本篇文章主要介绍了Spring Boot 添加MySQL数据库及JPA,小编觉得挺不错的,现在分享给大家,也给大家做个参考。一起跟随小编过来看看吧
最近在学习Spring Boot,继续前面的学习,这一次我们加入MySQL数据库和JPA。
配置:
pom.xml文件
<!-- 添加Mysql和JPA--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> </dependency>
在Application.properties(在resource文件夹下新建,进行配置)文件中添加数据进行配置:
spring.datasource.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_boot spring.datasource.username = root spring.datasource.password = root spring.datasource.driverClassName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver # Specify the DBMS spring.jpa.database = MYSQL # Show or not log for each sql query spring.jpa.show-sql = true # Hibernate ddl auto (create, create-drop, update) spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update # Naming strategy spring.jpa.hibernate.naming-strategy = org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy # stripped before adding them to the entity manager) spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect
User类
package com.seawater.bean;
import javax.persistence.*;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
/**
* Created by zhouhs on 2016/12/30.
*/
@Entity
@Table(name = "user")
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Long id;
private String name;
private int age;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}UserController
package com.seawater.controller;
import com.seawater.Dao.UserDao;
import com.seawater.bean.User;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParams;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* Created by zhouhs on 2016/12/30.
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/user")
@Api(description = "用户")
public class UserController {
@Resource
UserDao userDAO;
@ApiOperation(value = "添加用户")
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "name" , value = "name" , paramType = "query" , required = true ),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "age" , value = "age" , paramType = "query" , required = true )
})
@RequestMapping(value = "/addUser" , method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String addUser(@RequestParam(value = "name") String name,@RequestParam(value = "age") int age){
User user = new User();
user.setName(name);
user.setAge(age);
userDAO.save(user);
return "add user success !";
}
@ApiOperation(value = "查找用户")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id" , value = "id" , paramType = "query" , required = true , dataType = "int")
@RequestMapping(value = "/findById" , method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String findById(@RequestParam(value = "id") Long id){
User user = userDAO.findById(id);
if(user == null){
return "error";
}else{
return "name:" + user.getName() + " , age:" + user.getAge();
}
}
@ApiOperation(value = "查询所有用户")
@RequestMapping(value = "/findAll" , method = RequestMethod.POST)
public Iterable findAll(){
Iterable<User> userList = userDAO.findAll();
return userList;
}
@ApiOperation(value = "删除用户")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id" , value = "id" , paramType = "query" , required = true , dataType = "int")
@RequestMapping(value = "/deleteById" , method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String deleteById(@RequestParam(value = "id") Long id){
userDAO.delete(id);
return "delete success !";
}
}数据表(id定义为Integer):
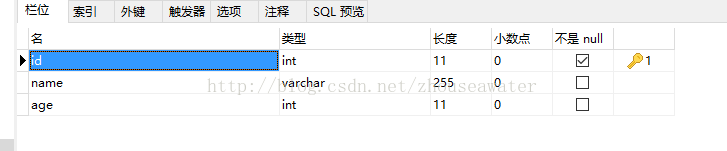
UserDao:
package com.seawater.Dao;
import com.seawater.bean.User;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
/**
* Created by zhouhs on 2016/12/30.
*/
public interface UserDao extends CrudRepository<User, Long> {
public User findById(Long id);
}然后启动项目:访问localhost:8081/swagger-ui.html
结果:
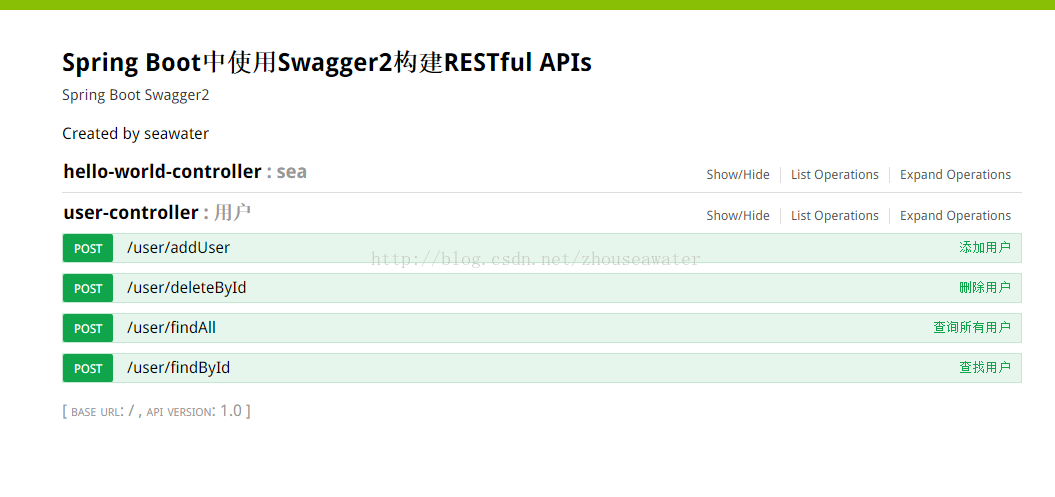
方法我就不一一操作了。
以上是Spring Boot添加MySQL数据库及JPA实例的示例代码分享的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 解释酸的特性(原子,一致性,隔离,耐用性)。Apr 16, 2025 am 12:20 AM
解释酸的特性(原子,一致性,隔离,耐用性)。Apr 16, 2025 am 12:20 AMACID属性包括原子性、一致性、隔离性和持久性,是数据库设计的基石。1.原子性确保事务要么完全成功,要么完全失败。2.一致性保证数据库在事务前后保持一致状态。3.隔离性确保事务之间互不干扰。4.持久性确保事务提交后数据永久保存。
 MySQL:数据库管理系统与编程语言Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
MySQL:数据库管理系统与编程语言Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AMMySQL既是数据库管理系统(DBMS),也与编程语言紧密相关。1)作为DBMS,MySQL用于存储、组织和检索数据,优化索引可提高查询性能。2)通过SQL与编程语言结合,嵌入在如Python中,使用ORM工具如SQLAlchemy可简化操作。3)性能优化包括索引、查询、缓存、分库分表和事务管理。
 mySQL:使用SQL命令管理数据Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
mySQL:使用SQL命令管理数据Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AMMySQL使用SQL命令管理数据。1.基本命令包括SELECT、INSERT、UPDATE和DELETE。2.高级用法涉及JOIN、子查询和聚合函数。3.常见错误有语法、逻辑和性能问题。4.优化技巧包括使用索引、避免SELECT*和使用LIMIT。
 MySQL的目的:有效存储和管理数据Apr 16, 2025 am 12:16 AM
MySQL的目的:有效存储和管理数据Apr 16, 2025 am 12:16 AMMySQL是一种高效的关系型数据库管理系统,适用于存储和管理数据。其优势包括高性能查询、灵活的事务处理和丰富的数据类型。实际应用中,MySQL常用于电商平台、社交网络和内容管理系统,但需注意性能优化、数据安全和扩展性。
 SQL和MySQL:了解关系Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
SQL和MySQL:了解关系Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AMSQL和MySQL的关系是标准语言与具体实现的关系。1.SQL是用于管理和操作关系数据库的标准语言,允许进行数据的增、删、改、查。2.MySQL是一个具体的数据库管理系统,使用SQL作为其操作语言,并提供高效的数据存储和管理。
 说明InnoDB重做日志和撤消日志的作用。Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
说明InnoDB重做日志和撤消日志的作用。Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AMInnoDB使用redologs和undologs确保数据一致性和可靠性。1.redologs记录数据页修改,确保崩溃恢复和事务持久性。2.undologs记录数据原始值,支持事务回滚和MVCC。
 在解释输出(类型,键,行,额外)中要查找的关键指标是什么?Apr 15, 2025 am 12:15 AM
在解释输出(类型,键,行,额外)中要查找的关键指标是什么?Apr 15, 2025 am 12:15 AMEXPLAIN命令的关键指标包括type、key、rows和Extra。1)type反映查询的访问类型,值越高效率越高,如const优于ALL。2)key显示使用的索引,NULL表示无索引。3)rows预估扫描行数,影响查询性能。4)Extra提供额外信息,如Usingfilesort提示需要优化。
 在解释中使用临时状态以及如何避免它是什么?Apr 15, 2025 am 12:14 AM
在解释中使用临时状态以及如何避免它是什么?Apr 15, 2025 am 12:14 AMUsingtemporary在MySQL查询中表示需要创建临时表,常见于使用DISTINCT、GROUPBY或非索引列的ORDERBY。可以通过优化索引和重写查询避免其出现,提升查询性能。具体来说,Usingtemporary出现在EXPLAIN输出中时,意味着MySQL需要创建临时表来处理查询。这通常发生在以下情况:1)使用DISTINCT或GROUPBY时进行去重或分组;2)ORDERBY包含非索引列时进行排序;3)使用复杂的子查询或联接操作。优化方法包括:1)为ORDERBY和GROUPB


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) 是一个PHP/MySQL的Web应用程序,非常容易受到攻击。它的主要目标是成为安全专业人员在合法环境中测试自己的技能和工具的辅助工具,帮助Web开发人员更好地理解保护Web应用程序的过程,并帮助教师/学生在课堂环境中教授/学习Web应用程序安全。DVWA的目标是通过简单直接的界面练习一些最常见的Web漏洞,难度各不相同。请注意,该软件中

VSCode Windows 64位 下载
微软推出的免费、功能强大的一款IDE编辑器

SublimeText3 Linux新版
SublimeText3 Linux最新版

Atom编辑器mac版下载
最流行的的开源编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用





