MongoDB 的Replication是通过一个日志来存储写操作的,这个日志就叫做oplog,而下面这篇文章主要给大家介绍了利用MongoDB中oplog机制实现准实时数据的操作监控的相关资料,需要的朋友可以参考借鉴,下面来一起看看吧。
前言
最近有一个需求是要实时获取到新插入到MongoDB的数据,而插入程序本身已经有一套处理逻辑,所以不方便直接在插入程序里写相关程序,传统的数据库大多自带这种触发器机制,但是Mongo没有相关的函数可以用(也可能我了解的太少了,求纠正),当然还有一点是需要python实现,于是收集整理了一个相应的实现方法。
一、引子
首先可以想到,这种需求其实很像数据库的主从备份机制,从数据库之所以能够同步主库是因为存在某些指标来做控制,我们知道MongoDB虽然没有现成触发器,但是它能够实现主从备份,所以我们就从它的主从备份机制入手。
二、OPLOG
首先,需要以master模式来打开mongod守护,命令行使用–master,或者配置文件增加master键为true。
此时,我们可以在Mongo的系统库local里见到新增的collection——oplog,此时oplog.$main里就会存储进oplog信息,如果此时还有充当从数据库的Mongo存在,就会还有一些slaves的信息,由于我们这里并不是主从同步,所以不存在这些集合。
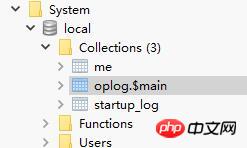
再来看看oplog结构:
"ts" : Timestamp(6417682881216249, 1), 时间戳
"h" : NumberLong(0), 长度
"v" : 2,
"op" : "n", 操作类型
"ns" : "", 操作的库和集合
"o2" : "_id" update条件
"o" : {} 操作值,即document这里需要知道op的几种属性:
insert,'i' update, 'u' remove(delete), 'd' cmd, 'c' noop, 'n' 空操作
从上面的信息可以看出,我们只要不断读取到ts来做对比,然后根据op即可判断当前出现的是什么操作,相当于使用程序实现了一个从数据库的接收端。
三、CODE
在Github上找到了别人的实现方式,不过它的函数库太老旧,所以在他的基础上进行修改。
Github地址:github.com/RedBeard0531/mongo-oplog-watcher
mongo_oplog_watcher.py如下:
#!/usr/bin/python
import pymongo
import re
import time
from pprint import pprint # pretty printer
from pymongo.errors import AutoReconnect
class OplogWatcher(object):
def init(self, db=None, collection=None, poll_time=1.0, connection=None, start_now=True):
if collection is not None:
if db is None:
raise ValueError('must specify db if you specify a collection')
self._ns_filter = db + '.' + collection
elif db is not None:
self._ns_filter = re.compile(r'^%s\.' % db)
else:
self._ns_filter = None
self.poll_time = poll_time
self.connection = connection or pymongo.Connection()
if start_now:
self.start()
@staticmethod
def get_id(op):
id = None
o2 = op.get('o2')
if o2 is not None:
id = o2.get('_id')
if id is None:
id = op['o'].get('_id')
return id
def start(self):
oplog = self.connection.local['oplog.$main']
ts = oplog.find().sort('$natural', -1)[0]['ts']
while True:
if self._ns_filter is None:
filter = {}
else:
filter = {'ns': self._ns_filter}
filter['ts'] = {'$gt': ts}
try:
cursor = oplog.find(filter, tailable=True)
while True:
for op in cursor:
ts = op['ts']
id = self.get_id(op)
self.all_with_noop(ns=op['ns'], ts=ts, op=op['op'], id=id, raw=op)
time.sleep(self.poll_time)
if not cursor.alive:
break
except AutoReconnect:
time.sleep(self.poll_time)
def all_with_noop(self, ns, ts, op, id, raw):
if op == 'n':
self.noop(ts=ts)
else:
self.all(ns=ns, ts=ts, op=op, id=id, raw=raw)
def all(self, ns, ts, op, id, raw):
if op == 'i':
self.insert(ns=ns, ts=ts, id=id, obj=raw['o'], raw=raw)
elif op == 'u':
self.update(ns=ns, ts=ts, id=id, mod=raw['o'], raw=raw)
elif op == 'd':
self.delete(ns=ns, ts=ts, id=id, raw=raw)
elif op == 'c':
self.command(ns=ns, ts=ts, cmd=raw['o'], raw=raw)
elif op == 'db':
self.db_declare(ns=ns, ts=ts, raw=raw)
def noop(self, ts):
pass
def insert(self, ns, ts, id, obj, raw, **kw):
pass
def update(self, ns, ts, id, mod, raw, **kw):
pass
def delete(self, ns, ts, id, raw, **kw):
pass
def command(self, ns, ts, cmd, raw, **kw):
pass
def db_declare(self, ns, ts, **kw):
pass
class OplogPrinter(OplogWatcher):
def all(self, **kw):
pprint (kw)
print #newline
if name == 'main':
OplogPrinter()首先是实现一个数据库的初始化,设定一个延迟时间(准实时):
self.poll_time = poll_time self.connection = connection or pymongo.MongoClient()
主要的函数是start() ,实现一个时间的比对并进行相应字段的处理:
def start(self):
oplog = self.connection.local['oplog.$main']
#读取之前提到的库
ts = oplog.find().sort('$natural', -1)[0]['ts']
#获取一个时间边际
while True:
if self._ns_filter is None:
filter = {}
else:
filter = {'ns': self._ns_filter}
filter['ts'] = {'$gt': ts}
try:
cursor = oplog.find(filter)
#对此时间之后的进行处理
while True:
for op in cursor:
ts = op['ts']
id = self.get_id(op)
self.all_with_noop(ns=op['ns'], ts=ts, op=op['op'], id=id, raw=op)
#可以指定处理插入监控,更新监控或者删除监控等
time.sleep(self.poll_time)
if not cursor.alive:
break
except AutoReconnect:
time.sleep(self.poll_time)循环这个start函数,在all_with_noop这里就可以编写相应的监控处理逻辑。
这样就可以实现一个简易的准实时Mongo数据库操作监控器,下一步就可以配合其他操作来对新入库的程序进行相应处理。
以上是分享用MongoDB中oplog机制实现数据监控实例的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 MySQL的位置:数据库和编程Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL的位置:数据库和编程Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AMMySQL在数据库和编程中的地位非常重要,它是一个开源的关系型数据库管理系统,广泛应用于各种应用场景。1)MySQL提供高效的数据存储、组织和检索功能,支持Web、移动和企业级系统。2)它使用客户端-服务器架构,支持多种存储引擎和索引优化。3)基本用法包括创建表和插入数据,高级用法涉及多表JOIN和复杂查询。4)常见问题如SQL语法错误和性能问题可以通过EXPLAIN命令和慢查询日志调试。5)性能优化方法包括合理使用索引、优化查询和使用缓存,最佳实践包括使用事务和PreparedStatemen
 MySQL:从小型企业到大型企业Apr 13, 2025 am 12:17 AM
MySQL:从小型企业到大型企业Apr 13, 2025 am 12:17 AMMySQL适合小型和大型企业。1)小型企业可使用MySQL进行基本数据管理,如存储客户信息。2)大型企业可利用MySQL处理海量数据和复杂业务逻辑,优化查询性能和事务处理。
 幻影是什么读取的,InnoDB如何阻止它们(下一个键锁定)?Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
幻影是什么读取的,InnoDB如何阻止它们(下一个键锁定)?Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AMInnoDB通过Next-KeyLocking机制有效防止幻读。1)Next-KeyLocking结合行锁和间隙锁,锁定记录及其间隙,防止新记录插入。2)在实际应用中,通过优化查询和调整隔离级别,可以减少锁竞争,提高并发性能。
 mysql:不是编程语言,而是...Apr 13, 2025 am 12:03 AM
mysql:不是编程语言,而是...Apr 13, 2025 am 12:03 AMMySQL不是一门编程语言,但其查询语言SQL具备编程语言的特性:1.SQL支持条件判断、循环和变量操作;2.通过存储过程、触发器和函数,用户可以在数据库中执行复杂逻辑操作。
 MySQL:世界上最受欢迎的数据库的简介Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL:世界上最受欢迎的数据库的简介Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AMMySQL是一种开源的关系型数据库管理系统,主要用于快速、可靠地存储和检索数据。其工作原理包括客户端请求、查询解析、执行查询和返回结果。使用示例包括创建表、插入和查询数据,以及高级功能如JOIN操作。常见错误涉及SQL语法、数据类型和权限问题,优化建议包括使用索引、优化查询和分表分区。
 MySQL的重要性:数据存储和管理Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL的重要性:数据存储和管理Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AMMySQL是一个开源的关系型数据库管理系统,适用于数据存储、管理、查询和安全。1.它支持多种操作系统,广泛应用于Web应用等领域。2.通过客户端-服务器架构和不同存储引擎,MySQL高效处理数据。3.基本用法包括创建数据库和表,插入、查询和更新数据。4.高级用法涉及复杂查询和存储过程。5.常见错误可通过EXPLAIN语句调试。6.性能优化包括合理使用索引和优化查询语句。
 为什么要使用mysql?利益和优势Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
为什么要使用mysql?利益和优势Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM选择MySQL的原因是其性能、可靠性、易用性和社区支持。1.MySQL提供高效的数据存储和检索功能,支持多种数据类型和高级查询操作。2.采用客户端-服务器架构和多种存储引擎,支持事务和查询优化。3.易于使用,支持多种操作系统和编程语言。4.拥有强大的社区支持,提供丰富的资源和解决方案。
 描述InnoDB锁定机制(共享锁,独家锁,意向锁,记录锁,间隙锁,下一键锁)。Apr 12, 2025 am 12:16 AM
描述InnoDB锁定机制(共享锁,独家锁,意向锁,记录锁,间隙锁,下一键锁)。Apr 12, 2025 am 12:16 AMInnoDB的锁机制包括共享锁、排他锁、意向锁、记录锁、间隙锁和下一个键锁。1.共享锁允许事务读取数据而不阻止其他事务读取。2.排他锁阻止其他事务读取和修改数据。3.意向锁优化锁效率。4.记录锁锁定索引记录。5.间隙锁锁定索引记录间隙。6.下一个键锁是记录锁和间隙锁的组合,确保数据一致性。


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

适用于 Eclipse 的 SAP NetWeaver 服务器适配器
将Eclipse与SAP NetWeaver应用服务器集成。

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) 是一个PHP/MySQL的Web应用程序,非常容易受到攻击。它的主要目标是成为安全专业人员在合法环境中测试自己的技能和工具的辅助工具,帮助Web开发人员更好地理解保护Web应用程序的过程,并帮助教师/学生在课堂环境中教授/学习Web应用程序安全。DVWA的目标是通过简单直接的界面练习一些最常见的Web漏洞,难度各不相同。请注意,该软件中

SublimeText3 英文版
推荐:为Win版本,支持代码提示!

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

Atom编辑器mac版下载
最流行的的开源编辑器





