oracle的建表sql转成sqlserver的建表sql时的注意点 :
1.所有的comment语句需要删除。
2.clob类型转换为text类型。
3.blob类型转换为image类型。
4.number类型转换为int,number(16,2)等转换为decimal(16,2),number(18)转换为bigint。
5.default sysdate改为default getDate()。
6.to_date('2009-12-18','yyyy-mm-dd')改为cast('2009-12-18' as datetime)
SQLSERVER:
变量的声明:
声明变量时必须在变量前加@符号
DECLARE @I INT
变量的赋值:
变量赋值时变量前必须加set
SET @I = 30
声明多个变量:
DECLARE @s varchar(10),@a INT
if语句:
Java代码
if .. begin ... end else if .. begin ... end else begin ... end
Example:
Sql代码
DECLARE @d INT set @d = 1 IF @d = 1 BEGIN PRINT '正确' END ELSE BEGIN PRINT '错误' END
多条件选择语句:
Example:
Sql代码
declare @today int
declare @week nvarchar(3)
set @today=3
set @week= case
when @today=1 then '星期一'
when @today=2 then '星期二'
when @today=3 then '星期三'
when @today=4 then '星期四'
when @today=5 then '星期五'
when @today=6 then '星期六'
when @today=7 then '星期日'
else '值错误'
end
print @week循环语句:
Java代码
WHILE 条件 BEGIN 执行语句 END
Example:
Java代码
DECLARE @i INT SET @i = 1 WHILE @i<1000000 BEGIN set @i=@i+1 END
定义游标:
Sql代码
DECLARE @cur1 CURSOR FOR SELECT ......... OPEN @cur1 FETCH NEXT FROM @cur1 INTO 变量 WHILE(@@FETCH_STATUS=0) BEGIN 处理..... FETCH NEXT FROM @cur1 INTO 变量 END CLOSE @cur1 DEALLOCATE @cur1
Sql代码
AS
declare @CATEGORY_CI_TABLENAME VARCHAR(50) =''
declare @result VARCHAR(2000) = ''
declare @CI_ID DECIMAL = 0
declare @num int = 1
declare @countnum int = 1
BEGIN
select @countnum = count(ATTRIBUTE_CONFIG_ID) from T_ATTRIBUTE_CONFIG where CMDB_UPDATE_FLAG= 'Y' and CATEGORY_CODE =@CATEGORY_CODE
IF (@ATTRIBUTE2='A')
begin
DECLARE MyCursor CURSOR for select ATTRIBUTE_CONFIG_CODE from T_ATTRIBUTE_CONFIG where CMDB_UPDATE_FLAG= 'Y' and CATEGORY_CODE =@CATEGORY_CODE
OPEN MyCursor FETCH NEXT FROM MyCursor INTO @CONFIG_CODE
set @result = @result+@CONFIG_CODE+','
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
FETCH NEXT FROM MyCursor INTO @CONFIG_CODE
set @num = @num+ 1
if(@num<@countnum)
begin
set @result = @result+@CONFIG_CODE+','
end
else if(@num=@countnum)
begin
set @result = @result +@CONFIG_CODE
end
END
CLOSE MyCursor
DEALLOCATE MyCursor
set @result = 'insert into ' + @ATTRIBUTE1 + '(' + @result +') select '+ @result +' from '+@CATEGORY_CI_TABLENAME +' where CI_ORDER_LINE_ID='+@KEY_ID
end
else if((@ATTRIBUTE2='U'))临时表:
-- Select INTO 从一个查询的计算结果中创建一个新表。 数据并不返回给客户端,这一点和普通的Select 不同。 新表的字段具有和 Select 的输出字段相关联(相同)的名字和数据类型。
select * into NewTable
from Uname
-- Insert INTO ABC Select
-- 表ABC必须存在
-- 把表Uname里面的字段Username复制到表ABC
Insert INTO ABC Select Username FROM Uname
-- 创建临时表
Create TABLE #temp(
UID int identity(1, 1) PRIMARY KEY,
UserName varchar(16),
Pwd varchar(50),
Age smallint,
Sex varchar(6)
)
-- 打开临时表
Select * from #temp
1、局部临时表(#开头)只对当前连接有效,当前连接断开时自动删除。
2、全局临时表(##开头)对其它连接也有效,在当前连接和其他访问过它的连接都断开时自动删除。
3、不管局部临时表还是全局临时表,只要连接有访问权限,都可以用drop table #Tmp(或者drop table ##Tmp)来显式删除临时表。
临时表对执行效率应该影响不大,只要不是太过份,相反可以提高效率特别是连接查询的地方,只要你的数据库临时表空间足够
游标多,会严重执行效率,能免则免!
其他:
--有输入参数的存储过程--
create proc GetComment
(@commentid int)
as
select * from Comment where CommentID=@commentid
--有输入与输出参数的存储过程--
create proc GetCommentCount
@newsid int,
@count int output
as
select @count=count(*) from Comment where NewsID=@newsid
--返回单个值的函数--
create function MyFunction
(@newsid int)
returns int
as
begin
declare @count int
select @count=count(*) from Comment where NewsID=@newsid
return @count
end
--调用方法--
declare @count int
exec @count=MyFunction 2
print @count
--返回值为表的函数--
Create function GetFunctionTable
(@newsid int)
returns table
as
return
(select * from Comment where NewsID=@newsid)
--返回值为表的函数的调用--
select * from GetFunctionTable(2)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SQLServer 存储过程中不拼接SQL字符串实现多条件查询
以前拼接的写法
set @sql=' select * from table where 1=1 '
if (@addDate is not null)
set @sql = @sql+' and addDate = '+ @addDate + ' '
if (@name a8093152e673feb7aba1828c43532094'' and is not null)
set @sql = @sql+ ' and name = ' + @name + ' '
exec(@sql)
下面是 不采用拼接SQL字符串实现多条件查询的解决方案
第一种写法是 感觉代码有些冗余
if (@addDate is not null) and (@name a8093152e673feb7aba1828c43532094 '')
select * from table where addDate = @addDate and name = @name
else if (@addDate is not null) and (@name ='')
select * from table where addDate = @addDate
else if(@addDate is null) and (@name a8093152e673feb7aba1828c43532094 '')
select * from table where and name = @name
else if(@addDate is null) and (@name = '')
select * from table
第二种写法是
select * from table where (addDate = @addDate or @addDate is null) and (name = @name or @name = '')
第三种写法是
SELECT * FROM table where
addDate = CASE @addDate IS NULL THEN addDate ELSE @addDate END,
name = CASE @name WHEN '' THEN name ELSE @name END
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SQLSERVER存储过程基本语法
一、定义变量
--简单赋值
declare @a int
set @a=5
print @a
--使用select语句赋值
declare @user1 nvarchar(50)
select @user1= '张三'
print @user1
declare @user2 nvarchar(50)
select @user2 = Name from ST_User where ID=1
print @user2
--使用update语句赋值
declare @user3 nvarchar(50)
update ST_User set @user3 = Name where ID=1
print @user3
二、表、临时表、表变量
--创建临时表1
create table #DU_User1
(
[ID] [ int ] NOT NULL ,
[Oid] [ int ] NOT NULL ,
[Login] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL ,
[Rtx] [nvarchar](4) NOT NULL ,
[ Name ] [nvarchar](5) NOT NULL ,
[ Password ] [nvarchar]( max ) NULL ,
[State] [nvarchar](8) NOT NULL
);
--向临时表1插入一条记录
insert into #DU_User1 (ID,Oid,[Login],Rtx, Name ,[ Password ],State) values (100,2, 'LS' ,'0000' , '临时' , '321' , '特殊' );
--从ST_User查询数据,填充至新生成的临时表
select * into #DU_User2 from ST_User where ID<8
--查询并联合两临时表
select * from #DU_User2 where ID<3 union select * from #DU_User1
--删除两临时表
drop table #DU_User1
drop table #DU_User2
--创建临时表
CREATE TABLE #t
(
[ID] [ int ] NOT NULL ,
[Oid] [ int ] NOT NULL ,
[Login] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL ,
[Rtx] [nvarchar](4) NOT NULL ,
[ Name ] [nvarchar](5) NOT NULL ,
[ Password ] [nvarchar]( max ) NULL ,
[State] [nvarchar](8) NOT NULL ,
)
--将查询结果集(多条数据)插入临时表
insert into #t select * from ST_User
--不能这样插入
--select * into #t from dbo.ST_User
--添加一列,为int型自增长子段
alter table #t add [myid] int NOT NULL IDENTITY(1,1)
--添加一列,默认填充全球唯一标识
alter table #t add [myid1] uniqueidentifier NOT NULL default (newid())
select * from #t
drop table #t
--给查询结果集增加自增长列
--无主键时:
select IDENTITY( int ,1,1) as ID, Name ,[Login],[ Password ] into #t from ST_User
select * from #t
--有主键时:
select ( select SUM (1) from ST_User where ID<= a.ID) as myID,* from ST_User a order bymyID
--定义表变量
declare @t table
(
id int not null ,
msg nvarchar(50) null
)
insert into @t values (1, '1' )
insert into @t values (2, '2' )
select * from @t
三、循环
--while循环计算1到100的和
declare @a int
declare @ sum int
set @a=1
set @ sum =0
while @a<=100
begin
set @ sum +=@a
set @a+=1
end
print @ sum
四、条件语句
--if,else条件分支
if(1+1=2)
begin
print '对'
end
else
begin
print '错'
end
--when then条件分支
declare @today int
declare @week nvarchar(3)
set @today=3
set @week= case
when @today=1 then '星期一'
when @today=2 then '星期二'
when @today=3 then '星期三'
when @today=4 then '星期四'
when @today=5 then '星期五'
when @today=6 then '星期六'
when @today=7 then '星期日'
else '值错误'
end
print @week
五、游标
declare @ID int
declare @Oid int
declare @Login varchar (50)
--定义一个游标
declare user_cur cursor for select ID,Oid,[Login] from ST_User
--打开游标
open user_cur
while @@fetch_status=0
begin
--读取游标
fetch next from user_cur into @ID,@Oid,@Login
print @ID
--print @Login
end
close user_cur
--摧毁游标
deallocate user_cur
六、触发器
触发器中的临时表:
Inserted
存放进行insert和update 操作后的数据
Deleted
存放进行delete 和update操作前的数据
--创建触发器
Create trigger User_OnUpdate
On ST_User
for Update
As
declare @msg nvarchar(50)
--@msg记录修改情况
select @msg = N '姓名从“' + Deleted. Name + N '”修改为“' + Inserted. Name + '”' fromInserted,Deleted
--插入日志表
insert into [LOG](MSG) values (@msg)
--删除触发器
drop trigger User_OnUpdate
七、存储过程
--创建带output参数的存储过程
CREATE PROCEDURE PR_Sum
@a int ,
@b int ,
@ sum int output
AS
BEGIN
set @ sum =@a+@b
END
--创建Return返回值存储过程
CREATE PROCEDURE PR_Sum2
@a int ,
@b int
AS
BEGIN
Return @a+@b
END
--执行存储过程获取output型返回值
declare @mysum int
execute PR_Sum 1,2,@mysum output
print @mysum
--执行存储过程获取Return型返回值
declare @mysum2 int
execute @mysum2= PR_Sum2 1,2
print @mysum2
八、自定义函数
函数的分类:
1)标量值函数
2)表值函数
a:内联表值函数
b:多语句表值函数
3)系统函数
--新建标量值函数
create function FUNC_Sum1
(
@a int ,
@b int
)
returns int
as
begin
return @a+@b
end
--新建内联表值函数
create function FUNC_UserTab_1
(
@myId int
)
returns table
as
return ( select * from ST_User where ID<@myId)
--新建多语句表值函数
create function FUNC_UserTab_2
(
@myId int
)
returns @t table
(
[ID] [ int ] NOT NULL ,
[Oid] [ int ] NOT NULL ,
[Login] [nvarchar](50) NOT NULL ,
[Rtx] [nvarchar](4) NOT NULL ,
[ Name ] [nvarchar](5) NOT NULL ,
[ Password ] [nvarchar]( max ) NULL ,
[State] [nvarchar](8) NOT NULL
)
as
begin
insert into @t select * from ST_User where ID<@myId
return
end
--调用表值函数
select * from dbo.FUNC_UserTab_1(15)
--调用标量值函数
declare @s int
set @s=dbo.FUNC_Sum1(100,50)
print @s
--删除标量值函数
drop function FUNC_Sum1
谈谈自定义函数与存储过程的区别:
一、自定义函数:
1. 可以返回表变量
2. 限制颇多,包括
不能使用output参数;
不能用临时表;
函数内部的操作不能影响到外部环境;
不能通过select返回结果集;
不能update,delete,数据库表;
3. 必须return 一个标量值或表变量
自定义函数一般用在复用度高,功能简单单一,争对性强的地方。
二、存储过程
1. 不能返回表变量
2. 限制少,可以执行对数据库表的操作,可以返回数据集
3. 可以return一个标量值,也可以省略return
存储过程一般用在实现复杂的功能,数据操纵方面。
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SqlServer存储过程--实例
实例1:只返回单一记录集的存储过程。
表银行存款表(bankMoney)的内容如下
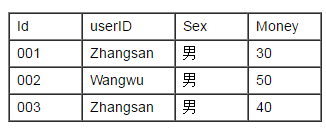
要求1:查询表bankMoney的内容的存储过程
create procedure sp_query_bankMoney
as
select * from bankMoney
go
exec sp_query_bankMoney
注* 在使用过程中只需要把T-Sql中的SQL语句替换为存储过程名,就可以了很方便吧!
实例2(向存储过程中传递参数):
加入一笔记录到表bankMoney,并查询此表中userID= Zhangsan的所有存款的总金额。
Create proc insert_bank @param1 char(10),@param2 varchar(20),@param3 varchar(20),@param4 int,@param5 int output
with encryption ---------加密
as
insert into bankMoney (id,userID,sex,Money)
Values(@param1,@param2,@param3, @param4)
select @param5=sum(Money) from bankMoney where userID='Zhangsan'
go
在SQL Server查询分析器中执行该存储过程的方法是:
declare @total_price int
exec insert_bank '004','Zhangsan','男',100,@total_price output
print '总余额为'+convert(varchar,@total_price)
go
在这里再啰嗦一下存储过程的3种传回值(方便正在看这个例子的朋友不用再去查看语法内容):
1.以Return传回整数
2.以output格式传回参数
3.Recordset
传回值的区别:
output和return都可在批次程式中用变量接收,而recordset则传回到执行批次的客户端中。
实例3:使用带有复杂 SELECT 语句的简单过程
下面的存储过程从四个表的联接中返回所有作者(提供了姓名)、出版的书籍以及出版社。该存储过程不使用任何参数。
USE pubs
IF EXISTS (SELECT name FROM sysobjects
WHERE name = 'au_info_all' AND type = 'P')
DROP PROCEDURE au_info_all
GO
CREATE PROCEDURE au_info_all
AS
SELECT au_lname, au_fname, title, pub_name
FROM authors a INNER JOIN titleauthor ta
ON a.au_id = ta.au_id INNER JOIN titles t
ON t.title_id = ta.title_id INNER JOIN publishers p
ON t.pub_id = p.pub_id
GO
au_info_all 存储过程可以通过以下方法执行:
EXECUTE au_info_all
-- Or
EXEC au_info_all
如果该过程是批处理中的第一条语句,则可使用:
au_info_all
实例4:使用带有参数的简单过程
CREATE PROCEDURE au_info
@lastname varchar(40),
@firstname varchar(20)
AS
SELECT au_lname, au_fname, title, pub_name
FROM authors a INNER JOIN titleauthor ta
ON a.au_id = ta.au_id INNER JOIN titles t
ON t.title_id = ta.title_id INNER JOIN publishers p
ON t.pub_id = p.pub_id
WHERE au_fname = @firstname
AND au_lname = @lastname
GO
au_info 存储过程可以通过以下方法执行:
EXECUTE au_info 'Dull', 'Ann'
-- Or
EXECUTE au_info @lastname = 'Dull', @firstname = 'Ann'
-- Or
EXECUTE au_info @firstname = 'Ann', @lastname = 'Dull'
-- Or
EXEC au_info 'Dull', 'Ann'
-- Or
EXEC au_info @lastname = 'Dull', @firstname = 'Ann'
-- Or
EXEC au_info @firstname = 'Ann', @lastname = 'Dull'
如果该过程是批处理中的第一条语句,则可使用:
au_info 'Dull', 'Ann'
-- Or
au_info @lastname = 'Dull', @firstname = 'Ann'
-- Or
au_info @firstname = 'Ann', @lastname = 'Dull'
实例5:使用带有通配符参数的简单过程
CREATE PROCEDURE au_info2
@lastname varchar(30) = 'D%',
@firstname varchar(18) = '%'
AS
SELECT au_lname, au_fname, title, pub_name
FROM authors a INNER JOIN titleauthor ta
ON a.au_id = ta.au_id INNER JOIN titles t
ON t.title_id = ta.title_id INNER JOIN publishers p
ON t.pub_id = p.pub_id
WHERE au_fname LIKE @firstname
AND au_lname LIKE @lastname
GO
au_info2 存储过程可以用多种组合执行。下面只列出了部分组合:
EXECUTE au_info2
-- Or
EXECUTE au_info2 'Wh%'
-- Or
EXECUTE au_info2 @firstname = 'A%'
-- Or
EXECUTE au_info2 '[CK]ars[OE]n'
-- Or
EXECUTE au_info2 'Hunter', 'Sheryl'
-- Or
EXECUTE au_info2 'H%', 'S%'
= 'proc2'
实例6:if...else
存储过程,其中@case作为执行update的选择依据,用if...else实现执行时根据传入的参数执行不同的修改.
--下面是if……else的存储过程:
if exists (select 1 from sysobjects where name = 'Student' and type ='u' )
drop table Student
go
if exists (select 1 from sysobjects where name = 'spUpdateStudent' and type ='p' )
drop proc spUpdateStudent
go
create table Student
(
fName nvarchar (10),
fAge
smallint ,
fDiqu varchar (50),
fTel int
)
go
insert into Student values ('X.X.Y' , 28, 'Tesing' , 888888)
go
create proc spUpdateStudent
(
@fCase int ,
@fName nvarchar (10),
@fAge smallint ,
@fDiqu varchar (50),
@fTel int
)
as
update Student
set fAge = @fAge, -- 传 1,2,3 都要更新 fAge 不需要用 case
fDiqu = (case when @fCase = 2 or @fCase = 3 then @fDiqu else fDiqu end ),
fTel = (case when @fCase = 3 then @fTel else fTel end )
where fName = @fName
select * from Student
go
-- 只改 Age
exec spUpdateStudent
@fCase = 1,
@fName = N'X.X.Y' ,
@fAge = 80,
@fDiqu = N'Update' ,
@fTel = 1010101
-- 改 Age 和 Diqu
exec spUpdateStudent
@fCase = 2,
@fName = N'X.X.Y' ,
@fAge = 80,
@fDiqu = N'Update' ,
@fTel = 1010101
-- 全改
exec spUpdateStudent
@fCase = 3,
@fName = N'X.X.Y' ,
@fAge = 80,
@fDiqu = N'Update' ,
@fTel = 1010101

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

AI Hentai Generator
免费生成ai无尽的。

热门文章

热工具

VSCode Windows 64位 下载
微软推出的免费、功能强大的一款IDE编辑器

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)

SecLists
SecLists是最终安全测试人员的伙伴。它是一个包含各种类型列表的集合,这些列表在安全评估过程中经常使用,都在一个地方。SecLists通过方便地提供安全测试人员可能需要的所有列表,帮助提高安全测试的效率和生产力。列表类型包括用户名、密码、URL、模糊测试有效载荷、敏感数据模式、Web shell等等。测试人员只需将此存储库拉到新的测试机上,他就可以访问到所需的每种类型的列表。

SublimeText3 英文版
推荐:为Win版本,支持代码提示!

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具




