授权即访问控制,它将判断用户在应用程序中对资源是否拥有相应的访问权限。
如,判断一个用户有查看页面的权限,编辑数据的权限,拥有某一按钮的权限,以及是否拥有打印的权限等等。
一、授权的三要素
授权有着三个核心元素:权限、角色和用户。
权限
权限是Apache Shiro安全机制最核心的元素。它在应用程序中明确声明了被允许的行为和表现。一个格式良好好的权限声明可以清晰表达出用户对该资源拥有的权限。
大多数的资源会支持典型的CRUD操作(create,read,update,delete),但是任何操作建立在特定的资源上才是有意义的。因此,权限声明的根本思想就是建立在资源以及操作上。
而我们通过权限声明仅仅能了解这个权限可以在应用程序中做些什么,而不能确定谁拥有此权限。
于是,我们就需要在应用程序中对用户和权限建立关联。
通常的做法就是将权限分配给某个角色,然后将这个角色关联一个或多个用户。
权限声明及粒度
Shiro权限声明通常是使用以冒号分隔的表达式。就像前文所讲,一个权限表达式可以清晰的指定资源类型,允许的操作,可访问的数据。同时,Shiro权限表达式支持简单的通配符,可以更加灵活的进行权限设置。
下面以实例来说明权限表达式。
可查询用户数据
User:view
可查询或编辑用户数据
User:view,edit
可对用户数据进行所有操作
User:* 或 user
可编辑id为123的用户数据
User:edit:123
角色
Shiro支持两种角色模式:
1、传统角色:一个角色代表着一系列的操作,当需要对某一操作进行授权验证时,只需判断是否是该角色即可。这种角色权限相对简单、模糊,不利于扩展。
2、权限角色:一个角色拥有一个权限的集合。授权验证时,需要判断当前角色是否拥有该权限。这种角色权限可以对该角色进行详细的权限描述,适合更复杂的权限设计。
下面将详细描述对两种角色模式的授权实现。
二、授权实现
Shiro支持三种方式实现授权过程:
编码实现
注解实现
JSP Taglig实现
1、基于编码的授权实现
1.1基于传统角色授权实现
当需要验证用户是否拥有某个角色时,可以调用Subject 实例的hasRole*方法验证。
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
if (currentUser.hasRole("administrator")) {
//show the admin button
} else {
//don't show the button? Grey it out?
}相关验证方法如下:
Subject方法 描述
hasRole(String roleName) 当用户拥有指定角色时,返回true
hasRoles(Listf7e83be87db5cd2d9a8a0b8117b38cd4 roleNames) 按照列表顺序返回相应的一个boolean值数组
hasAllRoles(Collectionf7e83be87db5cd2d9a8a0b8117b38cd4 roleNames) 如果用户拥有所有指定角色时,返回true
断言支持
Shiro还支持以断言的方式进行授权验证。断言成功,不返回任何值,程序继续执行;断言失败时,将抛出异常信息。使用断言,可以使我们的代码更加简洁。
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//guarantee that the current user is a bank teller and
//therefore allowed to open the account:
currentUser.checkRole("bankTeller");
openBankAccount();断言的相关方法:
Subject方法 描述
checkRole(String roleName) 断言用户是否拥有指定角色
checkRoles(Collectionf7e83be87db5cd2d9a8a0b8117b38cd4 roleNames) 断言用户是否拥有所有指定角色
checkRoles(String... roleNames) 对上一方法的方法重载
1.2 基于权限角色授权实现
相比传统角色模式,基于权限的角色模式耦合性要更低些,它不会因角色的改变而对源代码进行修改,因此,基于权限的角色模式是更好的访问控制方式。
它的代码实现有以下几种实现方式:
1、基于权限对象的实现
创建org.apache.shiro.authz.Permission的实例,将该实例对象作为参数传递给Subject.isPermitted()进行验证。
Permission printPermission = new PrinterPermission("laserjet4400n", "print");
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
if (currentUser.isPermitted(printPermission)) {
//show the Print button
} else {
//don't show the button? Grey it out?
}
Permission printPermission = new PrinterPermission("laserjet4400n", "print");
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
if (currentUser.isPermitted(printPermission)) {
//show the Print button
} else {
//don't show the button? Grey it out?
}相关方法如下:
Subject方法 描述
isPermitted(Permission p) Subject拥有制定权限时,返回treu
isPermitted(List4021e4fcee2d18f954cbe4ec9db50982 perms) 返回对应权限的boolean数组
isPermittedAll(Collection4021e4fcee2d18f954cbe4ec9db50982 perms) Subject拥有所有制定权限时,返回true
2、 基于字符串的实现
相比笨重的基于对象的实现方式,基于字符串的实现便显得更加简洁。
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
if (currentUser.isPermitted("printer:print:laserjet4400n")) {
//show the Print button
} else {
//don't show the button? Grey it out?
}使用冒号分隔的权限表达式是org.apache.shiro.authz.permission.WildcardPermission 默认支持的实现方式。
这里分别代表了 资源类型:操作:资源ID
类似基于对象的实现相关方法,基于字符串的实现相关方法:
isPermitted(String perm)、isPermitted(String... perms)、isPermittedAll(String... perms)
基于权限对象的断言实现
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//guarantee that the current user is permitted
//to open a bank account:
Permission p = new AccountPermission("open");
currentUser.checkPermission(p);
openBankAccount();基于字符串的断言实现
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//guarantee that the current user is permitted
//to open a bank account:
currentUser.checkPermission("account:open");
openBankAccount();断言实现的相关方法
Subject方法 说明
checkPermission(Permission p) 断言用户是否拥有制定权限
checkPermission(String perm) 断言用户是否拥有制定权限
checkPermissions(Collection4021e4fcee2d18f954cbe4ec9db50982 perms) 断言用户是否拥有所有指定权限
checkPermissions(String... perms) 断言用户是否拥有所有指定权限
2、基于注解的授权实现
Shiro注解支持AspectJ、Spring、Google-Guice等,可根据应用进行不同的配置。
相关的注解:
@ RequiresAuthentication
可以用户类/属性/方法,用于表明当前用户需是经过认证的用户。
@RequiresAuthentication
public void updateAccount(Account userAccount) {
//this method will only be invoked by a
//Subject that is guaranteed authenticated
...
}
@ RequiresGuest表明该用户需为”guest”用户
@ RequiresPermissions
当前用户需拥有制定权限
@RequiresPermissions("account:create")
public void createAccount(Account account) {
//this method will only be invoked by a Subject
//that is permitted to create an account
...
}
@RequiresRoles当前用户需拥有制定角色
@ RequiresUser
当前用户需为已认证用户或已记住用户
3、基于JSP TAG的授权实现
Shiro提供了一套JSP标签库来实现页面级的授权控制。
在使用Shiro标签库前,首先需要在JSP引入shiro标签:
<%@ taglib prefix="shiro" uri="http://shiro.apache.org/tags" %>
下面一一介绍Shiro的标签:
guest标签
验证当前用户是否为“访客”,即未认证(包含未记住)的用户
<shiro:guest> Hi there! Please <a href="login.jsp">Login</a> or <a href="signup.jsp">Signup</a> today! </shiro:guest>
user标签
认证通过或已记住的用户
<shiro:user> Welcome back John! Not John? Click <a href="login.jsp">here<a> to login. </shiro:user>
authenticated标签
已认证通过的用户。不包含已记住的用户,这是与user标签的区别所在。
<shiro:authenticated> <a href="updateAccount.jsp">Update your contact information</a>. </shiro:authenticated> notAuthenticated标签
未认证通过用户,与authenticated标签相对应。与guest标签的区别是,该标签包含已记住用户。
<shiro:notAuthenticated> Please <a href="login.jsp">login</a> in order to update your credit card information. </shiro:notAuthenticated>
principal 标签
输出当前用户信息,通常为登录帐号信息
Hello, <shiro:principal/>, how are you today?
验证当前用户是否属于该角色
<shiro:hasRole name="administrator"> <a href="admin.jsp">Administer the system</a> </shiro:hasRole>
lacksRole标签
与hasRole标签逻辑相反,当用户不属于该角色时验证通过
<shiro:lacksRole name="administrator"> Sorry, you are not allowed to administer the system. </shiro:lacksRole>
hasAnyRole标签
验证当前用户是否属于以下任意一个角色。
<shiro:hasAnyRoles name="developer, project manager, administrator"> You are either a developer, project manager, or administrator. </shiro:lacksRole>
hasPermission标签
验证当前用户是否拥有制定权限
<shiro:hasPermission name="user:create"> <a href="createUser.jsp">Create a new User</a> </shiro:hasPermission>
lacksPermission标签
与hasPermission标签逻辑相反,当前用户没有制定权限时,验证通过
<shiro:hasPermission name="user:create"> <a href="createUser.jsp">Create a new User</a> </shiro:hasPermission>
三、Shiro授权的内部处理机制
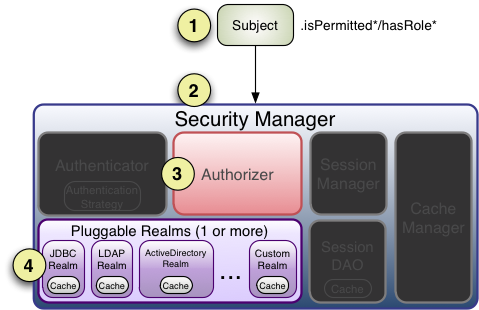
1、在应用程序中调用授权验证方法(Subject的isPermitted*或hasRole*等)
2、Sbuject的实例通常是DelegatingSubject类(或子类)的实例对象,在认证开始时,会委托应用程序设置的securityManager实例调用相应的isPermitted*或hasRole*方法。
3、接下来SecurityManager会委托内置的Authorizer的实例(默认是ModularRealmAuthorizer 类的实例,类似认证实例,它同样支持一个或多个Realm实例认证)调用相应的授权方法。
4、每一个Realm将检查是否实现了相同的 Authorizer 接口。然后,将调用Reaml自己的相应的授权验证方法。
当使用多个Realm时,不同于认证策略处理方式,授权处理过程中:
1、当调用Realm出现异常时,将立即抛出异常,结束授权验证。
2、只要有一个Realm验证成功,那么将认为授权成功,立即返回,结束认证。
以上就是Apache Shiro 使用手册(三)Shiro 授权的内容,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网(www.php.cn)!
 图文详解apache2.4+php8.0的安装配置方法Dec 06, 2022 pm 04:53 PM
图文详解apache2.4+php8.0的安装配置方法Dec 06, 2022 pm 04:53 PM本文给大家介绍如何安装apache2.4,以及如何配置php8.0,文中附有图文详细步骤,下面就带大家一起看看怎么安装配置apache2.4+php8.0吧~
 apache版本怎么查看?Jun 14, 2019 pm 02:40 PM
apache版本怎么查看?Jun 14, 2019 pm 02:40 PM查看apache版本的步骤:1、进入cmd命令窗口;2、使用cd命令切换到Apache的bin目录下,语法“cd bin目录路径”;3、执行“httpd -v”命令来查询版本信息,在输出结果中即可查看apache版本号。
 Linux apache怎么限制并发连接和下载速度May 12, 2023 am 10:49 AM
Linux apache怎么限制并发连接和下载速度May 12, 2023 am 10:49 AMmod_limitipconn,这个是apache的一个非官方模块,根据同一个来源ip进行并发连接控制,bw_mod,它可以根据来源ip进行带宽限制,它们都是apache的第三方模块。1.下载:wgetwget2.安装#tar-zxvfmod_limitipconn-0.22.tar.gz#cdmod_limitipconn-0.22#vimakefile修改:apxs=“/usr/local/apache2/bin/apxs”#这里是自己apache的apxs路径,加载模块或者#/usr/lo
 超细!Ubuntu20.04安装Apache+PHP8环境Mar 21, 2023 pm 03:26 PM
超细!Ubuntu20.04安装Apache+PHP8环境Mar 21, 2023 pm 03:26 PM本篇文章给大家带来了关于PHP的相关知识,其中主要跟大家分享在Ubuntu20.04 LTS环境下安装Apache的全过程,并且针对其中可能出现的一些坑也会提供解决方案,感兴趣的朋友下面一起来看一下吧,希望对大家有帮助。
 nginx,tomcat,apache的区别是什么May 15, 2023 pm 01:40 PM
nginx,tomcat,apache的区别是什么May 15, 2023 pm 01:40 PM1.Nginx和tomcat的区别nginx常用做静态内容服务和代理服务器,直接外来请求转发给后面的应用服务器(tomcat,Django等),tomcat更多用来做一个应用容器,让javawebapp泡在里面的东西。严格意义上来讲,Apache和nginx应该叫做HTTPServer,而tomcat是一个ApplicationServer是一个Servlet/JSO应用的容器。客户端通过HTTPServer访问服务器上存储的资源(HTML文件,图片文件等),HTTPServer是中只是把服务器
 php站用iis乱码而apache没事怎么解决Mar 23, 2023 pm 02:48 PM
php站用iis乱码而apache没事怎么解决Mar 23, 2023 pm 02:48 PM在使用 PHP 进行网站开发时,你可能会遇到字符编码问题。特别是在使用不同的 Web 服务器时,会发现 IIS 和 Apache 处理字符编码的方法不同。当你使用 IIS 时,可能会发现在使用 UTF-8 编码时出现了乱码现象;而在使用 Apache 时,一切正常,没有出现任何问题。这种情况应该怎么解决呢?
 如何在 RHEL 9/8 上设置高可用性 Apache(HTTP)集群Jun 09, 2023 pm 06:20 PM
如何在 RHEL 9/8 上设置高可用性 Apache(HTTP)集群Jun 09, 2023 pm 06:20 PMPacemaker是适用于类Linux操作系统的高可用性集群软件。Pacemaker被称为“集群资源管理器”,它通过在集群节点之间进行资源故障转移来提供集群资源的最大可用性。Pacemaker使用Corosync进行集群组件之间的心跳和内部通信,Corosync还负责集群中的投票选举(Quorum)。先决条件在我们开始之前,请确保你拥有以下内容:两台RHEL9/8服务器RedHat订阅或本地配置的仓库通过SSH访问两台服务器root或sudo权限互联网连接实验室详情:服务器1:node1.exa
 Linux下如何查看nginx、apache、mysql和php的编译参数May 14, 2023 pm 10:22 PM
Linux下如何查看nginx、apache、mysql和php的编译参数May 14, 2023 pm 10:22 PM快速查看服务器软件的编译参数:1、nginx编译参数:your_nginx_dir/sbin/nginx-v2、apache编译参数:catyour_apache_dir/build/config.nice3、php编译参数:your_php_dir/bin/php-i|grepconfigure4、mysql编译参数:catyour_mysql_dir/bin/mysqlbug|grepconfigure以下是完整的实操例子:查看获取nginx的编译参数:[root@www~]#/usr/lo


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

螳螂BT
Mantis是一个易于部署的基于Web的缺陷跟踪工具,用于帮助产品缺陷跟踪。它需要PHP、MySQL和一个Web服务器。请查看我们的演示和托管服务。

SecLists
SecLists是最终安全测试人员的伙伴。它是一个包含各种类型列表的集合,这些列表在安全评估过程中经常使用,都在一个地方。SecLists通过方便地提供安全测试人员可能需要的所有列表,帮助提高安全测试的效率和生产力。列表类型包括用户名、密码、URL、模糊测试有效载荷、敏感数据模式、Web shell等等。测试人员只需将此存储库拉到新的测试机上,他就可以访问到所需的每种类型的列表。

PhpStorm Mac 版本
最新(2018.2.1 )专业的PHP集成开发工具

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境





