.NET工厂方法模式讲解
- 高洛峰原创
- 2016-12-10 09:17:501233浏览
工厂方法模式介绍:
工厂方法(Factory Method)模式的意义是定义一个创建产品对象的工厂接口,将实际创建工作推迟到子类当中。核心工厂类不再负责产品的创建,这样核心类成为一个抽象工厂角色,仅负责具体工厂子类必须实现的接口,这样进一步抽象化的好处是使得工厂方法模式可以使系统在不修改具体工厂角色的情况下引进新的产品。
工厂方法模式结构图:
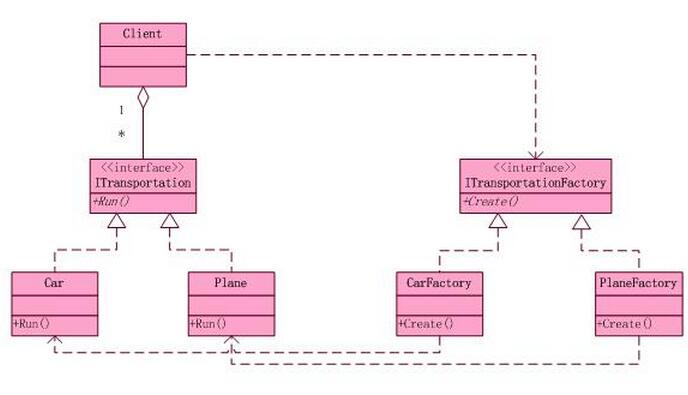
角色分类:
抽象工厂角色:是工厂方法模式的核心,与应用程序无关。任何在模式中创建的对象的工厂类必须实现这个接口。
具体工厂角色:这是实现抽象工厂接口的具体工厂类,包含与应用程序密切相关的逻辑,并且受到应用程序调用以创建产品对象
抽象产品角色:工厂方法模式所创建的对象的超类型,也就是产品对象的共同父类或共同拥有的接口。在上图中,这个角色是Light。
具体产品角色:这个角色实现了抽象产品角色所定义的接口。某具体产品有专门的具体工厂创建,它们之间往往一一对应。
引入实际例子:
在上一篇博文简单工厂模式中,使用简单工厂模式进行了以下实现:如果有一个住户管理系统,里面的住户类型是可变的,每一种租户类型的租金计算公式都存在差异例如:A类型的住户租金额=天数*单价+绩效*0.005;B类型的住户租金额=月份*(每月价格+performance*0.001)这里我们虽然实现了客户的需求,但是如果客户后期需要增加了C类型商店和D类型商店,而它们的算法要求又不一样,这个时候我们就需要进行C,D类型商店的创建,并继承Ishop接口,实现里面的方法,同时还得继续修改工厂类在switc中增加case进行捕捉创建相应的商店对象,一旦出现这样的情况,是不利于程序的扩展性和项目后期的维护性的。
1.分析:商店有共同的行为特征,都要进行店铺租金计算行为,我们抽象了Ishop ,里面有待实现的计算商店租金方法行为。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace FactoryEntiy
{
public interface Ishop
{
double Getrent(int days, double dayprice, double performance);
}
}
2.我们实现Isho接口里面的方法,创建A,B类型店铺。
using FactoryEntiy;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace ProductEnity
{
/// <summary>
/// 继承商店接口,实现里面的行为方法,即算法
/// </summary>
public class Ashop:Ishop
{
/// <summary>
/// /// A类型商店租金额,天数*单价+绩效*0.005
/// </summary>
/// <param name="days">天数</param>
/// <param name="dayprice">每天单价</param>
/// <param name="performance">日平均绩效</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public double Getrent(int days, double dayprice, double performance)
{
Console.WriteLine("A商店的租金算法");
return days * dayprice + performance * 0.01;
}
}
}
using FactoryEntiy;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace ProductEnity
{
/// <summary>
/// 继承商店接口,实现里面的行为方法,即算法
/// </summary>
public class Bshop:Ishop
{
/// <summary>
/// B类型商店的租金=月份*(每月价格+performance*0.001)
/// </summary>
/// <param name="month">月数</param>
/// <param name="monthprice">月单价</param>
/// <param name="performance">月平均绩效</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public double Getrent(int month, double monthprice, double performance)
{
Console.WriteLine("B商店的租金算法");
return month * (monthprice + performance * 0.001);
}
}
}
3.现在考虑在什么情况下创建商店的实体,对不同的商店进行租金计算,并且方便以后的增加和修改。于是我们创建IFactroy接口,里面有待实现的创建商店对象的方法。
using FactoryEntiy;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace FactoryMethod
{
/// <summary>
/// 工厂类,创建商店类型实体
/// </summary>
public interface IFactory
{
Ishop CreateShop();
}
}
4.现在我们就可以继承自IFactory,实现里面创建对应的商店对象了。
using FactoryEntiy;
using FactoryMethod;
using ProductEnity;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace ProductEnity
{
/// <summary>
/// 继承工厂类,创建A类型商店实体
/// </summary>
public class CreateBshop : IFactory
{
public Ishop CreateShop()
{
return new Ashop();
}
}
}
using FactoryEntiy;
using FactoryMethod;
using ProductEnity;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace ProductEnity
{
/// <summary>
/// 继承工厂类,创建B类型商店实体
/// </summary>
public class CreateAshop : IFactory
{
public Ishop CreateShop()
{
return new Bshop();
}
}
}
5.之后根据当前的商店类型进行判断,该类型的商店应该进行哪一种算法:
using FactoryEntiy;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Configuration;
using System.Linq;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Text;
namespace FactoryMethod.App
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string shopname = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["CreateShopClassName"];
//shopname为创建商店类名称,此处=CreateAshop
IFactory af = (IFactory)Assembly.Load("ProductEnity").CreateInstance("ProductEnity." + shopname);
//第一个ProductEnity是dll的名称,第二个ProductEnity是项目的命名空间。
Ishop As = af.CreateShop(); double total = As.Getrent(30, 300, 2000); //30 天/100元 日平均绩效为2000
Console.WriteLine("该A类型商店的租金为:" + total);
Console.WriteLine("=============");
IFactory bf = (IFactory)Assembly.Load("ProductEnity").CreateInstance("ProductEnity." + "CreateBshop");
//CreateBshop可以保存为配置或者存在数据库中,
//注意该保存字符串应该与项目中创建的类名一样,
//否则反射的方式会找不到该项目下的类。
Ishop Bs = bf.CreateShop(); total = Bs.Getrent(30, 300, 2000); //30 天/100元 日平均绩效为2000
Console.WriteLine("该A类型商店的租金为:" + total);
}
}
}
这里我们使用反射的方式创建对象,替换了之前的工厂类通过switch创建对象的方式,有利于后面的新类型商店增加和算法修改增加和维护以后在项目需求在有变革,我们只需要重新在项目中增加C,D类型商店,继承Ishop实现里面的方法,同时,添加继承IFactroy接口,创建对应的商店对象编译该项目的ProductEnity.dll,以后再进行计算该C,D类型的商店算法就可以通过反射的方式进行计算,不需要修改原来的工程类代码。
整个项目的结构图如下:


