
本系列文章在实现一个 (x)react 的同时理顺 React 框架的主干内容(JSX/虚拟DOM/组件/生命周期/diff算法/...)
从 0 到 1 实现 React 系列 —— JSX 和 Virtual DOM
从 0 到 1 实现 React 系列 —— 组件和 state|props
生命周期
先来回顾 React 的生命周期,用流程图表示如下:
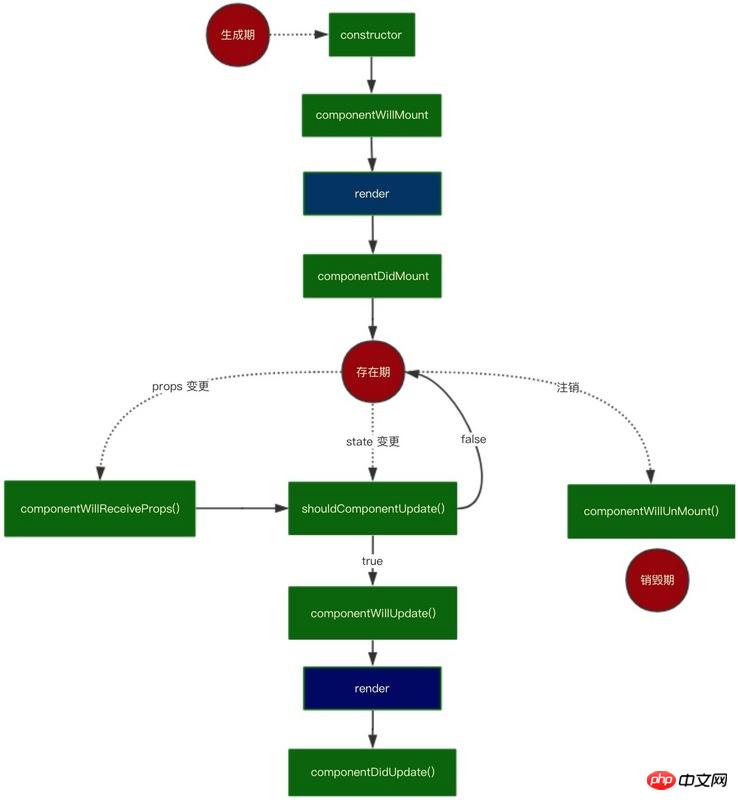
该流程图比较清晰地呈现了 react 的生命周期。其分为 3 个阶段 —— 生成期,存在期,销毁期。
因为生命周期钩子函数存在于自定义组件中,将之前 _render 函数作些调整如下:
// 原来的 _render 函数,为了将职责拆分得更细,将 virtual dom 转为 real dom 的函数单独抽离出来
function vdomToDom(vdom) {
if (_.isFunction(vdom.nodeName)) { // 为了更加方便地书写生命周期逻辑,将解析自定义组件逻辑和一般 html 标签的逻辑分离开
const component = createComponent(vdom) // 构造组件
setProps(component) // 更改组件 props
renderComponent(component) // 渲染组件,将 dom 节点赋值到 component
return component.base // 返回真实 dom
}
...
}我们可以在 setProps 函数内(渲染前)加入 componentWillMount,componentWillReceiveProps 方法,setProps 函数如下:
function setProps(component) {
if (component && component.componentWillMount) {
component.componentWillMount()
} else if (component.base && component.componentWillReceiveProps) {
component.componentWillReceiveProps(component.props) // 后面待实现
}
}而后我们在 renderComponent 函数内加入 componentDidMount、shouldComponentUpdate、componentWillUpdate、componentDidUpdate 方法
function renderComponent(component) {
if (component.base && component.shouldComponentUpdate) {
const bool = component.shouldComponentUpdate(component.props, component.state)
if (!bool && bool !== undefined) {
return false // shouldComponentUpdate() 返回 false,则生命周期终止
}
}
if (component.base && component.componentWillUpdate) {
component.componentWillUpdate()
}
const rendered = component.render()
const base = vdomToDom(rendered)
if (component.base && component.componentDidUpdate) {
component.componentDidUpdate()
} else if (component && component.componentDidMount) {
component.componentDidMount()
}
if (component.base && component.base.parentNode) { // setState 进入此逻辑
component.base.parentNode.replaceChild(base, component.base)
}
component.base = base // 标志符
}测试生命周期
测试如下用例:
class A extends Component {
componentWillReceiveProps(props) {
console.log('componentWillReceiveProps')
}
render() {
return (
<p>{this.props.count}</p>
)
}
}
class B extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
count: 1
}
}
componentWillMount() {
console.log('componentWillMount')
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('componentDidMount')
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
console.log('shouldComponentUpdate', nextProps, nextState)
return true
}
componentWillUpdate() {
console.log('componentWillUpdate')
}
componentDidUpdate() {
console.log('componentDidUpdate')
}
click() {
this.setState({
count: ++this.state.count
})
}
render() {
console.log('render')
return (
<p>
<button onClick={this.click.bind(this)}>Click Me!</button>
<A count={this.state.count} />
</p>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(
<B />,
document.getElementById('root')
)页面加载时输出结果如下:
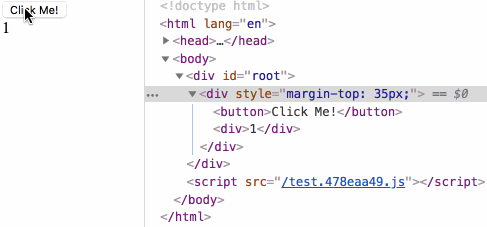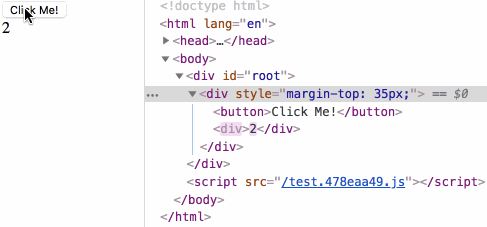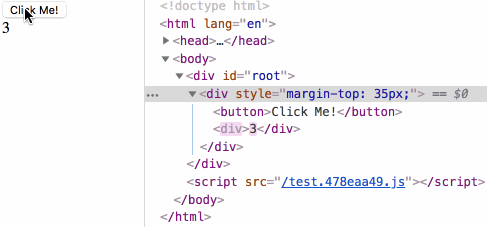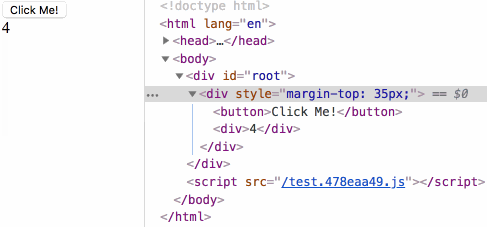
componentWillMount render componentDidMount
点击按钮时输出结果如下:
shouldComponentUpdate componentWillUpdate render componentDidUpdate
diff 的实现
在 react 中,diff 实现的思路是将新老 virtual dom 进行比较,将比较后的 patch(补丁)渲染到页面上,从而实现局部刷新;本文借鉴了 preact 和 simple-react 中的 diff 实现,总体思路是将旧的 dom 节点和新的 virtual dom 节点进行了比较,根据不同的比较类型(文本节点、非文本节点、自定义组件)调用相应的逻辑,从而实现页面的局部渲染。代码总体结构如下:
/**
* 比较旧的 dom 节点和新的 virtual dom 节点:
* @param {*} oldDom 旧的 dom 节点
* @param {*} newVdom 新的 virtual dom 节点
*/
function diff(oldDom, newVdom) {
...
if (_.isString(newVdom)) {
return diffTextDom(oldDom, newVdom) // 对比文本 dom 节点
}
if (oldDom.nodeName.toLowerCase() !== newVdom.nodeName) {
diffNotTextDom(oldDom, newVdom) // 对比非文本 dom 节点
}
if (_.isFunction(newVdom.nodeName)) {
return diffComponent(oldDom, newVdom) // 对比自定义组件
}
diffAttribute(oldDom, newVdom) // 对比属性
if (newVdom.children.length > 0) {
diffChild(oldDom, newVdom) // 遍历对比子节点
}
return oldDom
}下面根据不同比较类型实现相应逻辑。
对比文本节点
首先进行较为简单的文本节点的比较,代码如下:
// 对比文本节点
function diffTextDom(oldDom, newVdom) {
let dom = oldDom
if (oldDom && oldDom.nodeType === 3) { // 如果老节点是文本节点
if (oldDom.textContent !== newVdom) { // 这里一个细节:textContent/innerHTML/innerText 的区别
oldDom.textContent = newVdom
}
} else { // 如果旧 dom 元素不为文本节点
dom = document.createTextNode(newVdom)
if (oldDom && oldDom.parentNode) {
oldDom.parentNode.replaceChild(dom, oldDom)
}
}
return dom
}对比非文本节点
对比非文本节点,其思路为将同层级的旧节点替换为新节点,代码如下:
// 对比非文本节点
function diffNotTextDom(oldDom, newVdom) {
const newDom = document.createElement(newVdom.nodeName);
[...oldDom.childNodes].map(newDom.appendChild) // 将旧节点下的元素添加到新节点下
if (oldDom && oldDom.parentNode) {
oldDom.parentNode.replaceChild(oldDom, newDom)
}
}对比自定义组件
对比自定义组件的思路为:如果新老组件不同,则直接将新组件替换老组件;如果新老组件相同,则将新组件的 props 赋到老组件上,然后再对获得新 props 前后的老组件做 diff 比较。代码如下:
// 对比自定义组件
function diffComponent(oldDom, newVdom) {
if (oldDom._component && (oldDom._component.constructor !== newVdom.nodeName)) { // 如果新老组件不同,则直接将新组件替换老组件
const newDom = vdomToDom(newVdom)
oldDom._component.parentNode.insertBefore(newDom, oldDom._component)
oldDom._component.parentNode.removeChild(oldDom._component)
} else {
setProps(oldDom._component, newVdom.attributes) // 如果新老组件相同,则将新组件的 props 赋到老组件上
renderComponent(oldDom._component) // 对获得新 props 前后的老组件做 diff 比较(renderComponent 中调用了 diff)
}
}遍历对比子节点
遍历对比子节点的策略有两个:一是只比较同层级的节点,二是给节点加上 key 属性。它们的目的都是降低空间复杂度。代码如下:
// 对比子节点
function diffChild(oldDom, newVdom) {
const keyed = {}
const children = []
const oldChildNodes = oldDom.childNodes
for (let i = 0; i < oldChildNodes.length; i++) {
if (oldChildNodes[i].key) { // 将含有 key 的节点存进对象 keyed
keyed[oldChildNodes[i].key] = oldChildNodes[i]
} else { // 将不含有 key 的节点存进数组 children
children.push(oldChildNodes[i])
}
}
const newChildNodes = newVdom.children
let child
for (let i = 0; i < newChildNodes.length; i++) {
if (keyed[newChildNodes[i].key]) { // 对应上面存在 key 的情形
child = keyed[newChildNodes[i].key]
keyed[newChildNodes[i].key] = undefined
} else { // 对应上面不存在 key 的情形
for (let j = 0; j < children.length; j++) {
if (isSameNodeType(children[i], newChildNodes[i])) { // 如果不存在 key,则优先找到节点类型相同的元素
child = children[i]
children[i] = undefined
break
}
}
}
diff(child, newChildNodes[i]) // 递归比较
}
}测试
在生命周期的小节中,componentWillReceiveProps 方法还未跑通,稍加修改 setProps 函数即可:
/**
* 更改属性,componentWillMount 和 componentWillReceiveProps 方法
*/
function setProps(component, attributes) {
if (attributes) {
component.props = attributes // 这段逻辑对应上文自定义组件比较中新老组件相同时 setProps 的逻辑
}
if (component && component.base && component.componentWillReceiveProps) {
component.componentWillReceiveProps(component.props)
} else if (component && component.componentWillMount) {
component.componentWillMount()
}
}来测试下生命周期小节中最后的测试用例:
生命周期测试
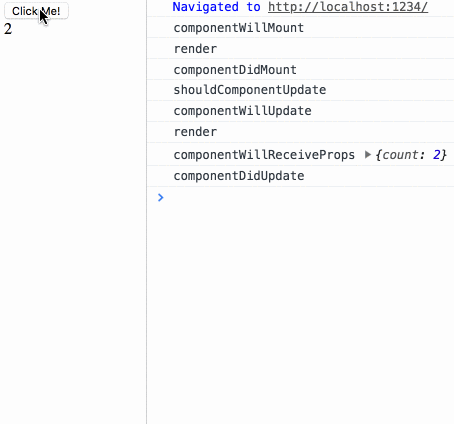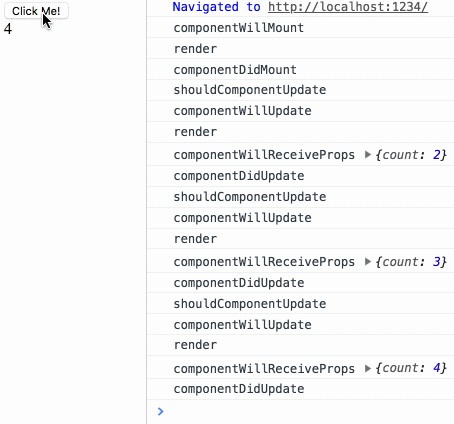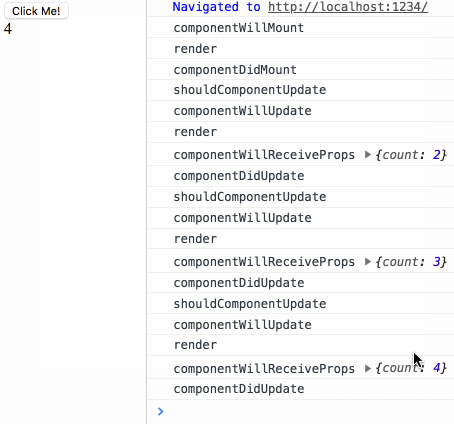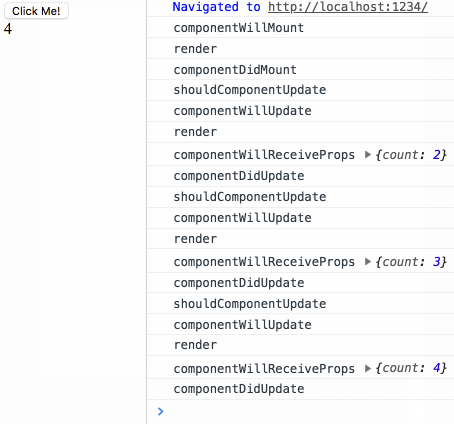
diff 测试
项目地址,关于如何 pr
相关文章:
相关视频:
以上是从 0 到 1 实现 React 系列:生命周期和diff 的实现的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 Python vs. JavaScript:开发人员的比较分析May 09, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:开发人员的比较分析May 09, 2025 am 12:22 AMPython和JavaScript的主要区别在于类型系统和应用场景。1.Python使用动态类型,适合科学计算和数据分析。2.JavaScript采用弱类型,广泛用于前端和全栈开发。两者在异步编程和性能优化上各有优势,选择时应根据项目需求决定。
 Python vs. JavaScript:选择合适的工具May 08, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:选择合适的工具May 08, 2025 am 12:10 AM选择Python还是JavaScript取决于项目类型:1)数据科学和自动化任务选择Python;2)前端和全栈开发选择JavaScript。Python因其在数据处理和自动化方面的强大库而备受青睐,而JavaScript则因其在网页交互和全栈开发中的优势而不可或缺。
 Python和JavaScript:了解每个的优势May 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python和JavaScript:了解每个的优势May 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMPython和JavaScript各有优势,选择取决于项目需求和个人偏好。1.Python易学,语法简洁,适用于数据科学和后端开发,但执行速度较慢。2.JavaScript在前端开发中无处不在,异步编程能力强,Node.js使其适用于全栈开发,但语法可能复杂且易出错。
 JavaScript的核心:它是在C还是C上构建的?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript的核心:它是在C还是C上构建的?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AMjavascriptisnotbuiltoncorc; saninterpretedlanguagethatrunsonenginesoftenwritteninc.1)javascriptwasdesignedAsalightweight,解释edganguageforwebbrowsers.2)Enginesevolvedfromsimpleterterterpretpreterterterpretertestojitcompilerers,典型地提示。
 JavaScript应用程序:从前端到后端May 04, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript应用程序:从前端到后端May 04, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript可用于前端和后端开发。前端通过DOM操作增强用户体验,后端通过Node.js处理服务器任务。1.前端示例:改变网页文本内容。2.后端示例:创建Node.js服务器。
 Python vs. JavaScript:您应该学到哪种语言?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:您应该学到哪种语言?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM选择Python还是JavaScript应基于职业发展、学习曲线和生态系统:1)职业发展:Python适合数据科学和后端开发,JavaScript适合前端和全栈开发。2)学习曲线:Python语法简洁,适合初学者;JavaScript语法灵活。3)生态系统:Python有丰富的科学计算库,JavaScript有强大的前端框架。
 JavaScript框架:为现代网络开发提供动力May 02, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JavaScript框架:为现代网络开发提供动力May 02, 2025 am 12:04 AMJavaScript框架的强大之处在于简化开发、提升用户体验和应用性能。选择框架时应考虑:1.项目规模和复杂度,2.团队经验,3.生态系统和社区支持。
 JavaScript,C和浏览器之间的关系May 01, 2025 am 12:06 AM
JavaScript,C和浏览器之间的关系May 01, 2025 am 12:06 AM引言我知道你可能会觉得奇怪,JavaScript、C 和浏览器之间到底有什么关系?它们之间看似毫无关联,但实际上,它们在现代网络开发中扮演着非常重要的角色。今天我们就来深入探讨一下这三者之间的紧密联系。通过这篇文章,你将了解到JavaScript如何在浏览器中运行,C 在浏览器引擎中的作用,以及它们如何共同推动网页的渲染和交互。JavaScript与浏览器的关系我们都知道,JavaScript是前端开发的核心语言,它直接在浏览器中运行,让网页变得生动有趣。你是否曾经想过,为什么JavaScr


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

Dreamweaver Mac版
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)

EditPlus 中文破解版
体积小,语法高亮,不支持代码提示功能

MinGW - 适用于 Windows 的极简 GNU
这个项目正在迁移到osdn.net/projects/mingw的过程中,你可以继续在那里关注我们。MinGW:GNU编译器集合(GCC)的本地Windows移植版本,可自由分发的导入库和用于构建本地Windows应用程序的头文件;包括对MSVC运行时的扩展,以支持C99功能。MinGW的所有软件都可以在64位Windows平台上运行。

SecLists
SecLists是最终安全测试人员的伙伴。它是一个包含各种类型列表的集合,这些列表在安全评估过程中经常使用,都在一个地方。SecLists通过方便地提供安全测试人员可能需要的所有列表,帮助提高安全测试的效率和生产力。列表类型包括用户名、密码、URL、模糊测试有效载荷、敏感数据模式、Web shell等等。测试人员只需将此存储库拉到新的测试机上,他就可以访问到所需的每种类型的列表。






