AI agents are designed to act autonomously, solving problems and executing tasks in dynamic environments. A key feature in Autogen, enabling their adaptability is AutoGen’s code executors. This feature along with LLMs enables AI agents to generate, evaluate, and execute code in real-time. This capability bridges the gap between static AI models and actionable intelligence. By automating workflows, performing data analysis, and debugging complex systems, it transforms agents from mere thinkers into effective doers. In this article, we will learn more about code executors in AutoGen and how to implement them.
Table of Contents
- Types of Code Executors in AutoGen
- How to Build AI Agents with Code Executors in AutoGen?
- Pre-requisites
- Building an AI Agent Using Command Line Executor
- Building an ML Model Using Jupyter Code Executor
- Building an AI Agent Using Custom Executor
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Types of Code Executors in AutoGen
AutoGen has three kinds of code executors that can be used for different purposes.
- Command Line Executor: It allows AI agents to run the code in the command line. It will save each code block to a separate file and execute that file. This executor is ideal for automating tasks like file management, script execution, or handling external tools. It provides flexibility and low-level control in a workflow.
- Jupyter Code Executor: It enables agents to execute Python code within a Jupyter-like environment. Here, you can define variables in one code block and reuse them in subsequent blocks. One advantage of this setup is that when an error occurs, only the specific block of code with the error needs to be re-executed, rather than the entire script.
- Custom Code Executor: It gives developers the ability to create specialized code execution logic. For example, the custom code executor can access variables defined in the environment without explicitly providing them to the LLM.
These Code Executors can be run on both the host machine (local) as well as the Docker containers.
Also Read: 4 Steps to Build Multi-Agent Nested Chats with AutoGen
How to Build AI Agents with Code Executors in AutoGen?
Now let’s learn how you can use these different code executors in AutoGen:
Pre-requisites
Before building AI agents, ensure you have the necessary API keys for the required LLMs.
Load the .env file with the API keys needed.
from dotenv import load_dotenv load_dotenv(./env)
Key Libraries Required
autogen-agentchat – 0.2.38
jupyter_kernel_gateway-3.0.1
Building an AI Agent Using Command Line Executor
Let’s build an AI agent to know the offers and discounts available on an e-commerce website using the command line executor. Here are the steps to follow.
1. Import the necessary libraries.
from autogen import ConversableAgent, AssistantAgent, UserProxyAgent from autogen.coding import LocalCommandLineCodeExecutor, DockerCommandLineCodeExecutor
2. Define the agents.
user_proxy = UserProxyAgent(
name="User",
llm_config=False,
is_termination_msg=lambda msg: msg.get("content") is not None and "TERMINATE" in msg["content"],
human_input_mode="TERMINATE",
code_execution_config=False
)
code_writer_agent = ConversableAgent(
name="CodeWriter",
system_message="""You are a Python developer.
You use your coding skill to solve problems.
Once the task is done, returns 'TERMINATE'.""",
llm_config={"config_list": [{"model": "gpt-4o-mini"}]},
)
local_executor = LocalCommandLineCodeExecutor(
timeout=15,
work_dir='./code files')
local_executor_agent = ConversableAgent(
"local_executor_agent",
llm_config=False,
code_execution_config={"executor": local_executor},
human_input_mode="ALWAYS",
)
We are using the ‘local_executor’ in the code_execution_config of the local_executor_agent.
3. Define the messages which are used to initialize the chat.
messages = ["""To check whether there are any offers or discounts available on a given e-commerce website -
https://www.flipkart.com/
Follow these steps,
1. download the html page of the given URL
2. we only need html content, so remove any CSS, JavaScript, and Image tags content
3. save the remaining html content.
""" ,
"read the text and list all the offers and discounts available"]
# Intialize the chat
chat_result = local_executor_agent.initiate_chat(
code_writer_agent,
message=messages[0],
)
It will ask for human input after each message from the codeWriter agent. You just need to press the ‘Enter’ key to execute the code written by the agent. We can also any further instructions if there is any problem with the code.
Here are the questions we have asked and the output at the end.
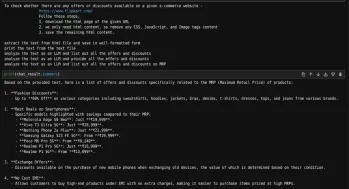
As we can see, with the mentioned questions, we can get a list of offers and discounts from an e-commerce website.
Also Read: Hands-on Guide to Building Multi-Agent Chatbots with AutoGen
Building an ML Model Using Jupyter Code Executor
By using this, we can access the variables defined in one code block from another code block, unlike the command line executor.
Now, let’s try to build an ML model using this.
1. Import the additional methods.
from autogen.coding.jupyter import LocalJupyterServer, DockerJupyterServer, JupyterCodeExecutor from pathlib import Path
2. Initialize the jupyter server and output directory.
server = LocalJupyterServer()
output_dir = Path("coding")
output_dir.mkdir()
Note that LocalJupyterServer may not function on Windows due to a bug. In this case, you can use the DockerJupyterServer instead or use the EmbeddedIPythonCodeExecutor.
3. Define the executor agent and writer agent with a custom system message.
jupyter_executor_agent = ConversableAgent(
name="jupyter_executor_agent",
llm_config=False,
code_execution_config={
"executor": JupyterCodeExecutor(server, output_dir=output_dir),
},
human_input_mode="ALWAYS",
)
code_writer_system_message = """
You have been given coding capability to solve tasks using Python code in a stateful IPython kernel.
You are responsible for writing the code, and the user is responsible for executing the code.
When you write Python code, put the code in a markdown code block with the language set to Python.
For example:
```python
x = 3
```
You can use the variable `x` in subsequent code blocks.
```python
print(x)
```
Always use print statements for the output of the code.
Write code incrementally and leverage the statefulness of the kernel to avoid repeating code.
Import libraries in a separate code block.
Define a function or a class in a separate code block.
Run code that produces output in a separate code block.
Run code that involves expensive operations like download, upload, and call external APIs in a separate code block.
When your code produces an output, the output will be returned to you.
Because you have limited conversation memory, if your code creates an image,
the output will be a path to the image instead of the image itself."""
code_writer_agent = ConversableAgent(
"code_writer",
system_message=code_writer_system_message,
llm_config={"config_list": [{"model": "gpt-4o"}]},
human_input_mode="TERMINATE",
)
4. Define the initial message and initialize the chat
message = "read the datasets/user_behavior_dataset.csv and print what the data is about" chat_result = jupyter_executor_agent.initiate_chat( code_writer_agent, message=message, ) # Once the chat is completed we can stop the server. server.stop()
5. Once the chat is completed we can stop the server.
We can print the messages as follows
for chat in chat_result.chat_history[:]:
if chat['name'] == 'code_writer' and 'TERMINATE' not in chat['content']:
print("--------agent-----------")
print(chat['content'])
if chat['name'] == 'jupyter_executor_agent' and 'exitcode' not in chat['content']:
print("--------user------------")
print(chat['content'])
Here’s the sample
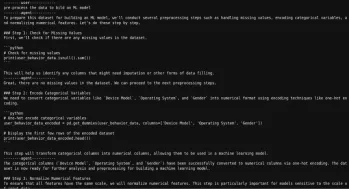
As we can see, we can get the code generated by the agent and also the results after executing the code.
Also Read: Building Agentic Chatbots Using AutoGen
Building an AI Agent Using Custom Executor
Now, let’s try to create a custom executor that can run the code in the same jupyter notebook where we are creating this executor. So, we can read a CSV file, and then ask an agent to build an ML model on the already imported file.
Here’s how we’ll do it.
1. Import the necessary libraries.
import pandas as pd from typing import List from IPython import get_ipython from autogen.coding import CodeBlock, CodeExecutor, CodeExtractor, CodeResult, MarkdownCodeExtractor
2. Define the executor that can extract and run the code from jupyter cells.
class NotebookExecutor(CodeExecutor):
@property
def code_extractor(self) -> CodeExtractor:
# Extact code from markdown blocks.
return MarkdownCodeExtractor()
def __init__(self) -> None:
# Get the current IPython instance running in this notebook.
self._ipython = get_ipython()
def execute_code_blocks(self, code_blocks: List[CodeBlock]) -> CodeResult:
log = ""
for code_block in code_blocks:
result = self._ipython.run_cell("%%capture --no-display cap\n" + code_block.code)
log += self._ipython.ev("cap.stdout")
log += self._ipython.ev("cap.stderr")
if result.result is not None:
log += str(result.result)
exitcode = 0 if result.success else 1
if result.error_before_exec is not None:
log += f"\n{result.error_before_exec}"
exitcode = 1
if result.error_in_exec is not None:
log += f"\n{result.error_in_exec}"
exitcode = 1
if exitcode != 0:
break
return CodeResult(exit_code=exitcode, output=log)
3. Define the agents.
code_writer_agent = ConversableAgent(
name="CodeWriter",
system_message="You are a helpful AI assistant.\n"
"You use your coding skill to solve problems.\n"
"You have access to a IPython kernel to execute Python code.\n"
"You can suggest Python code in Markdown blocks, each block is a cell.\n"
"The code blocks will be executed in the IPython kernel in the order you suggest them.\n"
"All necessary libraries have already been installed.\n"
"Add return or print statements to the code to get the output\n"
"Once the task is done, returns 'TERMINATE'.",
llm_config={"config_list": [{"model": "gpt-4o-mini"}]},
)
code_executor_agent = ConversableAgent(
name="CodeExecutor",
llm_config=False,
code_execution_config={"executor": NotebookExecutor()},
is_termination_msg=lambda msg: "TERMINATE" in msg.get("content", "").strip().upper(),
human_input_mode="ALWAYS"
)
4. Read the file and initiate the chat with the file.
df = pd.read_csv('datasets/mountains_vs_beaches_preferences.csv')
chat_result = code_executor_agent.initiate_chat(
code_writer_agent,
message="What are the column names in the dataframe defined above as df?",
)
5. We can print the chat history as follows:
for chat in chat_result.chat_history[:]:
if chat['name'] == 'CodeWriter' and 'TERMINATE' not in chat['content']:
print("--------agent-----------")
print(chat['content'])
if chat['name'] == 'CodeExecutor' and 'exitcode' not in chat['content']:
print("--------user------------")
print(chat['content'])
As we can see again, we can get the code generated by the agent and also the results after executing the code.
Conclusion
AutoGen’s code executors provide flexibility and functionality for AI agents to perform real-world tasks. The command line executor enables script execution, while the Jupyter code executor supports iterative development. Custom executors, on the other hand, allow developers to create tailored workflows.
These tools empower AI agents to transition from problem solvers to solution implementers. Developers can use these features to build intelligent systems that deliver actionable insights and automate complex processes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the primary purpose of Code Executors in AutoGen?A. Code Executors in AutoGen allow AI agents to generate, execute, and evaluate code in real time. This enables agents to automate tasks, perform data analysis, debug systems, and implement dynamic workflows.
Q2. What are the differences between Command Line and Jupyter Code Executors?A. The Command Line Executor saves and executes code as separate files, ideal for tasks like file management and script execution. The Jupyter Code Executor operates in a stateful environment, allowing reuse of variables and selective re-execution of code blocks, making it more suitable for iterative coding tasks like building ML models.
Q3. Can Code Executors be used with Docker containers?A. Yes, both the Command Line Executor and Jupyter Code Executor can be configured to run on Docker containers, providing a flexible environment for execution.
Q4. What is the advantage of using a Custom Code Executor?A. Custom Code Executors allow developers to define specialized execution logic, such as running code within the same Jupyter notebook. This is useful for tasks requiring a high level of integration or customization.
Q5. What are the prerequisites for using Code Executors in AutoGen?A. Before using Code Executors, ensure you have the necessary API keys for your preferred LLMs. You should also have the required libraries, such as `autogen-agentchat` and `jupyter_kernel_gateway`, installed in your environment.
以上是使用Autogen中的代码执行人完成复杂的任务的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
![无法使用chatgpt!解释可以立即测试的原因和解决方案[最新2025]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/001/242/473/174717025174979.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40) 无法使用chatgpt!解释可以立即测试的原因和解决方案[最新2025]May 14, 2025 am 05:04 AM
无法使用chatgpt!解释可以立即测试的原因和解决方案[最新2025]May 14, 2025 am 05:04 AMChatGPT无法访问?本文提供多种实用解决方案!许多用户在日常使用ChatGPT时,可能会遇到无法访问或响应缓慢等问题。本文将根据不同情况,逐步指导您解决这些问题。 ChatGPT无法访问的原因及初步排查 首先,我们需要确定问题是出在OpenAI服务器端,还是用户自身网络或设备问题。 请按照以下步骤进行排查: 步骤1:检查OpenAI官方状态 访问OpenAI Status页面 (status.openai.com),查看ChatGPT服务是否正常运行。如果显示红色或黄色警报,则表示Open
 计算ASI的风险始于人类的思想May 14, 2025 am 05:02 AM
计算ASI的风险始于人类的思想May 14, 2025 am 05:02 AM2025年5月10日,麻省理工学院物理学家Max Tegmark告诉《卫报》,AI实验室应在释放人工超级智能之前模仿Oppenheimer的三位一体测试演算。 “我的评估是'康普顿常数',这是一场比赛的可能性
 易于理解的解释如何编写和撰写歌词和推荐工具May 14, 2025 am 05:01 AM
易于理解的解释如何编写和撰写歌词和推荐工具May 14, 2025 am 05:01 AMAI音乐创作技术日新月异,本文将以ChatGPT等AI模型为例,详细讲解如何利用AI辅助音乐创作,并辅以实际案例进行说明。我们将分别介绍如何通过SunoAI、Hugging Face上的AI jukebox以及Python的Music21库进行音乐创作。 通过这些技术,每个人都能轻松创作原创音乐。但需注意,AI生成内容的版权问题不容忽视,使用时务必谨慎。 让我们一起探索AI在音乐领域的无限可能! OpenAI最新AI代理“OpenAI Deep Research”介绍: [ChatGPT]Ope
 什么是chatgpt-4?对您可以做什么,定价以及与GPT-3.5的差异的详尽解释!May 14, 2025 am 05:00 AM
什么是chatgpt-4?对您可以做什么,定价以及与GPT-3.5的差异的详尽解释!May 14, 2025 am 05:00 AMChatGPT-4的出现,极大地拓展了AI应用的可能性。相较于GPT-3.5,ChatGPT-4有了显着提升,它具备强大的语境理解能力,还能识别和生成图像,堪称万能的AI助手。在提高商业效率、辅助创作等诸多领域,它都展现出巨大的潜力。然而,与此同时,我们也必须注意其使用上的注意事项。 本文将详细解读ChatGPT-4的特性,并介绍针对不同场景的有效使用方法。文中包含充分利用最新AI技术的技巧,敬请参考。 OpenAI发布的最新AI代理,“OpenAI Deep Research”详情请点击下方链
 解释如何使用chatgpt应用程序!日本支持和语音对话功能May 14, 2025 am 04:59 AM
解释如何使用chatgpt应用程序!日本支持和语音对话功能May 14, 2025 am 04:59 AMCHATGPT应用程序:与AI助手释放您的创造力!初学者指南 ChatGpt应用程序是一位创新的AI助手,可处理各种任务,包括写作,翻译和答案。它是一种具有无限可能性的工具,可用于创意活动和信息收集。 在本文中,我们将以一种易于理解的方式解释初学者,从如何安装chatgpt智能手机应用程序到语音输入功能和插件等应用程序所独有的功能,以及在使用该应用时要牢记的要点。我们还将仔细研究插件限制和设备对设备配置同步
 如何使用中文版Chatgpt?注册程序和费用的说明May 14, 2025 am 04:56 AM
如何使用中文版Chatgpt?注册程序和费用的说明May 14, 2025 am 04:56 AMChatGPT中文版:解锁中文AI对话新体验 ChatGPT风靡全球,您知道它也提供中文版本吗?这款强大的AI工具不仅支持日常对话,还能处理专业内容,并兼容简体中文和繁体中文。无论是中国地区的使用者,还是正在学习中文的朋友,都能从中受益。 本文将详细介绍ChatGPT中文版的使用方法,包括账户设置、中文提示词输入、过滤器的使用、以及不同套餐的选择,并分析潜在风险及应对策略。此外,我们还将对比ChatGPT中文版和其他中文AI工具,帮助您更好地了解其优势和应用场景。 OpenAI最新发布的AI智能
 5 AI代理神话,您需要停止相信May 14, 2025 am 04:54 AM
5 AI代理神话,您需要停止相信May 14, 2025 am 04:54 AM这些可以将其视为生成AI领域的下一个飞跃,这为我们提供了Chatgpt和其他大型语言模型聊天机器人。他们可以代表我们采取行动,而不是简单地回答问题或产生信息
 易于理解使用Chatgpt创建和管理多个帐户的非法性的解释May 14, 2025 am 04:50 AM
易于理解使用Chatgpt创建和管理多个帐户的非法性的解释May 14, 2025 am 04:50 AM使用chatgpt有效的多个帐户管理技术|关于如何使用商业和私人生活的详尽解释! Chatgpt在各种情况下都使用,但是有些人可能担心管理多个帐户。本文将详细解释如何为ChatGpt创建多个帐户,使用时该怎么做以及如何安全有效地操作它。我们还介绍了重要的一点,例如业务和私人使用差异,并遵守OpenAI的使用条款,并提供指南,以帮助您安全地利用多个帐户。 Openai


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

适用于 Eclipse 的 SAP NetWeaver 服务器适配器
将Eclipse与SAP NetWeaver应用服务器集成。

MinGW - 适用于 Windows 的极简 GNU
这个项目正在迁移到osdn.net/projects/mingw的过程中,你可以继续在那里关注我们。MinGW:GNU编译器集合(GCC)的本地Windows移植版本,可自由分发的导入库和用于构建本地Windows应用程序的头文件;包括对MSVC运行时的扩展,以支持C99功能。MinGW的所有软件都可以在64位Windows平台上运行。

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

mPDF
mPDF是一个PHP库,可以从UTF-8编码的HTML生成PDF文件。原作者Ian Back编写mPDF以从他的网站上“即时”输出PDF文件,并处理不同的语言。与原始脚本如HTML2FPDF相比,它的速度较慢,并且在使用Unicode字体时生成的文件较大,但支持CSS样式等,并进行了大量增强。支持几乎所有语言,包括RTL(阿拉伯语和希伯来语)和CJK(中日韩)。支持嵌套的块级元素(如P、DIV),






