请我喝杯咖啡☕
*我的帖子解释了移动 MNIST。
MovingMNIST() 可以使用 Moving MNIST 数据集,如下所示:
*备忘录:
- 第一个参数是 root(必需类型:str 或 pathlib.Path)。 *绝对或相对路径都是可能的。
- 第二个参数是 split(Optional-Default:None-Type:str):
*备注:
- 没有,可以设置“train”或“test”。
- 如果为 None,则返回每个视频的所有 20 帧(图像),忽略 split_ratio。
- 第三个参数是 split_ratio(Optional-Default:10-Type:int):
*备注:
- 如果 split 为“train”,则返回 data[:, :split_ratio]。
- 如果 split 为“test”,则返回 data[:, split_ratio:]。
- 如果 split 为 None,则忽略它。 忽略 split_ratio。
- 第四个参数是transform(Optional-Default:None-Type:callable)。
- 第五个参数是 download(可选-默认:False-类型:bool):
*备注:
- 如果为 True,则数据集将从互联网下载到 root。
- 如果为 True 并且数据集已下载,则将其提取。
- 如果为 True 并且数据集已下载,则不会发生任何事情。
- 如果数据集已经下载,则应该为 False,因为它速度更快。
- 您可以从此处手动下载并提取数据集,例如数据/移动MNIST/。
from torchvision.datasets import MovingMNIST
all_data = MovingMNIST(
root="data"
)
all_data = MovingMNIST(
root="data",
split=None,
split_ratio=10,
download=False,
transform=None
)
train_data = MovingMNIST(
root="data",
split="train"
)
test_data = MovingMNIST(
root="data",
split="test"
)
len(all_data), len(train_data), len(test_data)
# (10000, 10000, 10000)
len(all_data[0]), len(train_data[0]), len(test_data[0])
# (20, 10, 10)
all_data
# Dataset MovingMNIST
# Number of datapoints: 10000
# Root location: data
all_data.root
# 'data'
print(all_data.split)
# None
all_data.split_ratio
# 10
all_data.download
# <bound method movingmnist.download of dataset movingmnist number datapoints: root location: data>
print(all_data.transform)
# None
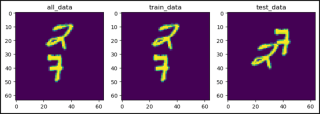
from torchvision.datasets import MovingMNIST
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 3))
plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)
plt.title("all_data")
plt.imshow(all_data[0].squeeze()[0])
plt.subplot(1, 3, 2)
plt.title("train_data")
plt.imshow(train_data[0].squeeze()[0])
plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)
plt.title("test_data")
plt.imshow(test_data[0].squeeze()[0])
plt.show()
</bound>
from torchvision.datasets import MovingMNIST
all_data = MovingMNIST(
root="data",
split=None
)
train_data = MovingMNIST(
root="data",
split="train"
)
test_data = MovingMNIST(
root="data",
split="test"
)
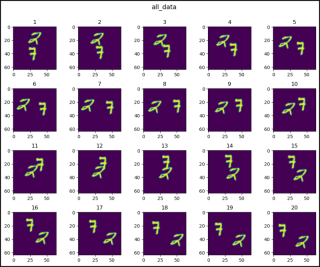
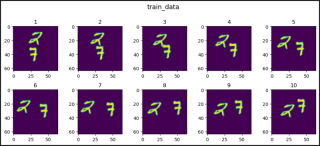
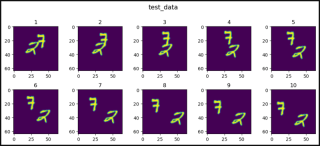
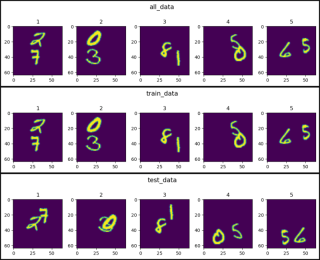
def show_images(data, main_title=None):
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
plt.suptitle(t=main_title, y=1.0, fontsize=14)
for i, image in enumerate(data, start=1):
plt.subplot(4, 5, i)
plt.tight_layout(pad=1.0)
plt.title(i)
plt.imshow(image)
plt.show()
show_images(data=all_data[0].squeeze(), main_title="all_data")
show_images(data=train_data[0].squeeze(), main_title="train_data")
show_images(data=test_data[0].squeeze(), main_title="test_data")
from torchvision.datasets import MovingMNIST
all_data = MovingMNIST(
root="data",
split=None
)
train_data = MovingMNIST(
root="data",
split="train"
)
test_data = MovingMNIST(
root="data",
split="test"
)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def show_images(data, main_title=None):
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
plt.suptitle(t=main_title, y=1.0, fontsize=14)
col = 5
for i, image in enumerate(data, start=1):
plt.subplot(4, 5, i)
plt.tight_layout(pad=1.0)
plt.title(i)
plt.imshow(image.squeeze()[0])
if i == col:
break
plt.show()
show_images(data=all_data, main_title="all_data")
show_images(data=train_data, main_title="train_data")
show_images(data=test_data, main_title="test_data")
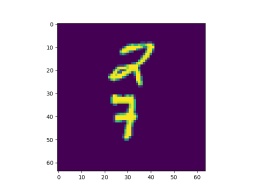
from torchvision.datasets import MovingMNIST
import matplotlib.animation as animation
all_data = MovingMNIST(
root="data"
)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from IPython.display import HTML
figure, axis = plt.subplots()
# ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ `ArtistAnimation()` ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
images = []
for image in all_data[0].squeeze():
images.append([axis.imshow(image)])
ani = animation.ArtistAnimation(fig=figure, artists=images,
interval=100)
# ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ `ArtistAnimation()` ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑
# ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ `FuncAnimation()` ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
# def animate(i):
# axis.imshow(all_data[0].squeeze()[i])
#
# ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig=figure, func=animate,
# frames=20, interval=100)
# ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ `FuncAnimation()` ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑
# ani.save('result.gif') # Save the animation as a `.gif` file
plt.ioff() # Hide a useless image
# ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ Show animation ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
HTML(ani.to_jshtml()) # Animation operator
# HTML(ani.to_html5_video()) # Animation video
# ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ Show animation ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑
# ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ Show animation ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
# plt.rcParams["animation.html"] = "jshtml" # Animation operator
# plt.rcParams["animation.html"] = "html5" # Animation video
# ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ Show animation ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑

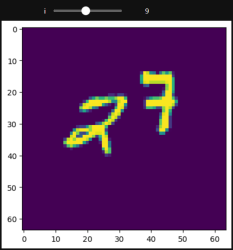
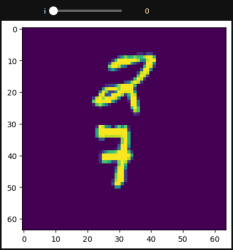
from torchvision.datasets import MovingMNIST
from ipywidgets import interact, IntSlider
all_data = MovingMNIST(
root="data"
)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from IPython.display import HTML
def func(i):
plt.imshow(all_data[0].squeeze()[i])
interact(func, i=(0, 19, 1))
# interact(func, i=IntSlider(min=0, max=19, step=1, value=0))
# ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ Set the start value ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑
plt.show()
以上是在 PyTorch 中移动 MNIST的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 Python中的合并列表:选择正确的方法May 14, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Python中的合并列表:选择正确的方法May 14, 2025 am 12:11 AMTomergelistsinpython,YouCanusethe操作员,estextMethod,ListComprehension,Oritertools
 如何在Python 3中加入两个列表?May 14, 2025 am 12:09 AM
如何在Python 3中加入两个列表?May 14, 2025 am 12:09 AM在Python3中,可以通过多种方法连接两个列表:1)使用 运算符,适用于小列表,但对大列表效率低;2)使用extend方法,适用于大列表,内存效率高,但会修改原列表;3)使用*运算符,适用于合并多个列表,不修改原列表;4)使用itertools.chain,适用于大数据集,内存效率高。
 Python串联列表字符串May 14, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Python串联列表字符串May 14, 2025 am 12:08 AM使用join()方法是Python中从列表连接字符串最有效的方法。1)使用join()方法高效且易读。2)循环使用 运算符对大列表效率低。3)列表推导式与join()结合适用于需要转换的场景。4)reduce()方法适用于其他类型归约,但对字符串连接效率低。完整句子结束。
 Python执行,那是什么?May 14, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Python执行,那是什么?May 14, 2025 am 12:06 AMpythonexecutionistheprocessoftransformingpypythoncodeintoExecutablestructions.1)InternterPreterReadSthecode,ConvertingTingitIntObyTecode,whepythonvirtualmachine(pvm)theglobalinterpreterpreterpreterpreterlock(gil)the thepythonvirtualmachine(pvm)
 Python:关键功能是什么May 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python:关键功能是什么May 14, 2025 am 12:02 AMPython的关键特性包括:1.语法简洁易懂,适合初学者;2.动态类型系统,提高开发速度;3.丰富的标准库,支持多种任务;4.强大的社区和生态系统,提供广泛支持;5.解释性,适合脚本和快速原型开发;6.多范式支持,适用于各种编程风格。
 Python:编译器还是解释器?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python:编译器还是解释器?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AMPython是解释型语言,但也包含编译过程。1)Python代码先编译成字节码。2)字节码由Python虚拟机解释执行。3)这种混合机制使Python既灵活又高效,但执行速度不如完全编译型语言。
 python用于循环与循环时:何时使用哪个?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
python用于循环与循环时:何时使用哪个?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMuseeAforloopWheniteratingOveraseQuenceOrforAspecificnumberoftimes; useAwhiLeLoopWhenconTinuingUntilAcIntiment.ForloopSareIdeAlforkNownsences,而WhileLeleLeleLeleLoopSituationSituationSituationsItuationSuationSituationswithUndEtermentersitations。
 Python循环:最常见的错误May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Python循环:最常见的错误May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMpythonloopscanleadtoerrorslikeinfiniteloops,modifyingListsDuringteritation,逐个偏置,零indexingissues,andnestedloopineflinefficiencies


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

SublimeText3 Linux新版
SublimeText3 Linux最新版

螳螂BT
Mantis是一个易于部署的基于Web的缺陷跟踪工具,用于帮助产品缺陷跟踪。它需要PHP、MySQL和一个Web服务器。请查看我们的演示和托管服务。

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

适用于 Eclipse 的 SAP NetWeaver 服务器适配器
将Eclipse与SAP NetWeaver应用服务器集成。

VSCode Windows 64位 下载
微软推出的免费、功能强大的一款IDE编辑器





