本篇文章主要介绍了Python守护进程和脚本单例运行,小编觉得挺不错的,现在分享给大家,也给大家做个参考。一起跟随小编过来看看吧
一、简介
守护进程最重要的特性是后台运行;它必须与其运行前的环境隔离开来,这些环境包括未关闭的文件描述符、控制终端、会话和进程组、工作目录以及文件创建掩码等;它可以在系统启动时从启动脚本/etc/rc.d中启动,可以由inetd守护进程启动,也可以有作业规划进程crond启动,还可以由用户终端(通常是shell)执行。
Python有时需要保证只运行一个脚本实例,以避免数据的冲突。
二、Python守护进程
1、函数实现
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf-8
import sys, os
'''将当前进程fork为一个守护进程
注意:如果你的守护进程是由inetd启动的,不要这样做!inetd完成了
所有需要做的事情,包括重定向标准文件描述符,需要做的事情只有chdir()和umask()了
'''
def daemonize (stdin='/dev/null', stdout='/dev/null', stderr='/dev/null'):
#重定向标准文件描述符(默认情况下定向到/dev/null)
try:
pid = os.fork()
#父进程(会话组头领进程)退出,这意味着一个非会话组头领进程永远不能重新获得控制终端。
if pid > 0:
sys.exit(0) #父进程退出
except OSError, e:
sys.stderr.write ("fork #1 failed: (%d) %s\n" % (e.errno, e.strerror) )
sys.exit(1)
#从母体环境脱离
os.chdir("/") #chdir确认进程不保持任何目录于使用状态,否则不能umount一个文件系统。也可以改变到对于守护程序运行重要的文件所在目录
os.umask(0) #调用umask(0)以便拥有对于写的任何东西的完全控制,因为有时不知道继承了什么样的umask。
os.setsid() #setsid调用成功后,进程成为新的会话组长和新的进程组长,并与原来的登录会话和进程组脱离。
#执行第二次fork
try:
pid = os.fork()
if pid > 0:
sys.exit(0) #第二个父进程退出
except OSError, e:
sys.stderr.write ("fork #2 failed: (%d) %s\n" % (e.errno, e.strerror) )
sys.exit(1)
#进程已经是守护进程了,重定向标准文件描述符
for f in sys.stdout, sys.stderr: f.flush()
si = open(stdin, 'r')
so = open(stdout, 'a+')
se = open(stderr, 'a+', 0)
os.dup2(si.fileno(), sys.stdin.fileno()) #dup2函数原子化关闭和复制文件描述符
os.dup2(so.fileno(), sys.stdout.fileno())
os.dup2(se.fileno(), sys.stderr.fileno())
#示例函数:每秒打印一个数字和时间戳
def main():
import time
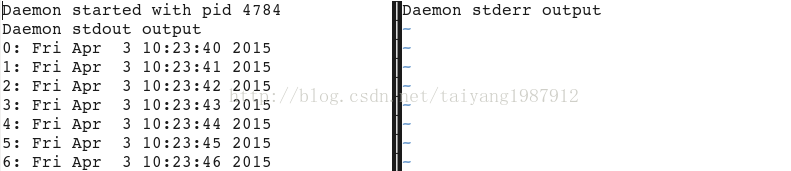
sys.stdout.write('Daemon started with pid %d\n' % os.getpid())
sys.stdout.write('Daemon stdout output\n')
sys.stderr.write('Daemon stderr output\n')
c = 0
while True:
sys.stdout.write('%d: %s\n' %(c, time.ctime()))
sys.stdout.flush()
c = c+1
time.sleep(1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
daemonize('/dev/null','/tmp/daemon_stdout.log','/tmp/daemon_error.log')
main()可以通过命令ps -ef | grep daemon.py查看后台运行的继承,在/tmp/daemon_error.log会记录错误运行日志,在/tmp/daemon_stdout.log会记录标准输出日志。
2、类实现
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf-8
#python模拟linux的守护进程
import sys, os, time, atexit, string
from signal import SIGTERM
class Daemon:
def __init__(self, pidfile, stdin='/dev/null', stdout='/dev/null', stderr='/dev/null'):
#需要获取调试信息,改为stdin='/dev/stdin', stdout='/dev/stdout', stderr='/dev/stderr',以root身份运行。
self.stdin = stdin
self.stdout = stdout
self.stderr = stderr
self.pidfile = pidfile
def _daemonize(self):
try:
pid = os.fork() #第一次fork,生成子进程,脱离父进程
if pid > 0:
sys.exit(0) #退出主进程
except OSError, e:
sys.stderr.write('fork #1 failed: %d (%s)\n' % (e.errno, e.strerror))
sys.exit(1)
os.chdir("/") #修改工作目录
os.setsid() #设置新的会话连接
os.umask(0) #重新设置文件创建权限
try:
pid = os.fork() #第二次fork,禁止进程打开终端
if pid > 0:
sys.exit(0)
except OSError, e:
sys.stderr.write('fork #2 failed: %d (%s)\n' % (e.errno, e.strerror))
sys.exit(1)
#重定向文件描述符
sys.stdout.flush()
sys.stderr.flush()
si = file(self.stdin, 'r')
so = file(self.stdout, 'a+')
se = file(self.stderr, 'a+', 0)
os.dup2(si.fileno(), sys.stdin.fileno())
os.dup2(so.fileno(), sys.stdout.fileno())
os.dup2(se.fileno(), sys.stderr.fileno())
#注册退出函数,根据文件pid判断是否存在进程
atexit.register(self.delpid)
pid = str(os.getpid())
file(self.pidfile,'w+').write('%s\n' % pid)
def delpid(self):
os.remove(self.pidfile)
def start(self):
#检查pid文件是否存在以探测是否存在进程
try:
pf = file(self.pidfile,'r')
pid = int(pf.read().strip())
pf.close()
except IOError:
pid = None
if pid:
message = 'pidfile %s already exist. Daemon already running!\n'
sys.stderr.write(message % self.pidfile)
sys.exit(1)
#启动监控
self._daemonize()
self._run()
def stop(self):
#从pid文件中获取pid
try:
pf = file(self.pidfile,'r')
pid = int(pf.read().strip())
pf.close()
except IOError:
pid = None
if not pid: #重启不报错
message = 'pidfile %s does not exist. Daemon not running!\n'
sys.stderr.write(message % self.pidfile)
return
#杀进程
try:
while 1:
os.kill(pid, SIGTERM)
time.sleep(0.1)
#os.system('hadoop-daemon.sh stop datanode')
#os.system('hadoop-daemon.sh stop tasktracker')
#os.remove(self.pidfile)
except OSError, err:
err = str(err)
if err.find('No such process') > 0:
if os.path.exists(self.pidfile):
os.remove(self.pidfile)
else:
print str(err)
sys.exit(1)
def restart(self):
self.stop()
self.start()
def _run(self):
""" run your fun"""
while True:
#fp=open('/tmp/result','a+')
#fp.write('Hello World\n')
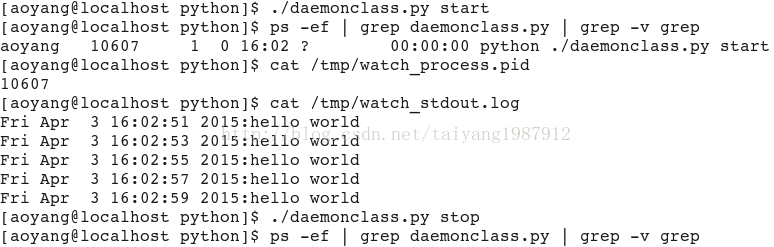
sys.stdout.write('%s:hello world\n' % (time.ctime(),))
sys.stdout.flush()
time.sleep(2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
daemon = Daemon('/tmp/watch_process.pid', stdout = '/tmp/watch_stdout.log')
if len(sys.argv) == 2:
if 'start' == sys.argv[1]:
daemon.start()
elif 'stop' == sys.argv[1]:
daemon.stop()
elif 'restart' == sys.argv[1]:
daemon.restart()
else:
print 'unknown command'
sys.exit(2)
sys.exit(0)
else:
print 'usage: %s start|stop|restart' % sys.argv[0]
sys.exit(2)运行结果:
它是当Daemon设计成一个模板,在其他文件中from daemon import Daemon,然后定义子类,重写run()方法实现自己的功能。
class MyDaemon(Daemon):
def run(self):
while True:
fp=open('/tmp/run.log','a+')
fp.write('Hello World\n')
time.sleep(1)
不足:信号处理signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, cleanup_handler)暂时没有安装,注册程序退出时的回调函数delpid()没有被调用。
然后,再写个shell命令,加入开机启动服务,每隔2秒检测守护进程是否启动,若没有启动则启动,自动监控恢复程序。
#/bin/sh while true do count=`ps -ef | grep "daemonclass.py" | grep -v "grep"` if [ "$?" != "0" ]; then daemonclass.py start fi sleep 2 done
三、python保证只能运行一个脚本实例
1、打开文件本身加锁
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf-8
import fcntl, sys, time, os
pidfile = 0
def ApplicationInstance():
global pidfile
pidfile = open(os.path.realpath(__file__), "r")
try:
fcntl.flock(pidfile, fcntl.LOCK_EX | fcntl.LOCK_NB) #创建一个排他锁,并且所被锁住其他进程不会阻塞
except:
print "another instance is running..."
sys.exit(1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
ApplicationInstance()
while True:
print 'running...'
time.sleep(1)
注意:open()参数不能使用w,否则会覆盖本身文件;pidfile必须声明为全局变量,否则局部变量生命周期结束,文件描述符会因引用计数为0被系统回收(若整个函数写在主函数中,则不需要定义成global)。
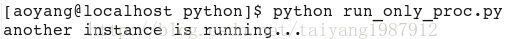
2、打开自定义文件并加锁
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf-8
import fcntl, sys, time
pidfile = 0
def ApplicationInstance():
global pidfile
pidfile = open("instance.pid", "w")
try:
fcntl.lockf(pidfile, fcntl.LOCK_EX | fcntl.LOCK_NB) #创建一个排他锁,并且所被锁住其他进程不会阻塞
except IOError:
print "another instance is running..."
sys.exit(0)
if __name__ == "__main__":
ApplicationInstance()
while True:
print 'running...'
time.sleep(1)
3、检测文件中PID
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf-8
import time, os, sys
import signal
pidfile = '/tmp/process.pid'
def sig_handler(sig, frame):
if os.path.exists(pidfile):
os.remove(pidfile)
sys.exit(0)
def ApplicationInstance():
signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, sig_handler)
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, sig_handler)
signal.signal(signal.SIGQUIT, sig_handler)
try:
pf = file(pidfile, 'r')
pid = int(pf.read().strip())
pf.close()
except IOError:
pid = None
if pid:
sys.stdout.write('instance is running...\n')
sys.exit(0)
file(pidfile, 'w+').write('%s\n' % os.getpid())
if __name__ == "__main__":
ApplicationInstance()
while True:
print 'running...'
time.sleep(1)

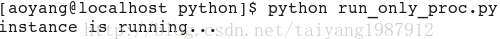
4、检测特定文件夹或文件
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf-8
import time, commands, signal, sys
def sig_handler(sig, frame):
if os.path.exists("/tmp/test"):
os.rmdir("/tmp/test")
sys.exit(0)
def ApplicationInstance():
signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, sig_handler)
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, sig_handler)
signal.signal(signal.SIGQUIT, sig_handler)
if commands.getstatusoutput("mkdir /tmp/test")[0]:
print "instance is running..."
sys.exit(0)
if __name__ == "__main__":
ApplicationInstance()
while True:
print 'running...'
time.sleep(1)
也可以检测某一个特定的文件,判断文件是否存在:
import os
import os.path
import time
#class used to handle one application instance mechanism
class ApplicationInstance:
#specify the file used to save the application instance pid
def __init__( self, pid_file ):
self.pid_file = pid_file
self.check()
self.startApplication()
#check if the current application is already running
def check( self ):
#check if the pidfile exists
if not os.path.isfile( self.pid_file ):
return
#read the pid from the file
pid = 0
try:
file = open( self.pid_file, 'rt' )
data = file.read()
file.close()
pid = int( data )
except:
pass
#check if the process with specified by pid exists
if 0 == pid:
return
try:
os.kill( pid, 0 ) #this will raise an exception if the pid is not valid
except:
return
#exit the application
print "The application is already running..."
exit(0) #exit raise an exception so don't put it in a try/except block
#called when the single instance starts to save it's pid
def startApplication( self ):
file = open( self.pid_file, 'wt' )
file.write( str( os.getpid() ) )
file.close()
#called when the single instance exit ( remove pid file )
def exitApplication( self ):
try:
os.remove( self.pid_file )
except:
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
#create application instance
appInstance = ApplicationInstance( '/tmp/myapp.pid' )
#do something here
print "Start MyApp"
time.sleep(5) #sleep 5 seconds
print "End MyApp"
#remove pid file
appInstance.exitApplication()
上述os.kill( pid, 0 )用于检测一个为pid的进程是否还活着,若该pid的进程已经停止则抛出异常,若正在运行则不发送kill信号。
5、socket监听一个特定端口
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf-8
import socket, time, sys
def ApplicationInstance():
try:
global s
s = socket.socket()
host = socket.gethostname()
s.bind((host, 60123))
except:
print "instance is running..."
sys.exit(0)
if __name__ == "__main__":
ApplicationInstance()
while True:
print 'running...'
time.sleep(1)
可以将该函数使用装饰器实现,便于重用(效果与上述相同):
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf-8
import socket, time, sys
import functools
#使用装饰器实现
def ApplicationInstance(func):
@functools.wraps(func)
def fun(*args,**kwargs):
import socket
try:
global s
s = socket.socket()
host = socket.gethostname()
s.bind((host, 60123))
except:
print('already has an instance...')
return None
return func(*args,**kwargs)
return fun
@ApplicationInstance
def main():
while True:
print 'running...'
time.sleep(1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
四、总结
(1)守护进程和单脚本运行在实际应用中比较重要,方法也比较多,可选择合适的来进行修改,可以将它们做成一个单独的类或模板,然后子类化实现自定义。
(2)daemon监控进程自动恢复避免了nohup和&的使用,并配合shell脚本可以省去很多不定时启动挂掉服务器的麻烦。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持PHP中文网。
更多Python守护进程和脚本单例运行详解相关文章请关注PHP中文网!
 Python vs.C:申请和用例Apr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python vs.C:申请和用例Apr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AMPython适合数据科学、Web开发和自动化任务,而C 适用于系统编程、游戏开发和嵌入式系统。 Python以简洁和强大的生态系统着称,C 则以高性能和底层控制能力闻名。
 2小时的Python计划:一种现实的方法Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM
2小时的Python计划:一种现实的方法Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM2小时内可以学会Python的基本编程概念和技能。1.学习变量和数据类型,2.掌握控制流(条件语句和循环),3.理解函数的定义和使用,4.通过简单示例和代码片段快速上手Python编程。
 Python:探索其主要应用程序Apr 10, 2025 am 09:41 AM
Python:探索其主要应用程序Apr 10, 2025 am 09:41 AMPython在web开发、数据科学、机器学习、自动化和脚本编写等领域有广泛应用。1)在web开发中,Django和Flask框架简化了开发过程。2)数据科学和机器学习领域,NumPy、Pandas、Scikit-learn和TensorFlow库提供了强大支持。3)自动化和脚本编写方面,Python适用于自动化测试和系统管理等任务。
 您可以在2小时内学到多少python?Apr 09, 2025 pm 04:33 PM
您可以在2小时内学到多少python?Apr 09, 2025 pm 04:33 PM两小时内可以学到Python的基础知识。1.学习变量和数据类型,2.掌握控制结构如if语句和循环,3.了解函数的定义和使用。这些将帮助你开始编写简单的Python程序。
 如何在10小时内通过项目和问题驱动的方式教计算机小白编程基础?Apr 02, 2025 am 07:18 AM
如何在10小时内通过项目和问题驱动的方式教计算机小白编程基础?Apr 02, 2025 am 07:18 AM如何在10小时内教计算机小白编程基础?如果你只有10个小时来教计算机小白一些编程知识,你会选择教些什么�...
 如何在使用 Fiddler Everywhere 进行中间人读取时避免被浏览器检测到?Apr 02, 2025 am 07:15 AM
如何在使用 Fiddler Everywhere 进行中间人读取时避免被浏览器检测到?Apr 02, 2025 am 07:15 AM使用FiddlerEverywhere进行中间人读取时如何避免被检测到当你使用FiddlerEverywhere...
 Python 3.6加载Pickle文件报错"__builtin__"模块未找到怎么办?Apr 02, 2025 am 07:12 AM
Python 3.6加载Pickle文件报错"__builtin__"模块未找到怎么办?Apr 02, 2025 am 07:12 AMPython3.6环境下加载Pickle文件报错:ModuleNotFoundError:Nomodulenamed...
 如何提高jieba分词在景区评论分析中的准确性?Apr 02, 2025 am 07:09 AM
如何提高jieba分词在景区评论分析中的准确性?Apr 02, 2025 am 07:09 AM如何解决jieba分词在景区评论分析中的问题?当我们在进行景区评论分析时,往往会使用jieba分词工具来处理文�...


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

Atom编辑器mac版下载
最流行的的开源编辑器

SecLists
SecLists是最终安全测试人员的伙伴。它是一个包含各种类型列表的集合,这些列表在安全评估过程中经常使用,都在一个地方。SecLists通过方便地提供安全测试人员可能需要的所有列表,帮助提高安全测试的效率和生产力。列表类型包括用户名、密码、URL、模糊测试有效载荷、敏感数据模式、Web shell等等。测试人员只需将此存储库拉到新的测试机上,他就可以访问到所需的每种类型的列表。

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) 是一个PHP/MySQL的Web应用程序,非常容易受到攻击。它的主要目标是成为安全专业人员在合法环境中测试自己的技能和工具的辅助工具,帮助Web开发人员更好地理解保护Web应用程序的过程,并帮助教师/学生在课堂环境中教授/学习Web应用程序安全。DVWA的目标是通过简单直接的界面练习一些最常见的Web漏洞,难度各不相同。请注意,该软件中

SublimeText3 Linux新版
SublimeText3 Linux最新版

EditPlus 中文破解版
体积小,语法高亮,不支持代码提示功能





