本篇文章给大家带来的内容是关于React首次渲染的解析(纯DOM元素),有一定的参考价值,有需要的朋友可以参考一下,希望对你有所帮助。
React 是一个十分庞大的库,由于要同时考虑 ReactDom 和 ReactNative ,还有服务器渲染等,导致其代码抽象化程度很高,嵌套层级非常深,阅读其源码是一个非常艰辛的过程。在学习 React 源码的过程中,给我帮助最大的就是这个系列文章,于是决定基于这个系列文章谈一下自己的理解。本文会大量用到原文中的例子,想体会原汁原味的感觉,推荐阅读原文。
本系列文章将基于 React 15.4.2。
React.createElement
在写 React 项目的时候,我们一般会直接用 JSX 的形式来写,而 JSX 经过 Babel 编译后最终会将 HTML 标签转换为React.createElement的函数形式。如果想进行更深入的了解,可以看我之前写的这篇文章:你不知道的Virtual DOM(一):Virtual Dom介绍。文章中的h函数,如果不在 Babel 中配置的话,默认就是React.createElement。
下面,我们将从一个最简单的例子,来看React是如何渲染的
ReactDOM.render(
<h1 style={{"color":"blue"}}>hello world</h1>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
经过JSX编译后,会是下面这个样子
ReactDOM.render(
React.createElement(
'h1',
{ style: { "color": "blue" } },
'hello world'
),
document.getElementById('root')
);
先来看下React.createElement的源码。
// 文件位置:src/isomorphic/React.js
var ReactElement = require('ReactElement');
...
var createElement = ReactElement.createElement;
...
var React = {
...
createElement: createElement,
...
}
module.exports = React;
最终的实现需要查看ReactElement.createElement:
// 文件位置:src/isomorphic/classic/element/ReactElement.js
ReactElement.createElement = function (type, config, children) {
...
// 1. 将过滤后的有效的属性,从config拷贝到props
if (config != null) {
...
for (propName in config) {
if (hasOwnProperty.call(config, propName) &&
!RESERVED_PROPS.hasOwnProperty(propName)) {
props[propName] = config[propName];
}
}
}
// 2. 将children以数组的形式拷贝到props.children属性
var childrenLength = arguments.length - 2;
if (childrenLength === 1) {
props.children = children;
} else if (childrenLength > 1) {
var childArray = Array(childrenLength);
for (var i = 0; i < childrenLength; i++) {
childArray[i] = arguments[i + 2];
}
if (__DEV__) {
if (Object.freeze) {
Object.freeze(childArray);
}
}
props.children = childArray;
}
// 3. 默认属性赋值
if (type && type.defaultProps) {
var defaultProps = type.defaultProps;
for (propName in defaultProps) {
if (props[propName] === undefined) {
props[propName] = defaultProps[propName];
}
}
}
...
return ReactElement(
type,
key,
ref,
self,
source,
ReactCurrentOwner.current,
props
);
};本质上只做了3件事:
将过滤后的有效的属性,从config拷贝到props
将children以数组的形式拷贝到props.children属性
默认属性赋值
最终的返回值是ReactElement。我们再来看看它做了什么
// 文件位置:src/isomorphic/classic/element/ReactElement.js
var ReactElement = function (type, key, ref, self, source, owner, props) {
var element = {
// This tag allow us to uniquely identify this as a React Element
$$typeof: REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE,
// Built-in properties that belong on the element
type: type,
key: key,
ref: ref,
props: props,
// Record the component responsible for creating this element.
_owner: owner,
};
...
return element;
};最终只是返回了一个简单对象。调用栈是这样的:
React.createElement
|=ReactElement.createElement(type, config, children)
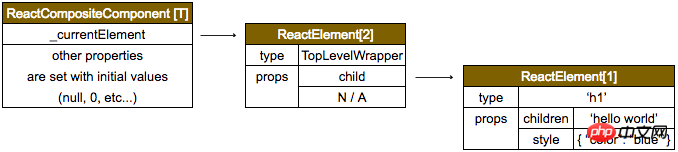
|-ReactElement(type,..., props)这里生成的 ReactElement 我们将其命名为ReactElement[1],它将作为参数传入到 ReactDom.render。
ReactDom.render
ReactDom.render 最终会调用 ReactMount 的 _renderSubtreeIntoContainer:
// 文件位置:src/renderers/dom/client/ReactMount.js
_renderSubtreeIntoContainer: function (parentComponent, nextElement, container, callback) {
...
var nextWrappedElement = React.createElement(
TopLevelWrapper,
{
child: nextElement
}
);
...
var component = ReactMount._renderNewRootComponent(
nextWrappedElement,
container,
shouldReuseMarkup,
nextContext
)._renderedComponent.getPublicInstance();
...
return component;
},
...
var TopLevelWrapper = function () {
this.rootID = topLevelRootCounter++;
};
TopLevelWrapper.prototype.isReactComponent = {};
TopLevelWrapper.prototype.render = function () {
return this.props.child;
};
TopLevelWrapper.isReactTopLevelWrapper = true;
...
_renderNewRootComponent: function (
nextElement,
container,
shouldReuseMarkup,
context
) {
...
var componentInstance = instantiateReactComponent(nextElement, false);
...
return componentInstance;
},这里又会调用到另一个文件 instantiateReactComponent:
// 文件位置:src/renders/shared/stack/reconciler/instantiateReactComponent.js
function instantiateReactComponent(node, shouldHaveDebugID) {
var instance;
...
instance = new ReactCompositeComponentWrapper(element);
...
return instance;
}
// To avoid a cyclic dependency, we create the final class in this module
var ReactCompositeComponentWrapper = function (element) {
this.construct(element);
};
Object.assign(
ReactCompositeComponentWrapper.prototype,
ReactCompositeComponent,
{
_instantiateReactComponent: instantiateReactComponent,
}
);这里又会调用到另一个文件 ReactCompositeComponent:
// 文件位置:src/renders/shared/stack/reconciler/ReactCompositeComponent.js
var ReactCompositeComponent = {
construct: function (element) {
this._currentElement = element;
this._rootNodeID = 0;
this._compositeType = null;
this._instance = null;
this._hostParent = null;
this._hostContainerInfo = null;
// See ReactUpdateQueue
this._updateBatchNumber = null;
this._pendingElement = null;
this._pendingStateQueue = null;
this._pendingReplaceState = false;
this._pendingForceUpdate = false;
this._renderedNodeType = null;
this._renderedComponent = null;
this._context = null;
this._mountOrder = 0;
this._topLevelWrapper = null;
// See ReactUpdates and ReactUpdateQueue.
this._pendingCallbacks = null;
// ComponentWillUnmount shall only be called once
this._calledComponentWillUnmount = false;
if (__DEV__) {
this._warnedAboutRefsInRender = false;
}
}
...
}我们用ReactCompositeComponent[T]来表示这里生成的顶层 component。
整个的调用栈是这样的:
ReactDOM.render
|=ReactMount.render(nextElement, container, callback)
|=ReactMount._renderSubtreeIntoContainer()
|-ReactMount._renderNewRootComponent(
nextWrappedElement, // scr:------------------> ReactElement[2]
container, // scr:------------------> document.getElementById('root')
shouldReuseMarkup, // scr: null from ReactDom.render()
nextContext, // scr: emptyObject from ReactDom.render()
)
|-instantiateReactComponent(
node, // scr:------------------> ReactElement[2]
shouldHaveDebugID /* false */
)
|-ReactCompositeComponentWrapper(
element // scr:------------------> ReactElement[2]
);
|=ReactCompositeComponent.construct(element)
组件间的层级结构是这样的:
当顶层组件构建完毕后,下一步就是调用 batchedMountComponentIntoNode(来自 ReactMount 的 _renderNewRootComponent方法),进行页面的渲染了。
以上是React首次渲染的解析一(纯DOM元素)的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 Python vs. JavaScript:选择合适的工具May 08, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:选择合适的工具May 08, 2025 am 12:10 AM选择Python还是JavaScript取决于项目类型:1)数据科学和自动化任务选择Python;2)前端和全栈开发选择JavaScript。Python因其在数据处理和自动化方面的强大库而备受青睐,而JavaScript则因其在网页交互和全栈开发中的优势而不可或缺。
 Python和JavaScript:了解每个的优势May 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python和JavaScript:了解每个的优势May 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMPython和JavaScript各有优势,选择取决于项目需求和个人偏好。1.Python易学,语法简洁,适用于数据科学和后端开发,但执行速度较慢。2.JavaScript在前端开发中无处不在,异步编程能力强,Node.js使其适用于全栈开发,但语法可能复杂且易出错。
 JavaScript的核心:它是在C还是C上构建的?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript的核心:它是在C还是C上构建的?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AMjavascriptisnotbuiltoncorc; saninterpretedlanguagethatrunsonenginesoftenwritteninc.1)javascriptwasdesignedAsalightweight,解释edganguageforwebbrowsers.2)Enginesevolvedfromsimpleterterterpretpreterterterpretertestojitcompilerers,典型地提示。
 JavaScript应用程序:从前端到后端May 04, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript应用程序:从前端到后端May 04, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript可用于前端和后端开发。前端通过DOM操作增强用户体验,后端通过Node.js处理服务器任务。1.前端示例:改变网页文本内容。2.后端示例:创建Node.js服务器。
 Python vs. JavaScript:您应该学到哪种语言?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:您应该学到哪种语言?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM选择Python还是JavaScript应基于职业发展、学习曲线和生态系统:1)职业发展:Python适合数据科学和后端开发,JavaScript适合前端和全栈开发。2)学习曲线:Python语法简洁,适合初学者;JavaScript语法灵活。3)生态系统:Python有丰富的科学计算库,JavaScript有强大的前端框架。
 JavaScript框架:为现代网络开发提供动力May 02, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JavaScript框架:为现代网络开发提供动力May 02, 2025 am 12:04 AMJavaScript框架的强大之处在于简化开发、提升用户体验和应用性能。选择框架时应考虑:1.项目规模和复杂度,2.团队经验,3.生态系统和社区支持。
 JavaScript,C和浏览器之间的关系May 01, 2025 am 12:06 AM
JavaScript,C和浏览器之间的关系May 01, 2025 am 12:06 AM引言我知道你可能会觉得奇怪,JavaScript、C 和浏览器之间到底有什么关系?它们之间看似毫无关联,但实际上,它们在现代网络开发中扮演着非常重要的角色。今天我们就来深入探讨一下这三者之间的紧密联系。通过这篇文章,你将了解到JavaScript如何在浏览器中运行,C 在浏览器引擎中的作用,以及它们如何共同推动网页的渲染和交互。JavaScript与浏览器的关系我们都知道,JavaScript是前端开发的核心语言,它直接在浏览器中运行,让网页变得生动有趣。你是否曾经想过,为什么JavaScr
 node.js流带打字稿Apr 30, 2025 am 08:22 AM
node.js流带打字稿Apr 30, 2025 am 08:22 AMNode.js擅长于高效I/O,这在很大程度上要归功于流。 流媒体汇总处理数据,避免内存过载 - 大型文件,网络任务和实时应用程序的理想。将流与打字稿的类型安全结合起来创建POWE


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

WebStorm Mac版
好用的JavaScript开发工具

适用于 Eclipse 的 SAP NetWeaver 服务器适配器
将Eclipse与SAP NetWeaver应用服务器集成。

SublimeText3 英文版
推荐:为Win版本,支持代码提示!

MinGW - 适用于 Windows 的极简 GNU
这个项目正在迁移到osdn.net/projects/mingw的过程中,你可以继续在那里关注我们。MinGW:GNU编译器集合(GCC)的本地Windows移植版本,可自由分发的导入库和用于构建本地Windows应用程序的头文件;包括对MSVC运行时的扩展,以支持C99功能。MinGW的所有软件都可以在64位Windows平台上运行。






