简介
Api作为业务逻辑提供方,承载了项目的核心逻辑,因而具有相对高的逻辑复杂性。在这样的前提下如何简化代码编写,如何规范统一书写风格和逻辑规范,如何提高代码的维护性和扩展性。项目的搭建的高内聚低耦合变得重要。
示例的是一个企业级项目,框架图如下
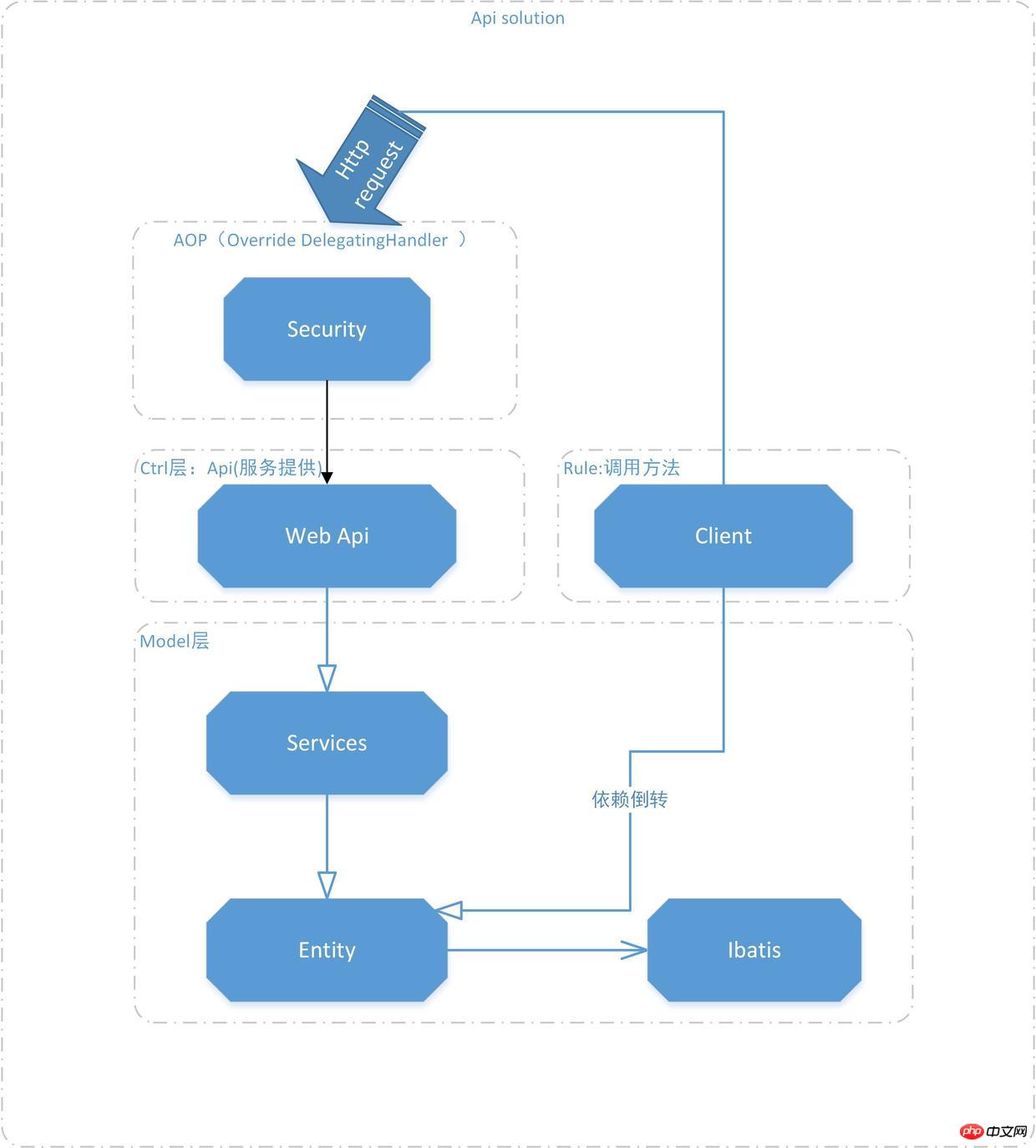
api层.jpg
Security:重写了Http请求(Override DelegatingHandler),在请求的切面进行合法性判断,顺便进行签名要求的预处理。
Client:定义了统一的接口调用方式共调用端使用,简化及统一了接口使用。
Ctrl层:作为服务的直接提供方,在服务器上直接提供类似于RestFul风格的接口(感觉严格的RestFul风格,需要有完备的领域模型驱动,实际上的情况总是不尽如人意,领域抽象能力不够。),获取请求数据,按需调用Filter过滤器,进一步判断,调用
Model层:作为业务模型层,提供业务逻辑的实际操作。使用统一的实体模型,并联系到Ibatis上,进行数据操作。
具体的代码结构如下图:
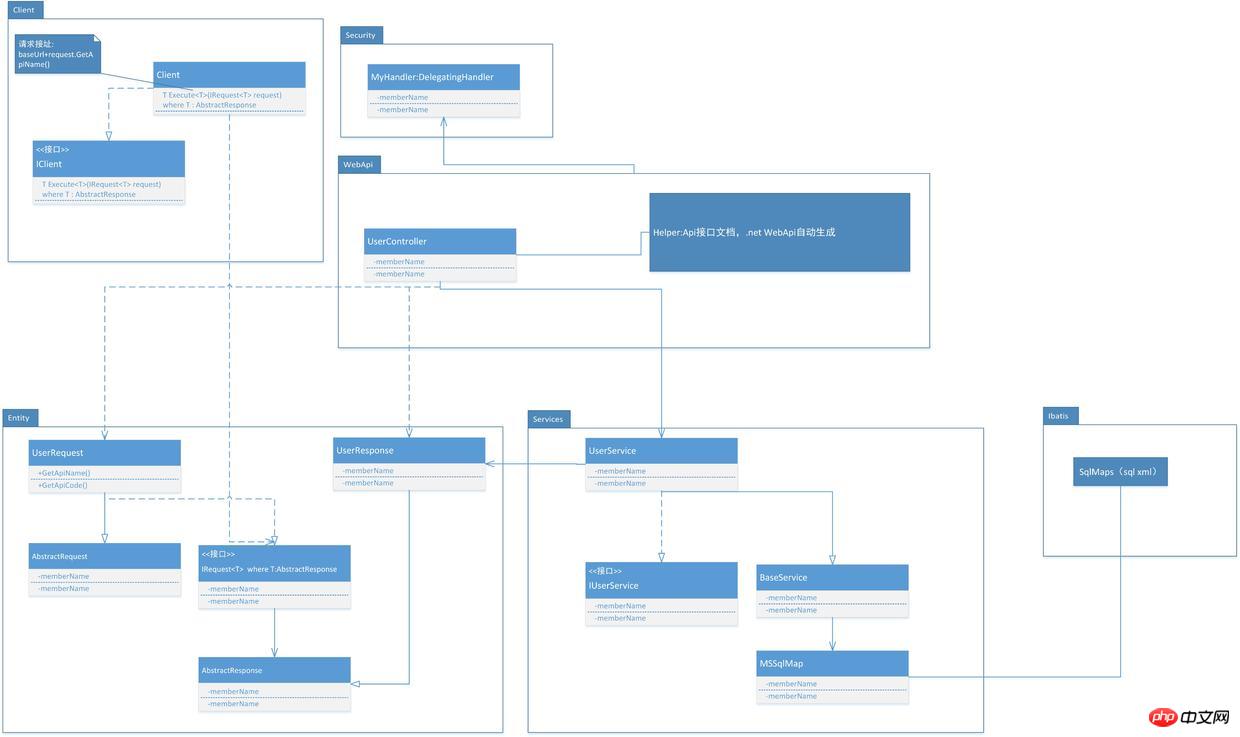
Api-UML.jpg
下面是各个模块的详细介绍和代码示例:
Entity library项目代码示例
项目结构如下图:
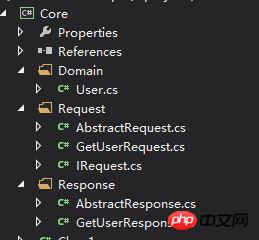
entity.jpg
Domain模块,作为实体模型,简易代码如下
public class User
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string NickName { get; set; }
public string Avatar { get; set; }
}
Request,请求结构模型,利用了泛型接口,将请求类和返回类联系,起到了控制倒转的作用。
public abstract class AbstractRequest
{
public bool ValidateParameters()
{
//公用方法示例,验证参数合法性
}
}
public interface IRequest<T> where T:AbstractResponse
{
//获取接口名称
string GetApiName();
//获取接口编码
string GetApiCode();
}
//获取User信息的请求结构定义
public class GetUserRequest:AbstractRequest,IRequest<GetUserResponse>
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string GetApiName()
{
return "User.GetUserDetail";
}
public string GetApiCode()
{
return "User001";
}
}
Response模块,作为请求的返回类型,定义统一的返回结构,便于消费者进行一致性返回码判断处理。
public abstract class AbstractResponse
{
//返回码
public int Code { get; set; }
//报错信息
public string Message { get; set; }
}
public class GetUserResponse:AbstractResponse
{
public User User { get; set; }
}
Service项目代码示例
项目结构如下图:
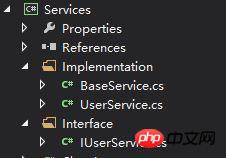
service.jpg
代码示例:
public interface IUserService
{
GetUserResponse GetUser(int id);
}
public class BaseService
{
//protected SqlInstance sqlInstance;
public BaseService()
{
//sqlInstance=new SqlInstance(); //实例化数据库连接
//...
}
//...
}
public class UserService:BaseService,IUserService
{
public GetUserResponse GetUser(int id)
{
//链接数据库获取数据
//...
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
Security类库代码示例
类库只是处理了安全性问题,在api请求入口处添加上权限判断。使用重写Http请求的方式。
代码示例
public class MyHandler : DelegatingHandler
{
protected async override Task<HttpResponseMessage> SendAsync(HttpRequestMessage request, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
IEnumerable<string> keyEnumerable;
var t1 = request.Headers.TryGetValues("key", out keyEnumerable);
var key = keyEnumerable.FirstOrDefault();
if (!true)//验证类似于token的权限
{
return await Task.Factory.StartNew<HttpResponseMessage>(
() => new HttpResponseMessage(HttpStatusCode.Forbidden)
{
Content = new StringContent("error message")
});
}
//如果有signature,判断,并加结果标志,没有的话,清除signature相关信息,防止伪造。
//.....
return await base.SendAsync(request, cancellationToken);
}
}
抽象出来的权限判断,可直接调用到webapi端,添加到路由配置代码中。
WebApi项目示例
作为接口的实际定义,webapi定义了接口文件的实际规则,并做出相应的安全管理及接口的权限控制。学习微信的权限控制,大概确定了几种接口:
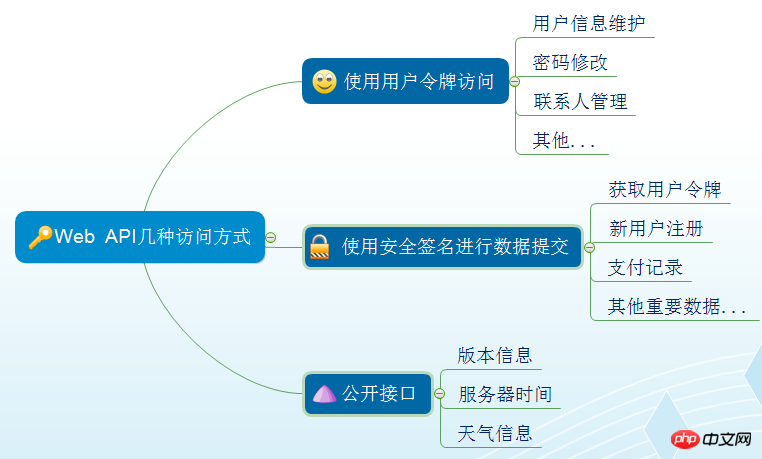
接口权限.png
这些权限的判断都放在了Security做了集中管理。接口定义只需要在相应的逻辑上使用判断合法性即可。
代码示例:
public class UserController : ApiController
{
private IUserService userService;
public UserController()
{
userService=new UserService();
}
[Signature]//安全签名过滤器判断
[HttpPost]
public GetUserResponse GetUser(GetUserRequest request)
{
//参数判断,安全性判断等等
var ret = userService.GetUser(request.Id);
return ret;
}
}
以上是一个获取用户信息的示例接口,而作为接口入口的路由配置,则需要对请求的合法性进行判断,路由配置代码如下:
public static void Register(HttpConfiguration config)
{
// Web API configuration and services
// Configure Web API to use only bearer token authentication.
config.SuppressDefaultHostAuthentication();
config.Filters.Add(new HostAuthenticationFilter(OAuthDefaults.AuthenticationType));
// Web API routes
config.MapHttpAttributeRoutes();
config.Routes.MapHttpRoute(
name: "DefaultApi",
routeTemplate: "api/{controller}/{action}",
defaults: new { id = RouteParameter.Optional }
);
//添加的代码,添加http请求的入口处理
config.MessageHandlers.Add(new MyHandler());
}
Client类库代码示例
Client类库定义了接口调用的公共方法。
1、利用泛型接口,将请求类和返回类进行了封装,简化调用的代码书写。
2、并使得消费者调用接口需要通过代理类,避开了跨域的问题。
3、消费者的调用都同意使用统一类库,是的日志的处理统一,返回的错误也可以进行一致化定义。
代码示例如下:
public interface IClient
{
T Execute<T>(IRequest<T> request) where T : AbstractResponse;
}
public class DefaultClient:IClient
{
private readonly string appKey;
private readonly string appSecret;
private readonly string baseUrl = "http://localhost:16469/api/";
private readonly bool isNeedLogFile = false;
private readonly LogFile logFile;
public static readonly string SecureHeaderAppKey = "secure_head_appkey";
public static readonly string SecureHeaderSignature = "secure_head_signature";
public DefaultClient()
{
baseUrl = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["service_base_url"];
appKey = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["app_key"];
appSecret = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["app_secret"];
isNeedLogFile = "1".Equals(ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["client_log_file"]);
logFile = new LogFile("client_log_path");
logFile.SubPath = appKey;
}
public DefaultClient(string serviceBase, string code, string key)
{
baseUrl = serviceBase;
appKey = code;
appSecret = key;
}
public T Execute<T>(IRequest<T> request) where T : AbstractResponse
{
var webRequest = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(baseUrl + request.GetApiName());
webRequest.Method = "POST";
string reqJson;
string sign;
using (Stream rs = webRequest.GetRequestStream())
{
reqJson = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(request);
byte[] reqBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(reqJson);
rs.Write(reqBytes, 0, reqBytes.Length);
rs.Close();
}
webRequest.ContentType = "application/json";
webRequest.Headers.Add(SecureHeaderAppKey, appKey);
sign = ComputeHash(appKey, appSecret, reqJson);
webRequest.Headers.Add(SecureHeaderSignature, sign);
//记录日志
if (isNeedLogFile)
{
logFile.Log(string.Format("[{0}] 请求内容: {1}", request.GetApiCode(), reqJson));
logFile.Log(string.Format("[{0}] 请求签名: {1}", request.GetApiCode(), sign));
}
try
{
using (var resp = (HttpWebResponse)webRequest.GetResponse())
{
try
{
Stream respStream = resp.GetResponseStream();
if (respStream == null)
{
throw new WebException("GetResponseStream returned null");
}
var streamReader = new StreamReader(respStream);
string respStr = streamReader.ReadToEnd();
//记录日志
if (isNeedLogFile)
{
logFile.Log(string.Format("[{0}] 响应内容: {1}", request.GetApiCode(), respStr));
}
return JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<T>(respStr);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
//记录日志
if (isNeedLogFile)
{
logFile.Log(string.Format("[{0}] 响应错误: {1}", request.GetApiCode(), e.Message));
}
throw new ApplicationException(e.Message, e);
}
}
}
catch (WebException e)
{
var errMsg = new StreamReader(e.Response.GetResponseStream()).ReadToEnd();
//记录日志
if (isNeedLogFile)
{
logFile.Log(string.Format("[{0}] 请求错误: {1}", request.GetApiCode(), errMsg));
}
throw new APIServiceException(errMsg);
}
}
private string ComputeHash(string key, string secret, string body)
{
return
Convert.ToBase64String(
SHA1.Create().ComputeHash(Encoding.Default.GetBytes(string.Concat(key, secret, body.Trim()))));
}
}
以上就是Api项目端的各个核心环节的详细介绍。
接下来会对调用端即前端进行简单的介绍。Asp.net(三)Web端展示
以上是Asp.net(二)业务处理接口项目(Web Api)的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 使用C#.NET开发:实用指南和示例May 12, 2025 am 12:16 AM
使用C#.NET开发:实用指南和示例May 12, 2025 am 12:16 AMC#和.NET提供了强大的功能和高效的开发环境。1)C#是一种现代、面向对象的编程语言,结合了C 的强大和Java的简洁性。2).NET框架是一个用于构建和运行应用程序的平台,支持多种编程语言。3)C#中的类和对象是面向对象编程的核心,类定义数据和行为,对象是类的实例。4).NET的垃圾回收机制自动管理内存,简化开发者的工作。5)C#和.NET提供了强大的文件操作功能,支持同步和异步编程。6)常见错误可以通过调试器、日志记录和异常处理来解决。7)性能优化和最佳实践包括使用StringBuild
 C#.NET:了解Microsoft .NET框架May 11, 2025 am 12:17 AM
C#.NET:了解Microsoft .NET框架May 11, 2025 am 12:17 AM.NETFramework是一个跨语言、跨平台的开发平台,提供一致的编程模型和强大的运行时环境。1)它由CLR和FCL组成,CLR管理内存和线程,FCL提供预构建功能。2)使用示例包括读取文件和LINQ查询。3)常见错误涉及未处理异常和内存泄漏,需使用调试工具解决。4)性能优化可通过异步编程和缓存实现,保持代码可读性和可维护性是关键。
 c#.net的寿命:其持久流行的原因May 10, 2025 am 12:12 AM
c#.net的寿命:其持久流行的原因May 10, 2025 am 12:12 AMC#.NET保持持久吸引力的原因包括其出色的性能、丰富的生态系统、强大的社区支持和跨平台开发能力。1)性能表现优异,适用于企业级应用和游戏开发;2).NET框架提供了广泛的类库和工具,支持多种开发领域;3)拥有活跃的开发者社区和丰富的学习资源;4).NETCore实现了跨平台开发,扩展了应用场景。
 掌握C#.NET设计模式:从单胎到依赖注入May 09, 2025 am 12:15 AM
掌握C#.NET设计模式:从单胎到依赖注入May 09, 2025 am 12:15 AMC#.NET中的设计模式包括Singleton模式和依赖注入。1.Singleton模式确保类只有一个实例,适用于需要全局访问点的场景,但需注意线程安全和滥用问题。2.依赖注入通过注入依赖提高代码灵活性和可测试性,常用于构造函数注入,但需避免过度使用导致复杂度增加。
 现代世界中的C#.NET:应用和行业May 08, 2025 am 12:08 AM
现代世界中的C#.NET:应用和行业May 08, 2025 am 12:08 AMC#.NET在现代世界中广泛应用于游戏开发、金融服务、物联网和云计算等领域。1)在游戏开发中,通过Unity引擎使用C#进行编程。2)金融服务领域,C#.NET用于开发高性能的交易系统和数据分析工具。3)物联网和云计算方面,C#.NET通过Azure服务提供支持,开发设备控制逻辑和数据处理。
 C#.NET开发人员社区:资源和支持May 06, 2025 am 12:11 AM
C#.NET开发人员社区:资源和支持May 06, 2025 am 12:11 AMC#.NET开发者社区提供了丰富的资源和支持,包括:1.微软的官方文档,2.社区论坛如StackOverflow和Reddit,3.GitHub上的开源项目,这些资源帮助开发者从基础学习到高级应用,提升编程技能。
 C#.NET优势:功能,好处和用例May 05, 2025 am 12:01 AM
C#.NET优势:功能,好处和用例May 05, 2025 am 12:01 AMC#.NET的优势包括:1)语言特性,如异步编程简化了开发;2)性能与可靠性,通过JIT编译和垃圾回收机制提升效率;3)跨平台支持,.NETCore扩展了应用场景;4)实际应用广泛,从Web到桌面和游戏开发都有出色表现。


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

安全考试浏览器
Safe Exam Browser是一个安全的浏览器环境,用于安全地进行在线考试。该软件将任何计算机变成一个安全的工作站。它控制对任何实用工具的访问,并防止学生使用未经授权的资源。

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) 是一个PHP/MySQL的Web应用程序,非常容易受到攻击。它的主要目标是成为安全专业人员在合法环境中测试自己的技能和工具的辅助工具,帮助Web开发人员更好地理解保护Web应用程序的过程,并帮助教师/学生在课堂环境中教授/学习Web应用程序安全。DVWA的目标是通过简单直接的界面练习一些最常见的Web漏洞,难度各不相同。请注意,该软件中







