了解了ICollection接口、迭代以及泛型集合,下面再详细了解一下IList接口。
通过MSDN可以看到IList接口有两种:
元素为object类型的IList接口,可以放不同类型的对象引用;
IList8742468051c85b06f0a0af9e3e506b5c泛型接口,只能存放指定类型的对象引用。
其实,IList和IList8742468051c85b06f0a0af9e3e506b5c也称之为向量,特点是可以动态的改变集合的长度,无需确定集合的初始长度,集合会随着存放数据的数量自动变化。
可以看到IList和IList8742468051c85b06f0a0af9e3e506b5c的继承关系:
[ComVisibleAttribute(true)] public interface IList : ICollection, IEnumerable public interface IList<T> : ICollection<T>, IEnumerable<T>, IEnumerable
现在再返回去看下,IList和IList8742468051c85b06f0a0af9e3e506b5c的区别,看如下代码,ArrayList是继承IList的,List继承IList8742468051c85b06f0a0af9e3e506b5c:
public class IListClass
{
void test()
{
TestClass1 c1 = null;
ArrayList arryList = new ArrayList();
arryList.Add(c1);
List<TestClass1> list = new List<TestClass1>();
list.Add(c1);
//取值
TestClass1 getC1Array = arryList[0] as TestClass1;//必须要一次强制转换
TestClass1 getC1List = list[0];//不需要转换,所谓泛型
}
}
public class TestClass1
{
}这下就比较明白了。
一、IList接口概述
ILis接口从ICollection接口继承,具备以下特性,
Count属性——获取集合元素个数;
GetEnumerator方法——可以迭代;
CopyTo方法——将指定元素复制到另一个数组中;
Clear方法——清空整个集合。
IList新增特性,
索引器属性——根据索引访问集合中任意元素;
Add方法——向集合末尾添加元素;
Insert方法——向集合指定位置插入元素;
Remove方法——移除指定元素;(包括RemoveAt)
Contains方法——判断对象是否在集合中;
IndexOf方法——查找指定对象在集合中的索引位置。
另外,IList接口集合按照顺序存放元素,不改变元素存放顺序。
2、算法
向量集合和数组一样,具备随即访问的特点。即无论访问向量集合的任何一个单元,所需的访问时间是完全相同的。在向量类中,实际上依然使用普通数组来记录集合数据,向量类使用了一些算法技巧,让整个类对外表现不同于普通数组的重要特点:可以动态改变数组长度。具体算法如下:
在内部数组足够长的情况下,直接进行添加和插入操作,在内部数组长度不足的情况下,按照内部数组长度增加2倍作为新的数组的长度,然后进行数据搬移(即把就数组数组移到新数组中)。向量在分配元素存储空间时,会多分配一些冗余空间,尽量减少内存分配次数。在数据删除时,并不改变内部数组长度,仅仅是使用被删除数据之后的数据覆盖被删除的数据。
不过向量每次分配空间时都多分配一些冗余空间,会造成内存的压力,因此在程序中应该尽量避免集中的次数繁多的内存分配。
三、实现类
IList和IList8742468051c85b06f0a0af9e3e506b5c的实现类,分别是ArrayList类和List8742468051c85b06f0a0af9e3e506b5c类。
ArrayList类处于System.Collection命名空间下;
List8742468051c85b06f0a0af9e3e506b5c类处于System.Collection.Specialized命名空间下。
四、实现代码(非泛型)
/// <summary>
/// 实现IList,非泛型
/// </summary>
public class ArrayList : IList
{
/// <summary>
/// 迭代
/// </summary>
public struct Enumertor : IEnumerator
{
/// <summary>
/// 迭代索引
/// </summary>
private int index;
/// <summary>
/// 迭代器所属的向量类对象的引用
/// </summary>
private ArrayList arrayList;
/// <summary>
/// 构造函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="arrayList">迭代器所属的集合类</param>
public Enumertor(ArrayList arrayList)
{
this.arrayList = arrayList;
this.index = -1;
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取当前对象,根据index的值返回向量对应的对象引用
/// </summary>
public object Current
{
get
{
return arrayList[index];
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 将迭代器指向下一个数据位置,通过改变index的值,加1或减1
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool MoveNext()
{
if (this.index < arrayList.Count)
{
++this.index;
}
return this.index < arrayList.Count;
}
/// <summary>
/// 迭代器回到起始位置,将index置为-1
/// </summary>
public void Reset()
{
this.index = -1;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 保存集合的数组
/// </summary>
private object[] array = new object[1];
/// <summary>
/// 当前集合的长度
/// </summary>
private int count;
/// <summary>
/// 默认构造函数
/// </summary>
public ArrayList()
{
}
/// <summary>
/// 参数构造函数,通过参数指定内部数组长度,减少重新分配空间
/// </summary>
/// <param name="capacity"></param>
public ArrayList(int capacity)
{
if (capacity < 0)
{
throw new Exception();
}
if (capacity == 0)
{
capacity = 1;
}
this.array = new object[capacity];
this.count = 0;
}
public int Count
{
get
{
return this.count;//该属性只读
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 集合实际使用长度
/// </summary>
public int Capacity
{
get
{
return this.array.Length;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 是否固定大小
/// </summary>
public bool IsFixedSize
{
get
{
return false;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 是否只读集合
/// </summary>
public bool IsReadOnly
{
get
{
return false;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 是否同步,即是否支持多线程访问
/// </summary>
public bool IsSynchronized
{
get
{
return false;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 同步对象
/// </summary>
public object SyncRoot
{
get
{
return null;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 当array长度不足时,重新分配新的长度足够的数组
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
private object[] GetNewArray()
{
return new object[(this.array.Length + 1) * 2];
}
public int Add(object value)
{
int newCount = this.count + 1;
if (this.array.Length < newCount)//长度不足
{
object[] newArray = GetNewArray();
Array.Copy(this.array, newArray, this.count);
this.array = newArray;//重新引用,指向新数组
}
//增加新元素
this.array[this.count] = value;
this.count = newCount;
//返回新元素的索引位置
return this.count - 1;
}
/// <summary>
/// 索引器属性,按索引返回向量中的某一项
/// </summary>
/// <param name="index"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public object this[int index]
{
get
{
if (index < 0 || index >= this.count)
{
throw new Exception();
}
return this.array[index];
}
set
{
if (index < 0 || index >= this.count)
{
throw new Exception();
}
this.array[index] = value;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 删除集合中的元素
/// </summary>
/// <param name="index"></param>
/// <param name="count"></param>
public void RemoveRange(int index, int count)
{
if (index < 0)
{
throw new Exception();
}
int removeIndex = index + count;//计算集合中最后一个被删元素的索引
if (count < 0 || removeIndex > this.count)
{
throw new Exception();
}
//删除其实是将要删除元素之后的所有元素拷贝到要删除元素的位置覆盖掉
Array.Copy(this.array, index + 1, this.array, index + count - 1, this.count - removeIndex);
//重新设置集合长度
this.count -= count;
}
/// <summary>
/// 查找对应的数组项,实际是遍历查找
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public int IndexOf(object value)
{
int index = 0;
if (value == null)
{
while (index < this.count)
{
if (this.array[index] == null)
{
return index;
}
++index;
}
}
else
{
while (index < this.count)
{
if (this.array[index].Equals(value))
{
return index;
}
++index;
}
}
return -1;
}
/// <summary>
/// 从集合中删除指定元素
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value"></param>
public void Remove(object value)
{
int index = this.IndexOf(value);
if (index >= 0)
{
this.RemoveRange(index, 1);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 从集合中删除指定位置的元素
/// </summary>
/// <param name="index"></param>
public void RemoveAt(int index)
{
RemoveRange(index, 1);
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取最后一个元素的引用后删除最后一个元素
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public object PopBack()
{
object obj = this.array[this.count - 1];
RemoveAt(this.count - 1);
return obj;
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取第一个元素引用并删除第一个元素
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public object PropFront()
{
object obj = this.array[0];
RemoveAt(0);
return obj;
}
/// <summary>
/// 插入元素
/// </summary>
/// <param name="index"></param>
/// <param name="value"></param>
public void Insert(int index, object value)
{
if (index >= this.count)
{
throw new Exception();
}
//插入元素当空间不足时也是声明新的2倍长度数组,并拷贝旧数据。
//插入数据原理是,将指定位置后的数据全部后移,再将新数据放在指定位置。
int newCount = this.count + 1;
if (this.array.Length < newCount)
{
object[] newArray = GetNewArray();
Array.Copy(this.array, newArray, index);
this.array = newArray;
}
Array.Copy(this.array, index, this.array, index + 1, this.count - index);
this.array[index] = value;
this.count = newCount;
}
/// <summary>
/// 查看当前集合是否包含指定对象
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool Contains(object value)
{
return this.IndexOf(value) >= 0;
}
/// <summary>
/// 将集合的长度改变为实际长度
/// </summary>
public void TrimToSize()
{
//为了消除Add和Insert时增加的冗余,原理是新生成一个和实际长度相同的数组,然后将值全部移过来。
if (this.array.Length > this.count)
{
object[] newArray = null;
if (this.count > 0)
{
newArray = new object[this.count];
Array.Copy(this.array, newArray, this.count);
}
else
{
newArray = new object[1];
}
this.array = newArray;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 清空集合
/// </summary>
public void Clear()
{
this.count = 0;
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取集合的迭代器
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
{
Enumertor enumerator = new Enumertor(this);
return enumerator;
}
/// <summary>
/// 转移集合元素
/// </summary>
/// <param name="targetArray"></param>
/// <param name="index"></param>
public void CopyTo(Array targetArray, int index)
{
Array.Copy(this.array, 0, targetArray, index, this.count);
}
}
调用测试:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//调用测试
ArrayList myArrayList = new ArrayList();
myArrayList.Add(40);
myArrayList.Add(80);
myArrayList.Add("Hello");
//使用for循环遍历
for (int i = 0; i < myArrayList.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(myArrayList[i]);
}
Console.WriteLine("---------------------");
//使用迭代循环
foreach (object obj in myArrayList)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
Console.WriteLine("---------------------");
myArrayList.Insert(1, "Insert");
foreach (object obj in myArrayList)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
Console.WriteLine("---------------------");
myArrayList.Remove("Insert");
foreach (object obj in myArrayList)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
Console.WriteLine("---------------------");
myArrayList.RemoveAt(1);
foreach (object obj in myArrayList)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
Console.WriteLine("---------------------");
myArrayList.Clear();
foreach (object obj in myArrayList)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
Console.WriteLine("---------------------");
Random rand = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
myArrayList.Add(rand.Next(10));
}
foreach (object obj in myArrayList)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
Console.WriteLine("---------------------");
Console.WriteLine("集合是否包含为1的元素 ? " + (myArrayList.Contains(0) ? "包含" : "不包含"));
Console.WriteLine("元素1的位置 " + myArrayList.IndexOf(1));
Console.ReadLine();
}结果: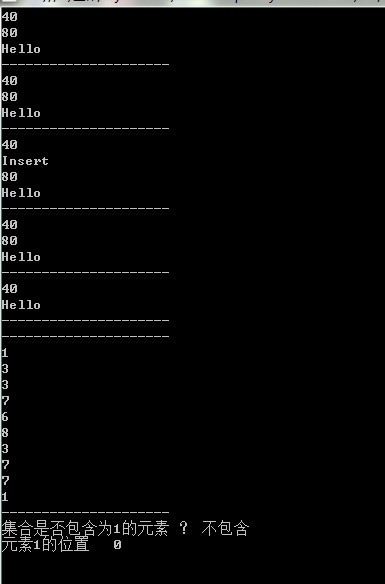
以上就是的内容,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网(www.php.cn)!
 使用C#.NET开发:实用指南和示例May 12, 2025 am 12:16 AM
使用C#.NET开发:实用指南和示例May 12, 2025 am 12:16 AMC#和.NET提供了强大的功能和高效的开发环境。1)C#是一种现代、面向对象的编程语言,结合了C 的强大和Java的简洁性。2).NET框架是一个用于构建和运行应用程序的平台,支持多种编程语言。3)C#中的类和对象是面向对象编程的核心,类定义数据和行为,对象是类的实例。4).NET的垃圾回收机制自动管理内存,简化开发者的工作。5)C#和.NET提供了强大的文件操作功能,支持同步和异步编程。6)常见错误可以通过调试器、日志记录和异常处理来解决。7)性能优化和最佳实践包括使用StringBuild
 C#.NET:了解Microsoft .NET框架May 11, 2025 am 12:17 AM
C#.NET:了解Microsoft .NET框架May 11, 2025 am 12:17 AM.NETFramework是一个跨语言、跨平台的开发平台,提供一致的编程模型和强大的运行时环境。1)它由CLR和FCL组成,CLR管理内存和线程,FCL提供预构建功能。2)使用示例包括读取文件和LINQ查询。3)常见错误涉及未处理异常和内存泄漏,需使用调试工具解决。4)性能优化可通过异步编程和缓存实现,保持代码可读性和可维护性是关键。
 c#.net的寿命:其持久流行的原因May 10, 2025 am 12:12 AM
c#.net的寿命:其持久流行的原因May 10, 2025 am 12:12 AMC#.NET保持持久吸引力的原因包括其出色的性能、丰富的生态系统、强大的社区支持和跨平台开发能力。1)性能表现优异,适用于企业级应用和游戏开发;2).NET框架提供了广泛的类库和工具,支持多种开发领域;3)拥有活跃的开发者社区和丰富的学习资源;4).NETCore实现了跨平台开发,扩展了应用场景。
 掌握C#.NET设计模式:从单胎到依赖注入May 09, 2025 am 12:15 AM
掌握C#.NET设计模式:从单胎到依赖注入May 09, 2025 am 12:15 AMC#.NET中的设计模式包括Singleton模式和依赖注入。1.Singleton模式确保类只有一个实例,适用于需要全局访问点的场景,但需注意线程安全和滥用问题。2.依赖注入通过注入依赖提高代码灵活性和可测试性,常用于构造函数注入,但需避免过度使用导致复杂度增加。
 现代世界中的C#.NET:应用和行业May 08, 2025 am 12:08 AM
现代世界中的C#.NET:应用和行业May 08, 2025 am 12:08 AMC#.NET在现代世界中广泛应用于游戏开发、金融服务、物联网和云计算等领域。1)在游戏开发中,通过Unity引擎使用C#进行编程。2)金融服务领域,C#.NET用于开发高性能的交易系统和数据分析工具。3)物联网和云计算方面,C#.NET通过Azure服务提供支持,开发设备控制逻辑和数据处理。
 C#.NET开发人员社区:资源和支持May 06, 2025 am 12:11 AM
C#.NET开发人员社区:资源和支持May 06, 2025 am 12:11 AMC#.NET开发者社区提供了丰富的资源和支持,包括:1.微软的官方文档,2.社区论坛如StackOverflow和Reddit,3.GitHub上的开源项目,这些资源帮助开发者从基础学习到高级应用,提升编程技能。
 C#.NET优势:功能,好处和用例May 05, 2025 am 12:01 AM
C#.NET优势:功能,好处和用例May 05, 2025 am 12:01 AMC#.NET的优势包括:1)语言特性,如异步编程简化了开发;2)性能与可靠性,通过JIT编译和垃圾回收机制提升效率;3)跨平台支持,.NETCore扩展了应用场景;4)实际应用广泛,从Web到桌面和游戏开发都有出色表现。


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

MinGW - 适用于 Windows 的极简 GNU
这个项目正在迁移到osdn.net/projects/mingw的过程中,你可以继续在那里关注我们。MinGW:GNU编译器集合(GCC)的本地Windows移植版本,可自由分发的导入库和用于构建本地Windows应用程序的头文件;包括对MSVC运行时的扩展,以支持C99功能。MinGW的所有软件都可以在64位Windows平台上运行。

安全考试浏览器
Safe Exam Browser是一个安全的浏览器环境,用于安全地进行在线考试。该软件将任何计算机变成一个安全的工作站。它控制对任何实用工具的访问,并防止学生使用未经授权的资源。

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) 是一个PHP/MySQL的Web应用程序,非常容易受到攻击。它的主要目标是成为安全专业人员在合法环境中测试自己的技能和工具的辅助工具,帮助Web开发人员更好地理解保护Web应用程序的过程,并帮助教师/学生在课堂环境中教授/学习Web应用程序安全。DVWA的目标是通过简单直接的界面练习一些最常见的Web漏洞,难度各不相同。请注意,该软件中

Dreamweaver Mac版
视觉化网页开发工具

EditPlus 中文破解版
体积小,语法高亮,不支持代码提示功能






