这次给大家带来知名的网站前端布局分析,知名的网站前端布局分析注意事项有哪些,下面就是实战案例,一起来看一下。
一、水平居中
一,二,三章都是parent+son的简单结构,html代码和效果图就不贴出来了,第四章以后才有
(1)文本/行内元素/行内块级元素▲
原理:text-align只控制行内内容(文字、行内元素、行内块级元素)如何相对他的块父元素对齐
#parent{
text-align: center;
}
优缺点
优点:简单快捷,容易理解,兼容性非常好
缺点:只对行内内容有效;属性会继承影响到后代行内内容;如果子元素宽度大于父元素宽度则无效,只有后代行内内容中宽度小于设置text-align属性的元素宽度的时候,才会水平居中
(2)单个块级元素▲
原理:根据规范介绍得很清楚了,有这么一种情况:在margin有节余的同时如果左右margin设置了auto,将会均分剩余空间。另外,如果上下的margin设置了auto,其计算值为0
#son{
width: 100px; /*必须定宽*/
margin: 0 auto;
}
优缺点
优点:简单;兼容性好
缺点:必须定宽,并且值不能为auto;宽度要小于父元素,否则无效
(3)多个块级元素
原理:text-align只控制行内内容(文字、行内元素、行内块级元素)如何相对他的块父元素对齐
#parent{
text-align: center;
}
.son{
display: inline-block; /*改为行内或者行内块级形式,以达到text-align对其生效*/
}
优缺点
优点:简单,容易理解,兼容性非常好
缺点:只对行内内容有效;属性会继承影响到后代行内内容;块级改为inline-block换行、空格会产生元素间隔
(4)使用绝对定位实现▲
原理:子绝父相,top、right、bottom、left的值是相对于父元素尺寸的,然后margin或者transform是相对于自身尺寸的,组合使用达到水平居中的目的
#parent{
height: 200px;
width: 200px; /*定宽*/
position: relative; /*父相*/
background-color: #f00;
}
#son{
position: absolute; /*子绝*/
left: 50%; /*父元素宽度一半,这里等同于left:100px*/
transform: translateX(-50%); /*自身宽度一半,等同于margin-left: -50px;*/
width: 100px; /*定宽*/
height: 100px;
background-color: #00ff00;
}
优缺点
优点:使用margin-left兼容性好;不管是块级还是行内元素都可以实现
缺点:代码较多;脱离文档流;使用margin-left需要知道宽度值;使用transform兼容性不好(ie9+)
(5)任意个元素(flex)
原理:就是设置当前主轴对齐方式为居中。说不上为什么,flex无非就是主轴侧轴是重点,然后就是排列方式的设置,可以去看看文末的flex阅读推荐
#parent{
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
优缺点
优点:功能强大;简单方便;容易理解
缺点:PC端兼容性不好,移动端(Android4.0+)
本章小结:
对于水平居中,我们应该先考虑,哪些元素有自带的居中效果,最先想到的应该就是
text-align:center了,但是这个只对行内内容有效,所以我们要使用text-align:center就必须将子元素设置为display: inline;或者display: inline-block;;其次就是考虑能不能用
margin: 0 auto;,因为这都是一两句代码能搞定的事,实在不行就是用绝对定位去实现了。移动端能用flex就用flex,简单方便,灵活并且功能强大,无愧为网页布局的一大利器!
二、垂直居中
一,二,三章都是parent+son的简单结构,html代码和效果图就不贴出来了,第四章以后才有
(1)单行文本/行内元素/行内块级元素▲
原理:line-height的最终表现是通过inline box实现的,而无论inline box所占据的高度是多少(无论比文字大还是比文字小),其占据的空间都是与文字内容公用水平中垂线的。
#parent{
height: 150px;
line-height: 150px; /*与height等值*/
}
优缺点
优点:简单;兼容性好
缺点:只能用于单行行内内容;要知道高度的值
(2)多行文本/行内元素/行内块级元素
原理同上
#parent{ /*或者用span把所有文字包裹起来,设置display:inline-block转换成图片的方式解决*/
height: 150px;
line-height: 30px; /*元素在页面呈现为5行,则line-height的值为height/5*/
}
优缺点
优点:简单;兼容性好
缺点:只能用于行内内容;需要知道高度和最终呈现多少行来计算出line-height的值,建议用span包裹多行文本
(3)图片▲
原理:vertical-align和line-height的基友关系
#parent{
height: 150px;
line-height: 150px;
font-size: 0;
}
img#son{vertical-align: middle;} /*默认是基线对齐,改为middle*/
优缺点
优点:简单;兼容性好
缺点:需要添加font-size: 0; 才可以完全的垂直居中;不过需要主要,html#parent包裹img之间需要有换行或空格
(4)单个块级元素
html代码:
<p id="parent"> <p id="son"></p> </p>
(4-1) 使用tabel-cell实现:
原理:CSS Table,使表格内容对齐方式为middle
#parent{
display: table-cell;
vertical-align: middle;
}
优缺点
优点:简单;宽高不定;兼容性好(ie8+)
缺点:设置tabl-cell的元素,宽度和高度的值设置百分比无效,需要给它的父元素设置display: table; 才生效;table-cell不感知margin,在父元素上设置table-row等属性,也会使其不感知height;设置float或position会对默认布局造成破坏,可以考虑为之增加一个父p定义float等属性;内容溢出时会自动撑开父元素
(4-2) 使用绝对定位实现:▲
/*原理:子绝父相,top、right、bottom、left的值是相对于父元素尺寸的,然后margin或者transform是相对于自身尺寸的,组合使用达到水平居中的目的*/
#parent{
height: 150px;
position: relative; /*父相*/
}
#son{
position: absolute; /*子绝*/
top: 50%; /*父元素高度一半,这里等同于top:75px;*/
transform: translateY(-50%); /*自身高度一半,这里等同于margin-top:-25px;*/
height: 50px;
}
/*优缺点
- 优点:使用margin-top兼容性好;不管是块级还是行内元素都可以实现
- 缺点:代码较多;脱离文档流;使用margin-top需要知道高度值;使用transform兼容性不好(ie9+)*/
或
/*原理:当top、bottom为0时,margin-top&bottom会无限延伸占满空间并且平分*/
#parent{position: relative;}
#son{
position: absolute;
margin: auto 0;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
height: 50px;
}
/*优缺点
- 优点:简单;兼容性较好(ie8+)
- 缺点:脱离文档流*/
(4-3) 使用flex实现:
原理:flex设置对齐方式罢了,请查阅文末flex阅读推荐
#parent{
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
或
#parent{display: flex;}
#son{align-self: center;}
或
/*原理:这个尚未搞清楚,应该是flex使margin上下边界无限延伸至剩余空间并平分了*/
#parent{display: flex;}
#son{margin: auto 0;}
优缺点
优点:简单灵活;功能强大
缺点:PC端兼容性不好,移动端(Android4.0+)
(5)任意个元素(flex)
原理:flex设置对齐方式罢了,请查阅文末flex阅读推荐
#parent{
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
或
#parent{
display: flex;
}
.son{
align-self: center;
}
或
#parent{
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: center;
}
优缺点
优点:简单灵活;功能强大
缺点:PC端兼容性不好,移动端(Android4.0+)
★本章小结:
对于垂直居中,最先想到的应该就是
line-height了,但是这个只能用于行内内容;其次就是考虑能不能用
vertical-align: middle;,不过这个一定要熟知原理才能用得顺手,建议看下vertical-align和line-height的基友关系 ;然后便是绝对定位,虽然代码多了点,但是胜在适用于不同情况;
移动端兼容性允许的情况下能用flex就用flex
三、水平垂直居中
一,二,三章都是parent+son的简单结构,html代码和效果图就不贴出来了,第四章以后才有
(1)行内/行内块级/图片▲
原理:text-align: center; 控制行内内容相对于块父元素水平居中,然后就是line-height和vertical-align的基友关系使其垂直居中,font-size: 0; 是为了消除近似居中的bug
#parent{
height: 150px;
line-height: 150px; /*行高的值与height相等*/
text-align: center;
font-size: 0; /*消除幽灵空白节点的bug*/
}
#son{
/*display: inline-block;*/ /*如果是块级元素需改为行内或行内块级才生效*/
vertical-align: middle;
}
优缺点
优点:代码简单;兼容性好(ie8+)
缺点:只对行内内容有效;需要添加
font-size: 0;才可以完全的垂直居中;不过需要注意html中#parent包裹#son之间需要有换行或空格;熟悉line-height和vertical-align的基友关系较难
(2)table-cell
原理:CSS Table,使表格内容垂直对齐方式为middle,然后根据是行内内容还是块级内容采取不同的方式达到水平居中
#parent{
height: 150px;
width: 200px;
display: table-cell;
vertical-align: middle;
/*text-align: center;*/ /*如果是行内元素就添加这个*/
}
#son{
/*margin: 0 auto;*/ /*如果是块级元素就添加这个*/
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
}
优缺点
优点:简单;适用于宽度高度未知情况;兼容性好(ie8+)
缺点:设置tabl-cell的元素,宽度和高度的值设置百分比无效,需要给它的父元素设置
display: table;才生效;table-cell不感知margin,在父元素上设置table-row等属性,也会使其不感知height;设置float或position会对默认布局造成破坏,可以考虑为之增加一个父p定义float等属性;内容溢出时会自动撑开父元素
(3)button作为父元素
原理:button的默认样式,再把需要居中的元素表现形式改为行内或行内块级就好
button#parent{ /*改掉button默认样式就好了,不需要居中处理*/
height: 150px;
width: 200px;
outline: none;
border: none;
}
#son{
display: inline-block; /*button自带text-align: center,改为行内水平居中生效*/
}
优缺点
优点:简单方便,充分利用默认样式
缺点:只适用于行内内容;需要清除部分默认样式;水平垂直居中兼容性很好,但是ie下点击会有凹陷效果!
(4)绝对定位
原理:子绝父相,top、right、bottom、left的值是相对于父元素尺寸的,然后margin或者transform是相对于自身尺寸的,组合使用达到几何上的水平垂直居中
#parent{
position: relative;
}
#son{
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
/*定宽高时等同于margin-left:负自身宽度一半;margin-top:负自身高度一半;*/
transform: translate(-50%,-50%);
}
优缺点
优点:使用margin兼容性好;不管是块级还是行内元素都可以实现
缺点:代码较多;脱离文档流;使用margin需要知道宽高;使用transform兼容性不好(ie9+)
(5)绝对居中
原理:当top、bottom为0时,margin-top&bottom设置auto的话会无限延伸占满空间并且平分;当left、right为0时,margin-left&right设置auto的话会无限延伸占满空间并且平分
#parent{
position: relative;
}
#son{
position: absolute;
margin: auto;
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
}
优缺点
优点:无需关注宽高;兼容性较好(ie8+)
缺点:代码较多;脱离文档流
(6)flex
原理:flex设置对齐方式罢了,请查阅文末flex阅读推荐
#parent{
display: flex;
}
#son{
margin: auto;
}
或
#parent{
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
或
#parent{
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
#son{
align-self: center;
}
优缺点
优点:简单灵活;功能强大
缺点:PC端兼容性不好,移动端(Android4.0+)
(7)视窗居中
原理:vh为视口单位,视口即文档可视的部分,50vh就是视口高度的50/100,设置50vh上边距再
#son{
/*0如果去掉,则会多出滚动条并且上下都是50vh的margin。如果去掉就给body加上overflow:hidden;*/
margin: 50vh auto 0;
transform: translateY(-50%);
}
优缺点
优点:简单;容易理解;两句代码达到屏幕水平垂直居中
缺点:兼容性不好(ie9+,Android4.4+)
★本章小结:
一般情况下,水平垂直居中,我们最常用的就是绝对定位加负边距了,缺点就是需要知道宽高,使用transform倒是可以不需要,但是兼容性不好(ie9+);
其次就是绝对居中,绝对定位设置top、left、right、bottom为0,然后
margin:auto;让浏览器自动平分边距以达到水平垂直居中的目的;如果是行内/行内块级/图片这些内容,可以优先考虑
line-height和vertical-align结合使用,不要忘了还有text-align,这个方法代码其实不多,就是理解原理有点困难,想要熟练应对各种情况还需好好研究;移动端兼容性允许的情况下能用flex就用flex。
四、两列布局
4.1 左列定宽,右列自适应
效果:

(1)利用float+margin实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="left">左列定宽</p> <p id="right">右列自适应</p> </body>
css代码:
#left {
background-color: #f00;
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 500px;
}
#right {
background-color: #0f0;
height: 500px;
margin-left: 100px; /*大于等于#left的宽度*/
}
(2)利用float+margin(fix)实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="left">左列定宽</p> <p id="right-fix"> <p id="right">右列自适应</p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#left {
background-color: #f00;
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 500px;
}
#right-fix {
float: right;
width: 100%;
margin-left: -100px; /*正值大于或等于#left的宽度,才能显示在同一行*/
}
#right{
margin-left: 100px; /*大于或等于#left的宽度*/
background-color: #0f0;
height: 500px;
}
(3)使用float+overflow实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="left">左列定宽</p> <p id="right">右列自适应</p> </body>
css代码:
#left {
background-color: #f00;
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 500px;
}
#right {
background-color: #0f0;
height: 500px;
overflow: hidden; /*触发bfc达到自适应*/
}
优缺点:
优点:代码简单,容易理解,无需关注定宽的宽度,利用bfc达到自适应效果
缺点:浮动脱离文档流,需要手动清除浮动,否则会产生高度塌陷;不支持ie6
(4)使用table实现
html代码:
<p id="parent"> <p id="left">左列定宽</p> <p id="right">右列自适应</p> </p>
css代码:
#parent{
width: 100%;
display: table;
height: 500px;
}
#left {
width: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
}
#right {
background-color: #0f0;
}
#left,#right{
display: table-cell; /*利用单元格自动分配宽度*/
}
优缺点:
优点:代码简单,容易理解,无需关注定宽的宽度,利用单元格自动分配达到自适应效果
缺点:margin失效;设置间隔比较麻烦;不支持ie8-
(5)使用绝对定位实现
html代码:
<p id="parent"> <p id="left">左列定宽</p> <p id="right">右列自适应</p> </p>
css代码:
#parent{
position: relative; /*子绝父相*/
}
#left {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
background-color: #f00;
width: 100px;
height: 500px;
}
#right {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 100px; /*值大于等于#left的宽度*/
right: 0;
background-color: #0f0;
height: 500px;
}
(6)使用flex实现
html代码:
<p id="parent"> <p id="left">左列定宽</p> <p id="right">右列自适应</p> </p>
css代码:
#parent{
width: 100%;
height: 500px;
display: flex;
}
#left {
width: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
}
#right {
flex: 1; /*均分了父元素剩余空间*/
background-color: #0f0;
}
(7)使用Grid实现
html代码:
<p id="parent"> <p id="left">左列定宽</p> <p id="right">右列自适应</p> </p>
css代码:
#parent {
width: 100%;
height: 500px;
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: 100px auto; /*设定2列就ok了,auto换成1fr也行*/
}
#left {
background-color: #f00;
}
#right {
background-color: #0f0;
}
4.2 左列自适应,右列定宽
效果:

(1)使用float+margin实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p id="left">左列自适应</p> <p id="right">右列定宽</p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent{
height: 500px;
padding-left: 100px; /*抵消#left的margin-left以达到#parent水平居中*/
}
#left {
width: 100%;
height: 500px;
float: left;
margin-left: -100px; /*正值等于#right的宽度*/
background-color: #f00;
}
#right {
height: 500px;
width: 100px;
float: right;
background-color: #0f0;
}
(2)使用float+overflow实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p id="right">右列定宽</p> <p id="left">左列自适应</p> <!--顺序要换一下--> </p> </body>
css代码:
#left {
overflow: hidden; /*触发bfc*/
height: 500px;
background-color: #f00;
}
#right {
margin-left: 10px; /*margin需要定义在#right中*/
float: right;
width: 100px;
height: 500px;
background-color: #0f0;
}
优缺点:
优点:代码简单,容易理解,无需关注定宽的宽度,利用bfc达到自适应效果
缺点:浮动脱离文档流,需要手动清除浮动,否则会产生高度塌陷;不支持ie6
(3)使用table实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p id="left">左列自适应</p> <p id="right">右列定宽</p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent{
width: 100%;
height: 500px;
display: table;
}
#left {
background-color: #f00;
display: table-cell;
}
#right {
width: 100px;
background-color: #0f0;
display: table-cell;
}
优缺点:
优点:代码简单,容易理解,无需关注定宽的宽度,利用单元格自动分配达到自适应效果
缺点:margin失效;设置间隔比较麻烦;不支持ie8-
(4)使用绝对定位实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p id="left">左列自适应</p> <p id="right">右列定宽</p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent{
position: relative; /*子绝父相*/
}
#left {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
right: 100px; /*大于等于#rigth的宽度*/
background-color: #f00;
height: 500px;
}
#right {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
right: 0;
background-color: #0f0;
width: 100px;
height: 500px;
}
(5)使用flex实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p id="left">左列自适应</p> <p id="right">右列定宽</p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent{
height: 500px;
display: flex;
}
#left {
flex: 1;
background-color: #f00;
}
#right {
width: 100px;
background-color: #0f0;
}
(6)使用Grid实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p id="left">左列自适应</p> <p id="right">右列定宽</p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent {
height: 500px;
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: auto 100px; /*设定2列,auto换成1fr也行*/
}
#left {
background-color: #f00;
}
#right {
background-color: #0f0;
}
4.3 一列不定,一列自适应
(盒子宽度随着内容增加或减少发生变化,另一个盒子自适应)
效果图:

变化后:

(1)使用float+overflow实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p id="left">左列不定宽</p> <p id="right">右列自适应</p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#left {
margin-right: 10px;
float: left; /*只设置浮动,不设宽度*/
height: 500px;
background-color: #f00;
}
#right {
overflow: hidden; /*触发bfc*/
height: 500px;
background-color: #0f0;
}
优缺点:
优点:代码简单,容易理解,无需关注宽度,利用bfc达到自适应效果
缺点:浮动脱离文档流,需要手动清除浮动,否则会产生高度塌陷;不支持ie6
(2)使用flex实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p id="left">左列不定宽</p> <p id="right">右列自适应</p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent{
display: flex;
}
#left { /*不设宽度*/
margin-right: 10px;
height: 500px;
background-color: #f00;
}
#right {
height: 500px;
background-color: #0f0;
flex: 1; /*均分#parent剩余的部分*/
}
(3)使用Grid实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p id="left">左列不定宽</p> <p id="right">右列自适应</p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent{
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: auto 1fr; /*auto和1fr换一下顺序就是左列自适应,右列不定宽了*/
}
#left {
margin-right: 10px;
height: 500px;
background-color: #f00;
}
#right {
height: 500px;
background-color: #0f0;
}
左列自适应,右列不定宽同理(参考4.1和4.3对应代码示例)
五、三列布局
5.1 两列定宽,一列自适应
效果图:
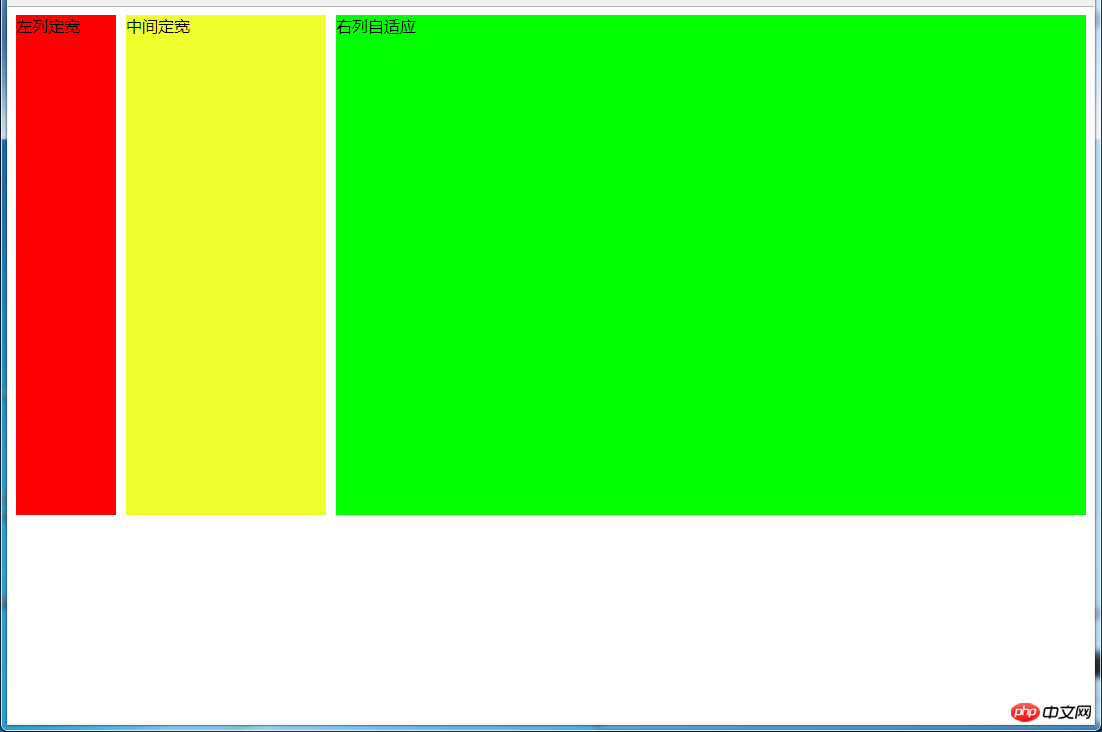

(1)使用float+margin实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p id="left">左列定宽</p> <p id="center">中间定宽</p> <p id="right">右列自适应</p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent{
min-width: 310px; /*100+10+200,防止宽度不够,子元素换行*/
}
#left {
margin-right: 10px; /*#left和#center间隔*/
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 500px;
background-color: #f00;
}
#center{
float: left;
width: 200px;
height: 500px;
background-color: #eeff2b;
}
#right {
margin-left: 320px; /*等于#left和#center的宽度之和加上间隔,多出来的就是#right和#center的间隔*/
height: 500px;
background-color: #0f0;
}
(2)使用float+overflow实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p id="left">左列定宽</p> <p id="center">中间定宽</p> <p id="right">右列自适应</p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent{
min-width: 320px; /*100+10+200+20,防止宽度不够,子元素换行*/
}
#left {
margin-right: 10px; /*间隔*/
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 500px;
background-color: #f00;
}
#center{
margin-right: 10px; /*在此定义和#right的间隔*/
float: left;
width: 200px;
height: 500px;
background-color: #eeff2b;
}
#right {
overflow: hidden; /*触发bfc*/
height: 500px;
background-color: #0f0;
}
优缺点:
优点:代码简单,容易理解,无需关注定宽的宽度,利用bfc达到自适应效果
缺点:浮动脱离文档流,需要手动清除浮动,否则会产生高度塌陷;不支持ie6
(3)使用table实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p id="left">左列定宽</p> <p id="center">中间定宽</p> <p id="right">右列自适应</p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent {
width: 100%;
height: 520px; /*抵消上下间距10*2的高度影响*/
margin: -10px 0; /*抵消上下边间距10的位置影响*/
display: table;
/*左右两边间距大了一点,子元素改用padding设置盒子间距就没有这个问题*/
border-spacing: 10px; /*关键!!!设置间距*/
}
#left {
display: table-cell;
width: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
}
#center {
display: table-cell;
width: 200px;
background-color: #eeff2b;
}
#right {
display: table-cell;
background-color: #0f0;
}
优缺点:
优点:代码简单,容易理解,无需关注定宽的宽度,利用单元格自动分配达到自适应效果
缺点:margin失效;设置间隔比较麻烦;不支持ie8-
(4)使用flex实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p id="left">左列定宽</p> <p id="center">中间定宽</p> <p id="right">右列自适应</p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent {
height: 500px;
display: flex;
}
#left {
margin-right: 10px; /*间距*/
width: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
}
#center {
margin-right: 10px; /*间距*/
width: 200px;
background-color: #eeff2b;
}
#right {
flex: 1; /*均分#parent剩余的部分达到自适应*/
background-color: #0f0;
}
(5)使用Grid实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p id="left">左列定宽</p> <p id="center">中间定宽</p> <p id="right">右列自适应</p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent {
height: 500px;
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: 100px 200px auto; /*设置3列,固定第一第二列的宽度,第三列auto或者1fr*/
}
#left {
margin-right: 10px; /*间距*/
background-color: #f00;
}
#center {
margin-right: 10px; /*间距*/
background-color: #eeff2b;
}
#right {
background-color: #0f0;
}
5.2 两侧定宽,中间自适应
5.2.1 双飞翼布局方法
效果图:

html代码:
<body> <p id="header"></p> <!--中间栏需要放在前面--> <p id="parent"> <p id="center"> <p id="center_inbox">中间自适应</p> <hr> <!--方便观察原理--> </p> <p id="left">左列定宽</p> <p id="right">右列定宽</p> </p> <p id="footer"></p> </body>
css代码:
#header {
height: 60px;
background-color: #ccc;
}
#left {
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 500px;
margin-left: -100%; /*调整#left的位置,值等于自身宽度*/
background-color: #f00;
opacity: 0.5;
}
#center {
height: 500px;
float: left;
width: 100%;
background-color: #eeff2b;
}
#center_inbox{
height: 480px;
border: 1px solid #000;
margin: 0 220px 0 120px; /*关键!!!左右边界等于左右盒子的宽度,多出来的为盒子间隔*/
}
#right {
float: left;
width: 200px;
height: 500px;
margin-left: -200px; /*使right到指定的位置,值等于自身宽度*/
background-color: #0f0;
opacity: 0.5;
}
#footer {
clear: both; /*注意清除浮动!!*/
height: 60px;
background-color: #ccc;
}
5.2.2 圣杯布局方法
效果图:
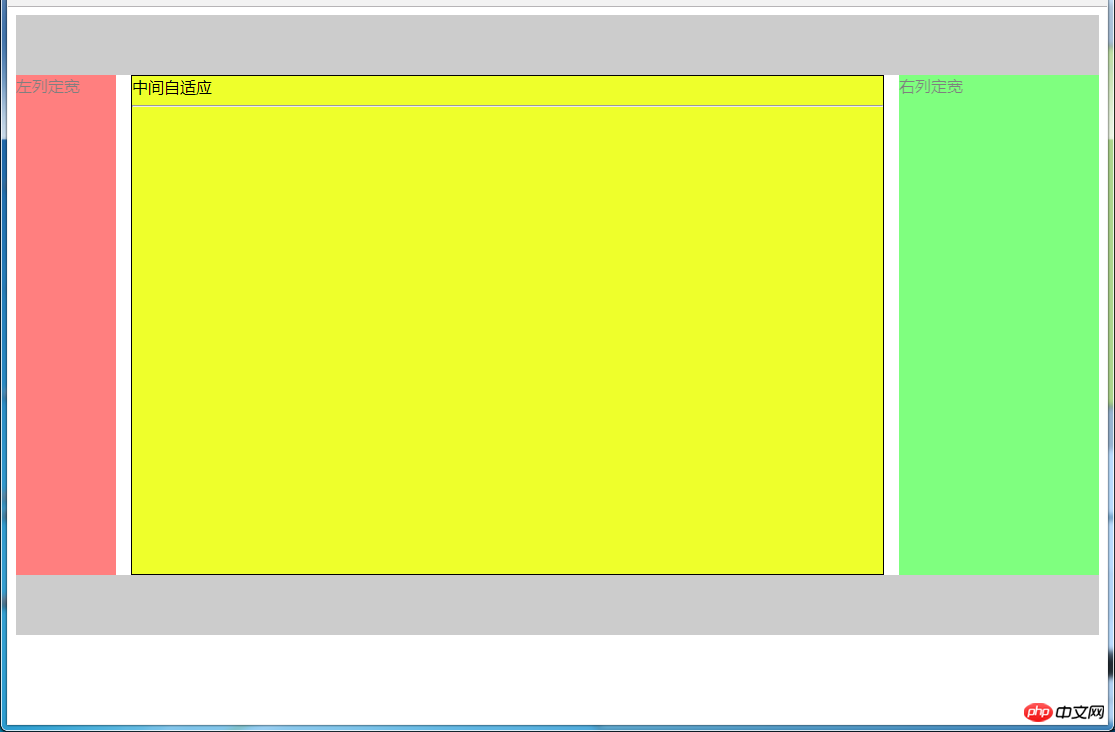
html代码:
<body> <p id="header"></p> <p id="parent"> <!--#center需要放在前面--> <p id="center">中间自适应 <hr> </p> <p id="left">左列定宽</p> <p id="right">右列定宽</p> </p> <p id="footer"></p> </body>
css代码:
#header{
height: 60px;
background-color: #ccc;
}
#parent {
box-sizing: border-box;
height: 500px;
padding: 0 215px 0 115px; /*为了使#center摆正,左右padding分别等于左右盒子的宽,可以结合左右盒子相对定位的left调整间距*/
}
#left {
margin-left: -100%; /*使#left上去一行*/
position: relative;
left: -115px; /*相对定位调整#left的位置,正值大于或等于自身宽度*/
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 500px;
background-color: #f00;
opacity: 0.5;
}
#center {
float: left;
width: 100%; /*由于#parent的padding,达到自适应的目的*/
height: 500px;
box-sizing: border-box;
border: 1px solid #000;
background-color: #eeff2b;
}
#right {
position: relative;
left: 215px; /*相对定位调整#right的位置,大于或等于自身宽度*/
width: 200px;
height: 500px;
margin-left: -200px; /*使#right上去一行*/
float: left;
background-color: #0f0;
opacity: 0.5;
}
#footer{
height: 60px;
background-color: #ccc;
}
5.2.3 使用Grid实现
效果图:
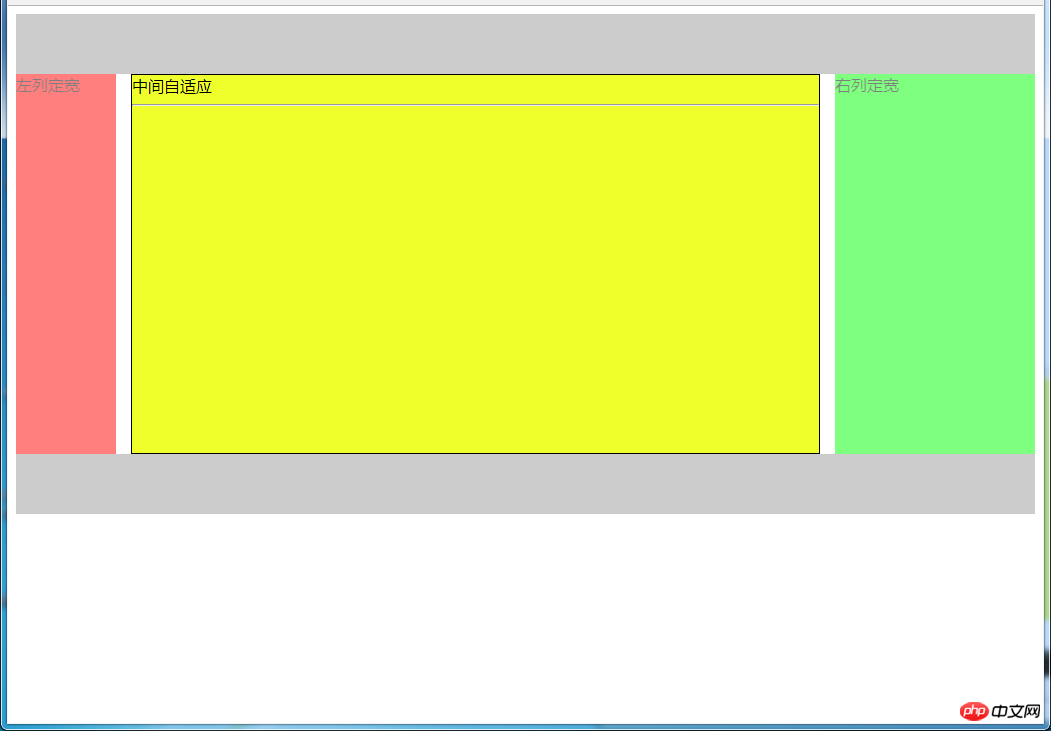
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p id="header"></p> <!--#center需要放在前面--> <p id="center">中间自适应 <hr> </p> <p id="left">左列定宽</p> <p id="right">右列定宽</p> <p id="footer"></p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent {
height: 500px;
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: 100px auto 200px; /*设定3列*/
grid-template-rows: 60px auto 60px; /*设定3行*/
/*设置网格区域分布*/
grid-template-areas:
"header header header"
"leftside main rightside"
"footer footer footer";
}
#header {
grid-area: header; /*指定在哪个网格区域*/
background-color: #ccc;
}
#left {
grid-area: leftside;
background-color: #f00;
opacity: 0.5;
}
#center {
grid-area: main; /*指定在哪个网格区域*/
margin: 0 15px; /*设置间隔*/
border: 1px solid #000;
background-color: #eeff2b;
}
#right {
grid-area: rightside; /*指定在哪个网格区域*/
background-color: #0f0;
opacity: 0.5;
}
#footer {
grid-area: footer; /*指定在哪个网格区域*/
background-color: #ccc;
}
5.2.4 其他方法
效果图:

(1)使用table实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p id="left">左列定宽</p> <p id="center">中间自适应</p> <p id="right">右列定宽</p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent {
width: 100%;
height: 500px;
display: table;
}
#left {
display: table-cell;
width: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
}
#center {
display: table-cell;
background-color: #eeff2b;
}
#right {
display: table-cell;
width: 200px;
background-color: #0f0;
}
优缺点:
优点:代码简洁,容易理解;
缺点:margin失效,采用border-spacing表格两边的间隔无法消除;不支持ie8-
(2)使用flex实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p id="left">左列定宽</p> <p id="center">中间自适应</p> <p id="right">右列定宽</p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent {
height: 500px;
display: flex;
}
#left {
width: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
}
#center {
flex: 1; /*均分#parent剩余的部分*/
background-color: #eeff2b;
}
#right {
width: 200px;
background-color: #0f0;
}
(3)使用position实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p id="left">左列定宽</p> <p id="center">中间自适应</p> <p id="right">右列定宽</p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent {
position: relative; /*子绝父相*/
}
#left {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 100px;
height: 500px;
background-color: #f00;
}
#center {
height: 500px;
margin-left: 100px; /*大于等于#left的宽度,或者给#parent添加同样大小的padding-left*/
margin-right: 200px; /*大于等于#right的宽度,或者给#parent添加同样大小的padding-right*/
background-color: #eeff2b;
}
#right {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
right: 0;
width: 200px;
height: 500px;
background-color: #0f0;
}
优缺点:
优点:容易理解,兼容性比较好
缺点:需手动计算宽度确定边距;脱离文档流;代码繁多
六、多列布局
6.1 等宽布局
6.1.1 四列等宽
(1)使用float实现
效果图:

html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p class="column">1 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">2 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">3 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">4 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent {
margin-left: -20px; /*使整体内容看起来居中,抵消padding-left的影响*/
}
.column{
padding-left: 20px; /*盒子的边距*/
width: 25%;
float: left;
box-sizing: border-box;
border: 1px solid #000;
background-clip: content-box; /*背景色从内容开始绘制,方便观察*/
height: 500px;
}
.column:nth-child(odd){
background-color: #f00;
}
.column:nth-child(even){
background-color: #0f0;
}
优缺点:
优点:代码简单,容易理解;兼容性较好
缺点:需要手动清除浮动,否则会产生高度塌陷
(2)使用table实现
效果图:

html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p class="column">1 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">2 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">3 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">4 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent {
height: 540px; /*抵消上下边20*2间距的高度影响*/
display: table;
margin: -20px 0; /*抵消上下边20*2间距的位置影响*/
/*两边离页面间距较大,改用子元素设置padding来当成间隔就不会有这样的问题*/
border-spacing: 20px; /*设置间距*/
}
.column{
display: table-cell;
}
.column:nth-child(odd){
background-color: #f00;
}
.column:nth-child(even){
background-color: #0f0;
}
优缺点:
优点:代码简单,容易理解;无需关注宽度,单元格自动等分
缺点:margin失效;设置间隔比较麻烦;不支持ie8-
(3)使用flex实现
效果图:

html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p class="column">1 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">2 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">3 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">4 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent {
margin-left: -15px; /*使内容看起来居中*/
height: 500px;
display: flex;
}
.column{
flex: 1; /*一起平分#parent*/
margin-left: 15px; /*设置间距*/
}
.column:nth-child(odd){
background-color: #f00;
}
.column:nth-child(even){
background-color: #0f0;
}
多列等宽
效果图:
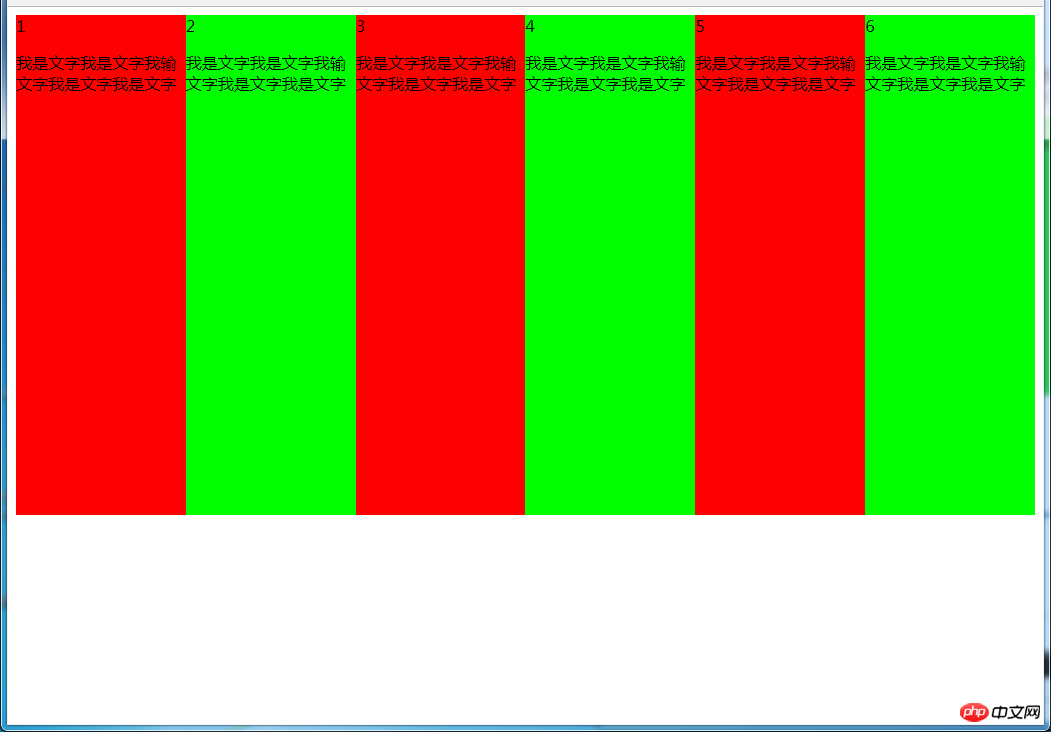

(1)使用float实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p class="column">1 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">2 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">3 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">4 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">5 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">6 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent {
height: 500px;
}
.column{
float: left; /*添加浮动*/
width: 16.66666666666667%; /*100÷列数,得出百分比*/
height: 500px;
}
.column:nth-child(odd){
background-color: #f00;
}
.column:nth-child(even){
background-color: #0f0;
}
优缺点:
优点:代码简单,容易理解;兼容性较好
缺点:需要手动清除浮动,否则会产生高度塌陷
(2)使用table实现
html代码
<body> <p id="parent"> <p class="column">1 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">2 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">3 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">4 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">5 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">6 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent {
width: 100%;
height: 500px;
display: table;
}
.column{
display: table-cell; /*无需关注列数,单元格自动平分*/
}
.column:nth-child(odd){
background-color: #f00;
}
.column:nth-child(even){
background-color: #0f0;
}
优缺点:
优点:代码简单,容易理解;无需关注宽度。单元格自动等分
缺点:margin失效;设置间隔比较麻烦;不兼容ie8-
(3)使用flex实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p class="column">1 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">2 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">3 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">4 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">5 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">6 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent {
height: 500px;
display: flex;
}
.column{
flex: 1; /*无需关注列数,一起平分#parent*/
}
.column:nth-child(odd){
background-color: #f00;
}
.column:nth-child(even){
background-color: #0f0;
}
(4)使用Grid实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p class="column">1 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">2 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">3 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">4 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">5 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> <p class="column">6 <p>我是文字我是文字我输文字我是文字我是文字</p></p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent {
height: 500px;
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: repeat(6,1fr); /*6就是列数*/
}
.column{}
.column:nth-child(odd){
background-color: #f00;
}
.column:nth-child(even){
background-color: #0f0;
}
6.2 九宫格布局
效果图:
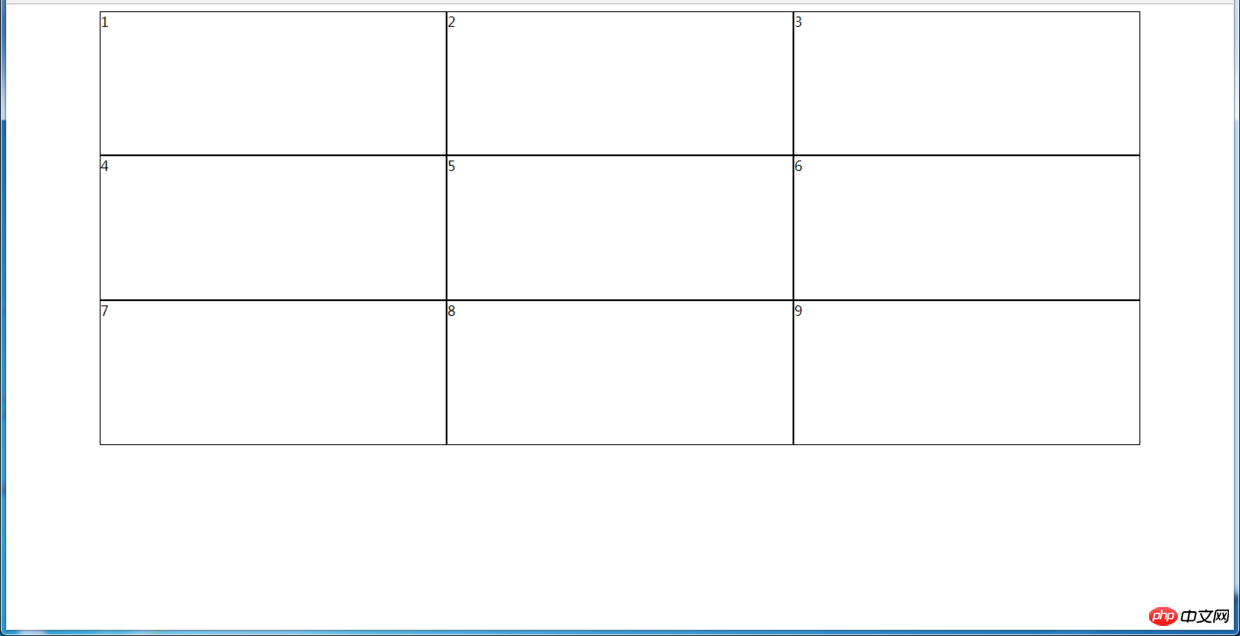
(1)使用table实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p class="row"> <p class="item">1</p> <p class="item">2</p> <p class="item">3</p> </p> <p class="row"> <p class="item">4</p> <p class="item">5</p> <p class="item">6</p> </p> <p class="row"> <p class="item">7</p> <p class="item">8</p> <p class="item">9</p> </p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent {
width: 1200px;
height: 500px;
margin: 0 auto;
display: table;
}
.row {
display: table-row;
}
.item {
border: 1px solid #000;
display: table-cell;
}
优缺点:
优点:代码简洁,容易理解;
缺点:margin失效,采用border-spacing表格两边的间隔无法消除;不支持ie8-
(2)使用flex实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p class="row"> <p class="item">1</p> <p class="item">2</p> <p class="item">3</p> </p> <p class="row"> <p class="item">4</p> <p class="item">5</p> <p class="item">6</p> </p> <p class="row"> <p class="item">7</p> <p class="item">8</p> <p class="item">9</p> </p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent {
width: 1200px;
height: 500px;
margin: 0 auto;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
.row {
display: flex;
flex: 1;
}
.item {
flex: 1;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
(3)使用Grid实现
CSS Grid非常强大,可以实现各种各样的三维布局,可查阅本文结尾的阅读推荐
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p class="item">1</p> <p class="item">2</p> <p class="item">3</p> <p class="item">4</p> <p class="item">5</p> <p class="item">6</p> <p class="item">7</p> <p class="item">8</p> <p class="item">9</p> </p> </body>
css代码:
#parent {
width: 1200px;
height: 500px;
margin: 0 auto;
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: repeat(3, 1fr); /*等同于1fr 1fr 1fr,此为重复的合并写法*/
grid-template-rows: repeat(3, 1fr); /*等同于1fr 1fr 1fr,此为重复的合并写法*/
}
.item {
border: 1px solid #000;
}
6.3 栅格系统
优缺点:
优点:代码简洁,容易理解;提高页面内容的流动性,能适应多种设备;
(1)用Less生成
/*生成栅格系统*/
@media screen and (max-width: 768px){
.generate-columns(12); /*此处设置生成列数*/
.generate-columns(@n, @i: 1) when (@i <= @n) {
.column-xs-@{i} {
width: (@i * 100% / @n);
}
.generate-columns(@n, (@i+1));
}
}
@media screen and (min-width: 768px){
.generate-columns(12); /*此处设置生成列数*/
.generate-columns(@n, @i: 1) when (@i <= @n) {
.column-sm-@{i} {
width: (@i * 100% / @n);
}
.generate-columns(@n, (@i+1));
}
}
p[class^="column-xs-"]{
float: left;
}
p[class^="column-sm-"]{
float: left;
}
编译后的CSS代码:
@media screen and (max-width: 768px) {
.column-xs-1 { width: 8.33333333%; }
.column-xs-2 { width: 16.66666667%; }
.column-xs-3 { width: 25%; }
.column-xs-4 { width: 33.33333333%; }
.column-xs-5 { width: 41.66666667%; }
.column-xs-6 { width: 50%; }
.column-xs-7 { width: 58.33333333%; }
.column-xs-8 { width: 66.66666667%; }
.column-xs-9 { width: 75%; }
.column-xs-10 { width: 83.33333333%; }
.column-xs-11 { width: 91.66666667%; }
.column-xs-12 { width: 100%; }
}
@media screen and (min-width: 768px) {
.column-sm-1 { width: 8.33333333%; }
.column-sm-2 { width: 16.66666667%; }
.column-sm-3 { width: 25%; }
.column-sm-4 { width: 33.33333333%; }
.column-sm-5 { width: 41.66666667%; }
.column-sm-6 { width: 50%; }
.column-sm-7 { width: 58.33333333%; }
.column-sm-8 { width: 66.66666667%; }
.column-sm-9 { width: 75%; }
.column-sm-10 { width: 83.33333333%; }
.column-sm-11 { width: 91.66666667%; }
.column-sm-12 { width: 100%; }
}
p[class^="column-xs-"]{
float: left;
}
p[class^="column-sm-"]{
float: left;
}
七、全屏布局
效果图:
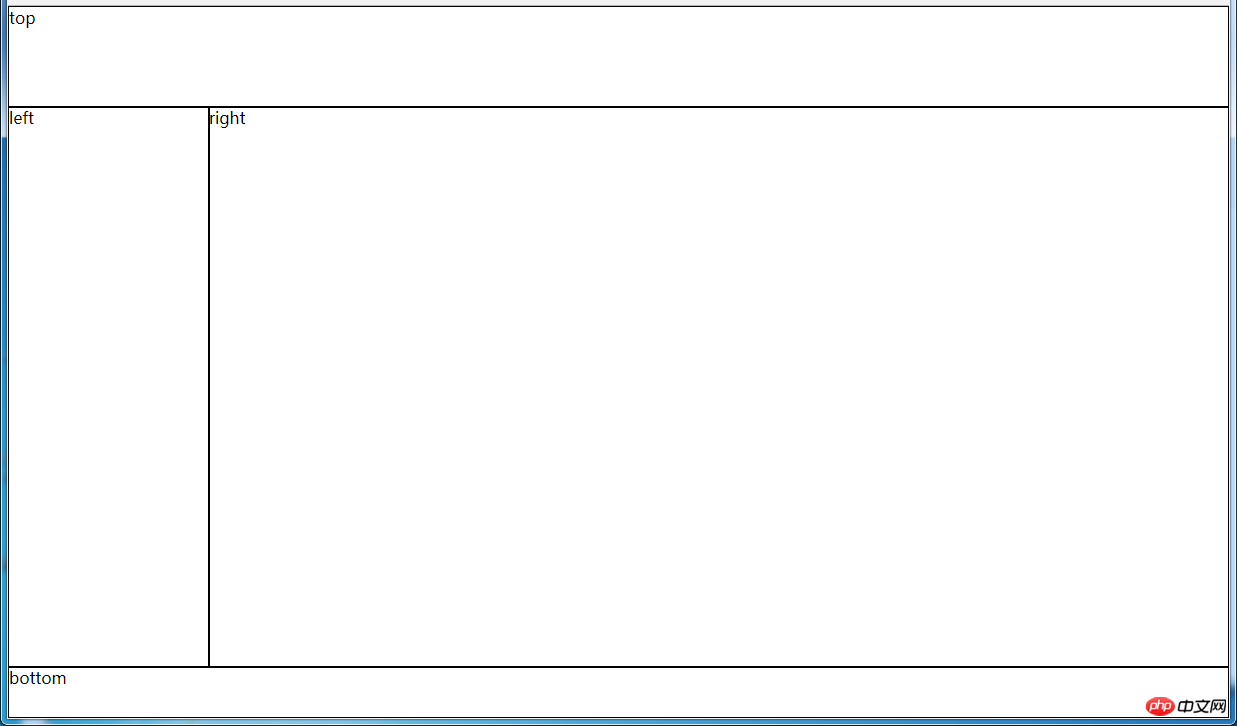
(1)使用绝对定位实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p id="top">top</p> <p id="left">left</p> <p id="right">right</p> <p id="bottom">bottom</p> </p> </body>
css代码:
html, body, #parent {height: 100%;overflow: hidden;}
#parent > p {
border: 1px solid #000;
}
#top {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
height: 100px;
}
#left {
position: absolute;
top: 100px; /*值大于等于#top的高度*/
left: 0;
bottom: 50px; /*值大于等于#bottom的高度*/
width: 200px;
}
#right {
position: absolute;
overflow: auto;
left: 200px; /*值大于等于#left的宽度*/
right: 0;
top: 100px; /*值大于等于#top的高度*/
bottom: 50px; /*值大于等于#bottom的高度*/
}
#bottom {
position: absolute;
left: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
height: 50px;
}
优缺点:
优点:容易理解
缺点:代码繁多;需要计算好各个盒子的宽高;
(2)使用flex实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p id="top">top</p> <p id="middle"> <p id="left">left</p> <p id="right">right</p> </p> <p id="bottom">bottom</p> </p> </body>
css代码:
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
html,body,#parent{
height:100%;
}
#parent {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
#top {
height: 100px;
}
#bottom {
height: 50px;
}
#middle {
flex: 1;
display: flex;
}
#left {
width: 200px;
}
#right {
flex: 1;
overflow: auto;
}
(3)使用Grid实现
html代码:
<body> <p id="parent"> <p id="top">top</p> <p id="left">left</p> <p id="right">right</p> <p id="bottom">bottom</p> </p> </body>
css代码:
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
html, body, #parent {
height: 100%;
}
#parent {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
display: grid;
/*分成2列,第一列宽度200px,第二列1fr平分剩余的部分,此处换成auto也行*/
grid-template-columns: 200px 1fr;
/*分成3行,第一行高度100px,第二行auto为自适应,此处换成1fr也行,第3行高度为50px*/
grid-template-rows: 100px auto 50px;
/*定义网格区域分布*/
grid-template-areas:
"header header"
"aside main"
"footer footer";
}
#parent>p{
border: 1px solid #000;
}
#top{
grid-area: header; /*指定在哪个网格区域*/
}
#left{
grid-area: aside; /*指定在哪个网格区域*/
}
#right{
grid-area: main; /*指定在哪个网格区域*/
}
#bottom{
grid-area: footer; /*指定在哪个网格区域*/
}
八、网站实例布局分析:
由于方法众多,分析的时候想到哪种用哪种了,只要IE9和谷歌上表现一致,我就不一一测试其他浏览器了,如果有什么问题或意见,请留言!
8.1 小米官网
https://www.mi.com/
8.1.1 兼容IE9+的方法
(1)页面整体
整个页面我们可以分成顶、上、中、下、底五个结构,如图所示:
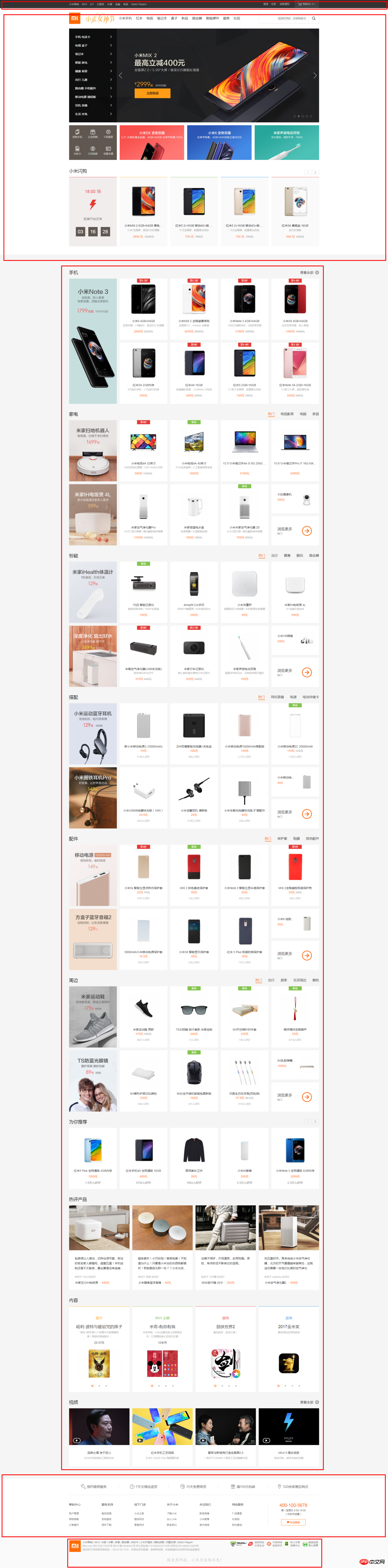
html代码:
<body> <p class="header"></p> <p class="top"></p> <p class="center"></p> <p class="bottom"></p> <p class="footer"></p> </body>
css代码:
*{ /*为了方便,就这样清空默认样式了*/
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
list-style: none;
}
body{
background-color: #f5f5f5;
}
.header{
margin-bottom: 20px;
height: 40px;
background-color: #333;
}
.top{
height: 1210px;
background-color: #fff;
}
.center{
width: 1226px;
margin: 0 auto;
margin-bottom: 60px;
height: 1791px;
background-color: #fff;
}
.bottom{
height: 274px;
background-color: #fff;
}
.footer{
margin: 0 auto;
width: 1226px;
height: 166px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
(2)局部——header
header部分首先是一个水平居中的内容,内容盒子可以分成左右两个部分,如图所示:

html代码:
<p class="header"> <p class="container"> <p class="header-left"></p> <p class="header-rigth"></p> </p> </p>
css代码:
.container{ /*后面会继续用到*/
width: 1226px;
height: 100%;
margin: 0 auto;
border: 1px solid #f00;
}
.header-left{
width: 380px;
height: 100%;
float: left;
background-color: #0f0;
}
.header-rigth{
width: 260px;
height: 100%;
float: right;
background-color: #0f0;
}
(3)局部——top
top部分先有一个水平居中的内容,再就是内容由上到下可以分成四个部分,然后每个部分再细分......说不下去了,直接上图:
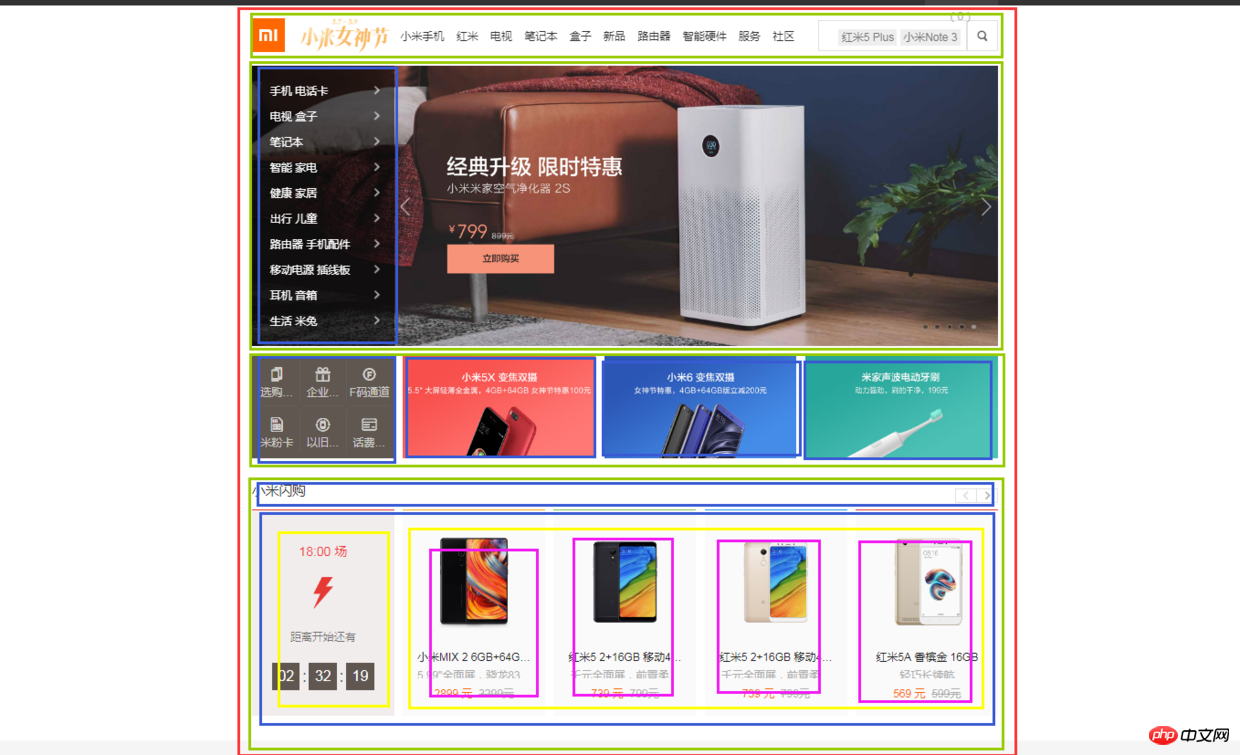
html代码:
<p class="top"> <p class="container"> <p class="top-nav"></p> <p class="top-slider"> <p class="slider-navbar"></p> </p> <p class="top-recommend"> <p class="recommend-left"></p> <p class="recommend-right"> <ul> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> </ul> </p> </p> <p class="top-flashsale"> <p class="flashsale-title"></p> <p class="flashsale-content"> <p class="content-timer"></p> <ul class="content-shops"> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> </ul> </p> </p> </p> </p>
css代码:
.top {
height: 1210px;
background-color: #fff;
}
.top-nav {
height: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
}
.top-slider {
margin-bottom: 14px;
position: relative;
height: 460px;
background-color: #00f;
}
.slider-navbar {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 234px;
height: 100%;
background-color: black;
opacity: .5;
}
.top-recommend {
margin-bottom: 26px;
height: 170px;
background-color: #0f0;
}
.recommend-left {
float: left;
height: 100%;
width: 234px;
background-color: skyblue;
}
.recommend-right {
float: right;
width: 978px;
height: 100%;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.recommend-right > ul {
height: 100%;
}
.recommend-right > ul li {
float: left;
width: 316px;
height: 100%;
background-color: deepskyblue;
}
.recommend-right > ul li + li {
margin-left: 14px;
}
.top-flashsale {
height: 438px;
background-color: #ff4455;
}
.flashsale-title {
height: 58px;
background-color: purple;
}
.flashsale-content {
border: 1px solid #000;
padding-bottom: 40px;
height: 380px;
}
.content-timer {
margin-right: 14px;
float: left;
width: 234px;
height: 100%;
background-color: #fff;
}
.content-shops {
overflow: hidden;
height: 100%;
background-color: #6effb1;
}
.content-shops > li {
float: left;
width: 234px;
height: 100%;
background-color: #fff;
}
.content-shops > li+li {
margin-left: 12.5px;
}
(4)局部——center
center部分都是一些单元格展示,有很多类似的模块,就挑几个来实现了,直接看图吧:
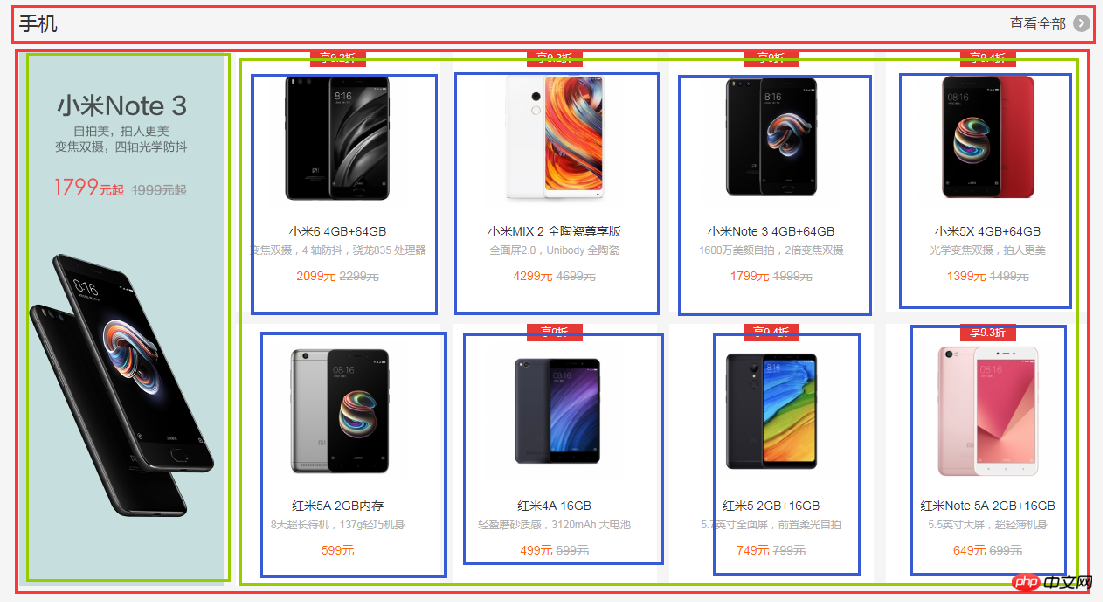
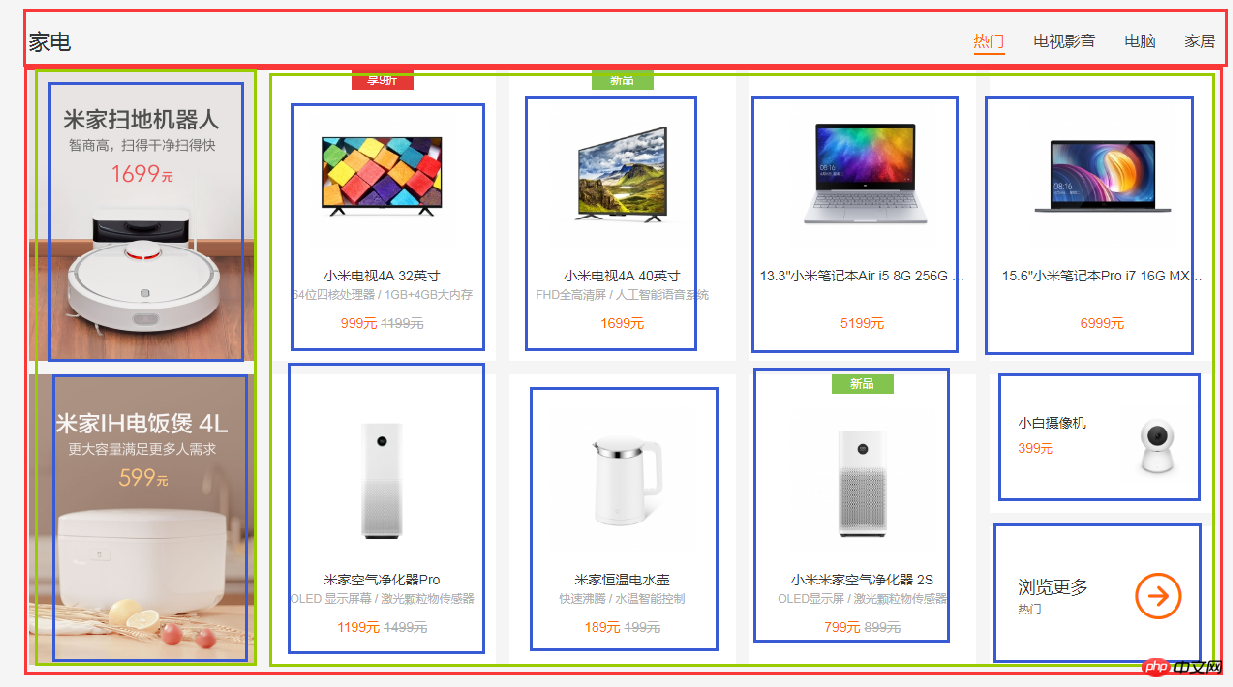
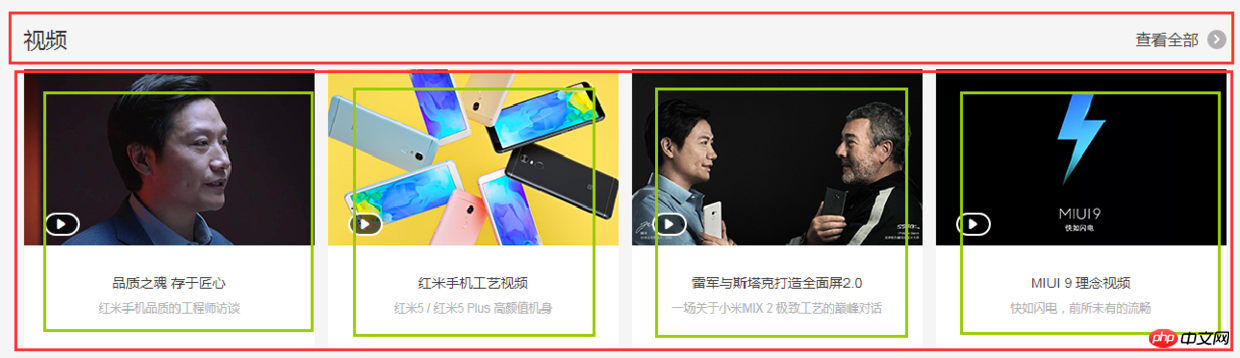
html代码:
<p class="center"> <p class="center-phone"> <p class="phone-title"></p> <p class="phone-content"> <p class="phone-left"></p> <ul class="phone-right"> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> </ul> </p> </p> <p class="center-household"> <p class="household-title"></p> <p class="household-content"> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li> <p></p> <p></p> </li> </p> </p> <p class="center-video"> <p class="video-title"></p> <ul class="video-content"> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> </ul> </p> </p>
css代码:
.center {
margin: 0 auto;
margin-bottom: 60px;
padding-top: 60px;
width: 1226px;
height: 1791px;
background-color: #fff;
}
.center-phone{
margin-bottom: 8px;
height: 686px;
background-color: yellow;
}
.phone-title{
height: 58px;
background-color: black;
}
.phone-content{
height: 628px;
background-color: pink;
}
.phone-left{
margin-right: 14px;
float: left;
width: 234px;
height: 100%;
background-color: darkseagreen;
}
.phone-right{
overflow: hidden;
height: 100%;
background-color: #ccc;
}
.phone-right>li{
margin-bottom: 28px;
padding-left: 14px;
float: left;
width: 25%;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid #000;
background-color: #f00;
background-clip: content-box;
}
.phone-right>li:nth-child(1),
.phone-right>li:nth-child(5){
margin-left: 0;
}
.center-household{
margin-bottom: 8px;
height: 686px;
background-color: yellow;
}
.household-title{
height: 58px;
background-color: black;
}
.household-content{
height: 614px;
}
.household-content>li{
position: relative;
margin-left: 14px;
margin-bottom: 28px;
float: left;
width: 234px;
height: 300px;
background-color: #d7d7d7;
}
.household-content>li:nth-child(1),
.household-content>li:nth-child(6){
margin-left: 0;
}
.household-content>li:last-child p:first-child{
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
height: 143px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.household-content>li:last-child p:last-child{
position: absolute;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
height: 143px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.center-video{
height: 343px;
background-color: pink;
}
.video-title{
height: 58px;
background-color: black;
}
.video-content{
height: 285px;
}
.video-content>li{
float: left;
width: 296px;
height: 100%;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.video-content>li+li{
margin-left: 14px;
}
(5)局部——bottom
bottom部分首先是一个水平居中的内容,然后内容可以划分为上下两部分,每个部分都是浮动的li,如图:
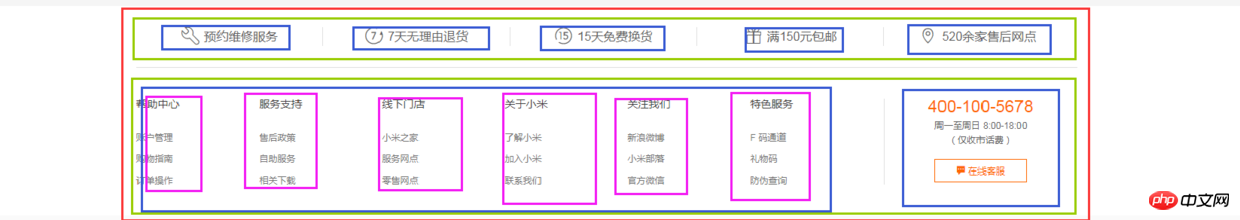
html代码:
<p class="bottom"> <p class="container"> <p class="bottom-service"> <ul> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> </ul> </p> <p class="bottom-links"> <p class="links-left"> <ul> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> </ul> </p> <p class="links-right"></p> </p> </p> </p>
css代码:
.bottom {
height: 274px;
background-color: #fff;
}
.bottom-service{
height: 80px;
background-color: seagreen;
}
.bottom-service>ul{
height: 100%;
}
.bottom-service>ul li{
position: relative;
padding: 0 50px;
float: left;
width: 20%;
height: 100%;
background-color: goldenrod;
background-clip: content-box;
}
.bottom-service>ul li+li::before{
position: absolute;
top: 28px;
left: 0;
content: '';
width: 1px;
height: 24px;
background-color: #999;
}
.bottom-links{
height: 192px;
background-color: #8545e0;
}
.links-left{
float: left;
width: 960px;
height: 100%;
background-color: yellow;
}
.links-left>ul{
height: 100%;
}
.links-left>ul li{
padding-right: 60px;
float: left;
width: 16.666666666666667%;
height: 100%;
border: 1px solid #000;
background-color: #ff0000;
background-clip: content-box;
}
.links-right{
float: right;
width: 252px;
height: 100%;
background-color: yellow;
}
(6)局部——footer
footer划分如图:
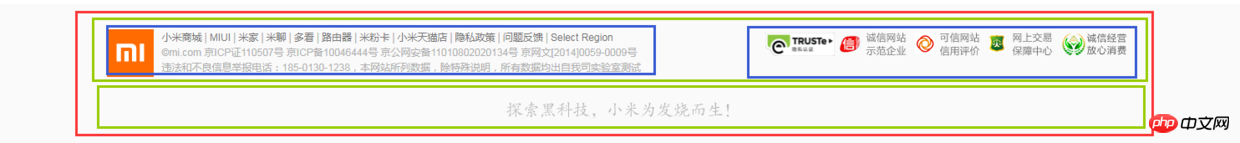
html代码:
<p class="footer"> <p class="footer-info"> <p class="info-left"></p> <p class="info-right"></p> </p> <p class="footer-slogan"></p> </p>
css代码:
.footer {
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 30px 0;
width: 1226px;
height: 166px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.footer-info{
height: 57px;
background-color: #6effb1;
}
.info-left{
float: left;
width: 630px;
height: 100%;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.info-right{
float: right;
width: 436px;
height: 100%;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.footer-slogan{
margin-top: 30px;
height: 19px;
background-color: #8545e0;
}
(7)全部代码(优化后)
html代码:
<body> <p class="header"> <p class="container"> <p class="header-left fl"></p> <p class="header-rigth fr"></p> </p> </p> <p class="top"> <p class="container"> <p class="top-nav"></p> <p class="top-slider"> <p class="slider-navbar"></p> </p> <p class="top-recommend"> <p class="recommend-left fl"></p> <p class="recommend-right fr"> <ul> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> </ul> </p> </p> <p class="top-flashsale"> <p class="flashsale-title common-title"></p> <p class="flashsale-content"> <p class="content-timer fl"></p> <ul class="content-shops"> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> </ul> </p> </p> </p> </p> <p class="center"> <p class="center-phone module-box"> <p class="phone-title common-title"></p> <p class="phone-content"> <p class="phone-left fl"></p> <ul class="phone-right"> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> </ul> </p> </p> <p class="center-household module-box"> <p class="household-title common-title"></p> <p class="household-content"> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li> <p></p> <p></p> </li> </p> </p> <p class="center-video"> <p class="video-title common-title"></p> <ul class="video-content"> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> </ul> </p> </p> <p class="bottom"> <p class="container"> <p class="bottom-service"> <ul> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> </ul> </p> <p class="bottom-links"> <p class="links-left fl"> <ul> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> </ul> </p> <p class="links-right fr"></p> </p> </p> </p> <p class="footer"> <p class="footer-info"> <p class="info-left fl"></p> <p class="info-right fr"></p> </p> <p class="footer-slogan"></p> </p> </body>
css代码:
/*-------------------抽取公共样式-----------------*/
* { /*为了方便,就这样清空默认样式了*/
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
list-style: none;
}
body {
background-color: #f5f5f5;
}
.container { /*水平居中的内容盒子*/
width: 1226px;
height: 100%;
margin: 0 auto;
border: 1px solid #f00;
}
.common-title {
height: 58px;
background-color: #000;
}
.fl {float: left;}
.fr {float: right;}
.recommend-right,
.flashsale-content,
.phone-right > li,
.household-content > li:last-child > p,
.video-content > li,
.links-left > ul li,
.footer,
.info-left,
.info-right {border: 1px solid #000;} /*添加边框样式只是为了方便观察,不是布局必须,可删*/
/*-----header部分-----*/
.header {
margin-bottom: 20px;
height: 40px;
background-color: #333;
}
.header-left {
width: 380px;
height: 100%;
background-color: #0f0;
}
.header-rigth {
width: 260px;
height: 100%;
background-color: #0f0;
}
/*--------top部分--------*/
.top {
/*height: 1210px;*/
background-color: #fff;
}
.top-nav {
height: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
}
.top-slider {
margin-bottom: 14px;
position: relative; /*父相*/
height: 460px;
background-color: #00f;
}
.slider-navbar {
position: absolute; /*子绝*/
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 234px;
height: 100%;
background-color: black;
opacity: .5;
}
.top-recommend {
margin-bottom: 26px;
height: 170px;
background-color: #0f0;
}
.recommend-left {
height: 100%;
width: 234px;
background-color: skyblue;
}
.recommend-right {
width: 978px;
height: 100%;
}
.recommend-right > ul {height: 100%;}
.recommend-right > ul li {
float: left; /*三列等宽,浮动布局*/
width: 316px;
height: 100%;
background-color: deepskyblue;
}
.recommend-right > ul li + li { margin-left: 14px;} /*设置浮动间隔*/
.top-flashsale {
height: 438px;
background-color: #ff4455;
}
.flashsale-title {}
.flashsale-content {
padding-bottom: 40px;
height: 380px;
}
.content-timer {
margin-right: 14px;
width: 234px;
height: 100%;
background-color: #fff;
}
.content-shops {
overflow: hidden; /*触发bfc,以达到自适应*/
height: 100%;
background-color: #6effb1;
}
.content-shops > li {
float: left; /*四列等宽,浮动布局*/
width: 234px;
height: 100%;
background-color: #fff;
}
.content-shops > li + li {margin-left: 12.5px;} /*设置浮动间隔*/
/*--------center部分--------*/
.module-box { /*类似的模块*/
margin-bottom: 8px;
height: 686px;
}
.center {
margin: 0 auto;
margin-bottom: 60px;
padding-top: 60px;
width: 1226px;
/*height: 1791px;*/
background-color: #fff;
}
.center-phone {background-color: yellow;}
.phone-title {}
.phone-content {
height: 628px;
background-color: pink;
}
.phone-left {
width: 234px;
height: 100%;
background-color: darkseagreen;
}
.phone-right {
overflow: hidden; /*触发bfc以达到自适应*/
height: 100%;
background-color: #ccc;
}
.phone-right > li {
margin-bottom: 28px; /*设置下边距*/
padding-left: 14px; /*用padding模拟盒子间隔*/
float: left; /*四列等宽,浮动布局*/
width: 25%;
height: 300px;
background-color: #f00;
background-clip: content-box; /*背景色从content开始绘起*/
}
.center-household {background-color: yellow;}
.household-title {}
.household-content {height: 614px;}
.household-content > li {
position: relative; /*父相*/
margin-left: 14px; /*设置浮动间隔*/
margin-bottom: 28px; /*设置下边距*/
float: left; /*五列等宽,浮动布局*/
width: 234px;
height: 300px;
background-color: #d7d7d7;
}
.household-content > li:nth-child(1),
.household-content > li:nth-child(6) {margin-left: 0; } /*消除每行第一个的间隔*/
.household-content > li:last-child p:first-child {
position: absolute; /*子绝*/
top: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
height: 143px;
}
.household-content > li:last-child p:last-child {
position: absolute; /*子绝*/
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
height: 143px;
}
.center-video {
height: 343px;
background-color: pink;
}
.video-title {}
.video-content {height: 285px;}
.video-content > li {
float: left; /*四列等宽,浮动布局*/
width: 296px;
height: 100%;
}
.video-content > li + li {margin-left: 14px; } /*设定浮动间隔*/
/*--------bottom部分--------*/
.bottom {
/*height: 274px;*/
background-color: #fff;
}
.bottom-service {
height: 80px;
background-color: seagreen;
}
.bottom-service > ul {height: 100%;}
.bottom-service > ul li {
position: relative; /*父相*/
padding: 0 50px; /*用padding模拟盒子间隔*/
float: left; /*五列等宽,浮动布局*/
width: 20%;
height: 100%;
background-color: goldenrod;
background-clip: content-box; /*背景色从content开始绘起*/
}
.bottom-service > ul li + li::before { /*用伪元素模拟分割线*/
position: absolute; /*子绝*/
top: 28px;
left: 0;
content: ''; /*伪元素必须有content*/
width: 1px;
height: 24px;
background-color: #999;
}
.bottom-links {
height: 192px;
background-color: #8545e0;
}
.links-left {
width: 960px;
height: 100%;
background-color: yellow;
}
.links-left > ul {height: 100%;}
.links-left > ul li {
padding-right: 60px;
float: left; /*六列等宽,浮动布局*/
width: 16.666666666666667%;
height: 100%;
background-color: #ff0000;
background-clip: content-box; /*背景色从content开始绘起*/
}
.links-right {
width: 252px;
height: 100%;
background-color: yellow;
}
/*--------footer部分---------*/
.footer {
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 30px 0;
width: 1226px;
height: 166px;
}
.footer-info {
height: 57px;
background-color: #6effb1;
}
.info-left {
width: 630px;
height: 100%;
}
.info-right {
width: 436px;
height: 100%;
}
.footer-slogan {
margin-top: 30px;
height: 19px;
background-color: #8545e0;
}
以上就是优化后的代码了,由于在下才疏学浅,所用方法不敢保证是最简单的,优化也肯定不是最优的,仅仅是的我的一种思路而已,各位参考参考就好。
8.1.2 Flexbox+Grid搭配用法(未来...)
html代码:
<p class="header"> <p class="container"> <p class="header-left"></p> <p class="header-rigth"></p> </p> </p>
<p class="footer"> <p class="footer-info"> <p class="info-left"></p> <p class="info-right"></p> </p> <p class="footer-slogan"></p> </p>
css代码:
/*-------------------抽取公共样式-----------------*/
* { /*为了方便,就这样清空默认样式了*/
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
list-style: none;
}
body {
background-color: #f5f5f5;
display: grid;
/*整体布局 设置网格列,设置网格行,再设定网格区域*/
grid-template-columns: 1fr 1226px 1fr;
grid-template-rows: 40px 20px auto auto 274px 166px;
grid-template-areas:
"header header header"
". . ."
"top top top"
". center ."
"bottom bottom bottom"
". footer .";
}
.container { /*水平居中的内容盒子*/
width: 1226px;
height: 100%;
margin: 0 auto;
border: 1px solid #f00;
}
.top-recommend-right,
.top-flashsale-timer,
.top-flashsale-shops li,
.center-phone-content > p,
.center-household-content .row,
.household-content-item:last-of-type p,
.center-video-content li,
.service-item,
.links-left-item,
.info-left,
.info-right,
.info-right {border: 1px solid #000;} /*添加边框样式只是为了方便观察,不是布局必须,可删*/
/*-----header部分-----*/
.header {
grid-area: header; /*指定网格区域*/
background-color: #333;
}
.header .container {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
}
.header-left {
width: 380px;
background-color: #0f0;
}
.header-rigth {
width: 260px;
background-color: #0f0;
}
/*--------top部分--------*/
.top {
grid-area: top; /*指定网格区域*/
background-color: #fff;
}
.top .container {
display: grid;
/*top部分布局 设置网格行,设置网格列,再设定网格区域*/
grid-template-rows: 100px 460px 14px 170px 26px 58px 340px 40px;
grid-template-columns: auto 14px 978px;
grid-template-areas:
"top-nav top-nav top-nav"
"top-slider top-slider top-slider"
". . ."
"recommend-left . recommend-right"
". . ."
"flashsale-title flashsale-title flashsale-title"
"flashsale-timer . flashsale-shops"
". . .";
}
.top-nav {
grid-area: top-nav;
background-color: #f00;
}
.top-slider {
position: relative;
grid-area: top-slider;
background-color: #00f;
}
.top-slider .slider-navbar {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
width: 234px;
background-color: black;
opacity: .5;
}
.top-recommend-left {
grid-area: recommend-left;
background-color: skyblue;
}
.top-recommend-right {grid-area: recommend-right;}
.top-recommend-right > ul {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
height: 100%;
}
.top-recommend-right li {
width: 316px;
background-color: deepskyblue;
}
.top-flashsale-title {
grid-area: flashsale-title;
background-color: #000;
}
.top-flashsale-timer {
grid-area: flashsale-timer;
background-color: #fff;
}
.top-flashsale-shops {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
grid-area: flashsale-shops;
background-color: #6effb1;
}
.top-flashsale-shops li {width: 234px;}
/*--------center部分--------*/
.center {
margin-bottom: 60px; /*边距可以在网格分区的时候考虑进去,把边距设成一行或一列,不要放内容就好了*/
padding-top: 60px;
grid-area: center; /*指定网格区域*/
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
background-color: #fff;
}
.center-phone-title {
height: 58px;
background-color: black;
}
.center-phone-content {
margin-bottom: 8px;
display: grid;
/*这里用flex分格更好,代码更少更简洁*/
grid-template-columns: repeat(5, 1fr);
grid-template-rows: repeat(2, 1fr);
grid-template-areas:
"big1 normal2 normal3 normal4 normal5"
"big1 normal6 normal7 normal8 normal9";
grid-gap: 14px; /*网格间隔*/
height: 628px;
background-color: pink;
}
.phone-content-item1 {grid-area: big1;}
.phone-content-item2 {grid-area: normal2;}
.phone-content-item3 {grid-area: normal3;}
.phone-content-item4 {grid-area: normal4;}
.phone-content-item5 {grid-area: normal5;}
.phone-content-item6 {grid-area: normal6;}
.phone-content-item7 {grid-area: normal7;}
.phone-content-item8 {grid-area: normal8;}
.phone-content-item9 {grid-area: normal9;}
.center-household-title {
height: 58px;
background-color: black;
}
.center-household-content {
margin-bottom: 8px;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
height: 614px;
background-color: pink;
}
.center-household-content .row {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
flex: 1;
}
.row .household-content-item {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: space-between;
width: 234px;
background-color: #fff;
}
.household-content-item:last-of-type p {height: 143px;}
.center-video-title {
height: 58px;
background-color: black;
}
.center-video-content {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
height: 285px;
background-color: pink;
}
.center-video-content li {width: 296px;}
/*--------bottom部分--------*/
.bottom {
grid-area: bottom; /*指定网格区域*/
background-color: #fff;
}
.bottom .container {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: auto 252px;
grid-template-rows: 80px auto;
grid-template-areas: "service service" "links-left links-right";
}
.container .bottom-service {
display: flex;
grid-area: service;
background-color: seagreen;
}
.service-item {flex: 1;}
.container .bottom-links-left {
display: flex;
grid-area: links-left;
background-color: yellow;
}
.links-left-item {flex: 1;}
.container .bottom-links-right {
grid-area: links-right;
background-color: yellowgreen;
}
/*--------footer部分---------*/
.footer {
padding: 30px 0;
grid-area: footer; /*指定网格区域*/
}
.footer-info {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
height: 57px;
background-color: #6effb1;
}
.info-left {width: 630px;}
.info-right {width: 436px;}
.footer-slogan {
margin-top: 30px;
height: 19px;
background-color: #8545e0;
}
九、其他补充:
9.1 移动端viewport
设置viewport:
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, user-scalable=0">
阅读推荐:
解读 viewport—网页自适应移动 app 神器
https://juejin.im/entry/58e750a02f301e0062367ded
9.2 媒体查询
代码示例:
@media (max-width: 767px) { ...css代码... }
@media (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 991px) { ...css代码... }
@media (min-width: 992px) and (max-width: 1199px) { ...css代码... }
@media (min-width: 1200px) { ...css代码... }
相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
推荐阅读:
以上是知名的网站前端布局分析的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 Python和JavaScript的未来:趋势和预测Apr 27, 2025 am 12:21 AM
Python和JavaScript的未来:趋势和预测Apr 27, 2025 am 12:21 AMPython和JavaScript的未来趋势包括:1.Python将巩固在科学计算和AI领域的地位,2.JavaScript将推动Web技术发展,3.跨平台开发将成为热门,4.性能优化将是重点。两者都将继续在各自领域扩展应用场景,并在性能上有更多突破。
 Python vs. JavaScript:开发环境和工具Apr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:开发环境和工具Apr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AMPython和JavaScript在开发环境上的选择都很重要。1)Python的开发环境包括PyCharm、JupyterNotebook和Anaconda,适合数据科学和快速原型开发。2)JavaScript的开发环境包括Node.js、VSCode和Webpack,适用于前端和后端开发。根据项目需求选择合适的工具可以提高开发效率和项目成功率。
 JavaScript是用C编写的吗?检查证据Apr 25, 2025 am 12:15 AM
JavaScript是用C编写的吗?检查证据Apr 25, 2025 am 12:15 AM是的,JavaScript的引擎核心是用C语言编写的。1)C语言提供了高效性能和底层控制,适合JavaScript引擎的开发。2)以V8引擎为例,其核心用C 编写,结合了C的效率和面向对象特性。3)JavaScript引擎的工作原理包括解析、编译和执行,C语言在这些过程中发挥关键作用。
 JavaScript的角色:使网络交互和动态Apr 24, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript的角色:使网络交互和动态Apr 24, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript是现代网站的核心,因为它增强了网页的交互性和动态性。1)它允许在不刷新页面的情况下改变内容,2)通过DOMAPI操作网页,3)支持复杂的交互效果如动画和拖放,4)优化性能和最佳实践提高用户体验。
 C和JavaScript:连接解释Apr 23, 2025 am 12:07 AM
C和JavaScript:连接解释Apr 23, 2025 am 12:07 AMC 和JavaScript通过WebAssembly实现互操作性。1)C 代码编译成WebAssembly模块,引入到JavaScript环境中,增强计算能力。2)在游戏开发中,C 处理物理引擎和图形渲染,JavaScript负责游戏逻辑和用户界面。
 从网站到应用程序:JavaScript的不同应用Apr 22, 2025 am 12:02 AM
从网站到应用程序:JavaScript的不同应用Apr 22, 2025 am 12:02 AMJavaScript在网站、移动应用、桌面应用和服务器端编程中均有广泛应用。1)在网站开发中,JavaScript与HTML、CSS一起操作DOM,实现动态效果,并支持如jQuery、React等框架。2)通过ReactNative和Ionic,JavaScript用于开发跨平台移动应用。3)Electron框架使JavaScript能构建桌面应用。4)Node.js让JavaScript在服务器端运行,支持高并发请求。
 Python vs. JavaScript:比较用例和应用程序Apr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:比较用例和应用程序Apr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AMPython更适合数据科学和自动化,JavaScript更适合前端和全栈开发。1.Python在数据科学和机器学习中表现出色,使用NumPy、Pandas等库进行数据处理和建模。2.Python在自动化和脚本编写方面简洁高效。3.JavaScript在前端开发中不可或缺,用于构建动态网页和单页面应用。4.JavaScript通过Node.js在后端开发中发挥作用,支持全栈开发。
 C/C在JavaScript口译员和编译器中的作用Apr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AM
C/C在JavaScript口译员和编译器中的作用Apr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AMC和C 在JavaScript引擎中扮演了至关重要的角色,主要用于实现解释器和JIT编译器。 1)C 用于解析JavaScript源码并生成抽象语法树。 2)C 负责生成和执行字节码。 3)C 实现JIT编译器,在运行时优化和编译热点代码,显着提高JavaScript的执行效率。


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

Atom编辑器mac版下载
最流行的的开源编辑器

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

EditPlus 中文破解版
体积小,语法高亮,不支持代码提示功能

Dreamweaver Mac版
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 英文版
推荐:为Win版本,支持代码提示!






