剑锋1.3B
Janus 是一个新的自回归框架,集成了多模态理解和生成。与之前的模型使用单个视觉编码器来执行理解和生成任务不同,Janus 为这些功能引入了两个独立的视觉编码路径。
理解和生成编码的差异
- 在多模态理解任务中,视觉编码器提取高级语义信息,例如对象类别和视觉属性。该编码器专注于推断复杂的含义,强调高维语义元素。
- 另一方面,在视觉生成任务中,重点放在生成精细细节并保持整体一致性。因此,需要能够捕获空间结构和纹理的低维编码。
设置环境
以下是在 Google Colab 中运行 Janus 的步骤:
git clone https://github.com/deepseek-ai/Janus cd Janus pip install -e . # If needed, install the following as well # pip install wheel # pip install flash-attn --no-build-isolation
愿景任务
加载模型
使用以下代码加载视觉任务所需的模型:
import torch from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM from janus.models import MultiModalityCausalLM, VLChatProcessor from janus.utils.io import load_pil_images # Specify the model path model_path = "deepseek-ai/Janus-1.3B" vl_chat_processor = VLChatProcessor.from_pretrained(model_path) tokenizer = vl_chat_processor.tokenizer vl_gpt = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_path, trust_remote_code=True) vl_gpt = vl_gpt.to(torch.bfloat16).cuda().eval()
加载和准备图像以进行编码
接下来,加载图像并将其转换为模型可以理解的格式:
conversation = [
{
"role": "User",
"content": "<image_placeholder>\nDescribe this chart.",
"images": ["images/pie_chart.png"],
},
{"role": "Assistant", "content": ""},
]
# Load the image and prepare input
pil_images = load_pil_images(conversation)
prepare_inputs = vl_chat_processor(
conversations=conversation, images=pil_images, force_batchify=True
).to(vl_gpt.device)
# Run the image encoder and obtain image embeddings
inputs_embeds = vl_gpt.prepare_inputs_embeds(**prepare_inputs)
</image_placeholder>
生成响应
最后,运行模型以生成响应:
# Run the model and generate a response
outputs = vl_gpt.language_model.generate(
inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds,
attention_mask=prepare_inputs.attention_mask,
pad_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
bos_token_id=tokenizer.bos_token_id,
eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
max_new_tokens=512,
do_sample=False,
use_cache=True,
)
answer = tokenizer.decode(outputs[0].cpu().tolist(), skip_special_tokens=True)
print(f"{prepare_inputs['sft_format'][0]}", answer)
示例输出
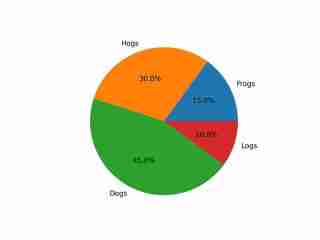
The image depicts a pie chart that illustrates the distribution of four different categories among four distinct groups. The chart is divided into four segments, each representing a category with a specific percentage. The categories and their corresponding percentages are as follows: 1. **Hogs**: This segment is colored in orange and represents 30.0% of the total. 2. **Frog**: This segment is colored in blue and represents 15.0% of the total. 3. **Logs**: This segment is colored in red and represents 10.0% of the total. 4. **Dogs**: This segment is colored in green and represents 45.0% of the total. The pie chart is visually divided into four segments, each with a different color and corresponding percentage. The segments are arranged in a clockwise manner starting from the top-left, moving clockwise. The percentages are clearly labeled next to each segment. The chart is a simple visual representation of data, where the size of each segment corresponds to the percentage of the total category it represents. This type of chart is commonly used to compare the proportions of different categories in a dataset. To summarize, the pie chart shows the following: - Hogs: 30.0% - Frog: 15.0% - Logs: 10.0% - Dogs: 45.0% This chart can be used to understand the relative proportions of each category in the given dataset.
输出展示了对图像的适当理解,包括其颜色和文本。
图像生成任务
加载模型
使用以下代码加载图像生成任务所需的模型:
import os import PIL.Image import torch import numpy as np from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM from janus.models import MultiModalityCausalLM, VLChatProcessor # Specify the model path model_path = "deepseek-ai/Janus-1.3B" vl_chat_processor = VLChatProcessor.from_pretrained(model_path) tokenizer = vl_chat_processor.tokenizer vl_gpt = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_path, trust_remote_code=True) vl_gpt = vl_gpt.to(torch.bfloat16).cuda().eval()
准备提示
接下来,根据用户的要求准备提示:
# Set up the prompt
conversation = [
{
"role": "User",
"content": "cute japanese girl, wearing a bikini, in a beach",
},
{"role": "Assistant", "content": ""},
]
# Convert the prompt into the appropriate format
sft_format = vl_chat_processor.apply_sft_template_for_multi_turn_prompts(
conversations=conversation,
sft_format=vl_chat_processor.sft_format,
system_prompt="",
)
prompt = sft_format + vl_chat_processor.image_start_tag
生成图像
以下函数用于生成图像。默认情况下,生成 16 张图像:
@torch.inference_mode()
def generate(
mmgpt: MultiModalityCausalLM,
vl_chat_processor: VLChatProcessor,
prompt: str,
temperature: float = 1,
parallel_size: int = 16,
cfg_weight: float = 5,
image_token_num_per_image: int = 576,
img_size: int = 384,
patch_size: int = 16,
):
input_ids = vl_chat_processor.tokenizer.encode(prompt)
input_ids = torch.LongTensor(input_ids)
tokens = torch.zeros((parallel_size*2, len(input_ids)), dtype=torch.int).cuda()
for i in range(parallel_size*2):
tokens[i, :] = input_ids
if i % 2 != 0:
tokens[i, 1:-1] = vl_chat_processor.pad_id
inputs_embeds = mmgpt.language_model.get_input_embeddings()(tokens)
generated_tokens = torch.zeros((parallel_size, image_token_num_per_image), dtype=torch.int).cuda()
for i in range(image_token_num_per_image):
outputs = mmgpt.language_model.model(
inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds,
use_cache=True,
past_key_values=outputs.past_key_values if i != 0 else None,
)
hidden_states = outputs.last_hidden_state
logits = mmgpt.gen_head(hidden_states[:, -1, :])
logit_cond = logits[0::2, :]
logit_uncond = logits[1::2, :]
logits = logit_uncond + cfg_weight * (logit_cond - logit_uncond)
probs = torch.softmax(logits / temperature, dim=-1)
next_token = torch.multinomial(probs, num_samples=1)
generated_tokens[:, i] = next_token.squeeze(dim=-1)
next_token = torch.cat([next_token.unsqueeze(dim=1), next_token.unsqueeze(dim=1)], dim=1).view(-1)
img_embeds = mmgpt.prepare_gen_img_embeds(next_token)
inputs_embeds = img_embeds.unsqueeze(dim=1)
dec = mmgpt.gen_vision_model.decode_code(
generated_tokens.to(dtype=torch.int),
shape=[parallel_size, 8, img_size // patch_size, img_size // patch_size],
)
dec = dec.to(torch.float32).cpu().numpy().transpose(0, 2, 3, 1)
dec = np.clip((dec + 1) / 2 * 255, 0, 255)
visual_img = np.zeros((parallel_size, img_size, img_size, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
visual_img[:, :, :] = dec
os.makedirs('generated_samples', exist_ok=True)
for i in range(parallel_size):
save_path = os.path.join('generated_samples', f"img_{i}.jpg")
PIL.Image.fromarray(visual_img[i]).save(save_path)
# Run the image generation
generate(vl_gpt, vl_chat_processor, prompt)
生成的图像将保存在 generated_samples 文件夹中。
生成结果示例
下面是生成图像的示例:

- 狗的描绘相对较好。
- 建筑物保持整体形状,但某些细节(例如窗户)可能显得不切实际。
- 人类,然而,要很好地生成是很有挑战性的,在真实感和类似动漫的风格中都存在明显的扭曲。
以上是Janus B:多模态理解和生成任务的统一模型的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!
 python中两个列表的串联替代方案是什么?May 09, 2025 am 12:16 AM
python中两个列表的串联替代方案是什么?May 09, 2025 am 12:16 AM可以使用多种方法在Python中连接两个列表:1.使用 操作符,简单但在大列表中效率低;2.使用extend方法,效率高但会修改原列表;3.使用 =操作符,兼具效率和可读性;4.使用itertools.chain函数,内存效率高但需额外导入;5.使用列表解析,优雅但可能过于复杂。选择方法应根据代码上下文和需求。
 Python:合并两个列表的有效方法May 09, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python:合并两个列表的有效方法May 09, 2025 am 12:15 AM有多种方法可以合并Python列表:1.使用 操作符,简单但对大列表不内存高效;2.使用extend方法,内存高效但会修改原列表;3.使用itertools.chain,适用于大数据集;4.使用*操作符,一行代码合并小到中型列表;5.使用numpy.concatenate,适用于大数据集和性能要求高的场景;6.使用append方法,适用于小列表但效率低。选择方法时需考虑列表大小和应用场景。
 编译的与解释的语言:优点和缺点May 09, 2025 am 12:06 AM
编译的与解释的语言:优点和缺点May 09, 2025 am 12:06 AMCompiledLanguagesOffersPeedAndSecurity,而interneterpretledlanguages provideeaseafuseanDoctability.1)commiledlanguageslikec arefasterandSecureButhOnderDevevelmendeclementCyclesclesclesclesclesclesclesclesclesclesclesclesclesclesclesclesclesclesandentency.2)cransportedeplatectentysenty
 Python:对于循环,最完整的指南May 09, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Python:对于循环,最完整的指南May 09, 2025 am 12:05 AMPython中,for循环用于遍历可迭代对象,while循环用于条件满足时重复执行操作。1)for循环示例:遍历列表并打印元素。2)while循环示例:猜数字游戏,直到猜对为止。掌握循环原理和优化技巧可提高代码效率和可靠性。
 python concatenate列表到一个字符串中May 09, 2025 am 12:02 AM
python concatenate列表到一个字符串中May 09, 2025 am 12:02 AM要将列表连接成字符串,Python中使用join()方法是最佳选择。1)使用join()方法将列表元素连接成字符串,如''.join(my_list)。2)对于包含数字的列表,先用map(str,numbers)转换为字符串再连接。3)可以使用生成器表达式进行复杂格式化,如','.join(f'({fruit})'forfruitinfruits)。4)处理混合数据类型时,使用map(str,mixed_list)确保所有元素可转换为字符串。5)对于大型列表,使用''.join(large_li
 Python的混合方法:编译和解释合并May 08, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python的混合方法:编译和解释合并May 08, 2025 am 12:16 AMpythonuseshybridapprace,ComminingCompilationTobyTecoDeAndInterpretation.1)codeiscompiledtoplatform-Indepententbybytecode.2)bytecodeisisterpretedbybythepbybythepythonvirtualmachine,增强效率和通用性。
 了解python的' for”和' then”循环之间的差异May 08, 2025 am 12:11 AM
了解python的' for”和' then”循环之间的差异May 08, 2025 am 12:11 AMtheKeyDifferencesBetnewpython's“ for”和“ for”和“ loopsare:1)” for“ loopsareIdealForiteringSequenceSquencesSorkNowniterations,而2)”,而“ loopsareBetterforConterContinuingUntilacTientInditionIntionismetismetistismetistwithOutpredefinedInedIterations.un
 Python串联列表与重复May 08, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python串联列表与重复May 08, 2025 am 12:09 AM在Python中,可以通过多种方法连接列表并管理重复元素:1)使用 运算符或extend()方法可以保留所有重复元素;2)转换为集合再转回列表可以去除所有重复元素,但会丢失原有顺序;3)使用循环或列表推导式结合集合可以去除重复元素并保持原有顺序。


热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

EditPlus 中文破解版
体积小,语法高亮,不支持代码提示功能

安全考试浏览器
Safe Exam Browser是一个安全的浏览器环境,用于安全地进行在线考试。该软件将任何计算机变成一个安全的工作站。它控制对任何实用工具的访问,并防止学生使用未经授权的资源。

WebStorm Mac版
好用的JavaScript开发工具

mPDF
mPDF是一个PHP库,可以从UTF-8编码的HTML生成PDF文件。原作者Ian Back编写mPDF以从他的网站上“即时”输出PDF文件,并处理不同的语言。与原始脚本如HTML2FPDF相比,它的速度较慢,并且在使用Unicode字体时生成的文件较大,但支持CSS样式等,并进行了大量增强。支持几乎所有语言,包括RTL(阿拉伯语和希伯来语)和CJK(中日韩)。支持嵌套的块级元素(如P、DIV),

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具





