组合模式,将对象组合成树形结构以表示“部分-整体”的层次结构,组合模式使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性。
它使我们树型结构的问题中,模糊了简单元素和复杂元素的概念,客户程序可以像处理简单元素一样来处理复杂元素,从而使得客户程序与复杂元素的内部结构解耦。它可以帮助开发者对多个具有相似功能对象进行分类, 提高规范化设计
有许多关于分级数据结构的例子,使得组合模式非常有用武之地。关于分级数据结构的一个普遍性的例子是你每次使用电脑时所遇到的:文件系统。文件系统由目录和文件组成。每个目录都可以装内容。目录的内容可以是文件,也可以是目录。按照这种方式,计算机的文件系统就是以递归结构来组织的。如果你想要描述这样的数据结构,那么你可以使用组合模式Composite。
涉及角色
特点
在组合模式的层次体系中有两种类型的对象: 叶对象和组合对象, 这是一种递归定义, 但者也是其有用的原因所在, 一个组合对象可以由其他组合对象和叶子对象组成, 但叶子对象不再包含子对象, 组合对象用于叶子节点的分类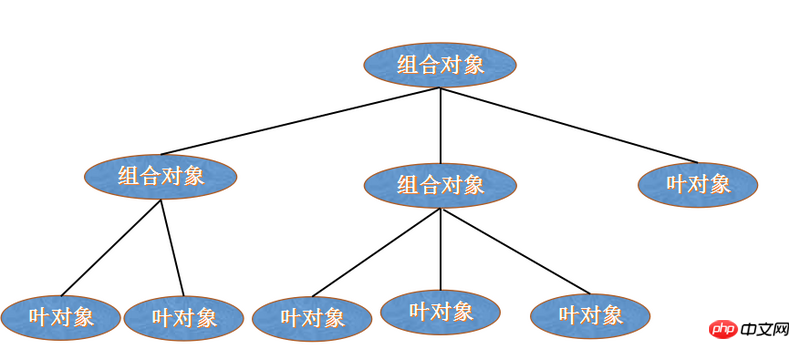
设计
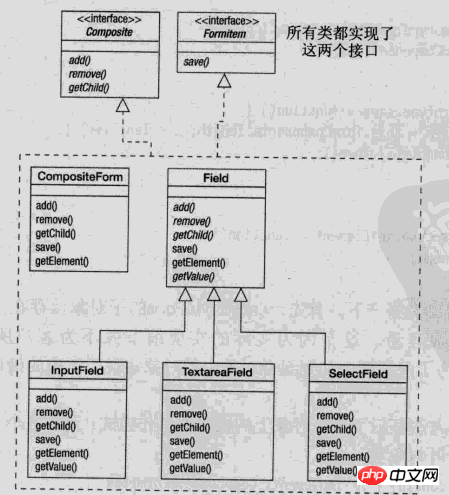
这里借用 javascript设计模式 的图来说明组合模式的设计
Interface 是组合中的对象声明接口,在适当的情况下,实现所有类共有接口的默认行为。声明一个接口用于访问和管理Component子部件。
Field 在组合中表示叶子结点对象,叶子结点没有子结点, 可以设计成抽象类, 通过继承设计出不同类别的叶子对象.
Composite 定义有子节点行为,用来存储子部件,在Component接口中实现与子部件有关操作,如增加(add)和删除(remove)等。

-
接口
/* Interfaces. */ var Composite = new Interface('Composite', ['add', 'remove', 'getChild']); var FormItem = new Interface('FormItem', ['save']); -
组合对象类
/* CompositeForm class. */ var CompositeForm = function(id, method, action) { // implements Composite, FormItem this.formComponents = []; this.element = document.createElement('form'); this.element.id = id; this.element.method = method || 'POST'; this.element.action = action || '#'; }; CompositeForm.prototype.add = function(child) { Interface.ensureImplements(child, Composite, FormItem); this.formComponents.push(child); this.element.appendChild(child.getElement()); }; CompositeForm.prototype.remove = function(child) { for(var i = 0, len = this.formComponents.length; i < len; i++) { if(this.formComponents[i] === child) { this.formComponents.splice(i, 1); // Remove one element from the array at // position i. break; } } }; CompositeForm.prototype.getChild = function(i) { return this.formComponents[i]; }; CompositeForm.prototype.save = function() { for(var i = 0, len = this.formComponents.length; i < len; i++) { this.formComponents[i].save(); } }; CompositeForm.prototype.getElement = function() { return this.element; }; -
叶子对象类
叶子对象可以是简单的一个类, 也可以设计成抽象类构建不同类别的叶子, 在此采用抽象类设计不同类别的叶子/* Field class, abstract. */ var Field = function(id) { // implements Composite, FormItem this.id = id; this.element; }; Field.prototype.add = function() {}; Field.prototype.remove = function() {}; Field.prototype.getChild = function() {}; Field.prototype.save = function() { setCookie(this.id, this.getValue); }; Field.prototype.getElement = function() { return this.element; }; Field.prototype.getValue = function() { throw new Error('Unsupported operation on the class Field.'); }; -
InputField 类
/* InputField class. */ var InputField = function(id, label) { // implements Composite, FormItem Field.call(this, id); this.input = document.createElement('input'); this.input.id = id; this.label = document.createElement('label'); var labelTextNode = document.createTextNode(label); this.label.appendChild(labelTextNode); this.element = document.createElement('p'); this.element.className = 'input-field'; this.element.appendChild(this.label); this.element.appendChild(this.input); }; extend(InputField, Field); // Inherit from Field. InputField.prototype.getValue = function() { return this.input.value; }; -
TextareaField 类
/* TextareaField class. */ var TextareaField = function(id, label) { // implements Composite, FormItem Field.call(this, id); this.textarea = document.createElement('textarea'); this.textarea.id = id; this.label = document.createElement('label'); var labelTextNode = document.createTextNode(label); this.label.appendChild(labelTextNode); this.element = document.createElement('p'); this.element.className = 'input-field'; this.element.appendChild(this.label); this.element.appendChild(this.textarea); }; extend(TextareaField, Field); // Inherit from Field. TextareaField.prototype.getValue = function() { return this.textarea.value; }; -
SelectField 类
/* SelectField class. */ var SelectField = function(id, label) { // implements Composite, FormItem Field.call(this, id); this.select = document.createElement('select'); this.select.id = id; this.label = document.createElement('label'); var labelTextNode = document.createTextNode(label); this.label.appendChild(labelTextNode); this.element = document.createElement('p'); this.element.className = 'input-field'; this.element.appendChild(this.label); this.element.appendChild(this.select); }; extend(SelectField, Field); // Inherit from Field. SelectField.prototype.getValue = function() { return this.select.options[this.select.selectedIndex].value; };
使用
/* Usage. */
var contactForm = new CompositeForm('contact-form', 'POST', 'contact.php');
contactForm.add(new InputField('first-name', 'First Name'));
contactForm.add(new InputField('last-name', 'Last Name'));
contactForm.add(new InputField('address', 'Address'));
contactForm.add(new InputField('city', 'City'));
contactForm.add(new SelectField('state', 'State', stateArray));
// var stateArray =[{'al', 'Alabama'}, ...]
contactForm.add(new InputField('zip', 'Zip'));
contactForm.add(new TextareaField('comments', 'Comments'));
addEvent(window, 'unload', contactForm.save);
组合模式适合对大批对象进行操作, 且操作对象具有层次关系, 通过对对象的分类操作籍此弱化对象之间的耦合, 这种模式使得代码模块化程度更高, 层次更鲜明, 维护性较好
相关推荐:
以上是js组合设计模式详解的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 C和JavaScript:连接解释Apr 23, 2025 am 12:07 AM
C和JavaScript:连接解释Apr 23, 2025 am 12:07 AMC 和JavaScript通过WebAssembly实现互操作性。1)C 代码编译成WebAssembly模块,引入到JavaScript环境中,增强计算能力。2)在游戏开发中,C 处理物理引擎和图形渲染,JavaScript负责游戏逻辑和用户界面。
 从网站到应用程序:JavaScript的不同应用Apr 22, 2025 am 12:02 AM
从网站到应用程序:JavaScript的不同应用Apr 22, 2025 am 12:02 AMJavaScript在网站、移动应用、桌面应用和服务器端编程中均有广泛应用。1)在网站开发中,JavaScript与HTML、CSS一起操作DOM,实现动态效果,并支持如jQuery、React等框架。2)通过ReactNative和Ionic,JavaScript用于开发跨平台移动应用。3)Electron框架使JavaScript能构建桌面应用。4)Node.js让JavaScript在服务器端运行,支持高并发请求。
 Python vs. JavaScript:比较用例和应用程序Apr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:比较用例和应用程序Apr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AMPython更适合数据科学和自动化,JavaScript更适合前端和全栈开发。1.Python在数据科学和机器学习中表现出色,使用NumPy、Pandas等库进行数据处理和建模。2.Python在自动化和脚本编写方面简洁高效。3.JavaScript在前端开发中不可或缺,用于构建动态网页和单页面应用。4.JavaScript通过Node.js在后端开发中发挥作用,支持全栈开发。
 C/C在JavaScript口译员和编译器中的作用Apr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AM
C/C在JavaScript口译员和编译器中的作用Apr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AMC和C 在JavaScript引擎中扮演了至关重要的角色,主要用于实现解释器和JIT编译器。 1)C 用于解析JavaScript源码并生成抽象语法树。 2)C 负责生成和执行字节码。 3)C 实现JIT编译器,在运行时优化和编译热点代码,显着提高JavaScript的执行效率。
 JavaScript在行动中:现实世界中的示例和项目Apr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AM
JavaScript在行动中:现实世界中的示例和项目Apr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AMJavaScript在现实世界中的应用包括前端和后端开发。1)通过构建TODO列表应用展示前端应用,涉及DOM操作和事件处理。2)通过Node.js和Express构建RESTfulAPI展示后端应用。
 JavaScript和Web:核心功能和用例Apr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
JavaScript和Web:核心功能和用例Apr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AMJavaScript在Web开发中的主要用途包括客户端交互、表单验证和异步通信。1)通过DOM操作实现动态内容更新和用户交互;2)在用户提交数据前进行客户端验证,提高用户体验;3)通过AJAX技术实现与服务器的无刷新通信。
 了解JavaScript引擎:实施详细信息Apr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
了解JavaScript引擎:实施详细信息Apr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM理解JavaScript引擎内部工作原理对开发者重要,因为它能帮助编写更高效的代码并理解性能瓶颈和优化策略。1)引擎的工作流程包括解析、编译和执行三个阶段;2)执行过程中,引擎会进行动态优化,如内联缓存和隐藏类;3)最佳实践包括避免全局变量、优化循环、使用const和let,以及避免过度使用闭包。
 Python vs. JavaScript:学习曲线和易用性Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:学习曲线和易用性Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AMPython更适合初学者,学习曲线平缓,语法简洁;JavaScript适合前端开发,学习曲线较陡,语法灵活。1.Python语法直观,适用于数据科学和后端开发。2.JavaScript灵活,广泛用于前端和服务器端编程。


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

适用于 Eclipse 的 SAP NetWeaver 服务器适配器
将Eclipse与SAP NetWeaver应用服务器集成。

螳螂BT
Mantis是一个易于部署的基于Web的缺陷跟踪工具,用于帮助产品缺陷跟踪。它需要PHP、MySQL和一个Web服务器。请查看我们的演示和托管服务。

Atom编辑器mac版下载
最流行的的开源编辑器

Dreamweaver Mac版
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Linux新版
SublimeText3 Linux最新版