更强大的类型系统、服务器端JavaScript的发展、人工智能和机器学习的扩展以及物联网和边缘计算的潜力。
 神秘的JavaScript:它的作用以及为什么重要Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
神秘的JavaScript:它的作用以及为什么重要Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AMJavaScript是现代Web开发的基石,它的主要功能包括事件驱动编程、动态内容生成和异步编程。1)事件驱动编程允许网页根据用户操作动态变化。2)动态内容生成使得页面内容可以根据条件调整。3)异步编程确保用户界面不被阻塞。JavaScript广泛应用于网页交互、单页面应用和服务器端开发,极大地提升了用户体验和跨平台开发的灵活性。


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

螳螂BT
Mantis是一个易于部署的基于Web的缺陷跟踪工具,用于帮助产品缺陷跟踪。它需要PHP、MySQL和一个Web服务器。请查看我们的演示和托管服务。

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) 是一个PHP/MySQL的Web应用程序,非常容易受到攻击。它的主要目标是成为安全专业人员在合法环境中测试自己的技能和工具的辅助工具,帮助Web开发人员更好地理解保护Web应用程序的过程,并帮助教师/学生在课堂环境中教授/学习Web应用程序安全。DVWA的目标是通过简单直接的界面练习一些最常见的Web漏洞,难度各不相同。请注意,该软件中

MinGW - 适用于 Windows 的极简 GNU
这个项目正在迁移到osdn.net/projects/mingw的过程中,你可以继续在那里关注我们。MinGW:GNU编译器集合(GCC)的本地Windows移植版本,可自由分发的导入库和用于构建本地Windows应用程序的头文件;包括对MSVC运行时的扩展,以支持C99功能。MinGW的所有软件都可以在64位Windows平台上运行。

SecLists
SecLists是最终安全测试人员的伙伴。它是一个包含各种类型列表的集合,这些列表在安全评估过程中经常使用,都在一个地方。SecLists通过方便地提供安全测试人员可能需要的所有列表,帮助提高安全测试的效率和生产力。列表类型包括用户名、密码、URL、模糊测试有效载荷、敏感数据模式、Web shell等等。测试人员只需将此存储库拉到新的测试机上,他就可以访问到所需的每种类型的列表。





