sql数据库语句优化分析和优化技巧总结(sql优化工具)
- php是最好的语言原创
- 2018-08-03 17:37:099874浏览
通常sql数据库需要进行优化分析,并且还有一定的技巧,sql优化的几种方法这里就不做详细介绍了,本文将会sql语句优化进行总结,后面还附了优化工具SQL Tuning Expert for Oracle及使用方法,首先我们要遵随数据库优化的几个原则:
1.尽量避免在列上做运算,这样会导致索引失败;
2.使用join是应该用小结果集驱动大结果集,同时把复杂的join查询拆分成多个query。不然join的越多表,就会导致越多的锁定和堵塞。
3.注意like模糊查询的使用,避免使用%%,例如select * from a where name like '%de%';
代替语句:select * from a where name >= 'de' and name < 'df';
4.仅列出需要查询的字段,不要使用select * from ...,节省内存;
5.使用批量插入语句,节省交互;
insert into a (id ,name) values(2,'a'), (3,'s');
6.limit基数比较大时,使用between ... and ...
7.不要使用rand函数随机获取记录;
8.避免使用null ,这就需要在建表时,尽量设置为not null,提升查询性能;
9,不要使用count(id),而应该是count(*)
10.不要做无谓的排序,尽可能在索引中完成排序;
我们先来看一个sql:
select
ii.product_id,
p.product_name,
count(distinct pim.pallet_id) count_pallet_id,
if(round(sum(itg.quantity),2) > -1 && round(sum(itg.quantity),2) < 0.005, 0, round(sum(itg.quantity),2)) quantity,
round(ifnull(sum(itag.locked_quantity), 0.00000),2) locked_quantity,
pc.container_unit_code_name,
if(round(sum(itg.qoh),2) > -1 && round(sum(itg.qoh),2) < 0.005, 0, round(sum(itg.qoh),2)) qoh,
round(ifnull(sum(itag.locked_qoh), 0.00000),2) locked_qoh,
p.unit_code,
p.unit_code_name
from (select
it.inventory_item_id item_id,
sum(it.quantity) quantity,
sum(it.real_quantity) qoh
from
ws_inventory_transaction it
where
it.enabled = 1
group by
it.inventory_item_id
) itg
left join (select
ita.inventory_item_id item_id,
sum(ita.quantity) locked_quantity,
sum(ita.real_quantity) locked_qoh
from
ws_inventory_transaction_action ita
where
1=1 and ita.type in ('locked', 'release')
group by
ita.inventory_item_id
)itag on itg.item_id = itag.item_id
inner join ws_inventory_item ii on itg.item_id = ii.inventory_item_id
inner join ws_pallet_item_mapping pim on ii.inventory_item_id = pim.inventory_item_id
inner join ws_product p on ii.product_id = p.product_id and p.status = 'OK'
left join ws_product_container pc on ii.container_id = pc.container_id
//总起来说关联太多表,设计表时可以多一些冗余字段,减少表之间的关联查询;
where
ii.inventory_type = 'raw_material' and
ii.inventory_status = 'in_stock' and
ii.facility_id = '25' and
datediff(now(),ii.last_updated_time) < 3 //违反了第一个原则
and p.product_type = 'goods'
and p.product_name like '%果%' // 违反原则3
group by
ii.product_id
having
qoh < 0.005
order by
qoh desc上面的sql我们在from 中使用了子查询,这样对查询是非常不利的;
更好的一种做法是下面的语句:
select
t.facility_id,
f.facility_name,
t.inventory_status,
wis.inventory_status_name,
t.inventory_type,
t.product_type,
t.product_id,
p.product_name,
t.container_id,
t.unit_quantity,
p.unit_code,
p.unit_code_name,
pc.container_unit_code_name,
t.secret_key,
sum(t.quantity) quantity,
sum(t.real_quantity) real_quantity,
sum(t.locked_quantity) locked_quantity,
sum(t.locked_real_quantity) locked_real_quantity
from ( select
ii.facility_id,
ii.inventory_status,
ii.inventory_type,
ii.product_type,
ii.product_id,
ii.container_id,
ii.unit_quantity,
ita.secret_key,
ii.quantity quantity,
ii.real_quantity real_quantity,
sum(ita.quantity) locked_quantity,
sum(ita.real_quantity) locked_real_quantity
from
ws_inventory_item ii
inner join ws_inventory_transaction_action ita on ii.inventory_item_id = ita.inventory_item_id
where
ii.facility_id = '{$facility_id}' and
ii.inventory_status = '{$inventory_status}' and
ii.product_type = '{$product_type}' and
ii.inventory_type = '{$inventory_type}' and
ii.locked_real_quantity > 0 and
ita.type in ('locked', 'release')
group by
ii.product_id, ita.secret_key, ii.container_id, ita.inventory_item_id
having
locked_real_quantity > 0
) as t
inner join ws_product p on t.product_id = p.product_id
left join ws_facility f on t.facility_id = f.facility_id
left join ws_inventory_status wis on wis.inventory_status = t.inventory_status
left join ws_product_container pc on pc.container_id = t.container_id
group by
t.product_id, t.secret_key, t.container_id注意:
1、from 语句中一定不要使用子查询;
2、使用更多的where加以限制,缩小查找范围;
3、合理利用索引;
4、通过explain查看sql性能;
使用工具 SQL Tuning Expert for Oracle 优化SQL语句
对于SQL开发人员和DBA来说,根据业务需求写出一条正确的SQL很容易。但是SQL的执行性能怎么样呢?能优化一下跑得更快吗?如果不是资深
DBA,估计很多人都没有信心。
幸运的是,自动化优化工具可以帮助我们解决这个难题。这就是今天要介绍的 Tosska SQL Tuning Expert for Oracle 工具。
下载 https://tosska.com/tosska-sql-tuning-expert-tse-oracle-free-download/
本工具发明人Richard To, Dell的前首席工程师, 拥有超过20年的SQL优化经验.
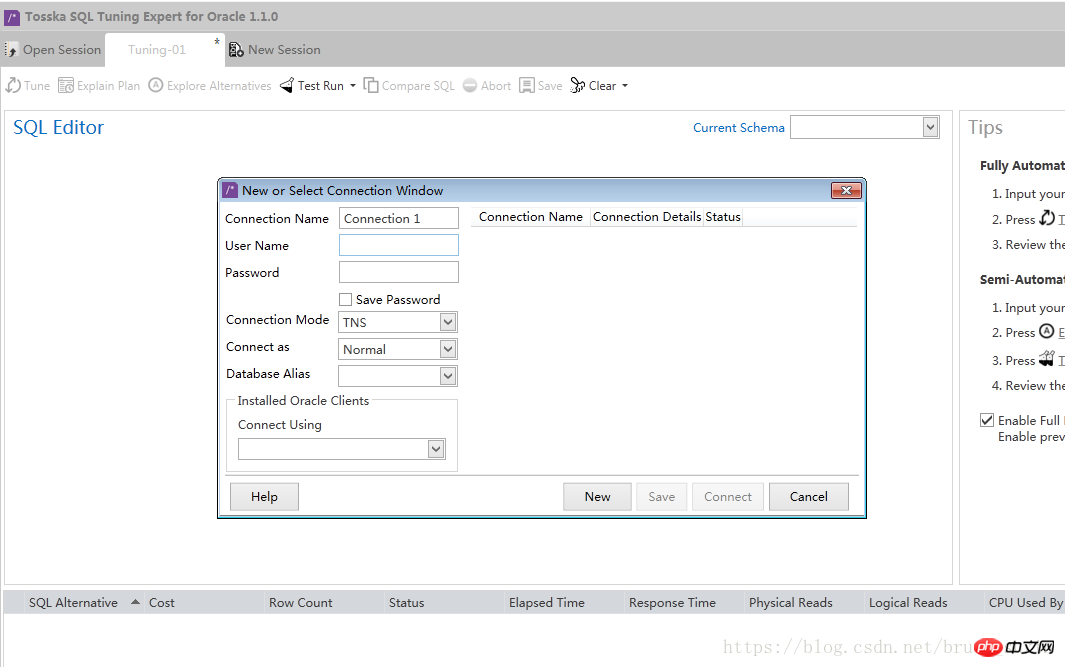
1、创建数据库连接,也可以稍后创建。填好连接信息,点击 “Connect” 按钮。
如果您已经安装Oracle客户端,并且在Oracle客户端配置了TNS,可以在本窗口选择“TNS”作为”Connection Mode”,然后在”Database Alias”中选择配置好的TNS作为数据库别名。
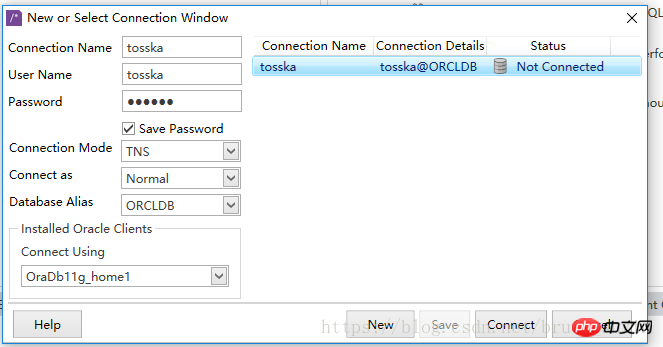
如果您没有安装Oracle客户端或者不想安装Oracle客户端, 可以选择“Basic Type”作为”Connection Mode”,只需数据库服务器IP, 端口和服务名即可。
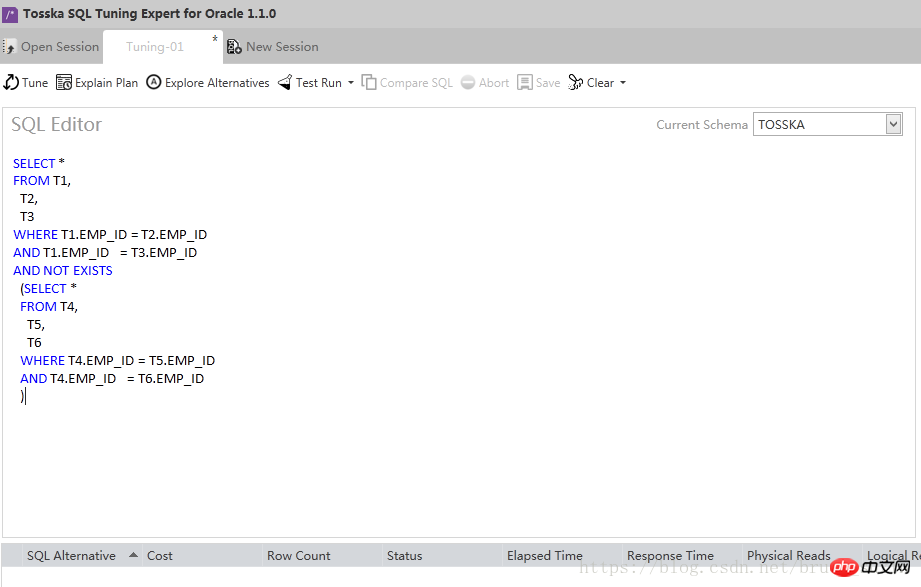
2、输入有性能问题的SQL
3、点击Tune按钮,自动生成大量的等价SQL并且开始执行。虽然测试还没有完成,我们已经可以看到 SQL 20 的性能提升了100%。
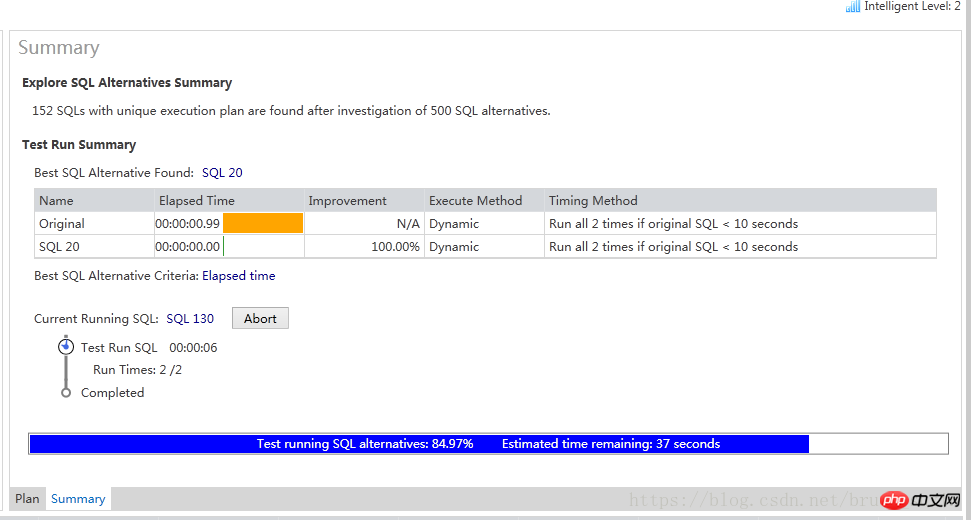
让我们仔细看一下SQL 20, 它使用了两个Hints, 以最快的执行速度脱颖而出。原来的SQL要0.99秒,优化后的SQL执行时间接近0秒。
由于这条SQL每天要在数据库中执行上万次,优化后可节省大约 165秒的数据库执行时间。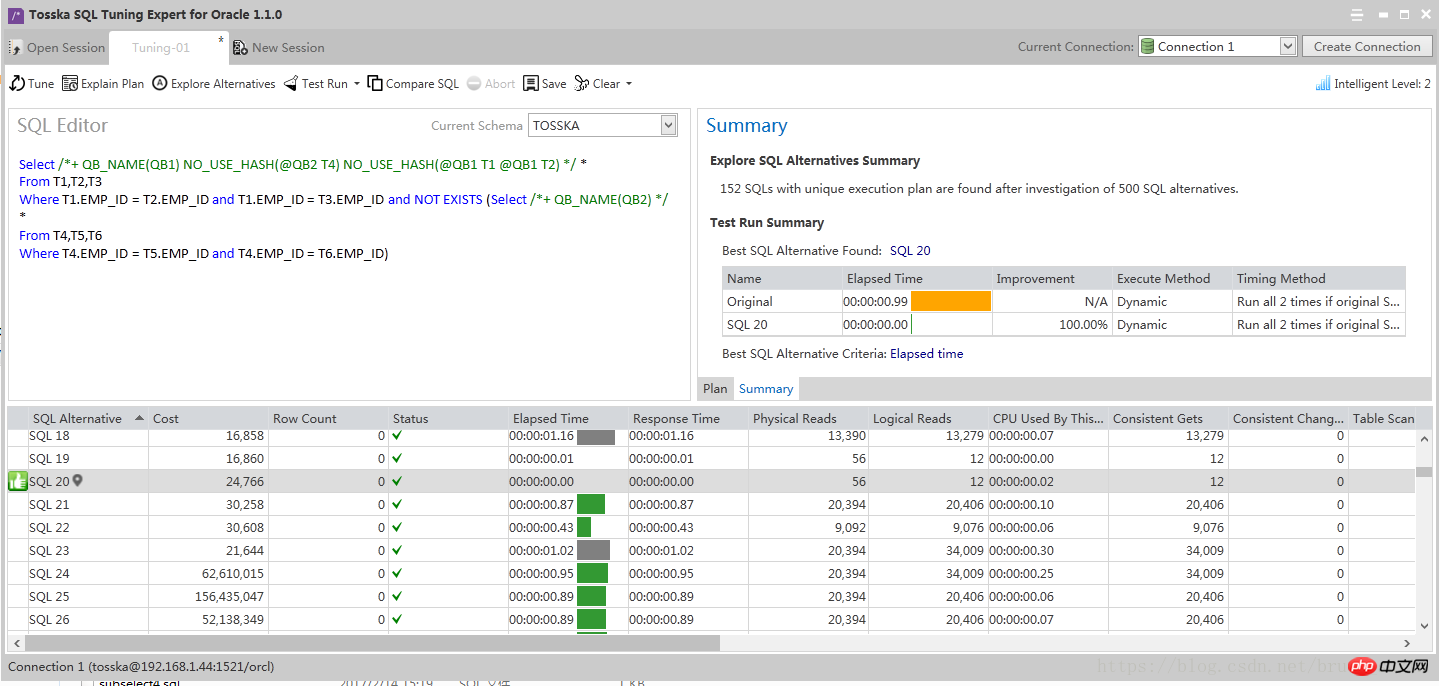
最后,用等价的SQL 20 替换 应用程序源代码中有性能问题的SQL。重新编译应用程序,性能得到了提高。
调优任务顺利完成!
相关文章:
相关视频:
以上是sql数据库语句优化分析和优化技巧总结(sql优化工具)的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

